São Tomé
| São Tomé | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| City | |||
_(2).jpg) Baía Ana Chaves, São Tomé | |||
| |||
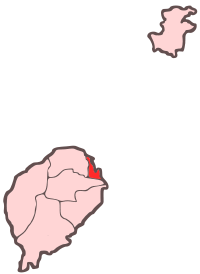
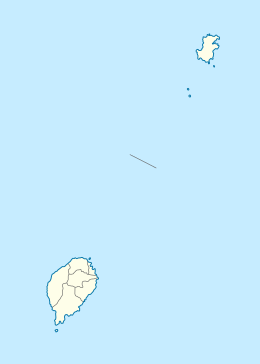 São Tomé Location on São Tomé Island  São Tomé São Tomé (Africa) | |||
| Coordinates: 0°20′10″N 6°43′50″E / 0.33611°N 6.73056°ECoordinates: 0°20′10″N 6°43′50″E / 0.33611°N 6.73056°E | |||
| Country |
| ||
| Province | São Tomé Province | ||
| District | Água Grande | ||
| Founded | 1485 | ||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 17 km2 (7 sq mi) | ||
| Elevation | 137 m (449 ft) | ||
| Population (2018 census) | |||
| • Total | 71,868 | ||
| • Density | 4,200/km2 (11,000/sq mi) | ||
| Time zone | UTC+1 (WAT) | ||
| Area code(s) | +239-11x-xxxx through 14x-xxxx | ||
São Tomé is the capital and largest city of São Tomé and Príncipe. Its name is Portuguese for "Saint Thomas". It had a population of 71,868 at the 2018 census, accounting for over a third of the total population of the country (208,000).[1]
History
Álvaro Caminha founded the colony of São Tomé in 1493. The Portuguese came to São Tomé in search of land to grow sugar. The island was uninhabited before the arrival of the Portuguese sometime around 1470. São Tomé, situated right on the equator, had a climate wet enough to grow sugar in wild abundance. The nearby African Kingdom of Kongo eventually became a source of slave labourers to work the sugar plantations. São Tomé is centred on a sixteenth-century cathedral. Another early building is Fort São Sebastião, built in 1575 and now the São Tomé National Museum. On July 9, 1595, Rei Amador and most of the slaves took part in the Revolta Angolar, marching into the capital; they were subjugated the following year.[2] Not long after, in 1599, the Dutch took the city as well as the islands for two days; they re-occupied it in 1641 for a year. The city served as the capital of the Portuguese colony of São Tomé and Príncipe and, from São Tomé and Príncipe's independence in 1975, as capital of the sovereign nation.
Geography and location
Important as a port, São Tomé is located on Ana Chaves Bay in the northeast of São Tomé Island, and Ilhéu das Cabras lies nearby offshore. São Tomé is located northeast of Trindade, southeast of Guadalupe and northwest of Santana. It is linked to these towns by various roadways, but especially by the highway encircling the entire island of São Tomé. It is linked to Cape Verde by a weekly ferry.
Features of the town include the Presidential Palace, the cathedral, and a cinema. The city is also home to schools, middle schools, high schools, one polytechnic, two markets, three radio stations, the public television station TVSP, several clinics and hospitals, the country's main airport - São Tomé International Airport (with direct regular scheduled flights to Angola, Gabon, Ghana and Portugal as well as occasional domestic flights to Príncipe), and many squares (praças). São Tomé also serves as the centre of the island's road and bus networks. The town is well known for the tchiloli playing.
Population history
| Historical population | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
| 1990 (June 23, Census) | 42,331 | — |
| 2000 (June 16, Census) | 49,957 | +18.0% |
| 2003 (Estimate) | 53,300 | +6.7% |
| 2018 (July 1, Estimate) | 71,868 | +34.8% |
Transport
São Tomé is served by São Tomé International Airport (IATA: TMS, ICAO: FPST) with regular flights to Europe and other African Countries.
