Ninohe, Iwate
| Ninohe 二戸市 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| City | |||
 Ninohe City Hall | |||
| |||
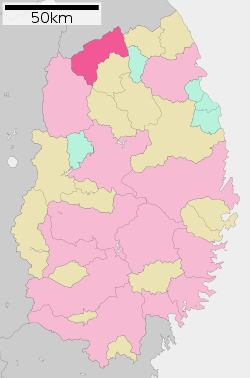 Location of Ninohe in Iwate Prefecture | |||
 Ninohe | |||
| Coordinates: 40°16′16.5″N 141°18′17.2″E / 40.271250°N 141.304778°ECoordinates: 40°16′16.5″N 141°18′17.2″E / 40.271250°N 141.304778°E | |||
| Country | Japan | ||
| Region | Tōhoku | ||
| Prefecture | Iwate | ||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 420.42 km2 (162.33 sq mi) | ||
| Population (February 28, 2017) | |||
| • Total | 27,947 | ||
| • Density | 66.47/km2 (172.2/sq mi) | ||
| Time zone | UTC+9 (Japan Standard Time) | ||
| City symbols | |||
| • Tree | Urushi | ||
| • Flower | Yamazakura | ||
| • Bird | Green pheasant | ||
| Phone number | 0195-23-3111 | ||
| Address | 47 Fukuoka Kawamata, Ninohe-shi, Iwate-ken 028-6192 | ||
| Website | http://www.city.ninohe.lg.jp/ | ||

Ninohe (二戸市 Ninohe-shi) is a city located in Iwate Prefecture, Japan. As of 28 February 2017, the city had an estimated population of 27,947, and a population density of 66.47 persons per km2 in 11,865 households.[1] The total area of the city is 420.42 square kilometres (162.33 sq mi).
Geography
Ninohe is located in far north-center Iwate Prefecture, bordered by Aomori Prefecture to the north. The northern end of the Kitakami Mountains, the 852.2 meter Mount Oritsume is in Ninohe. Approximately 70% of the city area is mountainous and forested. The upper reaches of the Mabechi River flows through the city. A portion of the city is within the borders of the Oritsume Basenkyō Prefectural Natural Park.
Neighboring municipalities
Climate
Ninohe has a humid continental climate (Köppen Dfb) characterized by mild summers and cold winters with heavy snowfall. The average annual temperature in Ninohe is 9.7 °C. The average annual rainfall is 1248 mm with September as the wettest month and February as the driest month. The temperatures are highest on average in August, at around 23.0 °C, and lowest in January, at around -2.4 °C.[2]
Demographics
Per Japanese census data,[3] the population of Ninohe has steadily declined over the past 40 years.
| Census Year | Population |
|---|---|
| 1970 | 38,289 |
| 1980 | 37,537 |
| 1990 | 35,017 |
| 2000 | 33,102 |
| 2010 | 29,818 |
History
The area of present-day Ninohe was part of ancient Mutsu Province, and has been settled since at least the Jōmon period. Many Jōmon and Kofun period remains have been found. Inhabited by the Emishi tribes, the Nihon Shoki describes the penetration of the area by forces of the Yamato dynasty in the Nara period; however, it was not under effective control of the central government until the mid-Heian period. The area was dominated by the Nanbu clan from the early Muromachi period, and was named for one of the nine numbered stockades, or fortified ranches, that established to secure this frontier area. During the Edo period, the area was under the control of Morioka Domain.
In the early Meiji period, the town of Fukuoka and the villages of Jōbōji, Kindaichi, Gohenchi, Tomai, Ishikiridokoro, and Nisattai were established within Ninohe District on April 1, 1889 with the establishment of the modern municipalities system. