109th United States Congress
| 109th United States Congress | |
|---|---|
|
108th ← → 110th | |
 House Speaker Dennis Hastert (2006) | |
| January 3, 2005 – January 3, 2007 | |
| Senate President | Dick Cheney (R) |
| Senate Pres. pro tem | Ted Stevens (R) |
| House Speaker | Dennis Hastert (R) |
| Members |
100 senators 435 representatives 5 non-voting delegates |
| Senate Majority | Republican |
| House Majority | Republican |
| Sessions | |
|
1st: January 4, 2005 – December 22, 2005 2nd: January 3, 2006 – December 8, 2006 | |
The One Hundred Ninth United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, composed of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives, from January 3, 2005 to January 3, 2007, during the fifth and sixth years of George W. Bush's presidency. House members were elected in the 2004 elections on November 2, 2004. Senators were elected in three classes in the 2000 elections on November 7, 2000, 2002 elections on November 5, 2002, or 2004 elections on November 2, 2004. The apportionment of seats in the House of Representatives was based on the Twenty-second Census of the United States in 2000. Both chambers had a Republican majority, the same party as President Bush.
Major events
- January 20, 2005 — President George W. Bush began his second term.
- November 7, 2006 — California Representative Nancy Pelosi and Nevada Senator Harry Reid lead the Democratic Party in taking control of both the House and the Senate in the 2006 congressional elections, the first time in 12 years the Democrats secure control of both houses of Congress simultaneously.
- Prominent events included the filibuster "nuclear option" scare, the failure of the federal government to promptly respond to Hurricane Katrina disaster relief, the Tom DeLay corruption investigation, Plamegate, the rising unpopularity of the Iraq War, the 2006 immigration reform protests and government involvement in the Terri Schiavo case.
- In addition to the DeLay indictment, this Congress also had a number of scandals: Bob Ney, Randy "Duke" Cunningham, William J. Jefferson, Mark Foley scandal, and the Jack Abramoff scandals.
- This Congress met for 242 days, the fewest since World War II and 12 days fewer than the 80th Congress.[1][2][3] As the Congress neared its conclusion, some media commentators labelled this the "Do Nothing Congress," [1][4][5][6][7] a pejorative originally given to the 80th United States Congress by President Harry Truman, although the number of bills passed by Congress is no measure of its success.
- The President vetoed only one bill, his first veto, the Stem Cell Research Enhancement Act of 2005.
Major legislation
Enacted

_looking_on%2C_President_George_W._Bush_signs_into_law_S-3728%2C_the_North_Korea_Nonproliferation_Act_of_2006%2C_Friday%2C_Oct._13%2C_2006%2C_in_the_Oval_Office.jpg)
- February 17, 2005: Class Action Fairness Act of 2005, Pub.L. 109–2
- March 21, 2005: Theresa Marie Schiavo's law, Pub.L. 109–3
- April 20, 2005: Bankruptcy Abuse Prevention and Consumer Protection Act, Pub.L. 109–8
- April 27, 2005: Family Entertainment and Copyright Act, Pub.L. 109–9
- July 28, 2005: Dominican Republic-Central America-United States Free Trade Agreement Implementation Act (CAFTA Implementation Act), Pub.L. 109–53
- July 29, 2005: Energy Policy Act of 2005, Pub.L. 109–58
- August 10, 2005: Transportation Equity Act of 2005, Pub.L. 109–59
- October 26, 2005: Protection of Lawful Commerce in Arms Act, Pub.L. 109–92
- December 1, 2005: Caribbean National Forest Act of 2005, Pub.L. 109–118
- December 22, 2005: Presidential $1 Coin Act of 2005, Pub.L. 109–145
- December 30, 2005: Department of Defense Appropriations Act, 2006, Pub.L. 109–148
- February 8, 2006: Deficit Reduction Act of 2005, Pub.L. 109–171
- March 8, 2006: USA PATRIOT Improvement and Reauthorization Act of 2006, Pub.L. 109–177
- May 17, 2006: Tax Increase Prevention and Reconciliation Act of 2005, Pub.L. 109–222
- May 29, 2006: Respect for America's Fallen Heroes Act, Pub.L. 109–228
- July 27, 2006: Adam Walsh Child Protection and Safety Act, Pub.L. 109–248
- September 26, 2006: Federal Funding Accountability and Transparency Act of 2006, Pub.L. 109–282
- October 13, 2006: Safe Port Act, Pub.L. 109–347, including title VIII, Unlawful Internet Gambling Enforcement Act of 2006
- October 17, 2006: Military Commissions Act of 2006, Pub.L. 109–366
- October 26, 2006: Secure Fence Act of 2006, Pub.L. 109–367
- December 20, 2006: Stolen Valor Act of 2005, Pub.L. 109–437
- December 20, 2006: Tax Relief and Health Act of 2006, Pub.L. 109–432
Proposed, but not enacted
- H.R. 554 — Personal Responsibility in Food Consumption Act
- H.R. 810 — Stem Cell Research Enhancement Act of 2005 (Vetoed)
- H.R. 1505 — Jessica Lunsford Act
- H.R. 4437 — Border Protection, Anti-terrorism and Illegal Immigration Control Act of 2005
- H.R. 4569 — Digital Transition Content Security Act
- S. 147 — Native Hawaiian Government Reorganization Act of 2005 (Akaka Bill)
- S. 2611 — Comprehensive Immigration Reform Act of 2006
More information: Complete index of Public and Private Laws for 109th Congress at U.S. Government Printing Office
Hearings
- Congressional response to the NSA warrantless surveillance program (Senate Judiciary; House Intelligence; Democrats of the House Judiciary)
Party summary
Senate
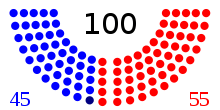
The party summary for the Senate remained the same during the entire 109th Congress. On January 16, 2006, Democrat Jon Corzine resigned, but Democrat Bob Menendez was appointed and took Corzine's seat the next day.