Climate
São Tomé features a tropical wet and dry climate (As) with a relatively lengthy wet season and a short dry season. The wet season runs from October through May while the dry season covers the remaining four months. São Tomé sees on average just under 1,000 mm (39 in) of precipitation per year. Temperatures in the city are relatively constant, with average high temperatures usually around 30 °C (86 °F) and average low temperatures around 22 °C (72 °F).
| Climate data for São Tomé (São Tomé International Airport) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 32.0 (89.6) |
33.6 (92.5) |
33.5 (92.3) |
33.4 (92.1) |
33.9 (93) |
31.0 (87.8) |
30.7 (87.3) |
31.0 (87.8) |
31.7 (89.1) |
31.5 (88.7) |
31.6 (88.9) |
32.0 (89.6) |
33.9 (93) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 29.4 (84.9) |
29.9 (85.8) |
30.2 (86.4) |
30.1 (86.2) |
29.3 (84.7) |
28.0 (82.4) |
27.3 (81.1) |
27.7 (81.9) |
28.6 (83.5) |
28.7 (83.7) |
29.0 (84.2) |
29.1 (84.4) |
28.9 (84) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 25.9 (78.6) |
26.2 (79.2) |
26.4 (79.5) |
26.4 (79.5) |
26.0 (78.8) |
24.7 (76.5) |
23.8 (74.8) |
24.1 (75.4) |
25.0 (77) |
25.2 (77.4) |
25.5 (77.9) |
25.6 (78.1) |
25.4 (77.7) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 22.4 (72.3) |
22.5 (72.5) |
22.6 (72.7) |
22.6 (72.7) |
22.6 (72.7) |
21.4 (70.5) |
20.4 (68.7) |
20.5 (68.9) |
21.3 (70.3) |
21.8 (71.2) |
22.0 (71.6) |
22.1 (71.8) |
21.8 (71.2) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 19.1 (66.4) |
19.6 (67.3) |
19.2 (66.6) |
19.4 (66.9) |
18.5 (65.3) |
14.0 (57.2) |
14.0 (57.2) |
13.4 (56.1) |
16.0 (60.8) |
18.3 (64.9) |
18.8 (65.8) |
19.6 (67.3) |
13.4 (56.1) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 81 (3.19) |
84 (3.31) |
131 (5.16) |
122 (4.8) |
113 (4.45) |
19 (0.75) |
0 (0) |
1 (0.04) |
17 (0.67) |
110 (4.33) |
99 (3.9) |
108 (4.25) |
884 (34.8) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 8 | 8 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 6 | 12 | 11 | 8 | 94 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 85 | 84 | 83 | 83 | 84 | 79 | 77 | 78 | 79 | 82 | 85 | 85 | 82 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 142.6 | 135.6 | 139.5 | 126.0 | 145.7 | 165.0 | 161.2 | 148.8 | 120.0 | 114.7 | 135.0 | 142.6 | 1,676.7 |
| Mean daily sunshine hours | 4.6 | 4.8 | 4.5 | 4.2 | 4.7 | 5.5 | 5.2 | 4.8 | 4.0 | 3.7 | 4.5 | 4.6 | 4.6 |
| Source: Deutscher Wetterdienst[3] | |||||||||||||
Education
- National Lyceum
- University of São Tomé and Príncipe, formed in 2016
The following Portuguese international schools are in the city:[4]
- Escola Portuguesa de S. Tomé
- Instituto Diocesano de Formação João Paulo II
- Escola Bambino
- Escola Internacional de S. Tomé e Príncipe
It has one of the few libraries in the country and the most used, the National Library of São Tomé and Príncipe.
Health
The city has a hospital named Centro hospitalar de São Tomé (Central Hospital), also known as Dr. Ayres Menezes Hospital.
Gallery
.jpg)
.jpg) São Tomé City.
São Tomé City..jpg) The city`s port seen from Baía Ana Chaves
The city`s port seen from Baía Ana Chaves São Tomé seen from space.
São Tomé seen from space..jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg) Kids pier jumping
Kids pier jumping.jpg) São Tomé city centre
São Tomé city centre.jpg) The old seat of Bank of São Tomé and Príncipe.
The old seat of Bank of São Tomé and Príncipe..jpg) Downtown São Tomé
Downtown São Tomé.jpg)
.jpg) Local stadium in the city.
Local stadium in the city..jpg) São Tomé, STP
São Tomé, STP.jpg) Baía Ana Chaves, São Tomé
Baía Ana Chaves, São Tomé
Points of interest
- Our Lady of Conception Church
- Our Lady of Grace Cathedral
- São Sebastião Museum
- São Sebastião Lighthouse - inside the museum, the only museum in the nation
- Supreme Court of Justice building
Sports
Sports clubs, notably football (soccer) based in the city include Sporting Praia Cruz, another one is Vitória FC based in the neighborhood of Riboque. All clubs play at Estádio Nacional 12 de Julho.
