Indonesian Air Force
| Indonesian Air Force | |
|---|---|
|
Tentara Nasional Indonesia Angkatan Udara TNI AU | |
 TNI-AU insignia | |
| Founded | 9 April 1946 |
| Country |
|
| Allegiance |
|
| Type | Air force |
| Role | Aerial warfare |
| Size |
37,850 personnel 224 aircraft[1] |
| Part of | Indonesian National Armed Forces |
| Motto(s) |
Swa Bhuwana Paksa (Sanskrit, "Wings of the Motherland") |
| Anniversaries | 9 April 1946 (founded) |
| Engagements | |
| Commanders | |
| Commander-in-Chief | President Joko Widodo |
| Chief of Staff | Air Chief Marshal Yuyu Sutisna |
| Vice Chief of Staff | Air Marshal Wieko Syofyan (id) |
| Notable commanders |
Halim Perdanakusuma Agustinus Adisutjipto Abdulrachman Saleh Iswahjudi |
| Insignia | |
| Roundel & Fin Flash |
  |
| Roundel 1946–1949 |
.svg.png) |
| Aircraft flown | |
| Attack | Su-30MKK, Hawk Mk. 209, EMB 314 Super Tucano |
| Fighter | F-16 Block 32+, Su-30MKK, Su-27 |
| Helicopter | AS332, SA330, MBB Bo 105 |
| Interceptor | Su-27, F-16 Block 32+, F-5 |
| Patrol | 737-2X9 Surveiller, CN235-220MPA |
| Trainer | KT-1, Hawk Mk.53/Mk.109, T-34, TA-4H/J, AS/SA-202, SF.260 |
| Transport | C-130, CN-235, F-28, NC-295, NC-212, 737-2Q8, A400M |
The Indonesian Air Force (Indonesian: Tentara Nasional Indonesia Angkatan Udara (TNI AU), literally "Indonesian National Military-Air Service") is the air force branch of the Indonesian National Armed Forces.
The Indonesian Air Force is headquartered in Jakarta, Indonesia. Its order of battle is split into three Air Force Operational Commands (Komando Operasi TNI Angkatan Udara /KOOPSAU). Most of its airbases are located on the island of Java.[2] The Indonesian Air Force also has its ground force unit, called Air Force Special Forces Corps (Paskhas). In addition, While not part of the Air Force, most of Indonesian National Air Defense Forces Command (Kohanudnas) personnel are picked from the Air Force and its commander is always an Air Force two-star Marshal.
The Indonesian Air Force has 37,850 personnel and equipped with 110 combat aircraft. The inventory includes SU-27 and SU-30 as the main fighters (from Russia) supplemented by F-16 Fighting Falcons (from the USA).[3] The Indonesian Air Force will purchase 11 Sukhoi SU-35[4] and around 50 KF-X [5] as a replacement for the already-aging US Northrop F-5 Tiger light fighters in its inventory.[6][7]
History
Before Indonesian independence (1941–1945)
After World War II ended, Indonesia became the second country (after Thailand) in Southeast Asia to acquire an air force. Indonesian pilots fought against the colonial forces of the Netherlands during 1945–1949 with former Japanese aircraft abandoned at the end of World War II, as well as aircraft of the Netherlands East Indies Air Force (including Curtiss P-36 Hawk (P-36 Mohawk), Brewster F2A Buffalo and Fokker D.XXI fighters; Martin B-10 bombers; Fokker C.X reconnaissance floatplanes) left before the Japanese occupation in 1941.
Indonesian War of Independence / Netherlands 'Police Action' (1945–1949)
After the Japanese announced their surrender at the end of WWII, Indonesian nationalist leader Sukarno declared Indonesian Independence on 17 August 1945. Several days later, Indonesian People's Security Force (Badan Keamanan Rakyat) was formed to undertake security duties. The Air Division of this force was also formed, using ex-Japanese planes scattered everywhere, especially in the island of Java, including Bugis Air Base in Malang (Established on 18 September 1945). The most numerous of these aeroplanes were the Yokosuka K5Y1 Willow (Cureng) trainers, which were hastily used to train newly recruited cadets. At the time of the founding, there was only one Indonesian holding a multi-engine pilot license from the pre-war Dutch Flying School, Agustinus Adisucipto (but did not have an opportunity to fly during the 3.5-year Japanese occupation). He was assisted by a few Japanese pilots who decided to stay in the newly born country. The new roundel was created simply by painting white on the lower part of the Japanese Hinomaru, reflecting the red and white of the Indonesian flag. The People's Security Force was then re-organized to form a formal armed force. This marked the birth of the Indonesian Air Force on 9 April 1946. However, tensions rose as the Dutch tried to re-claim their former colony and launched an assault on 21 July 1947, destroying most of the planes on the ground. Some planes survived though and were hidden in remote bases.
29 July 1947 was date of the first air operation by the newborn air force as three surviving aircraft, comprising two Yokosuka K5Y1 Willow (Cureng) and a Mitsubishi Ki-51 Sonia (the fourth aircraft, a Nakajima Ki-43 Oscar (Hayabusa) flown by Air Cadet Bambang Saptoadji, should also have been involved in the raid as an escort, but as of when it was launched, the aircraft was not airworthy due to engine troubles)[8] conducted air raids at dawn on the Dutch Army barracks in Semarang, Salatiga and Ambarawa, dropping incendiary bombs. Tactically, these raids did not have any effect on the Dutch positions, but psychologically, it was a great success as it proved that the Indonesian Air Force still existed. The Dutch had previously claimed the destruction of Indonesian Air Force in their assault before and they never expected any attack from the sky. Dutch Curtiss P-40E Warhawks tried to find all the guerrillas' planes, but they were too late to find those "ghost" aircraft which landed quickly in Maguwo Air Base, near Yogyakarta (now, Adisucipto International Airport). Indonesian pro-independence guerrillas tried to save captured aircraft in a number of remote areas, including examples of the Mitsubishi A6M Zero-Sen "Zeke", Aichi D3A "Val", and Mitsubishi G4M "Betty".
