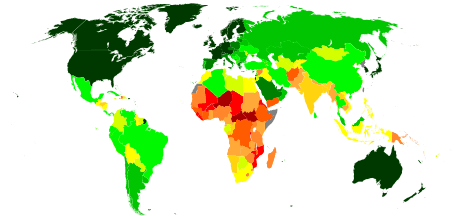
List of countries by Human Development Index
|
≥ 0.900
0.850–0.899
0.800–0.849
0.750–0.799
0.700–0.749 |
0.650–0.699
0.600–0.649
0.550–0.599
0.500–0.549
0.450–0.499 |
0.400–0.449
≤ 0.399
Data unavailable |
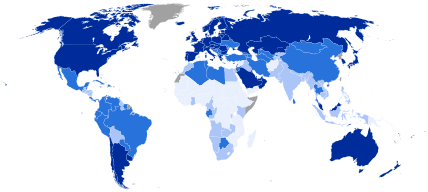
|
0.800–1.000 (very high)
0.700–0.799 (high)
0.555–0.699 (medium) |
0.350–0.554 (low)
Data unavailable |
This is a full list of all the countries by the Human Development Index as included in a United Nations Development Programme's Human Development Report. The latest report was released on 14 September 2018 and is based on data collected in 2017.[1]
In the 2010 Human Development Report, a further Inequality-adjusted Human Development Index (IHDI) was introduced. It stated that while the HDI remains useful, "the IHDI is the actual level of human development (accounting for inequality)" and "the HDI can be viewed as an index of "potential" human development (or the maximum IHDI that could be achieved if there were no inequality)".[2] The index does not take into account several factors, such as the net wealth per capita or the relative quality of goods in a country. This situation tends to lower the ranking for some of the most advanced countries, such as the G7 members and others.[3]
Methodology
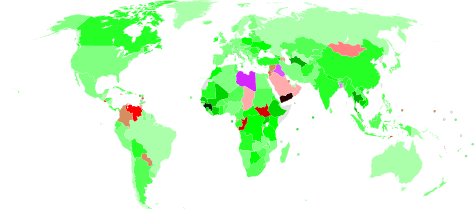
|
+ 0.013
+ 0.012
+ 0.011
+ 0.010
+ 0.009
+ 0.008
+ 0.007
+ 0.006 |
+ 0.005
+ 0.004
+ 0.003
+ 0.002
+ 0.001
No increase/decrease
− 0.001
− 0.002 |
− 0.003
− 0.004
− 0.005
− 0.006
− 0.007
− 0.008
− 0.009
− 0.010 |
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a composite statistic of life expectancy, education, and income per capita indicators. A country scores higher HDI when the life expectancy at birth is longer, the education period is longer, and the income per capita is higher. It is used to distinguish whether the country is a developed, a developing or an underdeveloped country. The index was developed in 1990 by Pakistani economist Mahbub ul Haq[4][5] and Indian economist Amartya Sen. The UN report covers 187 member states of the United Nations (out of 193), along with Hong Kong and Palestine; 7 UN member states are not included because of lack of data. The average HDI of regions of the world and groups of countries are also included for comparison.
Countries fall into four broad human development categories: Very High Human Development, High Human Development, Medium Human Development and Low Human Development.
Because of the new methodology adopted since the 2010 Human Development Report, the new reported HDI figures appear lower than the HDI figures in previous reports.
From 2007 to 2010, the first category was referred to as developed countries, and the last three are all grouped in developing countries. The original "high human development" category has been split into two as above in the report for 2007.
Some older groupings (high/medium/low income countries) that were based on the gross domestic product (GDP) in purchasing power parity (PPP) per capita have been replaced by another index based on the gross national income (GNI) in purchasing power parity per capita.
Frequency of issuing the index
The first index was launched in 1990, and the only year without a Human Development Report since 1990 was 2012.
The latest index—covering 189 countries—was launched on 14 September 2018.[6]
Complete list of countries



Very high human development
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
High human development
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Medium human development
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Low human development
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
List of countries by continent
Africa
|
10 highest HDIs
|
10 lowest HDIs
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Asia
|
10 highest HDIs
|
10 lowest HDIs
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Europe
|
10 highest HDIs
|
10 lowest HDIs
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
North America and the Caribbean
|
10 highest HDIs
|
10 lowest HDIs
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Oceania
|
10 highest HDIs
|
10 lowest HDIs
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
South America
|
10 highest HDIs
|
10 lowest HDIs
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
List of countries by intercontinental region
Arab League
|
10 highest HDIs
|
10 lowest HDIs
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Commonwealth of Nations
|
10 highest HDIs
|
10 lowest HDIs
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
East Asia and the Pacific
|
10 highest HDIs
|
10 lowest HDIs
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
European Union
|
10 highest HDIs
|
10 lowest HDIs
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
OECD
|
10 highest HDIs
|
10 lowest HDIs
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
HDI by regions and groups
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Countries missing from latest report
Note: The 2009 publication uses an older version of the HDI formula and classification standard. The ranges are 0–0.499 for low HDI, 0.500–0.799 for medium HDI, 0.800–0.899 for high HDI and greater than 0.900 for very high HDI.[7]
UN member states (not calculated by the UNDP)
Non-UN member states (latest UNDP data)
|
Non-UN members (not calculated by the UNDP)
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
See also
- American Human Development Project
- List of African countries by Human Development Index
- List of sovereign states in Europe by Human Development Index
- List of sovereign states in Asia and Oceania by Human Development Index
- Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe statistics
- List of countries by Human Development Index (1998)
- List of countries by Human Development Index (2009)
Notes
- ↑ The UN does not calculate the HDI of Macau. The government of Macau calculates its own HDI.[10]
- ↑ The UN does not recognize the Republic of China (Taiwan) as a sovereign state. The HDI report does not include Taiwan as part of the People's Republic of China when calculating China's figures (see[11]). Taiwan's government calculated its HDI to be 0.885, based on 2010 new methodology of UNDP.[12]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 "Human Development Report 2018 – "Human Development Indices and Indicators"" (PDF). HDRO (Human Development Report Office) United Nations Development Programme. pp. 22–25. Retrieved 14 September 2018.
- ↑ Human Development Report, The Real Wealth of Nations: Pathways to Human Development (2010) p.87
- ↑ The Courier. Commission of the European Communities. 1994.
- ↑ "The Human Development concept". UNDP. 2010. Retrieved 29 July 2011.
- ↑ "History of the Human Development Report". United Nations Development Programme. Archived from the original on 3 April 2009. Retrieved 26 March 2009.
- ↑ http://hdr.undp.org/sites/default/files/2018_human_development_statistical_update.pdf
- ↑ Human Development Report 2009, UNDP, p. 15
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 Filling Gaps in the Human Development Index, United Nations ESCAP, February 2009
- ↑ "About Kosovo". UNDP. Retrieved 19 February 2017.
- ↑ "Macao in Figures, 2018". www.dsec.gov.mo.
- ↑ "- Human Development Reports" (PDF). hdr.undp.org.
- ↑ "2017中華民國人類發展指數(HDI)" (Excel) (in Chinese). Directorate General of Budget, Accounting and Statistics, Executive Yuan, R.O.C. 2017. Retrieved 2017-04-21.
- ↑ "Human Development Index Trends and Inequality in Puerto Rico 2010-2015" Fuentes-Ramírez, Ricardo R. (2017). Ceteris Paribus: Journal of Socio-Economic Research. 7. Retrieved 8 January 2018.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Quel niveau de développement des départements et collectivités d‘outre-mer ? Une approche par l’indice de développement humain, Agence Française de Developpment, 2012 (in French)