Central–Eastern Malayo-Polynesian languages
| Central–Eastern Malayo-Polynesian | |
|---|---|
| Geographic distribution | East Indonesia and Pacific Islands |
| Linguistic classification |
Austronesian
|
| Subdivisions |
|
| Glottolog | cent2237[1] |
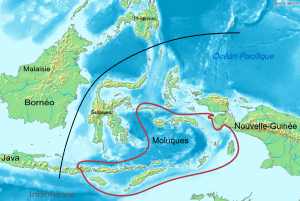 The Central MP languages (red). (In black is the Wallace Line.) | |
The Central–Eastern Malayo-Polynesian (CEMP) languages form a proposed branch of the Malayo-Polynesian languages consisting of over 700 languages (Blust 1993).[2] In the original proposal, CEMP is divided into Central Malayo-Polynesian (CMP) and Eastern Malayo-Polynesian (EMP). However, CMP is generally understood to be a cover term for the non-EMP languages within CEMP, which form a linkage at best rather than a valid clade.
The Central Malayo-Polynesian languages are spoken in the Lesser Sunda and Maluku Islands of the Banda Sea, in an area corresponding closely to the Indonesian provinces of East Nusa Tenggara and Maluku and the nation of East Timor (excepting the Papuan languages of Timor and nearby islands), but with the Bima language extending to the eastern half of Sumbawa Island in the province of West Nusa Tenggara and the Sula languages of the Sula Archipelago in the southwest corner of the province of North Maluku. The principal islands in this region are Sumbawa, Sumba, Flores, Timor, Buru, and Seram. The numerically most important languages are Nggahi Mbojo (Bimanese), Manggarai of western Flores, Uab Meto of West Timor, and Tetum, the national language of East Timor.
The Central Malayo-Polynesian languages may form a linkage. They are for the most part poorly attested, but they do not appear to constitute a coherent group. Many of the proposed defining features of CMP are not found in the geographic extremes of the area. Therefore some linguists consider it a linkage; a conservative classification might consider CMP to be a convenient term for those Central–Eastern languages which are not Eastern Malayo-Polynesian (Grimes 1991).
The Eastern Malayo-Polynesian languages extend from the coasts of Halmahera across the Pacific. This subgroup is still controversial as it is solely based on lexical evidence, with no shared phonological innovations.[3] In contrast, the two individual branches, South Halmahera–West New Guinea and Oceanic, each are well-defined by phonological and lexical innovations, and universally accepted as valid subgroups.
Languages
Given the poor support for larger groupings, some of the groups listed here are provisional.
- Central Malayo-Polynesian languages.
- Bima language, spoken on the eastern half of Sumbawa Island.
- Sumba–Flores languages, spoken on and around the islands of Sumba and western–central Flores in the Lesser Sundas.
- Flores–Lembata languages, spoken in the Lesser Sundas, on eastern Flores and small islands immediately east of Flores.
- Selaru languages, spoken in the Tanimbar Islands of Indonesia.
- Kei–Tanimbar languages, spoken in the Kei and Tanimbar Islands of the southern Malukus, and on the north side of the Bomberai Peninsula.
- Aru languages, spoken on the Aru Islands in Indonesia.
- Central Maluku languages, spoken principally on the Seram, Buru, Ambon, Kei, and the Sula Islands.
- Timoric, or Timor–Babar, languages, spoken on the islands of Timor, neighboring Wetar, and (depending on the classification) the Babar Islands to the east.
- Kowiai language, spoken on the Bomberai Peninsula in New Guinea.
- Teor-Kur language, spoken near Kei Island, Indonesia.
- Eastern Malayo-Polynesian languages.
- South Halmahera–West New Guinea languages, found in the islands and along the shores of the Halmahera Sea in the Indonesian province of North Maluku and of Cenderawasih Bay in the provinces of Papua and West Papua.
- Oceanic languages, spoken in Polynesia, as well as much of Melanesia and Micronesia.
Notes
- ↑ Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin, eds. (2017). "Central–Eastern Malayo-Polynesian". Glottolog 3.0. Jena, Germany: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History.
- ↑ Blust, R. (1993). Central and Central-Eastern Malayo-Polynesian. Oceanic Linguistics, 32(2), 241-293.
- ↑ Ross, Malcolm (2005), "Some current issues in Austronesian linguistics", in D.T. Tryon, ed., Comparative Austronesian Dictionary, 1, 45-120. Berlin: Mouton de Gruyter.
References
- Fay Wouk and Malcolm Ross (ed.), The history and typology of western Austronesian voice systems. Australian National University, 2002.
- K. Alexander Adelaar and Nikolaus Himmelmann, The Austronesian languages of Asia and Madagascar. Routledge, 2005.