Under pressure from the United Nations, the Dutch finally agreed to acknowledge Indonesian independence. Following the 1949 Round Table Conference, sovereignty was officially transferred to the United States of Indonesia. The Dutch armed forces left (but remained in West Papua until 1963) and the aeroplanes were handed over to the Indonesians. These comprised, among others, North American P-51 Mustang, North American B-25 Mitchell, North American T-6 Texan, Douglas A-26 Invader, Douglas C-47 Dakota and Consolidated PBY-5A Catalina, which served as the main forces of the Indonesian Air Force for the following decade. During this era, Indonesia received its first jet aircraft; De Havilland DH-115 Vampire. It was also during this era that the national roundels were changed to the red and white pentagon (which was supposed to signify Indonesia's national ideology of "Panca Sila", or the "Five Principles", created by Sukarno in 1945).
Action against rebellions (1950–1961)

Political instability meant that the Indonesian Air Force saw action against several regional rebellions in Indonesia such as PRRI, Permesta, Darul Islam-Tentara Islam Indonesia (DI/TII) and the Republic of South Maluku separatists.
Several Indonesian pilots scored their first kills, including Captain Ignatius Dewanto with his North American P-51 Mustang, who in 1958 shot down a Permesta Douglas B-26 Invader over Ambon. Its pilot, Allen Pope, an American CIA agent, was captured and tried in Jakarta, thus revealing the significant involvement of the CIA's "Operation Haik" in the rebellion.
The most famous Indonesian fighter pilot in this era was Rusmin Nurjadin, who became Chief of Staff of the Air Force from 1966–69. Nurjadin commanded MiG-21 squadrons in 1962–65 and founded an acrobatic team in 1962 that flew the MiG-17F/PF Fresco over some cities in Indonesia. Small numbers of Indonesian Air Force pilots gained their reputation as aces in this era.
Soviet influence (1962–1965)

The rise of the communist party in Indonesia (Communist Party of Indonesia) drew Indonesia closer to the Eastern Bloc. Several Soviet-built aircraft began to arrive in the early 1960s including the MiG-15UTI from Czechoslovakia, MiG-17F/PF, MiG-19S and MiG-21F-13, in addition to Ilyushin Il-28, Mil Mi-4, Mil Mi-6, Antonov An-12 and Avia 14 also from Czechoslovakia. Indonesia also received Lavochkin La-11. Some Tupolev Tu-2 from China also arrived, intended to replace the B-25, but they never reached operational status. These aircraft served along with the remaining American aircraft such as North American B-25 Mitchell, Douglas A-26 Invader, Douglas C-47 Dakota, and North American P-51 Mustang. It was during this period that the Indonesian Air Force became the first Air Force in Southeast Asia which acquired the capability of strategic bombing by acquiring the new Tupolev Tu-16 in 1961, before the acquisition of Ilyushin Il-28 by Vietnam People's Air Force. Around 25 Tu-16KS were delivered complete with AS-1 air-surface missiles. One crashed at the end of 1962.[9][10]
This era also marked the last confrontation with the Dutch in Papua, before the Dutch, again under pressure of the United Nations, left in 1963. Several missions of Taiwan-based Lockheed U-2s from 35th Squadron flew over Maluku (Mollucas) and reported to Dutch military that there was a strong possibility that Dutch would lose their air superiority over Papua if they continued the war.[11][12] During Operation Trikora, the air force was deployed as follows:
- 7 P-51Ds based at Laha airbase, Ambon. One aircraft piloted by Second Air Lieutenant Prasetyo lost due to engine failure during the ferry flight from Makassar to Ambon. The pilot, Second Air Lieutenant Prasetyo, died after bailing out from the aircraft and landed in a high-tide seas and couldn't be rescued by the Air Forces' PBY-5 Catalina due to the extreme weather after Prasetyo's accident[12]
- 40 MiG-17F/PF aircraft on three airfields: Morotai (in northern Maluku), Amahai (in Seram) and Letfuan (in Banda islands, located in the southwest of Papua). The aircraft had been stationed at Morotai before Operation Trikora for actions against PRRI-PERMESTA and the Republic of South Maluku separatists. The primary role of these aircraft were to provide air cover for the airlift and logistics aircraft during the early infiltration to Papua.[13] If the war broke out, these MiG-17F/PF would provide the air cover for Tu-16 anti-shipping missions and Il-28 bombing missions,[14] also for intercepting Netherlands' Hawker Hunters based in Numfor, Biak.[15]
.jpg)
- 4 B-25 Mitchells and two A-26 Invaders at Letfuan airbase. Their primary role was for transport and providing air cover for the airlift, until this role was assumed by the P-51Ds and MiG-17F/PFs.[13] Dutch Lockheed PV-2 Neptunes were known as the strongest rival for these Letfuan-based units.[16]
- 18 Il-28s stationed first at Laha airbase, but then moved to Amahai airbase, due to the shortness of runway at Laha for the landing of the aircraft.[17]
- 26 Tu-16s stationed in Iswahyudi airbase near Ngawi, Jawa Timur in 41st and 42nd Squadron. Six aircraft were scrambled to Morotai airbase for the operation. These units were to threaten the Dutch naval fleet in Papua including HNLMS Karel Doorman (R81), the only aircraft carrier of the Dutch naval fleet.
- 24 Douglas C-47 Dakotas stationed at three airfields; Laha, Amahai and Letfuan. One aircraft piloted by Air Captain Djalaludin Tantu and co-pilot Second Air Lieutenant Sukandar, was downed by a Dutch PV-2.[13] All crews bailed out safely from the aircraft, but were soon captured by the Dutch forces after hiding in Papua[16]
- 10 Lockheed C-130 Herculess stationed at Halim Perdanakusumah airbase at Jakarta. Despite the warning from United States to not use the aircraft for the operation, it soon scrambled over the Papua for the airlift mission, due to the loss of C-47s, to Dutch Hawker Hunters and PV-2s. The C-130's high altitude flying capability made it less vulnerable to interception.[13]
- 6 Douglas DC-3s and one Convair 240, under Wing Garuda 011. The aircraft were modified from civilian use for airlift operations.[17]
- 6 anti-submarine Fairey Gannet AS.4s, several PBY-5 Catalinas and two Grumman HU-16 Albatross (UF-1 variant). These aircraft belonged to the Indonesian Naval Air Force, but supporting the air forces for the Operation. Aircraft were stationed in Liang airbase at Seram, then moved to Morotai airbase. One Gannet AS.4 was lost due to an accident when it crashed into a mountain in Seram island, killing three crew members.[17]
- Several Bell 47s, Mil Mi-4 and Mil Mi-6 helicopters were planned to be used for the operation, but were not ready during the early phase of infiltration of the operation.[17]
Indonesian MiG pilots received training to fly their fighter aircraft in Egypt before the infiltration campaign.[18] During the infiltration of the airlift campaign, the air forces' special forces, Pasukan Gerak Tjepat (PGT) (now known as Paskhas) landed in Klamono-Sorong, Papua.[19]
Also during this period, the Indonesian Air Force also took part in the confrontation with the Malaysian Federation (which was backed by the United Kingdom) along the border of Kalimantan, the Malacca Strait and near the Singapore Border.
