El Salvador, Misamis Oriental
El Salvador, officially the City of El Salvador (Cebuano: Dakbayan sa El Salvador; Filipino: Lungsod ng El Salvador), is a 6th class city in the province of Misamis Oriental, Philippines. According to the 2015 census, it has a population of 50,204 people.[3]
El Salvador | |
|---|---|
| City of El Salvador | |
 From left to right: Divine Mercy Shrine; Barangay Poblacion of El Salvador; Our Lady of the Snows Parish Church | |
 Seal | |
Nicknames:
| |
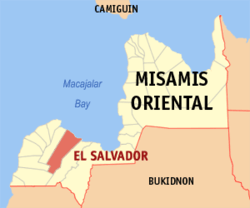 Map of Misamis Oriental with El Salvador highlighted | |

| |
.svg.png) El Salvador Location within the Philippines | |
| Coordinates: 8°34′N 124°31′E | |
| Country | |
| Region | Northern Mindanao (Region X) |
| Province | Misamis Oriental |
| District | 2nd District |
| Founded | June 15, 1948 |
| Cityhood | June 27, 2007 |
| Barangays | 15 (see Barangays) |
| Government | |
| • Type | Sangguniang Panlungsod |
| • Mayor | Edgar S. Lignes |
| • Vice Mayor | Agripino D. Estrada Jr. |
| • Congressman | Juliette T. Uy |
| • Electorate | 39,739 voters (2019) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 106.15 km2 (40.98 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 4.8 m (15.7 ft) |
| Population (2015 census)[3] | |
| • Total | 50,204 |
| • Density | 470/km2 (1,200/sq mi) |
| • Households | 11,769 |
| Demonym(s) | Salvadoreños, Salbadorenyos |
| Economy | |
| • Income class | 6th city income class |
| • Poverty incidence | 27.06% (2015)[4] |
| • Revenue (₱) | 325,840,292.15 (2016) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (PST) |
| ZIP code | 9017 |
| PSGC | |
| IDD : area code | +63 (0)88 |
| Climate type | tropical climate |
| Native languages | Cebuano Binukid Subanon language Tagalog |
| Feast date | Sunday after Easter |
| Catholic diocese | Archdiocese of Cagayan de Oro |
| Patron saint | The Divine Mercy |
| Website | elsalvadorcity |
The city serves as a pilgrimage site for Divine Mercy devotees, that is why it is also called the City of the Saviour, City of Mercy, and the Divine Mercy City of the Philippines.
Geography
El Salvador is located in the Province of Misamis Oriental in Northern Mindanao (Region X). It is bordered by the Municipality of Alubijid to the west, Opol to the east and Manticao and Naawan to the south. On the north, lies Macajalar Bay of the Bohol Sea.
Climate
| Climate data for El Salvador City, Misamis Oriental | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 28 (82) |
29 (84) |
30 (86) |
31 (88) |
30 (86) |
30 (86) |
30 (86) |
30 (86) |
30 (86) |
30 (86) |
29 (84) |
29 (84) |
30 (85) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 24 (75) |
24 (75) |
24 (75) |
25 (77) |
26 (79) |
26 (79) |
25 (77) |
25 (77) |
25 (77) |
25 (77) |
25 (77) |
25 (77) |
25 (77) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 271 (10.7) |
217 (8.5) |
193 (7.6) |
178 (7.0) |
344 (13.5) |
423 (16.7) |
362 (14.3) |
358 (14.1) |
329 (13.0) |
320 (12.6) |
322 (12.7) |
260 (10.2) |
3,577 (140.9) |
| Average rainy days | 23.2 | 19.5 | 22.0 | 22.8 | 29.6 | 28.9 | 30.3 | 29.8 | 28.1 | 28.8 | 26.1 | 24.1 | 313.2 |
| Source: Meteoblue [5] | |||||||||||||
Barangays
Administratively, El Salvador is subdivided into 15 barangays. One forms the center of the city (poblacion) whereas the other 14 are in the outlying areas. Some of them are even several kilometers away from the center of the city.
- Amoros
- Bolisong
- Cogon
- Himaya
- Hinigdaan
- Kalabaylabay
- Molugan
- Pedro S. Baculio (Bolo-Bolo)
- Poblacion
- Quibonbon
- Sambulawan
- San Francisco de Asis (Calongonan)
- Sinaloc
- Taytay
- Ulaliman
History
El Salvador was created from the barrios of El Salvador and Molugan with their sitios known as Sala, Sambulawan, Sinaloc, Lagtang, Talaba, Kalabaylabay and Hinigdaan, formerly part of Cagayan de Misamis, Misamis Oriental, in 1948.[6]
Hinigdaan was a ranch during the Spanish periods the areas covers the parts of Kalabay labay where the DJango's have 300 hectares of land and hundreds of cows..the area was famous of cattle ranching towards the areas of Tugasnon alubijid to Lourdes where the first Municipality was located now transferred to Alubijid and Sikitun of Gitagum Misamis Oriental.