| Party (shading shows control) |
Total | Vacant | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic (D) |
Independent (I) | Republican (R) | |||
| End of the previous congress | 48 | 1 | 51 | 100 | 0 |
| Begin | 44 | 1 | 55 | 100 | 0 |
| End | |||||
| Final voting share | 44.0% | 1.0% | 55.0% | ||
| Beginning of the next congress | 49 | 2 | 49 | 100 | 0 |
House of Representatives
Due to resignations and special elections, Republicans lost a net of three seats; Democrats gained one seat; three seats were left vacant; and one seat which was vacant at the beginning of the Congress was filled. All seats were filled though special elections. (See Changes in membership, below.)
| Affiliation | Party (Shading shows control) |
Total | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Independent | Republican | Vacant | ||
| End of previous Congress | 207 | 1 | 225 | 433 | 2 |
| Begin | 201 | 1 | 232 | 434 | 1 |
| March 10, 2005 | 202 | 435 | 0 | ||
| April 29, 2005 | 231 | 434 | 1 | ||
| August 2, 2005 | 230 | 433 | 2 | ||
| September 6, 2005 | 231 | 434 | 1 | ||
| December 1, 2005 | 230 | 433 | 2 | ||
| December 7, 2005 | 231 | 434 | 1 | ||
| January 16, 2006 | 201 | 433 | 2 | ||
| June 9, 2006 | 230 | 432 | 3 | ||
| June 13, 2006 | 231 | 433 | 2 | ||
| September 29, 2006 | 230 | 432 | 3 | ||
| November 3, 2006 | 229 | 431 | 4 | ||
| November 13, 2006 | 202 | 230 | 433 | 2 | |
| December 31, 2006 | 229 | 432 | 3 | ||
| Final voting share | 47.0% | 53.0% | |||
| Non-voting members | 4 | 1 | 0 | 5 | 0 |
| Beginning of next Congress | 233 | 0 | 202 | 435 | 0 |
Leadership
Section contents: Senate: Majority (R), Minority (D) • House: Majority (R), Minority (D)
Senate


- President of the Senate: Dick Cheney (R)
- President pro tempore: Ted Stevens (R)
- President pro tempore emeritus: Robert Byrd (D)
Majority (Republican) leadership
Minority (Democratic) leadership
- Minority Leader: Harry Reid
- Minority Whip: Richard Durbin
- Democratic Conference Chairman: Harry Reid
- Democratic Policy Committee Chairman: Byron Dorgan
- Democratic Conference Secretary: Debbie Stabenow
- Democratic Campaign Committee Chairman: Charles Schumer
- Democratic Steering and Outreach Committee Chair: Hillary Clinton
- Chief Deputy Whip: Barbara Boxer
House of Representatives

Majority (Republican) leadership
- Majority Leader: Tom DeLay, until September 28, 2005
- Roy Blunt, September 28, 2005 – February 2, 2006 ("Interim Leader")
- John Boehner, from February 2, 2006
- Majority Whip: Roy Blunt
- Senior Chief Deputy Whip: Eric Cantor
- Deputy Whip Team: Kevin Brady
- Assistant Deputy Whip Team: Doc Hastings
- Conference Chair: Deborah Pryce
- Conference Vice-Chair: Jack Kingston
- Conference Secretary: John T. Doolittle
- Policy Committee Chairman: John Shadegg, until February 2, 2006
- Adam Putnam, from February 2, 2006
- Campaign Committee Chairman: Tom Reynolds
Minority (Democratic) leadership
- Minority Leader: Nancy Pelosi
- Minority Whip: Steny Hoyer
- Senior Chief Deputy Whip: John Lewis
- Minority Deputy Whip Team: Joe Crowley, Diana DeGette, Ron Kind, Ed Pastor, Jan Schakowsky, John Tanner & Maxine Waters
- Democratic Caucus Chairman: Bob Menendez, until January 16, 2006
- Jim Clyburn, from January 16, 2006
- Democratic Caucus Vice Chairman: Jim Clyburn, until January 16, 2006
- John Larson, from January 16, 2006
- Assistant to the House Minority Leader: John Spratt
- Democratic Campaign Committee Chairman: Rahm Emanuel
- Democratic Steering Committee Co-Chairs: Rosa DeLauro, George Miller
Members
Senate
In this Congress, Class 1 meant their term ended with this Congress, requiring reelection in 2006; Class 2 meant their term began in the last Congress, requiring reelection in 2008; and Class 3 meant their term began in this Congress, requiring reelection in 2010.