30 September movement and the overthrow of Sukarno (1966–1970)
The coup attempt led by the 30 September Movement in 1965 changed everything and a new anti-communist regime from the Army, led by Major General Suharto, took power. The Chief of Staff of the Air Force, Air Marshall Omar Dani was removed from his position and court-martialed for his purported involvement in the coup. Ties with the Eastern bloc countries were cut, and thus support and spare parts for the planes became short. By August 1968 the situation was critical, and in early 1970, the Chief of Staff of the Air Force, Suwoto Sukandar, said that the spare parts situation meant that only 15–20 percent of aircraft were airworthy.[20] The MiG force made its farewell flight with a flypast of Jakarta in 1970. The relatively new MiG-19s were sold to Pakistan. By October 1970, only one Tu-16 was still flying, but after an in-flight engine failure, it too was grounded.[21]
Rebirth (1970–1980)

The Air Force began to be re-equipped by receiving former Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) CAC Sabres — an Australian re-design of the F-86 Sabre — to replace the MiG-21s. The Sabre was used by the TNI-AU until 1982. In 1973, the United States supplied military assistance including T33s trainers and UH-34D helicopters in exchange for four old MiG-21F-13s. Pakistan Air Force took over the responsibility to train Indonesian pilots in the Sabre and in logistical aspects of the Air Force. Over the next three years, the US supplied 16 North American Rockwell OV-10 Broncos counter-insurgency aircraft and F-5E/F Tiger II fighters, in exchange for which the Indonesian Air Force handed over the majority of its remaining MiG-21F-13s, which were used to form a US Air Force Aggressor squadron.[22] Indonesia also purchased BAE Hawk Mk 53s from the United Kingdom in the 1970s.
The Indonesian Air Force took part in the 1975 Indonesian invasion of East Timor.
Influence of American and allied products (1980–1998)
In the early 1980s, the Air Force, needing modern strike aircraft, organised Operation Alpha to clandestinely acquire ex-Israeli Air Force A-4 Skyhawks. Air Force personnel were sent in secret by different routes and eventually Indonesia received 32 aircraft.[23]
In 1982, Indonesia purchased 16 Northrop F-5E/F Tiger II from the United States to replace their Sabres. These were upgraded in Belgium from 1995.
During 1986–88, there was a competition for the contract to provide a new fighter bomber, between the General Dynamics F-16 and Dassault Mirage 2000. Indonesia eventually ordered 12 F-16A/B Fighting Falcon Block 15 OCU as a new fighter in 1989. The Indonesian Air Force had originally planned to acquire 60 F-16s to cover and defend its 12 million square kilometres of territory.[24] A total of 10 F-16A and F-16B are still in service with Indonesian Air Force: 2 planes crashed in two different accidents. A follow-up order for 9 more F-16A Block-15 OCU was cancelled in favour of 24 Su-30 MKK,[25] but this order was also cancelled due to the 1997 Asian Financial Crisis.
The Indonesian Air Force ordered eight BAE Hawk Mk 109s and 32 Mk 209s in 1993. The last of these was delivered by January 1997.
Embargoes 1998–2006
In 1999, the Indonesian Military staged a military intervention following the East Timor's referendum. The result was that more than 1,500 were civilians killed and 70 percent of Dili's infrastructure razed. In response, the United States and the European Union both imposed arms embargoes. Although the European Union chose not to renew its ban in 2000, the United States did not lift its embargo until November 2005. During this embargo the Indonesian government turned to Russia to supply them with arms including fighters, helicopters, missiles, radars and other equipment.
In 2002, the Indonesian Air Force conducted operations against separatists, such as the Free Aceh Movement ("Gerakan Aceh Merdeka", GAM) and Free Papua Movement (Organisasi Papua Merdeka, OPM). In the conflict with GAM in Aceh, the Indonesian Air Force utilised OV-10Fs for counter-insurgency actions along with BAe Hawk 53 and 209.
In that same year, the Air Force received two Sukhoi Su-27s and two Sukhoi Su-30s from Russia. The fighters were partly paid for in Indonesian palm oil. The purchase, however, did not include any weaponry. Seven KT-1B Korean basic trainers were also purchased.
By 2005 the Air Force was experiencing a logistical crisis. The F-16s and A-4s, which accounted for 80% of its air combat assets, were at the minimum or nil level of combat readiness. To respond to the crisis, in 2006, the Indonesian Air Force ordered three Sukhoi Su-27SKM and three Su-30MK2 to complete a full squadron. It was also made public that the four aircraft procured in 2003 were inactive and awaiting an upgrade of their communication systems, as they were incompatible with the Indonesian systems in use. The additional aircraft were ordered with systems complying with the Indonesian and international standards and would also include new weaponry for all variants.[25] A further 12 KT-1b Korean basic trainers were also ordered in 2006.
Until 2008, the Indonesian Air Force had only purchased four types of missiles: KS-1 Komet, Vympel K-13, AIM-9 Sidewinder and AGM-65 Maverick. Starting from 2008, it started receiving more advanced Russian made Vympel R-73 and Vympel R-77 air-to-air missiles for its new Su-27 and Su-30 fighters. Also a limited number of Kh-29, Kh-31 and Kh-59 air-to-ground missiles were delivered for Su-30 strike fighters.[26]
Local weapons are being developed such as P-100 air-to-ground bomb manufactured by CV Sari Bahari Malang, East Java. P-100 has been successfully tested in Su-27 and Su-30 for ground attack missions. Large-scale production is subject to approval from Ministry of Defence.
