Ana Chaves Bay
| Ana Chaves Bay Baía Ana Chaves | |
|---|---|
 Satellite image of the city of São Tomé and Ana Chaves Bay | |
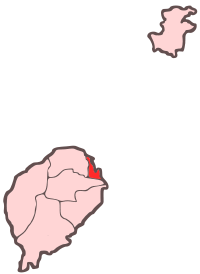
 Ana Chaves Bay Ana Chaves Bay at the northeast of São Tomé Island | |
| Location | São Tomé and Príncipe |
| Coordinates | 0°20′52.4″N 6°43′42.6″E / 0.347889°N 6.728500°E |
| Type | Bay |
| Ocean/sea sources | Atlantic Ocean |
| Max. depth | .3 miles (0.48 km) |
| Settlements | São Tomé |
Ana Chaves Bay (Portuguese: Baía Ana Chaves) is the harbour and port to the capital city of São Tomé in São Tomé and Príncipe. It ranges from the runway of São Tomé International Airport at the north to Ponta São Tomé at the south. Forte de São Sebastião, now part of São Sebastião Museum, formerly occupied Ponta São Tomé, but reclaimed land now extends .2 miles (0.32 km) past the point. The bay ranges in depth from 2 metres (6.6 ft) near shore to .3 miles (0.48 km) seaward. The bay provides safe anchorage to small vessels; those drawing more than 10 feet (3.0 m) cannot enter the bay.[1]
.jpg)
At the bay in the city of São Tomé is the bay's rear lighthouse, built in 1994 for ships entering and leaving the city's port. Its focal height is 9 metres and its range is nearly 12 km (6 nmi).[2]
History
Birds, frogs and other animals dominate the bay before the island was inhabited. Around the 19th century, wildlife became less dominant. Wildlife within the bay is not common as the earlier times. Several endangered birds includes the São Tomé olive pigeon are seen and rarely the São Tomé fiscal.
In the 18th and the 20th centuries, coffee and cocoa were exported to other countries particularly Portugal and also supplied to other parts of Europe, at the time, Portuguese São Tomé and Príncipe was one of the largest cocoa exporters in the world.
In the 1990s and the 2000s, as the country had insufficient food supply other than coffee, tropical fruits and cocoa, 90% of the foodstuffs are imported and almost all of it are sent into the port. Oil supplies are rarely imported into the port as the port of Neves has recently been enlarged in 2014.
In 2011, the government of São Tomé and Príncipe granted a long-term concession to Angolan state oil company Sonangol to control and develop the port in which Sonangol have been reported to have invested US$30 million in developing a free trade zone.[3]
Nature
Marine fauna native to the area includes Phymatolithon tenuissimum which is also founded in Praia Lagarto.
Other
Another feature named after Ana Chaves is Pico Ana Chaves located on the island near Pico de São Tomé.
See also
References
- ↑ No. 23: Sailing Directions (Enroute) , Southwest Coast Of Africa (PDF) (15 ed.). Springfield, Virginia: National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency. 2014. pp. 70–71. Retrieved 2016-09-14.
- ↑ "Sao Tome & Principe". ARLHS World of Lights (WLOL). Amateur Radio Lighthouse Society. April 8, 2009. Retrieved 4 May 2017.
- ↑ "Concession awarded in São Tomé". World Cargo News. 25 January 2011. Retrieved 11 November 2011.
External links