House of Representatives
The names of members of the House of Representatives are preceded by their district numbers.
Changes in membership
Members who came and left during this Congress.
Senate
| State (class) |
Vacator | Reason for change | Successor | Date of successor's formal installation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| New Jersey (1) |
Jon Corzine (D) | Corzine resigned to become Governor of New Jersey on January 17, 2006. | Bob Menendez (D) | January 18, 2006 |
| Connecticut (1) |
Joseph Lieberman (D) | Change of party affiliation | Joseph Lieberman (ID) | August 9, 2006 |
House of Representatives
| District | Vacator | Reason for change | Successor | Date of successor's formal installation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| California 5th | None | Representative Bob Matsui (D) died January 1, 2005 — before the end of the previous Congress. A special election was held March 8, 2005 | Doris Matsui (D) | March 10, 2005 |
| Ohio 2nd | Rob Portman (R) | Resigned April 29, 2005 to become the United States Trade Representative. A special election was held August 2, 2005 | Jean Schmidt (R) | September 6, 2005[9] |
| California 48th | Christopher Cox (R) | Resigned August 2, 2005 to become chairman of the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission. A special election was held December 6, 2005 | John Campbell (R) | December 7, 2005[10] |
| California 50th | Duke Cunningham (R) | Resigned December 1, 2005 after pleading guilty to conspiracy for bribes and tax evasion. A special election was held June 6, 2006 | Brian Bilbray (R) | June 13, 2006[11] |
| New Jersey 13th | Bob Menendez (D) | Resigned January 16, 2006 to become a U.S. Senator. A special election was held November 7, 2006 | Albio Sires (D) | November 13, 2006[12] |
| Texas 22nd | Tom DeLay (R) | Resigned June 9, 2006 after a series of criminal indictments. A special election was held November 6, 2006 | Shelley Sekula-Gibbs (R) | November 13, 2006[13] |
| Florida 16th | Mark Foley (R) | Resigned September 29, 2006 after a teen sex scandal. | Remained vacant until the next Congress.[14] | |
| Ohio 18th | Bob Ney (R) | Resigned November 3, 2006 after pleading guilty to conspiracy. | Remained vacant until the next Congress. | |
| Nevada 2nd | Jim Gibbons (R) | Resigned December 31, 2006 to become Governor of Nevada. | Remained vacant until the next Congress. | |
Committees
Lists of committees and their party leaders, for members (House and Senate) of the committees and their assignments, go into the Official Congressional Directory at the bottom of the article and click on the link (1 link), in the directory after the pages of terms of service, you will see the committees of the Senate, House (Standing with Subcommittees, Select and Special) and Joint and after the committee pages, you will see the House/Senate committee assignments in the directory, on the committees section of the House and Senate in the Official Congressional Directory, the committee's members on the first row on the left side shows the chairman of the committee and on the right side shows the ranking member of the committee.
Senate
- Aging (Special) (Gordon H. Smith, Chair; Herb Kohl, Ranking Member)
- Agriculture, Nutrition and Forestry (Saxby Chambliss, Chair; Tom Harkin, Ranking Member)
- Forestry, Conservation and Rural Revitalization (Mike Crapo, Chair; Blanche Lincoln, Ranking Member)
- Marketing, Inspection and Product Promotion (Jim Talent, Chair; Max Baucus, Ranking Member)
- Production and Price Competitiveness (Mitch McConnell, Chair; Kent Conrad, Ranking Member)
- Research, Nutrition and General Legislation (Rick Santorum, Chair; Patrick Leahy, Ranking Member)
- Appropriations (Thad Cochran, Chair; Robert C. Byrd, Ranking Member)
- Agriculture, Rural Development and Related Agencies (Robert F. Bennett, Chair; Herb Kohl, Ranking Member)
- Commerce, Justice, Science and Related Agencies (Richard Shelby, Chair; Barbara A. Mikulski, Ranking Member)
- Defense (Ted Stevens, Chair; Daniel K. Inouye, Ranking Member)
- District of Columbia (Sam Brownback, Chair; Mary Landrieu, Ranking Member)
- Energy, Water and Related Agencies (Pete Domenici, Chair; Harry Reid, Ranking Member)
- Homeland Security (Judd Gregg, Chair; Robert C. Byrd, Ranking Member)