Minimum Essential Force (MEF) 2010–present
During the visit of US President Barack Obama on 9–10 November 2010 in Jakarta, the TNI-AU Force was offered 24 ex-USAF F-16 Block 25 aircraft as part of the Peace Bima-Sena II agreement.[27][28] In October 2011, the House of Representatives approved the grant. The jets will be upgraded similar to the latest Block 50/52 variant with payment.[29] The TNI-AU is also progressing with the reactivation of all 10 units of F-16 Block 15 OCU, which resulted in the reactivation of TS-1606, TS-1609 and TS-1612 recently.[30] To replace the Fokker F-27s, the TNI-AU has ordered nine Spanish CASA C-295 in joint production with PT. Dirgantara Indonesia. New unmanned aerial vehicles will also be purchased to strengthen TNI-AU aerial observation and will be based at Supadio Air Force Base, Pontianak, Kalimantan Barat.
Starting in 2010,[31] Minister of Defence Purnomo Yusgiantoro stated that TNI-AU will gradually purchase a total of 180 Su-27s and Su-30s to complete the needs of 10 squadrons.[32] India also offered TNI-AU Indian-Russian made BrahMos missiles to equip its Su-27s and Su-30s.[33]

Indonesia signed a memorandum of understanding to participate in the South Korean KF-X programme in July 2010 and the terms of agreement was signed in 2011. Indonesia will finance 20 percent of the project and will receive 50 jets in return, while South Korea will get 200 jets. A Defence ministry spokesman claimed that the jet would be more capable than the F-16 but less capable that the F-35. The project was started in 2009 and the first prototype is expected to roll out in the second half of 2020.[34] But payment problems and technical difficulties had caused several delays and postponement of the KAI KF-X project.[34] Indonesia has also signed an MOU with China to produce C-705 missiles which will arm the Sukhoi jets.[35]
In April 2011,[36] Indonesia confirmed that it will buy 16 supersonic KAI T-50 Golden Eagle trainer jets from South Korea for up to $400 million after an evaluation of the Yakovlev Yak-130, Guizhou JL-9/FTC-2000 Mountain Eagle and Aero L-159 Alca. The T-50 would replace the BAE Hawk MK-53 trainer jets. Deliveries were completed by January 2014 and were commissioned on 13 February 2014.[37]
In June 2011, Indonesia signed the final contract for 8 Super Tucano as the replacement for the OV-10 Bronco in the counter-insurgency role [38] with a second contract for a further 8 aircraft in July 2012.[39] The first four units arrived in March 2012 with deliveries to complete by 2014.[40]
In August 2011,[41] Indonesia announced that it would acquire 18 Grob G120TP for its basic trainer requirements which would likely replace the FFA AS-202 Bravo and Beechcraft T-34 Mentor trainers.
On 29 December 2011 Indonesia committed to purchase 6 Su-30MK2 jet fighters in a $470 million procurement contract signed by the Defence Ministry and Russia's JSC Rosoboronexport.[42] Deliveries will reportedly start after 2013.[43]

In January 2012, the Australian and Indonesian governments agreed to the transfer of four used C-130H Hercules aircraft from the Royal Australian Air Force to the Indonesian Air Force in 2012, which was approved by the US as the Hercules' producer.[44]
In January 2014, Defence Minister Purnomo Yusgiantoro said that he hoped to start the replacement of the F-5 fighters under the upcoming 2015 to 2020 strategic plan. The Indonesian Air Force shortlisted five candidates for the replacement, comprising the Sukhoi Su-35S, Saab JAS 39 Gripen[45]', Dassault Rafale, Eurofighter Typhoon, and F-16C/D Block 60.[46]
In September 2014, Head of Indonesian National Armed Forces Public Relations and Media Office (Kapuspen TNI), Major General (TNI) Mochamad Fuad Basya explained the Minimum Essential Forces (MEF) Plan of TNI-AU consist of: 11 Fighter Squadrons, 6 Transport Squadrons, 2 VIP/VVIP Squadrons, 2 Patrol Squadrons, 4 Helicopter Squadrons, 2 Training Squadrons and 2 UAV Squadrons.[47]
In September 2015, Defence Minister Ryamizard Ryacudu said Indonesian had chosen the Su-35 Flanker-E to replace the F-5 Tiger II. Although in recent times, the deal to purchase Su-35 is in limbo due to Russia's refusal to give transfer of technology to Indonesia owing its small number of orders in addition to Indonesian concerns over price.[6]
In January 2017, Indonesia approved for the acquisition of 5 Airbus A400M Atlas multi-role aircraft worth USD2 billion, as part of the plans to boost the country's military capabilities. They are to be acquired in both transport and utility configurations and will be operated by the Indonesian Air Force (TNI-AU) Aviation Squadrons 31 and 32.[48]
In 12 May 2017, Defence Minister Ryamizard Ryacudu confirm that Indonesian Air Force (TNI-AU) will sign contract to buy 10 units Su-35. Russia will open the factory for Sukhoi Spare Part in Indonesia as part in the contract.[49]
In 28 November 2017, Defence Minister Ryamizard Ryacudu confirm that Indonesian Air Force (TNI-AU) have completed procurement process of 11 units Su-35.[50]
In 14 February 2018, Defence Ministry have signed purchase agreement of 11 units of Su-35 fighters with Rostec, which will replace the F-5s.[51]
Administrative and operational organization
The Indonesian Air Force is structured into the following in accordance with Presidential decree No. 62/ 2016:[52]
Leadership Elements
- Chief of Staff of the Air Force, position held by a four-star air marshal.
- Vice Chief of Staff of the Air Force, position held by a three-star air marshal.
Assistant for Leadership Element
- Office of the Inspector General of the Air Force, position held by a two-star air marshal.
