Astros II MLRS
| ASTROS-II Multiple Launch Rocket System (MLRS) | |
|---|---|
|
ASTROS-II | |
| Type | Rocket artillery |
| Place of origin | Brazil |
| Service history | |
| In service | Since 1983 |
| Wars |
Iran–Iraq War Gulf War Angolan Civil War Yemeni Civil War (2015-present) Military Intervention in Yemen |
| Production history | |
| Manufacturer | Avibras |
| No. built | at least 164 |
| Specifications | |
| Weight |
10,000 kg (22,046 lbs)[1] |
| Length | 7 m (20 ft) |
| Width | 2.9 m (9 ft 6 in) |
| Height | 2.6 m (8 ft 6 in) |
| Crew | 3 |
|
| |
| Cartridge |
Rocket length: 4.20 m (13 ft 9 in)[2] Rocket weight: 152 kg (335 lb) [2] |
| Caliber | 180mm (7.08in)[2] |
| Maximum firing range | 16,000m (17,500yds) [2] |
|
| |
Main armament | Launcher Loader Module |
Secondary armament | 1 × 12.7 mm M2 Browning machine gun[1] |
| Engine |
Mercedes OM422 8-cylinder diesel 280 hp (209 kW)[1] |
| Suspension | 6×6 |
Operational range | 480 km (298 mi) |
| Speed | 90 Km/h (56 mph) |
ASTROS II (Artillery Saturation Rocket System) is a self-propelled multiple rocket launcher produced in Brazil by the Avibras company. It features modular design and employs rockets with calibers ranging from 127 mm to 300 mm. It was developed on the basis of a Tectran VBT-2028 6×6 all-terrain vehicle for enhanced mobility.
Overview
Astros II are normally grouped in artillery batteries consisting on average of about 13 vehicles: 6 of them are Astros II launchers, 6 are rocket resupply trucks and 1 a special radar-equipped vehicle controlling the fire-control system.[3] The launcher is capable of firing rockets of different calibres armed with a range of warheads.[4]
Each rocket resupply truck carries up to two complete reloads.[3]
Service history
The ASTROS II artillery system entered service with the Brazilian Army in 1983. The system is battle proven, having been used in action by the Iraqi Army in the Gulf Wars.
In the 1980s, Avibrás sold an estimated sixty-six Astros II artillery systems to Iraq. Iraq also built the Sajeel-60 which is a license-built version of the Brazilian SS-60. Sixty Astros II were sold to Saudi Arabia[5] and an unspecified number sold to Bahrain and Qatar. Total sales of the Astros II between 1982 and 1987 reached US$1 billion.[3] This fact made the Astros II multiple rocket launcher the most profitable weapon produced by Avibrás.[6]
In the 1980s and early 1990s, Avibrás worked almost exclusively with the manufacturing of rockets and multiple-launch rocket systems (MLRS), such as the Astros II, in addition to developing antitank and antiship missiles. At its peak, Avibrás employed 6,000 people; later it would be reduced to 900 people in the early 1990s as the arms industry demand fell. Even so, in the first Gulf War in 1991, the Astros II was successfully used by Saudi Arabia against Iraq.[7] Years earlier, the Astros II system helped Angola to defeat the UNITA.
New generation
The next step is an ambitious program, the Astros 2020 (Mk6), based on a 6x6 wheeled chassis.[8] Being a new concept, it will require an estimated investment of R$1.2 billion, of which about US$210 million will be invested solely in development. It will be integrated with the cruise missile AVMT-300 with 300-km range during the stage of testing and certification. It is said that the venture will, for example, enable the Army to integrate the Astros with defense anti-aircraft guns, paving the way for the utilization of common platforms, trucks, parts of electronic sensors and command vehicles.[9][10] The Astros 2020 will also be equipped with a 180 mm GPS-guided rocket called the SS-AV-40 with a range of 40 km (25 mi) 40 rockets carried and SS-150 newly developed rockets with a claimed maximum range of 150 km. Four of them are carried.[11] 36 Astros 2020 systems are to be acquired.[12]
Variants
- SS-30 – fires 127 mm rockets – Loads 32
- SS-40 – fires 180 mm rockets – Loads 16
- SS-60 – fires 300 mm rockets – Loads 4
- SS-80 – fires 300 mm rockets – Loads 4
- SS-150 – fires 450 mm rockets – Loads 4
- MTC-300 – cruise missile with a range of 300 kilometers (under development)
Specifications
.jpg)
.jpg)
- Range in indirect fire mode[13] (first figure is minimum range):
- SS-30: 9–30 km
- SS-40: 15–35 km
- SS-60: 20–60 km
- SS-80: 22–90 km
- SS-150: 29–150 km
- Armour: classified. Probably light composite to give protection against small-arms fire.
- Armament: one battery of 4, 16 or 32 rocket-launcher tubes
- Performance:
- fording 1.1 m
- vertical obstacle 1 m
- trench 2.29 m
- Ammunition Type: High explosive (HE) with multiple warhead
Operators
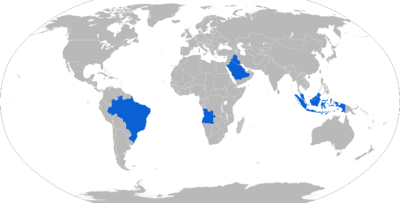
Current operators



- Brazilian Army 8 Astros II Mk3 more 12 Astros II Mk3M (3 batteries) and 5 Astros 2020 Mk6 (1 battery)
- Brazilian Marine Corps will use a naval variant, 6 Astros 2020 Mk6 (1 battery)




See also
References
- 1 2 3 ASTROS-II – Avibrás / Brasil
- 1 2 3 4 Hogg, Ian. Twentieth-Century Artillery. New York: Barnes & Noble Books, 2000. ISBN 0-7607-1994-2 Pg.304
- 1 2 3 4 "Page Not Found". Retrieved 28 December 2016.
- ↑ "Astros II Artillery Saturation Rocket System". Retrieved 28 December 2016.
- 1 2 Servaes, Army Recognition Alain. "Military army ground forces equipment Saudi Arabian Army Forces Saudi Arabia Equipements militaires armée forces terrestres Arabie Saoudite". Retrieved 28 December 2016.
- 1 2 Export Controls In Brazil
- ↑ "BBC News - BUSINESS - Cruise missiles 'Made in Brazil'". Retrieved 28 December 2016.
- ↑ http://www.military-today.com/artillery/astros_iii.htm
- ↑ Governo se torna sócio da Avibrás Aeroespecial
- ↑ "ANA株主優待券は安く買おう!便利な株主優待券の使い方!". Retrieved 28 December 2016.
- ↑ http://www.military-today.com/artillery/astros_iii.htm
- ↑ Brazilian army will continue to upgrade Astros rocket launchers – Armyrecognition.com, December 29, 2012
- ↑ ASTROS (Artillery SaTuration ROcket System)
- ↑ "Brazil releases funds to develop surface to surface missile system for the Army". Merco Press. 31 August 2011. Retrieved 20 May 2013.
- ↑ "Kosmo! Online - Negara". Retrieved 28 December 2016.
- ↑ "ЦАМТО / Главное / Компания "Авибрас" поставит СВ Индонезии РСЗО "Астрос-2"". Retrieved 28 December 2016.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to ASTROS II. |