- Interior and Related Agencies (Conrad Burns, Chair; Byron Dorgan, Ranking Member)
- Labor, Health, Human Services, Education and Related Agencies (Arlen Specter, Chair; Tom Harkin, Ranking Member)
- Legislative Branch (Wayne Allard, Chair; Richard Durbin, Ranking Member)
- Military Construction, Veterans Affairs and Related Agencies (Kay Bailey Hutchison, Chair; Dianne Feinstein, Ranking Member)
- State, Foreign Operations and Related Programs (Mitch McConnell, Chair; Patrick Leahy, Ranking Member)
- Transportation, Treasury, the Judiciary, Housing, Urban Development and Related Agencies (Kit Bond, Chair; Patty Murray, Ranking Member)
- Armed Services (John Warner, Chair; Carl Levin, Ranking Member)
- Airland (John McCain, Chair; Joe Lieberman, Ranking Member)
- Emerging Threats and Capabilities (John Cornyn, Chair; Jack Reed, Ranking Member)
- Personnel (Lindsey Graham, Chair; Ben Nelson, Ranking Member)
- Readiness and Management Support (John Ensign, Chair; Daniel Akaka, Ranking Member)
- Seapower (Jim Talent, Chair; Edward Kennedy, Ranking Member)
- Strategic Forces (Jeff Sessions, Chair; Bill Nelson, Ranking Member)
- Banking, Housing and Urban Affairs (Richard Shelby, Chair; Paul Sarbanes, Ranking Member)
- Economic Policy (Jim Bunning, Chair; Chuck Schumer, Ranking Member)
- Financial Institutions (Robert F. Bennett, Chair; Tim Johnson, Ranking Member)
- Housing and Transportation (Wayne Allard, Chair; Jack Reed, Ranking Member)
- International Trade and Finance (Mike Crapo, Chair; Evan Bayh, Ranking Member)
- Securities and Investment (Chuck Hagel, Chair; Chris Dodd, Ranking Member)
- Budget (Judd Gregg, Chair; Kent Conrad, Ranking Member)
- Commerce, Science and Transportation (Ted Stevens, Chair; Daniel K. Inouye, Ranking Member)
- Aviation (Conrad Burns, Chair; John D. Rockefeller IV, Ranking Member)
- Consumer Affairs, Product Safety and Insurance (George Allen, Chair; Mark Pryor, Ranking Member)
- Disaster Prevention and Prediction (Jim DeMint, Chair; Ben Nelson, Ranking Member)
- Fisheries and the Coast Guard (Olympia Snowe, Chair; Maria Cantwell, Ranking Member)
- Global Climate Change and Impacts (David Vitter, Chair; Frank Lautenberg, Ranking Member)
- National Ocean Policy Study (David Vitter, Chair; Frank Lautenberg, Ranking Member)
- Science and Space (Kay Bailey Hutchison, Chair; Bill Nelson, Ranking Member)
- Surface Transportation and Merchant Marine (Trent Lott, Chair; Daniel K. Inouye, Ranking Member)
- Technology, Innovation and Competitiveness (John Ensign, Chair; John F. Kerry, Ranking Member)
- Trade, Tourism and Economic Development (Gordon H. Smith, Chair; Byron L. Dorgan, Ranking Member)
- Energy and Natural Resources (Pete Domenici, Chair; Jeff Bingaman, Ranking Member)
- Energy (Lamar Alexander, Chair; Byron Dorgan, Ranking Member)
- National Parks (Craig Thomas, Chair; Daniel Akaka, Ranking Member)
- Public Lands and Forests (Larry E. Craig, Chair; Ron Wyden, Ranking Member)
- Water and Power (Lisa Murkowski, Chair; Tim Johnson, Ranking Member)
- Ethics (Select) (George V. Voinovich, Chair; Tim Johnson, Vice Chair)
- Environment and Public Works (Jim Inhofe, Chair; Jim Jeffords, Ranking Member)
- Clean Air, Climate Change and Nuclear Safety (George V. Voinovich, Chair; Thomas R. Carper, Ranking Member)
- Fisheries, Wildlife and Water (Lincoln Chafee, Chair; Hillary Rodham Clinton, Ranking Member)
- Superfund and Waste Management (John Thune, Chair; Barbara Boxer, Ranking Member)
- Transportation and Infrastructure (Kit Bond, Chair; Max Baucus, Ranking Member)
- Finance (Chuck Grassley, Chair; Max Baucus, Ranking Member)
- Health Care (Orrin Hatch, Chair; John D. Rockefeller IV, Ranking Member)
- International Trade (Craig Thomas, Chair; Jeff Bingaman, Ranking Member)
- Long-Term Growth and Debt Reduction (Gordon H. Smith, Chair; John F. Kerry, Ranking Member)
- Social Security and Family Policy (Rick Santorum, Chair; Kent Conrad, Ranking Member)
- Taxation and IRS Oversight (Jon Kyl, Chair; Jim Jeffords, Ranking Member)
- Foreign Relations (Richard Lugar, Chair; Joe Biden, Ranking Member)
- African Affairs (Mel Martinez, Chair; Russ Feingold, Ranking Member)
- East Asian and Pacific Affairs (Lisa Murkowski, Chair; John Kerry, Ranking Member)