- Air Force Expert Advisor, position held by two-star or one-star air marshal
- Air Force Planning and Budgeting Advisor
- Air Force Security Advisor
- Air Force Operations Advisor
- Air Force Human Resources Advisor
- Air Force Supply and Materiel Advisor
- Air Potency and Resources Advisor
Central Executive Agencies under Air Force Headquarters

- Air Force Finance Corps (Dinas Keuangan TNI Angkatan Udara)
- Air Force Information and Data Processing Service (Dinas Informasi dan Pengolahan Data TNI Angkatan Udara)
- Air Force Research and Development Service (Dinas Penelitian dan Pengembangan TNI Angkatan Udara)
- Air Force Signal and Security Service (Dinas Pengamanan dan Sandi TNI Angkatan Udara)
- Air Force Aerial Survey and Photography Service ( Dinas Survei dan Pemotretan Udara TNI Angkatan Udara)
- Air Force Public Relations and Media Directorate ( Dinas Penerangan TNI Angkatan Udara)
- Air Force Operation Development Service ( Dinas Pengembangan Operasi TNI Angkatan Udara)
- Air Force Occupational and Aviation safety Service ( Dinas Keselamatan Terbang dan Kerja TNI Angkatan Udara)
- Air Force Air Potential and Resources Service (Dinas Potensi Kedirgantaraan)
- Air Force Justice Service (Dinas Hukum TNI Angkatan Udara)
- Air Force Personnel Administration Service ( Dinas Administrasi Personel TNI Angkatan Udara)
- Air Force Education Division ( Dinas Pendidikan TNI Angkatan Udara)
- Air Force Personnel Maintenance Service ( Dinas Perawatan Personel TNI Angkatan Udara)
- Air Force Medical Department ( Dinas Kesehatan TNI Angkatan Udara)
- Air Force Psychology Service ( Dinas Psikologi TNI Angkatan Udara)
- Air Force Materiel Service ( Dinas Materiil TNI Angkatan Udara)
- Air Force Aeronautics Services Division ( Dinas Aeronautika TNI Angkatan Udara)
 Air Force academy cadets (left), Air Force Military Police (center), and Air Force female personnel (right)
Air Force academy cadets (left), Air Force Military Police (center), and Air Force female personnel (right) - Air Force Communication and Electronics Department ( Dinas Komunikasi dan Elektronika TNI Angkatan Udara)
- Air Force Facility and Construction Service ( Dinas Fasilitas dan Konstruksi TNI Angkatan Udara)
- Air Force Armaments and Equipment Procurement Service (Dinas Pengadaan TNI Angkatan Udara;)
- Air Force Operation and Training Service ( Dinas Operasi dan Latihan TNI Angkatan Udara)
- Air Force Space and Aviation Medicine Agency "Saryanto" ( Lembaga Kesehatan Penerbangan dan Ruang Angkasa "Saryanto" (Lakespra "Saryanto"))
- Air Force Military Police Command (Pusat Polisi Militer TNI Angkatan Udara /POMAU), POMAU also serve as Air Base Security Force and operate K9 brigade
- Indonesian Air Force Academy (Akademi TNI Angkatan Udara (AAU))
- Air Force Staff College ( Sekolah Staf dan Komando TNI Angkatan Udara (Seskoau))
Main Command
- Air Force Operational Commands ( Komando Operasi TNI Angkatan Udara )
- Air Force Operational Command 1 West
- Air Force Base Type A:
- Halim Perdanakusuma Air Base, Jakarta
- Atang Senjaya Air Base, Bogor
- Roesmin Nurjadin Air Base, Pekanbaru
- Supadio Air Base, Pontianak
- Suyadarma Air Base, Subang
- Air Force Base Type B:
- Sultan Iskandar Muda Air Base, Banda Aceh
- Soewondo Air Base, Medan
- Husein Sastranegara Air Base, Bandung
- Sutan Sjahrir Air Base, Padang
- Sri Mulyono Herlambang Air Base, Palembang
- Raden Sadjad Air Base, Natuna
- Maimun Saleh Air Base, Sabang
- Raja Haji Fisabilillah Air Base, Tanjungpinang
- Air Force Base Type C:
- Hang Nadim Air Base, Batam
- Pangeran M. Bunyamin Air Base, Lampung
- Haji Abdullah Sanusi Hanandjoeddin Air Base, Belitung
- Wiriadinata Air Base, Tasikmalaya
- Sugiri Sukani Air Base (id), Cirebon
- General Soedirman Air Base, Purbalingga
- Harry Hadisoemantri Air Base (id), Bengkayang
- Air Force Base Type A:
- Air Force Operational Command 2 Central
- Air Force Base Type A:
- Sultan Hasanuddin Air Base, Makassar
- Iswahyudi Air Base, Madiun
- Abdul Rachman Saleh Air Base, Malang
- I Gusti Ngurah Rai Air Base, Denpasar
- Mulyono Air Base, Surabaya
- Air Force Base Type B:
- Dhomber Air Base, Balikpapan
- Sam Ratulangi Air Base, Manado
- Muhammad Zainuddin Abdul Madjid Air Base, Mataram
- Anang Busra Air Base, Tarakan
- Syamsuddin Noor Air Base, Banjarmasin
- Air Force Base Type C:
- Air Force Base Type A:
- Air Force Operational Command 3 East
- Air Force Base Type A:
- Air Force Base Type B:
- Air Force Base Type C:
- Air Force Operational Command 1 West
- Air Force Doctrine, Education and Training Command (Komando Pembinaan Doktrin, Pendidikan dan Latihan TNI Angkatan Udara)
- Flight Education Wing (Wing Pendidikan Terbang (Wingdikterbang)), in Adisutjipto Air Base, Yogyakarta
- General Education Wing (Wing Pendidikan Umum (Wingdikum)), in Halim Perdanakusuma Air Base, Jakarta and Atang Senjaya Air Base, Bogor
- Technical, Supply and Ordnance Education Wing (Wing Pendidikan Teknik dan Pembekalan (Wingdiktekkal)) in Suryadarma Air Base, Subang and Husein Sastranegara Air Force Base, Bandung
- Air Force Material Maintenance Command (Komando Pemeliharaan Materiil TNI Angkatan Udara)
- Air Force Depot Maintenance 10 in Husein Sastranegara Air Base, Bandung
- Air Force Depot Maintenance 20 in Iswahyudi Air Base, Madiun
