Demographics of Angola
This article is about the demographic features of the population of Angola, including population density, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population.
According to 2014 census data, Angola had a population of 25,789,024 inhabitants in 2014.[1] Ethnically, there are three main groups, each speaking a Bantu language: the Ovimbundu who represent 37% of the population, the Ambundu with 25%, and the Bakongo 13%. Other numerically important groups include the closely interrelated Chokwe and Lunda, the Ganguela and Nyaneka-Khumbi (in both cases classification terms that stand for a variety of small groups), the Ovambo, the Herero, the Xindonga and scattered residual groups of San. In addition, mixed race (European and African) people amount to about 2%, with a small (1%) population of whites, mainly ethnically Portuguese.
As a former overseas territory of Portugal until 1975, Angola possesses a Portuguese population of over 200,000, a number that has been growing from 2000 onwards, because of Angola's growing demand for qualified human resources.[2][3][4][5] Besides the Portuguese, significant numbers of people from other European and from diverse Latin American countries (especially Brazil) can be found. From the 2000s, many Chinese have settled and started up small businesses, while at least as many have come as workers for large enterprises (construction or other). Observers claim that the Chinese community in Angola might include as many as 300,000 persons at the end of 2010, but reliable statistics are not at this stage available.[6] In 1974/75, over 25,000 Cuban soldiers arrived in Angola to help the MPLA forces at the beginning of the Angolan Civil War. Once this was over, a massive development cooperation in the field of health and education brought in numerous civil personnel from Cuba. However, only a very small percentage of all these people has remained in Angola, either for personal reasons (intermarriage) or as professionals (e.g., medical doctors).
The largest religious denomination is Catholicism, to which adheres about half the population. Roughly 26% are followers of traditional forms of Protestantism (Congregationals, Methodists, Baptista, Lutherans, Reformed), but over the last decades there has in addition been a growth of Pentecostal communities and African Initiated Churches. In 2006, one out of 221 people were Jehovah's Witnesses. Blacks from Mali, Nigeria and Senegal are mostly Sunnite Muslims, but do not make up more than 1 - 2% of the population. By now few Angolans retain African traditional religions following different ethnic faiths.
Population
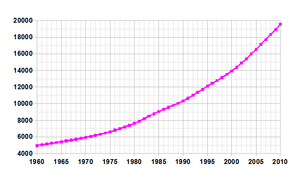
According to the 2017 revision of the World Population Prospects[7] the total population was 28,813,463 in 2016, compared to only 4 148 000 in 1950. The proportion of children below the age of 15 in 2010 was 46.6%, 50.9% was between 15 and 65 years of age, while 2.5% was 65 years or older .[8]
| Total population[9] | Population aged 0–14 (%) | Population aged 15–64 (%) | Population aged 65+ (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1950 | 4 148 000 | 41.2 | 55.7 | 3.1 |
| 1955 | 4 542 000 | 42.4 | 54.9 | 2.7 |
| 1960 | 4 963 000 | 43.7 | 53.6 | 2.7 |
| 1965 | 5 431 000 | 45.3 | 52.0 | 2.7 |
| 1970 | 5 926 000 | 46.0 | 51.3 | 2.7 |
| 1975 | 6 637 000 | 46.2 | 51.1 | 2.7 |
| 1980 | 7 638 000 | 46.5 | 50.8 | 2.7 |
| 1985 | 9 066 000 | 47.0 | 50.4 | 2.7 |