- European Affairs (George Allen, Chair; Joe Biden, Ranking Member)
- International Economic Policy, Export and Trade Promotion (Chuck Hagel, Chair; Paul Sarbanes, Ranking Member)
- International Operations and Terrorism (John E. Sununu, Chair; Bill Nelson, Ranking Member)
- Near Eastern and South African Affairs (Lincoln Chafee, Chair; Barbara Boxer, Ranking Member)
- Western Hemisphere, Peace Corps and Narcotics Affairs (Norm Coleman, Chair; Chris Dodd, Ranking Member)
- Health, Education, Labor and Pensions (Mike Enzi, Chair; Edward M. Kennedy, Ranking Member)
- Bioterrorism and Public Health and Preparedness (Richard Burr, Chair; Edward M. Kennedy, Ranking Member)
- Education and Early Childhood Development (Lamar Alexander, Chair; Chris Dodd, Ranking Member)
- Employment and Workplace Safety (Johnny Isakson, Chair; Patty Murray, Ranking Member)
- Retirement Security and Aging (Mike DeWine, Chair; Barbara A. Mikulski, Ranking Member)
- Homeland Security and Governmental Affairs (Susan Collins, Chair; Joe Lieberman, Ranking Member)
- Federal Financial Management, Government Information and International Security (Tom Coburn, Chair; Tom Carper, Ranking Member)
- Oversight of Government Management, the Federal Workforce and the District of Columbia (George V. Voinovich, Chair; Daniel Akaka, Ranking Member)
- Permanent Subcommittee on Investigations (Norm Coleman, Chair; Carl Levin, Ranking Member)
- Indian Affairs (John McCain, Chair; Byron Dorgan, Vice Chair)
- Intelligence (Select) (Pat Roberts, Chair; John D. Rockefeller IV, Vice Chair)
- Judiciary (Arlen Specter, Chair; Patrick Leahy, Ranking Member)
- Administrative Oversight and the Courts (Jeff Sessions, Chair; Chuck Schumer, Ranking Member)
- Antitrust, Competition Policy and Consumer Rights (Mike DeWine, Chair; Herb Kohl, Ranking Member)
- Constitution, Civil Rights and Property Rights (Sam Brownback, Chair; Russ Feingold, Ranking Member)
- Corrections and Rehabilitation (Tom Coburn, Chair; Richard Durbin, Ranking Member)
- Crime and Drugs (Lindsey Graham, Chair; Joe Biden, Ranking Member)
- Immigration, Border Security and Citizenship (John Cornyn, Chair; Edward M. Kennedy, Ranking Member)
- Intellectual Property (Orrin Hatch, Chair; Patrick Leahy, Ranking Member)
- Terrorism, Technology and Homeland Security (Jon Kyl, Chair; Dianne Feinstein, Ranking Member)
- Rules and Administration (Trent Lott, Chair; Chris Dodd, Ranking Member)
- Small Business and Entrepreneurship (Olympia Snowe, Chair; John F. Kerry, Ranking Member)
- Veterans' Affairs (Larry E. Craig, Chair; Daniel K. Akaka, Ranking Member)
House of Representatives
- Agriculture (Bob Goodlatte, Chair; Collin C. Peterson, Ranking Member)
- Conservation, Credit, Rural Development and Research (Tim Holden, Chair; Frank D. Lucas, Ranking Member)
- Department Operations, Oversight (Gil Gutknecht, Chair; Joe Baca, Ranking Member)
- General Farm Commodities and Risk Management (Jerry Moran, Chair; Bob Etheridge, Ranking Member)
- Livestock and Horticulture (Robin Hayes, Chair; Ed Case, Ranking Member)
- Speciality Crops and Foreign Agriculture Programs (William L. Jenkins, Chair; Mike McIntyre, Ranking Member)
- Appropriations (Jerry Lewis, Chair; David R. Obey, Ranking Member)
- Agriculture, Rural Development, Food and Drug Administration and Related Agencies (Henry Bonilla, Chair; Rosa L. DeLauro, Ranking Member)
- Defense (C. W. Bill Young, Chair; John P. Murtha, Ranking Member)
- Energy, Water Development and Related Agencies (David Hobson, Chair; John P. Murtha, Ranking Member)
- Foreign Operations, Export Financing and Related Agencies (Jim Kolbe, Chair; Nita Lowey, Ranking Member)
- Homeland Security (Harold Rogers, Chair; Martin Olav Sabo, Ranking Member)
- Interior, Environment and Related Agencies (David L. Hobson, Chair; Pete Visclosky, Ranking Member)
- Labor, Health, Human Services, Education and Related Agencies (Ralph Regula, Chair; David R. Obey, Ranking Member)
- Military Quality of Life and Veterans' Affairs and Related Agencies (James T. Walsh, Chair; Chet Edwards, Ranking Member)
- Science, The Departments of State, Justice and Commerce and Related Agencies (Charles H. Taylor, Chair; Norman D. Dicks, Ranking Member)
- Transportation, Treasury, HUD, The Judiciary, District of Columbia and Independent Agencies (Joe Knollenberg, Chair; John Olver, Ranking Member)