- Air Force Depot Maintenance 30 in Abdul Rachman Saleh Air Base, Malang
- Air Force Depot Maintenance 40 in Sulaiman Airbase (id), Bandung
- Air Force Depot Maintenance 50 in Adi Soemarmo Air Base, Surakarta
- Air Force Depot Maintenance 60 in Iswahyudi Air Base, Madiun
- Air Force Depot Maintenance 70 in Sulaiman Airbase (id), Bandung
- Air Force Infantry Corps
 Paskhas commandos in formation before parade in an Indonesian Air Force base for commemorating the Corp's anniversary
Paskhas commandos in formation before parade in an Indonesian Air Force base for commemorating the Corp's anniversary- Paskhas (Indonesian: Korps Pasukan Khas) Paskhas is the air force infantry and special forces of the Indonesian Air Force ("TNI-AU"). The corps is also known as the Orange Berets (Baret Jingga in Indonesian) because of their distinctive colour of their service headgear. Paskhas personnel is qualified for Para-Commando and land warfare. And, Paskhas is trained to seize and defend airfields from enemy forces known as Operasi Pembentukan dan Pengoperasian Pangkalan Udara Depan (OP 3 UD) (Frontline Air Base Establishment and Management Operation), airborne operations, and other specific military operations within the scope of the Indonesian Air Force. Paskhas detachment consists of:
- Paskhas Escort and Protocol unit (Satwalkol Paskhas) - Air Force HQs
- Paskhas Matra Detachment (Denmatra Paskhas)
- Paskhas Air Defense Detachment (Denhanud Paskhas)
- Para-Commandos Troop (461th-469th Commando Battalion)
- Paskhas Combat Support Regiment (Menbanpur Paskhas)
- Paskhas Training Centre (Pusdiklat Paskhas)
- Bravo Detachment 90, The Special Operations Unit (commando) of the Indonesian Air Force (TNI-AU) is known as Satuan Bravo 90 (SatBravo 90) which is the special operations detachment originating its members from the best chosen soldiers from the Paskhas air force corps. "SatBravo 90" is a specialized unit for hostage rescue of Aircraft hijacking, Anti-terror, and paralyzing heavy enemy equipment.
- Paskhas (Indonesian: Korps Pasukan Khas) Paskhas is the air force infantry and special forces of the Indonesian Air Force ("TNI-AU"). The corps is also known as the Orange Berets (Baret Jingga in Indonesian) because of their distinctive colour of their service headgear. Paskhas personnel is qualified for Para-Commando and land warfare. And, Paskhas is trained to seize and defend airfields from enemy forces known as Operasi Pembentukan dan Pengoperasian Pangkalan Udara Depan (OP 3 UD) (Frontline Air Base Establishment and Management Operation), airborne operations, and other specific military operations within the scope of the Indonesian Air Force. Paskhas detachment consists of:
Speciality Corps
- Pilot Corps (Bahasa Indonesia: Korps Penerbang, abbrv: (PNB))
- Navigator Corps (Bahasa Indonesia: Korps Navigator, abbrv: (NAV))
- Aviation Engineering Corps (Bahasa Indonesia: Korps Teknik, abbrv: (TEK)), such as Aircraft Engineer, Armaments Engineer and General Construction Engineering.
- Electronics Corps (Bahasa Indonesia: Korps Elektronika, abbrv: (LEK)), This corps is in charge of Avionics, RADAR, Communication and Air Traffic Control
- Administration Corps (Bahasa Indonesia: Korps Administrasi, abbrv: (ADM)), includes : Personnel Administration, Secretariat Administration and Finance Administration.
- Supply Corps (Bahasa Indonesia: Korps Perbekalan, abbrv: (KAL))
- Air Force Military Police Corps (Bahasa Indonesia: Korps Polisi Militer Angkatan Udara / POMAU, abbrv: (POM))
- Medical Service Corps of the Air Force (Bahasa Indonesia: Korps Kesehatan, abbrv: (KES)), includes: Medical Corps, Psychology and Physical Fitness and Sports Service Bureau.
- Special Corps (Bahasa Indonesia: Korps Dinas Khusus, abbrv: (SUS)), consist of Intelligence, Judge Advocate General's Corps, Military Band Service of the Air Force, Information and Communications Technology, Facility and Instrument, Electronic Data Processing, Foreign Language and Meteorology.
- Air Force Infantry Corps (Bahasa Indonesia: Korps Pasukan, abbrv: (PAS)), dedicated corps for Paskhas.
- Air Force Women's Service Corps (Bahasa Indonesia: Wanita Angkatan Udara, abbrv: (WARA)).
Force structure
| Indonesian Air Force Squadrons | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Aircraft
Chief of Staff of the Air Force
Rank Structure
In the Air Force, as well as in other armed forces branches in Indonesia, the rank consists of officer known as in Indonesian: "Perwira", NCO "Bintara" and enlisted "Tamtama".
The proper title to address of rank on official document are as follows, all high-ranking officers (Marshal) use their rank followed by "(TNI)", while other officers use their rank followed by respective branch/corps abbreviation. For example, an Air Force colonel from Flying Corps use the title "Kolonel (PNB)", while an Air Force Marshal from Flying Corps use the title "Marsekal (TNI)". Enlisted airmen are not required to put their respective branch/corps specialty.
Note: Indonesia is not a member of NATO, so there is not an official equivalence between the Indonesian military ranks and those defined by NATO. The displayed parallel is approximate and for illustration purposes only.