| 1990 | 10 335 000 | 47.5 | 49.9 | 2.6 |
| 1995 | 12 105 000 | 47.6 | 49.8 | 2.5 |
| 2000 | 13 926 000 | 47.7 | 49.9 | 2.5 |
| 2005 | 16 489 000 | 47.6 | 49.9 | 2.5 |
| 2010 | 19 082 000 | 46.6 | 50.9 | 2.5 |
| 2014 | 25 789 000 | 47.3 | 50.3 | 2.4 |
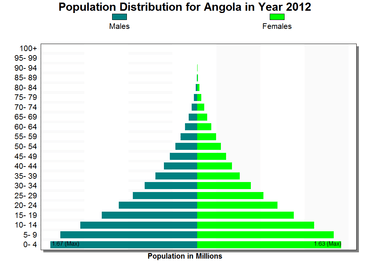
Structure of the population (DHS 2011) (Males 19 707, Females 20 356 = 40 063) :
| Age Group | Male (%) | Female (%) | Total (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0-4 | 21,3 | 21,3 | 21,3 |
| 5-9 | 15,5 | 13,7 | 14,6 |
| 10-14 | 12,2 | 12,1 | 12,1 |
| 15-19 | 9,7 | 10,9 | 10,3 |
| 20-24 | 8,1 | 10,1 | 9,1 |
| 25-29 | 7,8 | 7,7 | 7,7 |
| 30-34 | 5,5 | 5,0 | 5,3 |
| 35-39 | 4,4 | 4,5 | 4,4 |
| 40-44 | 3,4 | 2,8 | 3,1 |
| 45-49 | 3,1 | 2,0 | 2,5 |
| 50-54 | 2,9 | 4,7 | 3,8 |
| 55-59 | 2,0 | 1,9 | 1,9 |
| 60-64 | 1,6 | 1,5 | 1,6 |
| 65-69 | 1,0 | 0,7 | 0,8 |
| 70-74 | 0,8 | 0,5 | 0,6 |
| 75-79 | 0,4 | 0,3 | 0,3 |
| 80+ | 0,4 | 0,3 | 0,4 |
| unknown | 0,1 | 0,0 | 0,1 |
| Age group | Male (%) | Female (%) | Total (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0-14 | 49,0 | 47,1 | 48,0 |
| 15-64 | 48,3 | 51,1 | 49,8 |
| 65+ | 2,6 | 1,8 | 2,1 |
Vital statistics
Registration of vital events is in Angola not complete. The Population Department of the United Nations prepared the following estimates. [8]
| Period | Live births per year | Deaths per year | Natural change per year | CBR* | CDR* | NC* | TFR* | IMR* |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1950-1955 | 235 000 | 156 000 | 79 000 | 54.0 | 35.9 | 18.1 | 7.00 | 230 |
| 1955-1960 | 259 000 | 159 000 | 99 000 | 54.4 | 33.5 | 20.9 | 7.20 | 215 |
| 1960-1965 | 282 000 | 162 000 | 121 000 | 54.3 | 31.1 | 23.2 | 7.40 | 200 |
| 1965-1970 | 302 000 | 163 000 | 139 000 | 53.2 | 28.7 | 24.5 | 7.40 | 186 |
| 1970-1975 | 325 000 | 166 000 | 160 000 | 51.8 | 26.4 | 25.5 | 7.20 | 173 |
| 1975-1980 | 374 000 | 176 000 | 197 000 | 52.4 | 24.7 | 27.7 | 7.20 | 161 |
| 1980-1985 | 441 000 | 202 000 | 239 000 | 52.8 | 24.2 | 28.6 | 7.20 | 157 |
| 1985-1990 | 512 000 | 228 000 | 284 000 | 52.8 | 23.5 | 29.3 | 7.20 | 153 |
| 1990-1995 | 584 000 | 259 000 | 325 000 | 52.1 | 23.1 | 29.0 | 7.10 | 150 |
| 1995-2000 | 664 000 | 274 000 | 390 000 | 51.0 | 21.1 | 29.9 | 6.92 | 138 |
| 2000-2005 | 746 000 | 268 000 | 478 000 | 49.0 | 17.6 | 31.4 | 6.63 | 116 |
| 2005-2010 | 774 000 | 272 000 | 502 000 | 43.5 | 15.3 | 28.2 | 5.79 | 104 |
| * CBR = crude birth rate (per 1000); CDR = crude death rate (per 1000); NC = natural change (per 1000); IMR = infant mortality rate per 1000 births; TFR = total fertility rate (number of children per woman) | ||||||||
Fertility and Births
Total Fertility Rate (TFR) (Wanted TFR) and Crude Birth Rate (CBR):[10]
| Year | CBR (Total) | TFR (Total) | CBR (Urban) | TFR (Urban) | CBR (Rural) | TFR (Rural) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2006-2007 | 42.4 | 5.8 | 35.0 | 4.4 | 50.2 | 7.7 |
| 2011 | 45.5 | 6.3 | 36.5 | 4.6 | 51.8 | 7.7 |
| 2014 (census) | 5.7 | 5.2 | 6.5 | |||
| 2015-16 | 43.4 | 6.2 (5.2) | 40.6 | 5.3 (4.4) | 48.4 | 8.2 (7.1) |
Life expectancy
| Period | Life expectancy in Years[11] |
|---|---|
| 1950–1955 | 31.39 |
| 1955–1960 | |
| 1960–1965 | |
| 1965–1970 | |
| 1970–1975 | |
| 1975–1980 | |
| 1980–1985 | |
| 1985–1990 | |
| 1990–1995 | |
| 1995–2000 | |
| 2000–2005 | |
| 2005–2010 | |
| 2010–2015 |
CIA World Factbook demographic statistics
The following demographic statistics are from the CIA World Factbook, unless otherwise indicated.