Demographics
| Population census of El Salvador | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | Pop. | ±% p.a. |
| 1903 | 4,315 | — |
| 1948 | 16,899 | +3.08% |
| 1960 | 10,521 | −3.87% |
| 1970 | 14,529 | +3.28% |
| 1975 | 16,915 | +3.10% |
| 1980 | 20,446 | +3.86% |
| 1990 | 26,721 | +2.71% |
| 1995 | 31,500 | +3.13% |
| 2000 | 34,650 | +2.06% |
| 2007 | 41,905 | +2.66% |
| 2010 | 44,848 | +2.50% |
| 2015 | 50,204 | +2.17% |
| Source: Philippine Statistics Authority[3][7][8][9] | ||
Economy
El Salvador hosts several companies, plants and factories west of Misamis Oriental. These are Asia Brewery, Tanduay Rhum, Virgin Cola Bottling Plant (Visayas and Mindanao region distributor), Highland Fresh Daily Products, Monark Equipment, The Aoso, Zest-O Corporation, WL Foods Corporation, Universal Robina Corporation and Union Plywood Corporation.
With regards to financial institutions, Rural Bank of El Salvador and lending institutions such as FICCO, Oro Coop, M Lhuillier and others are accessible at office hours in this place.
Attractions
- Divine Mercy Shrine (Misamis Oriental), located in the Divine Mercy Hills, PSB-Ulaliman which is overlooking Macajalar Bay. The shrine has a 50-foot statue of the Divine Mercy Christ, the biggest in Asia. It serves as a pilgrimage site for the Divine Mercy devotees. As a pilgrimage and sacred site, visitors are not allowed to wear shorts and other revealing clothing. Those who do so will be forced to cover themselves with a blue cloth provided by the shrine administrators.
- Burias Island, located just a few kilometers off the coast of Molugan or about 3 km west of the town of Opol.
- El Salvador Night Café and Market, is set up on Friday night at Barangay Poblacion. Tagnipa-ons and visitors gather to have barbecue, enjoy the live band music, beer, and also the great bargains from the nearby Night Market
- Our Lady of Snows Parish Church, newly constructed church located within the city.
- Abaga & Sikiop Falls, Located in barangay San Francisco de Asis.
- Tag-ilas Falls, Located in barangay Hinigdaan.
- Tuburan Spring, Located in barangay Poblacion .
- House of Pasalubong, Located in Zone 2, Barangay Poblacion
Culture
Feast day:
- August 5 (Our Lady of Snows)
- August 16 (Saint Roch (aka San Roque))
Charter day:
- June 27
Infrastructure
Transportation
El Salvador city can be reached via plane through Laguindingan Airport, then about less than 10 minutes bus ride east. Like any other place the national highway snakes through it. Visitors and locals can go around the city by just hailing a "sikad-sikad" or motorboat, "jeepneys" or motorcycles to the outlying barangays.
Communication
PLDT and MISORTEL are among the major phone lines, also transmitters or "cell sites" for all major "telecom" providers like Globe, Smart and Sun Cellular are serviceable in this city. Internet access is also available. Internet cafes can be found in various places in within the city. Broadband service is also available.
References
- "City". Quezon City, Philippines: Department of the Interior and Local Government. Retrieved 30 May 2013.
- "Province: Misamis Oriental". PSGC Interactive. Quezon City, Philippines: Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved 12 November 2016.
- Census of Population (2015). "Region X (Northern Mindanao)". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. PSA. Retrieved 20 June 2016.
- "PSA releases the 2015 Municipal and City Level Poverty Estimates". Quezon City, Philippines. Retrieved 12 October 2019.
- "El Salvador: Average Temperatures and Rainfall". Meteoblue. Retrieved 29 April 2020.
- "An act creating the municipality of El Salvador, province of Misamis Oriental". LawPH.com. Archived from the original on 2012-07-10. Retrieved 2011-04-08.
- Census of Population and Housing (2010). "Region X (Northern Mindanao)". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. NSO. Retrieved 29 June 2016.
- Censuses of Population (1903–2007). "Region X (Northern Mindanao)". Table 1. Population Enumerated in Various Censuses by Province/Highly Urbanized City: 1903 to 2007. NSO.
- "Province of Misamis Oriental". Municipality Population Data. Local Water Utilities Administration Research Division. Retrieved 17 December 2016.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to El Salvador, Misamis Oriental. |