- Armed Services (Duncan Hunter, Chair; Ike Skelton, Ranking Member)
- Military Personnel (John M. McHugh, Chair; Vic Snyder, Ranking Member)
- Projection Forces (Roscoe G. Bartlett, Chair; Gene Taylor, Ranking Member)
- Readiness (Joel Hefley, Chair; Solomon P. Ortiz, Ranking Member)
- Strategic Forces (Terry Everett, Chair; Silvestre Reyes, Ranking Member)
- Tactical Air and Land Forces (Curt Weldon, Chair; Neil Abercrombie, Ranking Member)
- Terrorism, Unconventional Threats and Capabilities (Jim Saxton, Chair; Marty Meehan, Ranking Member)
- Budget (Jim Nussle, Chair; John M. Spratt, Jr., Ranking Member)
- Education and the Workforce (John Boehner, Chair; George Miller, Ranking Member)
- Education Reform (Michael Castle, Chair; Lynn Woolsey, Ranking Member)
- Employer-Employee Relations (Sam Johnson, Chair; Robert E. Andrews, Ranking Member)
- Select Education (Patrick Tiberi, Chair; Ruben Hinojosa, Ranking Member)
- 21st Century Competitiveness (Buck McKeon, Chair; Dale Kildee, Ranking Member)
- Workforce Protections (Charlie Norwood, Chair; Major Owens, Ranking Member)
- Energy and Commerce (Joe Barton, Chair; John D. Dingell, Ranking Member)
- Commerce, Trade and Consumer Protection (Cliff Stearns, Chair; Janice D. Schakowsky, Ranking Member)
- Energy and Air Quality (Ralph M. Hall, Chair; Rick Boucher, Ranking Member)
- Environment and Hazardous Materials (Paul E. Gillmor, Chair; Hilda Solis, Ranking Member)
- Health (Nathan Deal, Chair; Sherrod Brown, Ranking Member)
- Oversight and Investigations (Ed Whitfield, Chair; Bart Stupak, Ranking Member)
- Telecommunications and the Internet (Fred Upton, Chair; Ed Markey, Ranking Member)
- Financial Services (Mike Oxley, Chair; Barney Frank, Ranking Member)
- Capital Markets, Insurance and Government-Sponsored Enterprises (Richard H. Baker, Chair; Paul Kanjorski, Ranking Member)
- Domestic, International Monetary Policy, Trade and Technology (Deborah Pryce, Chair; Carolyn Maloney, Ranking Member)
- Financial Institutions and Consumer Credit (Spencer Bachus, Chair; Bernie Sanders, Ranking Member)
- Housing and Community Opportunity (Bob Ney, Chair; Maxine Waters, Ranking Member)
- Oversight and Investigations (Sue W. Kelly, Chair; Luis Guiterrez, Ranking Member)
- Government Reform (Tom Davis, Chair; Henry Waxman, Ranking Member)
- Criminal Justice, Drug Policy and Human Resources (Mark Souder, Chair; Elijah Cummings, Ranking Member)
- Energy and Resources (Darrell E. Issa, Chair; Diane E. Watson, Ranking Member)
- Federal Workforce and Agency Organization (Jon C. Porter, Chair; Danny K. Davis, Ranking Member)
- Federalism and the Census (Michael R. Turner, Chair; William Lacy Clay, Ranking Member)
- Governmental Management, Finance and Accountability (Todd Russell Platts, Chair; Edolphus Towns, Ranking Member)
- National Security, Emerging Threats and International Resources (Chris Shays, Chair; Dennis J. Kucinich, Ranking Member)
- Regulatory Affairs (Candice S. Miller, Chair; Stephen F. Lynch, Ranking Member)
- Homeland Security (Christopher Cox, Chair; Bennie Thompson, Ranking Member)
- Economic Security, Infrastructre Protection and Cybersecurity (Dan Lungren, Chair; Loretta Sanchez, Ranking Member)
- Emergency Preparedness, Science and Technology (Peter King, Chair; Bill Pascrell, Jr., Ranking Member)
- Intelligence, Information Sharing and Terrorism Risk Assessment (Rob Simmons, Chair; Zoe Lofgren, Ranking Member)
- Management, Integration and Oversight (Mike Rogers, Chair; Kendrick Meek, Ranking Member)
- Prevention of Nuclear and Biological Attack (John Linder, Chair; James R. Langevin, Ranking Member)
- House Administration (Bob Ney, later Vern Ehlers, Chair; Juanita Millender-McDonald, Ranking Member)
- Hurricane Katrina (Select)
- Intelligence (Select) (Peter Hoekstra, Chair; Jane Harman, Ranking Member)
- International Relations (Henry Hyde, Chair; Tom Lantos, Ranking Member)
- Africa, Global Human Rights and International Operations (Chris Smith, Chair; Donald M. Payne, Ranking Member)
- Asia and the Pacific (Jim Leach, Chair; Eni Faleomavaega, Ranking Member)
- Europe and Emerging Threats (Elton Gallegly, Chair; Robert Wexler, Ranking Member)