Officers
| Equivalent NATO Code | OF-10 | OF-9 | OF-8 | OF-7 | OF-6 | OF-5 | OF-4 | OF-3 | OF-2 | OF-1 | OF(D) & Student officer | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
(Edit) |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
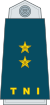
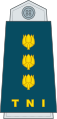
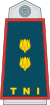
| Marsekal Besar | Marsekal | Marsekal Madya | Marsekal Muda | Marsekal Pertama | Kolonel | Letnan Kolonel | Mayor | Kapten | Letnan Satu | Letnan Dua | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Marshal of the Air Force | Air Chief Marshal | Air Marshal | Air Vice Marshal | Air Commodore | Colonel | Lieutenant Colonel | Major | Captain | First Lieutenant | Second Lieutenant | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Enlisted personnel
| Equivalent NATO Code | OR-9 | OR-8 | OR-7 | OR-6 | OR-5 | OR-4 | OR-3 | OR-2 | OR-1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
(Edit) |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pembantu Letnan Satu | Pembantu Letnan Dua | Sersan Mayor | Sersan Kepala | Sersan Satu | Sersan Dua | Kopral Kepala | Kopral Satu | Kopral Dua | Prajurit Kepala | Prajurit Satu | Prajurit Dua | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chief Warrant Officer | Warrant Officer | Sergeant Major | Master Sergeant | Staff Sergeant | Sergeant | Master Corporal | Corporal | Lance Corporal | Senior Airman | Airman First Class | Airman | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Notable incidents
- A Lockheed L-100-30 Hercules crashed on 20 November 1985, killing all 10 crew on board. The aircraft crashed into Mount Sibayak. The aircraft was conducting routine air patrol over Sumatra.
- A Lockheed C-130 Hercules crashed in Jakarta on 5 October 1991, killing 132 people comprising 119 passengers, 11 crew, and 2 people on ground. Only 1 survivor.[56]
- A Fokker F-27 crashed on 6 April 2009, killing all 24 occupants comprising 6 crew, an instructor and 17 special forces trainees on board.[57]
- A Lockheed L-100-30 Hercules, Model 382G-57C, A-1325, c/n 4917[58][59] crashed on 20 May 2009, killing at least 97 people and injuring 15 others, including some on the ground.[59][60] The aeroplane was carrying 98 passengers and 14 crew at the time[61] and was travelling from Halim Perdanakusuma International Airport in Jakarta to West Papua via Sulawesi.[60] Officials have stated that the plane crashed at about 6:30 a.m. around 5–7 kilometres from Iswahyudi Air Force Base.[60] An official statement has not been released.[59]
- A Fokker 27 crashed on 21 June 2012, 10 people were killed including all 7 crew on board the aircraft and 3 people on the ground. The aircraft crashed into a complex of military housing, and eight buildings were damaged or destroyed. The aircraft was conducting a routine training exercise.
- On 30 June 2015, a Lockheed C-130 Hercules crashed near a residential neighbourhood with 12 crew and 109 passengers on board shortly after taking off from Medan, killing all aboard, along with 22 people on the ground.
- 20 December 2015: An Indonesian Airforce T-50i Golden Eagle fighter plane had crashed in a flight demonstration during airshow in Adisutjipto Air Force Base in Yogyakarta, killing its two pilots.[62]
- On 18 December 2016 a Lockheed C-130 crashed while landing at Wamena Airport, killing all 13 passengers and crew aboard.
See also
References
- ↑ "Flightglobal – World Air Forces 2015" (PDF). Flightglobal.com. Retrieved 18 February 2018.
- ↑ "Scramble Magazine: Indonesian Air Arms Overview". Scramble.nl. Archived from the original on 16 September 2011. Retrieved 25 November 2011.
- ↑ Tempo English Edition magazine, 19–25 October 2011 p17
- ↑ Gady, Franz-Stefan (31 July 2017). "Confirmed: Indonesia to Buy 11 Su-35 Fighter Jets From Russia". The Diplomat. Archived from the original on 13 November 2017. Retrieved 13 November 2017.
- ↑ "Indonesia Invests in KFX Project". Business Korea. 23 November 2015. Archived from the original on 13 November 2017. Retrieved 13 November 2017.
- 1 2 3 Jon, Grevatt. "Indonesia reportedly negotiating price of Russian Su-35 fighters". IHS Janes 360. IHS Jane's Defence Weekly. Retrieved 6 March 2017.
- ↑ "Value of Indonesian Su-35 buy pegged at $1.14 billion". 23 August 2017. Retrieved 18 February 2018.
- ↑ "Mengenal Pesawat Nakajima Ki-43-II Hayabusa". TNI AU. Archived from the original on 2 April 2015. Retrieved 31 January 2015.
- ↑ Gordon & Rigmat(2004) p120
- ↑ Djoko Poerwoko (2001) p97
- ↑ Angkasa Edisi Koleksi No. 73, Year of 2011, Operasi Trikora, Page 3
- 1 2 Angkasa Edisi Koleksi No. 73, Operasi Udara Trikora, Year of 2011, Page 38.
- 1 2 3 4 Angkasa Edisi Koleksi No. 73, Operasi Udara Trikora, Year of 2011, Page 38
- ↑ Angkasa Edisi Koleksi No. 73, Operasi Udara Trikora, Year of 2011, Page 40–41
- ↑ Angkasa Edisi Koleksi No. 73, Operasi Udara Trikora, Year of 2011, Page 34
- 1 2 Angkasa Edisi Koleksi No. 73, Operasi Udara Trikora, Year of 2011, Page 44-46
- 1 2 3 4 Angkasa Edisi Koleksi No. 73, Operasi Udara Trikora, Year of 2011, Page 39
- ↑ Angkasa Edisi Koleksi No. 73, Operasi Udara Trikora, Year of 2011, Page 105
- ↑ Angkasa Edisi Koleksi No. 73, Operasi Udara Trikora, Year of 2011, Page 77
- ↑ [Crouch (2007), p. 240 ]
- ↑ [Djoko Poerwoko (2001) p92-96]
- ↑ Davies (2008) pp48, 51
- ↑ Djoko Poerwoko (2001) p153-155
- ↑ "F-16 Air Forces – Indonesia". F-16.net. Retrieved 25 November 2011.
- 1 2 Niels Hillebrand. "MILAVIA – Sukhoi Su-27 – Operator List". Milavia.net. Retrieved 25 November 2011.
- ↑ "Trade Registers". Retrieved 24 December 2014.
- ↑ Shamim, Asif. "Indonesia to get 24 F-16 block 25s". F-16.net. Retrieved 29 December 2017.
- ↑ "Indonesia F-16 Peace Bima-Sena". GlobalSecurity.org. Retrieved 29 December 2017.
- ↑ "US guarantees F-16 deal: House". 26 October 2011. Archived from the original on 9 November 2011.
- ↑ Angkasa (Sky) magazine, Gramedia, Jakarta No. 2 Year XXI November 2010. Page 42-43.