Population
- 29,310,273 (July 2017 est.)
Population growth
The population is growing by 3.52% annually. There are 44.2 births and 9.2 deaths per 1,000 citizens. The net migration rate is 0.2 migrants per 1,000 citizens. The fertility rate of Angola is 6.16 children born per woman as of 2017. The infant mortality rate is 67.6 deaths for every 1,000 live births with 73.3 deaths for males and 61.8 deaths for females for every 1,000 live births. Life expectancy at birth is 60.2 years; 58.2 years for males and 62.3 years for females.
Sex ratio
- At birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
- Under 15 years: 1.02 male(s)/female
- 15–64 years: 1.03 male(s)/female
- 65 years and older: .79 male(s)/female
- Total population: 1.02 male(s)/female (2011 est.)
Health
According to the CIA World Factbook, 2% of adults (aged 15–49) are living with HIV/AIDS (as of 2009).[12] The risk of contracting disease is very high. There are food and waterborne diseases, bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever; vectorborne diseases, malaria, African trypanosomiasis (sleeping sickness); respiratory disease: meningococcal meningitis, and schistosomiasis, a water contact disease, as of 2005.
Ethnic groups
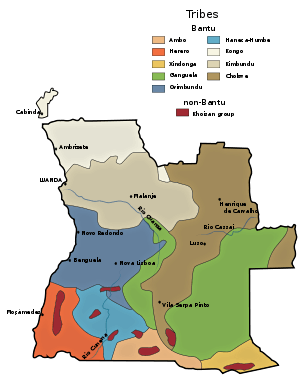
Roughly 37% of Angolans are Ovimbundu, 25% are Ambundu, 13% are Bakongo, 2% are mestiço, 1-2% are white Africans, and people from other African ethnicities make up 22% of Angola's population.
Religions
Angola is a majority Christian country. Official statistics don't exist, but it is estimated that over 80% belong to a Christian church or community. More than half are Catholic, the remaining ones comprising members of traditional Protestant churches as well as of Pentecostal communities. Only 1 - 2% are Muslims - generally immigrants from other African countries. Traditional indigenous religions are practized by a very small minority, generally in peripheral rural societies.
Education
Literacy is quite low, with 71.1% of the population over the age of 15 able to read and write in Portuguese. 82% of males and 60.7% of women are literate as of 2015.
Languages
Portuguese is the official language of Angola, but Bantu and other African languages are also widely spoken. In fact, Kikongo, Kimbundu, Umbundu, Tuchokwe, Nganguela, and Ukanyama have the official status of "national languages". The mastery of Portuguese is widespread; in the cities the overwhelming majority are either fluent in Portuguese or have at least a reasonable working knowledge of this language; an increasing minority are native Portuguese speakers and have a poor, if any, knowledge of an African language.
References
- ↑ Archived May 6, 2016, at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ In 1974, white Angolans made up a population of 330,000 to 350,000 people in an overall population of 6.3 million Angolans at that time. The only reliable source on these numbers is Gerald Bender & Stanley Yoder, Whites in Angola on the Eve of Independence: The Politics of Numbers, Africa Today, 21 (4) 1974, pp. 23 - 37. Today, many Angolans who are not ethnic Portuguese can claim Portuguese nationality under Portuguese law. Estimates on the overall population are given in O País
- ↑ "Flight from Angola". The Economist. 1975-08-16. ISSN 0013-0613. Retrieved 2017-07-10.
- ↑ "Angola - The Portuguese Coup d'Etat and the End of the Colonial Era". countrystudies.us. Retrieved 2017-07-10.
- ↑ (in Portuguese) Portugueses em Angola quadruplicaram, Jornal de Notícias (March 10, 2009)
- ↑ "BBC News - Chinese karaoke fans sing Angola's praises". news.bbc.co.uk. Retrieved 2017-07-18.
- ↑ "World Population Prospects: The 2017 Revision". ESA.UN.org (custom data acquired via website). United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. Retrieved 10 September 2017.
- 1 2 "Population Division of the Department of Economic and Social Affairs of the United Nations Secretariat, World Population Prospects: The 2010 Revision". Esa.un.org. Retrieved 2017-08-27.
- ↑ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on May 6, 2016. Retrieved January 10, 2017.
- ↑ "MEASURE DHS: Demographic and Health Surveys". microdata.worldbank.org. Retrieved 2017-07-18.
- ↑ "World Population Prospects - Population Division - United Nations". esa.un.org. Retrieved 2018-08-26.
- ↑ "The World Factbook — Central Intelligence Agency". www.cia.gov. Retrieved 2017-07-10.


External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Demographics of Angola. |