Warrego River
| Warrego | |
| River | |
The Warrego River at Cunnamulla | |
| Name origin: 1. Aboriginal Bidyara: bad;[1] 2. Aboriginal: river of sand.[2] | |
| Country | Australia |
|---|---|
| States | Queensland, New South Wales |
| Regions | South West Queensland, Orana |
| Part of | Darling River catchment, Murray-Darling basin |
| Tributaries | |
| - right | Nive River, Langlo River |
| Settlements | Augathella, Charleville, Wyandra, Cunnamulla |
| Source | Mount Ka Ka Mundi, Carnarvon Range |
| - location | east of Tambo, Queensland |
| - elevation | 625 m (2,051 ft) |
| - coordinates | 25°03′22″S 147°28′49″E / 25.05611°S 147.48028°E |
| Mouth | Darling River |
| - location | near Bourke, New South Wales |
| - elevation | 98 m (322 ft) |
| - coordinates | 30°24′13″S 145°20′54″E / 30.40361°S 145.34833°ECoordinates: 30°24′13″S 145°20′54″E / 30.40361°S 145.34833°E |
| Length | 1,380 km (857 mi) |
| Basin | 69,290 km2 (26,753 sq mi) |
| Discharge | |
| - average | 8 m3/s (283 cu ft/s) |
| Reservoirs | Dillalah Waterhole, Ten Mile Waterhole, Lower Lila Dam, Six Mile Dam, Turtle Waterhole, and Boera Dam |
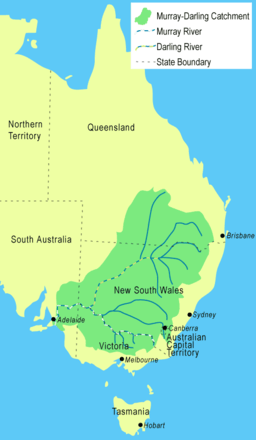 The Warrego River is the northernmost river located in the Murray–Darling basin | |
| [3] | |
The Warrego River, an intermittent river that is part of the Darling catchment within the Murray–Darling basin, is located in the south west of Queensland and in the Orana region of New South Wales, Australia. The Warrego River is northernmost tributary of the Darling River.[4]
Course and features
The river rises from below Mount Ka Ka Mundi in the Carnarvon Range, near Tambo in Queensland, and flows generally south, reaching its confluence with the Darling River, downstream from Bourke. The river is joined by thirty-seven tributaries, including the Nive and Langlo rivers; descending 528 metres (1,732 ft) over its 1,380-kilometre (860 mi) course. The river flows through a series of reservoirs, including the Dillalah Waterhole, Ten Mile Waterhole, Lower Lila Dam, Six Mile Dam, Turtle Waterhole, and Boera Dam.[3]
The towns of Augathella, Charleville, Wyandra, and Cunnamulla are located on the banks of the river.
Inflows
Most of the basin of the Warrego is too dry for cropping and has a very erratic rainfall of between 350 and 500 millimetres (14 and 20 in). It is covered with a natural vegetation of grassland of more fertile clay soils, and saltbush shrubland on less fertile red earths. The predominant land use is low-intensity grazing of sheep and cattle: the river's flow is much too erratic to permit irrigated cropping. The Warrego is essentially an ephemeral stream: it is not unknown for years to pass without any flow in the basin and substantial amounts of water reach the Darling River only in wet years almost always associated with La Niña events.
Outflows
Below Wyandra the river forms a series of outflowing creeks and anabranches. During floods, the Widgeegoara, Kudnapper and Noorama Creeks allow water to channel into Nebine Creek, a tributary of the Culgoa River.[5] Cuttaburra Creek connects the Warrego to the Paroo River via a distribution system that flows through channels, floodways and wetlands.[5] The Irrara Creek anabranch flows into Kerribree Creek which continues into a number of wetlands before filling Utah Lake.[5]
Flooding
When La Niña strikes, flooding is usual along the Warrego: major floods associated with La Niña events occurred in 1950, 1954 to 1956, 1971, 1973, 1998 and 2008. Oddly, the most destructive flood ever recorded on the river took place in the absence of La Niña. In April 1990, as a result of two extremely strong trough in the easterlies, over 400 millimetres (16 in) of rain fell in Cunnamulla in two weeks, being more than the annual rainfall in over 60 percent of years. The river, along with most tributaries of the Darling, reached near-record levels and the towns of Augathella and Charleville were devastated. At Charleville a river height peak of 8.54 metres (28.0 ft) was recorded.[6]
Fauna
The Warrego River is one of a few rivers where silver perch breed naturally.[4] Golden perch and murray cod are also found in the river.
Carnarvon Station, once a large cattle property at the rivers headwaters, was acquired by the Australian Bush Heritage Fund in 2001, with the 590 square kilometres (230 sq mi) property set aside for the protection of threatened species of birds and animals.
Etymology
The name Warrego is an Australian Aboriginal word from the Bidyara language, believed to mean "bad";[1] and is also an Aboriginal term meaning "river of sand".[2]
Two warships of the Royal Australian Navy have been named HMAS Warrego after the river. The Warrego Highway draws its name from the river.
See also
References
- 1 2 "Warrego River". Geographical Names Register (GNR) of NSW. Geographical Names Board of New South Wales. Retrieved 3 February 2013.
- 1 2 Warrego River - Things To See and Do - Queensland Holidays
- 1 2 "Map of Warrego River". Bonzle Digital Atlas of Australia. Retrieved 3 February 2013.
- 1 2 Harrison, Rod; Ernie James; Chris Sully; Bill Classon; Joy Eckermann (2008). Queensland Dams. Bayswater, Victoria: Australian Fishing Network. pp. 155–156. ISBN 978-1-86513-134-4.
- 1 2 3 "WISE Basins: Warrego River". National Parks and Wildlife Services. 5 June 2006. Archived from the original on 13 July 2009. Retrieved 22 September 2009.
- ↑ "Flood Warning System for the Warrego River". Bureau of Meteorology (Australia). Retrieved 2009-07-10.
External links
- "Barwon, Darling and Far Western catchments" (map). Office of Environment and Heritage. Government of New South Wales.