- International Terrorism and Nonproliferation (Edward R. Royce, Chair; Brad Sherman, Ranking Member)
- The Middle East and Central Asia (Ileana Ros-Lehtinen, Chair; Gary Ackerman, Ranking Member)
- Oversight and Investigations (Dana Rohrabacher, Chair; William D. Delahunt, Ranking Member)
- The Western Hemisphere (Dan Burton, Chair; Robert Menendez, Ranking Member)
- Judiciary (Jim Sensenbrenner, Chair; John Conyers, Ranking Member)
- Commercial and Administrative Law (Chris Cannon, Chair; Mel Watt, Ranking Member)
- The Constitution (Steve Chabot, Chair; Jerrold Nadler, Ranking Member)
- Courts, the Internet, and Intellectual Property (Lamar S. Smith, Chair; Howard L. Berman, Ranking Member)
- Crime, Terrorism and Homeland Security (Howard Coble, Chair; Bobby Scott, Ranking Member)
- Immigration, Border Security and Claims (John N. Hostettler, Chair; Sheila Jackson-Lee, Ranking Member)
- Resources (Richard W. Pombo, Chair; Nick J. Rahall, Ranking Member)
- Energy and Mineral Resources (Jim Gibbons, Chair; Raul Grijalva, Ranking Member)
- Fisheries Conservation, Wildlife and Oceans (Wayne T. Gilchrest, Chair; Frank Pallone, Jr., Ranking Member)
- Forests and Forest Health (Greg Walden, Chair; Tom Udall, Ranking Member)
- National Parks, Recreation and Public Lands (Devin Nunes, Chair; Donna Christian-Christensen, Ranking Member)
- Water and Power (George P. Radanovich, Chair; Grace F. Napolitano, Ranking Member)
- Rules (David Dreier, Chair; Louise M. Slaughter, Ranking Member)
- Legislative and Budget Process (Lincoln Diaz-Balart, Chair; Alcee Hastings, Ranking Member)
- Rules and Organization of the House (Doc Hastings, Chair; Jim McGovern, Ranking Member)
- Science (Sherwood Boehlert, Chair; Bart Gordon, Ranking Member)
- Energy (Judy Biggert, Chair; Michael M. Honda, Ranking Member)
- Environment, Technology and Standards (Vernon J. Ehlers, Chair; David Wu, Ranking Member)
- Research (Bob Inglis, Chair; Darlene Hooley, Ranking Member)
- Space and Aeronautics (Ken Calvert, Chair; Mark Udall, Ranking Member)
- Small Business (Donald A. Manzullo, Chair; Nydia M. Velazquez, Ranking Member)
- Regulatory Reform and Oversight (W. Todd Akin, Chair; Madeleine Bordallo, Ranking Member)
- Rural Enterprises, Agriculture and Technology Sam Graves Chair; John Barrow, Ranking Member)
- Tax, Finance and Exports (Jeb Bradley, Chair; Juanita Millender-McDonald, Ranking Member)
- Workforce, Empowerment and Government Programs (Marilyn Musgrave, Chair; Daniel Lipinski, Ranking Member)
- Standards of Official Conduct (Doc Hastings, Chair; Alan B. Mollohan, Ranking Member)
- Transportation and Infrastructure (Don Young, Chair; James L. Oberstar, Ranking Member)
- Aviation (John Mica, Chair; Jerry Costello, Ranking Member)
- Coast Guard and Maritime Transportation (Frank A. LoBiondo, Chair; Bob Filner, Ranking Member)
- Economic Development, Public Buildings and Emergency Management (Bill Shuster, Chair; Eleanor Holmes Norton, Ranking Member)
- Highways, Transit and Pipelines (Tom Petri, Chair; Peter DeFazio, Ranking Member)
- Railroads (Steve LaTourette, Chair; Corrine Brown, Ranking Member)
- Water Resources and Environment (John Duncan, Jr., Chair; Eddie Bernice Johnson, Ranking Member)
- Veterans' Affairs (Steve Buyer, Chair; Lane Evans, Ranking Member)
- Disability Assistance and Memorial Affairs (Jeff Miller, Chair; Shelley Berkley, Ranking Member)
- Economic Opportunity (John Boozman, Chair; Stephanie Herseth Sandlin, Ranking Member)
- Health (Henry E. Brown, Jr., Chair; Michael Michaud, Ranking Member)
- Oversight and Investigations (Michael Bilirakis, Chair; Ted Strickland, Ranking Member)
- Ways and Means (Bill Thomas, Chair; Charles B. Rangel, Ranking Member)
- Health (Nancy Johnson, Chair; Pete Stark, Ranking Member)
- Human Resources (Wally Herger, Chair; Jim McDermott, Ranking Member)
- Oversight (Jim Ramstad, Chair; John Lewis, Ranking Member)
- Select Revenue Measures (Dave Camp, Chair; Michael McNulty, Ranking Member)
- Social Security (Jim McCrery, Chair; Sander Levin, Ranking Member)
- Trade (E. Clay Shaw, Jr., Chair; Ben Cardin, Ranking Member)
- Whole
Joint committees
- Economic (Jim Saxton, Chair; Robert F. Bennett, Vice Chair)
- The Library (Bob Ney, Chair; Ted Stevens, Vice Chair)
- Printing (Trent Lott, Chair; Bob Ney, Vice Chair)