Notable people
- José Vianna da Motta (1868–1948) a distinguished Portuguese pianist, teacher and composer
- Alfredo Azancot (1872-??) a Portuguese architect who emigrated to Chile
- José de Almada Negreiros (1893–1970) a Portuguese artist, created literature and painting, and developed ballet choreographies
- Francisco José Tenreiro (1921-1963) a São Toméan geographer, poet and highly regarded writer of the colonial era
- Alda Neves da Graça do Espírito Santo (1926–2010) a poet working in Portuguese, she also served in the Santomean government after independence
- Guadalupe de Ceita (born 1929) a Santomean writer and a doctor and national hero
- Miguel Trovoada (born 1936) was Prime Minister 1975–1979 and President 1991–2001 of São Tomé and Príncipe
- Fradique de Menezes (born 1942) the President of São Tomé and Príncipe from 2003 to 2011
- Olinda Beja (born 1946) a São Tomé and Príncipe poet, writer and narrator, emigrated to Portugal and moved to Viseu
- Tomé Vera Cruz (born 1955?) Prime Minister of São Tomé and Príncipe from April 2006 to February 2008
- Conceição Lima (born 1961) a Santomean poet from the town of Santana
- Patrice Trovoada (born 1962) a São Toméan politician, Prime Minister of São Tomé and Príncipe 2008 to June 2008, 2010 to December 2012 and since November 2014
- Aurélio Martins (born 1966) a São Toméan journalist, businessman and politician
Sports
- Nuno Espírito Santo (born 1974) a retired Portuguese footballer, head coach of English club Wolverhampton Wanderers F.C.
- Naide Gomes (born 1979) a former heptathlete and long jumper, competed in 100 metres hurdles at the 2000 Summer Olympics
- Lasset dos Santos, (born 1986) a local footballer
- Yazaldes Nascimento (born 1986) a Portuguese athlete, runs the 100 metres, competed in the 2004 Summer Olympics
- Alcino Silva (born 1990) a sprint canoer, competed in the 2008 Summer Olympics in Beijing
- Harramiz (born 1990) a Santoméan professional footballer who plays in Portugal
- José da Silva (born 1991) local footballer
- Buly Da Conceição Triste (born 1991) a sprint canoeist, competed at the 2016 Summer Olympics
- Faduley (born 1992) footballer in Portugal
- Charles Monteiro (born 1994) a São Toméan footballer who plays in Portugal
- Gilson Costa (born 1996) a Portuguese professional footballer
- Romário Leitão (born 1997) a long distance runner, competed at the 2016 Summer Olympics in the men's 5000 metres
- Gedson Fernandes (born 1999) a Portuguese professional footballer
Twin towns and Sister cities
São Tomé is twinned with:
References
- ↑ Sao Tome
- ↑ Lemos, Carlos Neves. Esboço Histórico das Ilhas de S.Tomé e Príncipe. 1975
- ↑ "Klimatafel von Sao Tomé (Flugh.) / Sao Tomé und Principe" (PDF). Baseline climate means (1961-1990) from stations all over the world (in German). Deutscher Wetterdienst. Retrieved January 26, 2016.
- ↑ "ESCOLAS COM CURRÍCULO PORTUGUÊS EM S. TOMÉ" (Archive). Direção de Serviços de Ensino e Escolas Portuguesas no Estrangeiro (DSEEPE) of the Portuguese Education Ministry. Retrieved on October 26, 2015.
- ↑ "Lisboa - Geminações de Cidades e Vilas" [Lisbon - Twinning of Cities and Towns]. Associação Nacional de Municípios Portugueses [National Association of Portuguese Municipalities] (in Portuguese). Retrieved 2013-08-23.
- ↑ "Acordos de Geminação, de Cooperação e/ou Amizade da Cidade de Lisboa" [Lisbon - Twinning Agreements, Cooperation and Friendship]. Camara Municipal de Lisboa (in Portuguese). Retrieved 2013-08-23.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to São Tomé. |
- Sao Tome and Principe at Curlie (based on DMOZ)
- www.saotome.st - Facts about the country, how to get there, where to stay, what to do, images etc.
- Local travel agency Navetur-Equatour - information&pictures http://www.navetur-equatour.st/