- ↑ "More Sukhoi Fighters for China, Indonesia". Aviation International News. Retrieved 24 December 2014.
- ↑ Gatra, Jakarta No. 2 Year XVII 18–24 November 2010. Page 35.
- ↑ Gatra, Jakarta No. 2 Year XVII 18–24 November 2010. Page 33.
- 1 2 "KF-X Fighter: Koreas Future Homegrown Jet". Retrieved 18 February 2018.
- ↑ "RI, China initiate joint-procurement of missiles". The Jakarta Post. 23 March 2011. Retrieved 25 November 2011.
- ↑ "$400m Deal Outlined for S. Korean Jets". The Jakarta Globe. Archived from the original on 23 September 2012. Retrieved 25 November 2011.
- ↑ "$T50i fighter jets strengthen Indonesian Air Force". Antara News. 13 February 2014. Retrieved 18 February 2014.
- ↑ "Indonesia, Embraer sign Super Tucano contract". Flightglobal.com. Retrieved 25 November 2011.
- ↑ "Embraer to supply additional Super Tucanos to Indonesia". Retrieved 18 February 2014.
- ↑ "Air force to get new aircraft next year". The Jakarta Post. 27 May 2008. Archived from the original on 2 January 2012. Retrieved 25 November 2011.
- ↑ "GROB G120TP wins competition to supply Indonesian Air Force with future trainer aircraft". GROB Aircraft. 16 September 2011. Retrieved 25 November 2011.
- ↑ "Air Force Inks Deal for Six More Fighter Jets". 31 December 2011. Archived from the original on 15 January 2012.
- ↑ "Indonesia buys Russian jet fighters in $500 mln contract". Russia Today. 10 January 2012. Archived from the original on 11 January 2012. Retrieved 10 January 2012.
- ↑ "Australia, RI prepare for transfer of C-130H Hercules". 4 January 2012.
- ↑ "Saab Offers "100% Technology Transfer" in Bid to Secure TNI Gripen Deal". 19 September 2014.
- ↑ Waldron, Greg (7 January 2014). "Indonesia eyes F-5E replacement options". www.flightglobal.com. Reed Business Information. Retrieved 8 January 2014.
- ↑ "Menengok Rencana Strategis Minimum Essential Force (MEF) TNI AU th 2009–2024. – JakartaGreater". jakartagreater.com. 30 December 2014. Retrieved 6 August 2016.
- ↑ "Indonesia Approves US$2 Billion Five Airbus A400M Aircraft Acquisition". www.defenseworld.net. Retrieved 18 February 2018.
- ↑ "Kemenhan Pastikan Indonesia Beli 10 Unit Sukhoi SU 35 dari Rusia - Tribunnews.com". Retrieved 18 February 2018.
- ↑ Hantoro, Juli (28 November 2017). "Menhan: Pembelian 11 Pesawat Sukhoi Su-35 Sudah Selesai". Retrieved 18 February 2018.
- ↑ Saraswati, Dias. "Kemhan RI Sudah Meneken Kontrak Pembelian 11 Sukhoi SU-35". Retrieved 18 February 2018.
- ↑ "Law" (PDF). kemendagri.go.id. 14 July 2016. Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 January 2018. Retrieved 9 January 2018.
- ↑ "Pembangunan sarana dan prasarana Skadud 16 Lanud Roesmin Nurjadin". tni.mil.id. 17 May 2013. Retrieved 22 July 2013.
- ↑ "16 Unit Pesawat F-16 Hadir di Pekanbaru". Riau pos.co. 17 July 2012. Retrieved 22 July 2013.
- ↑ "Dua Pesawat Baru CN 295 Kembali Perkuat TNI AU". 26 May 2014.
- ↑ "Musibah Hercules". garudamiliter.blogspot.com. Retrieved 2012-04-15.
- ↑ "Fokker F-27 Accident". Aviation-safety.net. Retrieved 25 November 2011.
- ↑ Olausson, Lars, "Lockheed Hercules Production List – 1954–2005, 22nd ed.", self-published, page 104.
- 1 2 3 "93 killed in military plane crash". News.ninemsn.com.au. 13 September 2009. Archived from the original on 20 April 2010. Retrieved 25 November 2011.
- 1 2 3 Rondonuwu, Olivia (20 May 2009). "'97 killed' as Hercules crashes into homes". The Independent. London. Retrieved 5 May 2010.
- ↑ "97 dead in Indonesian Hercules crash – ABC News (Australian Broadcasting Corporation)". Abc.net.au. 20 May 2009. Retrieved 25 November 2011.
- ↑ "Two pilots die in terrifying plane crash at air show in Yogyakarta, Indonesia". News.com.au. December 20, 2015. Retrieved 20 December 2015.
Bibliography
- Aero-News Network. "Indonesian Air Force Grounds OV-10 Bronco Fleet" 25 July 2007
- Angkasa (Sky) magazine, Gramedia, Jakarta No. 7 Year XVII April 2008
- Crouch, Harold (2007) The Army and Politics in Indonesia, Equinox, Jakarta ISBN 979-3780-50-9
- Davies, Steve (2008) Red Eagles: America's Secret MiGs Osprey Publishing ISBN 9781846039706
- F. Djoko Poerwoko (2001) My Home My Base: Perjalanan Sejarah Pangkalan Udara Iswahjudi 1939–2000, Publisher – Iswahjudi Air Force Base, No ISBN
- Indonesian Embassy, Ottawa: US to help RI in repair/refurbishing 15 of 24 RI's C-130 transport
- Grodin, Yefim & Rigmat, Vladimir (2004) Tupelov Tu-16 Badger , Aerofax, London ISBN 1-85780-177-6
- Scramble Magazine. "Indonesian Air Arms Overview"
- Willis, David (Ed). Aerospace Encyclopedia of the World's Air Forces. Aerospace Publishing, London, 1999 ISBN 1-86184-045-4
Further reading
- Carlo Kopp, 'Indonesia's Air Capacity of Critical Concern to Australia,' Australian Aviation magazine, April 1993, pages 32–41
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Indonesian Air Force. |
- Official Website of TNI-AU (Air Force)
- Watch Su-30mk2 Indonesian Air Forces video from YouTube
.svg.png)