- Taxation (Bill Thomas, Chair; Chuck Grassley, Vice Chair)
Caucuses
|
|
|
Employees and legislative agency directors
Legislative branch agency directors
- Architect of the Capitol: Alan M. Hantman
- Attending Physician of the United States Congress: John F. Eisold
- Comptroller General of the United States: David M. Walker
- Director of the Congressional Budget Office: Douglas Holtz-Eakin (until December 29, 2005), Donald B. Marron Jr. (starting December 29, 2005)
- Librarian of Congress: James H. Billington
- Public Printer of the United States: Bruce James (until 2006), vacant (starting 2006)
Senate
- Chaplain: Barry C. Black
- Curator: Diane K. Skvarla
- Historian: Richard A. Baker
- Parliamentarian: Alan Frumin
- Secretary: Emily J. Reynolds
- Sergeant at Arms: William H. Pickle
- Secretary for the Majority: David J. Schiappa
- Secretary for the Minority: Martin P. Paone
House of Representatives
- Chaplain: Daniel P. Coughlin
- Chief Administrative Officer: James M. Eagen, III
- Clerk: Jeff Trandahl, until November 18, 2005
- Karen L. Haas, from December 1, 2005
- Historian: Robert V. Remini
- Parliamentarian: John V. Sullivan
- Reading Clerks: Paul Hays (R), Mary Kevin Niland (D)
- Sergeant at Arms: Wilson Livingood
- Inspector General of the United States House of Representatives: James J. Cornell
See also
- United States elections, 2004 (elections leading to this Congress)
- United States elections, 2006 (elections during this Congress, leading to the next Congress)
References
- 1 2 Shepard, Scott (December 10, 2006). "109th may be the real 'do nothing' Congress". Cox News Service. Atlanta, GA.
- ↑ USA Today Editorial (December 11, 2006). "Our view on Congress wrapping up: 109th Congress' big success: Lowering the achievement bar". USA Today. MacLean, VA. Archived from the original on 2007-10-21.
- ↑ Cochran, John (2006-05-12). "'Do-Nothing Congress' Raises Critics' Ire". This Week with George Stephanopoulos. ABC.
- ↑ "The Cafferty File: Do-Nothing Congress". The Situation Room with Wolf Blitzer. 2006-12-04. CNN. cnn.com
- ↑ "Goodbye To The Do-Nothing Congress". Face The Nation. 2006-12-10. CBS. cbsnews.com
- ↑ Dobbs, Lou (August 2, 2006). "Five-weeks off for 'do-nothing Congress'". CNN. Retrieved 2006-11-12.
- ↑ Mann, T.brookings.edu; Ornstein, N. (2006). "OUP USA". N.Y., N.Y.: OUP USA. Archived from the original on 2007-09-01.
- 1 2 3 4 5 The Democratic-Farmer-Labor Party (DFL) is affiliated with the United States Democratic Party.
- ↑ Ohio 2nd: A primary election was held on June 14, 2005. A runoff election was held on August 2, 2005. Jean Schmidt won and took her seat the next month. See Ohio 2nd congressional district election, 2005.
- ↑ California 48th: A primary election was held on October 4, 2005. A runoff election was held on December 6, 2005. John Campbell won and took his seat the next day.See California 48th Congressional District Election, 2005.
- ↑ California 50th: A primary election was held on April 11, 2006. A runoff election was held on June 6, 2006. Brian Bilbray won and took his seat one week later.See California 50th congressional district special election, 2006.
- ↑ New Jersey 13th: An election was held to fill the unexpired term at the November 7, 2006 General Election. Sires was sworn in on November 13. See New Jersey 13th congressional district special election, 2006.
- ↑ An election was held to fill the unexpired term at the November 7, 2006 General Election. Sekula-Gibbs took her seat on November 13.
- ↑ 2 Election Winners to Fill Vacancies", via wtopnews.com
External links
- Biographical Directory of the United States Congress
- House History from the U.S. House of Representatives
- Statistics & Lists from the U.S. Senate
- Legislative information from Congress.gov at the Library of Congress
- "Videos of House of Representatives Sessions for the 109th Congress from www.C-SPAN.org".
- "Videos of Senate Sessions for the 109th Congress from www.C-SPAN.org".
- "Videos of Committees from the House and Senate for the 109th Congress from www.C-SPAN.org".
- House of Representatives Session Calendar for the 109th Congress (PDF).
- Senate Session Calendar for the 109th Congress (PDF).
- Congressional Pictorial Directory for the 109th Congress.
- Official Congressional Directory for the 109th Congress.