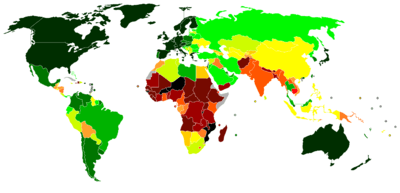
List of countries by Human Development Index (1998)
|
0.900 and over
0.850–0.899
0.800–0.849
0.750–0.799
0.700–0.749 |
0.650–0.699
0.600–0.649
0.550–0.599
0.500–0.549
0.450–0.499 |
0.400–0.449
0.350–0.399
0.300–0.349
under 0.300
Data unavailable |
This is a list of all countries by Human Development Index as reported in the United Nations Human Development Report for 1998, compiled on the basis of estimates for 1995.[2] It covers 158 UN member states (out of the then 192) and Hong Kong, China. 24 UN member states are not included due to lack of data. The average HDI of regions of the World and groups of countries are also included for comparison.
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a comparative measure of life expectancy, literacy, education and standards of living for countries worldwide. It is a standard means of measuring well-being, especially child welfare. It is used to distinguish whether the country is a developed, a developing or an underdeveloped country, and also to measure the impact of economic policies on quality of life. The index was developed in 1990 by Pakistani economist Mahbub ul Haq and Indian economist Amartya Sen.[3]
Countries fall into four broad human development categories, each of which comprises 42 countries (except for the second category, comprising 43 countries).[4] The divisions are:
| Division | comprising: |
| High | 63 countries |
| Medium | 51 countries |
| Low | 45 countries |
Due to the new methodology adopted in 2010 HD Report, its HDI figures appear lower than the HDI figures in previous reports.
Starting in the report for 2007, the first category is referred to as developed countries, and the last three are all grouped in developing countries. The original "high human development" category has been split into two as above in the report for 2007.
Some older groupings (high/medium/low income countries) have been removed that were based on the gross domestic product (GDP) in purchasing power parity (PPP) per capita, and have been replaced by another index based on the gross national income (GNI) in purchasing power parity per capita.
Complete list of countries
- Similar HDI values in the current list do not lead to ranking ties, since the HDI rank is actually determined using HDI values to the sixth decimal point.
- This revision of the index was released in 1999 and estimates the HDI of countries for 1998.
- The number in brackets represents the number of ranks the country has climbed (up or down) relative to the revised estimates for 1981, released in 1998.
High human development (developed countries)
|
|
|
|
|
|
See also
- Human Development Index
- List of countries by inequality-adjusted HDI
- List of African countries by Human Development Index
- List of Argentine provinces by Human Development Index
- List of Brazilian states by Human Development Index
- American Human Development Report
- List of Chilean regions by Human Development Index
- List of Chinese administrative divisions by Human Development Index
- List of European countries by Human Development Index
- List of Indian states by Human Development Index
- List of Indonesian provinces by HDI
- List of Mexican states by Human Development Index
- List of Pakistani Districts by Human Development Index
- List of Philippine provinces by HDI
- List of Russian federal subjects by HDI
- List of Venezuelan states by human development index
- Happy Planet Index
- OSCE countries statistics
- Satisfaction with Life Index
Notes
References
- ↑ Human Development Index (HDI) - 1998 Rankings, United Nations Development Programme
- ↑ United Nations Development Programme, Human Development Report 1998, pp. 19-21, Oxford University Press, 1998
- ↑ "History of the Human Development Report". United Nations Development Programme. Archived from the original on 3 April 2009. Retrieved 26 March 2009.
- ↑ "Human development Report". United Nations Development Programme. p. 139. Retrieved 4 November 2010.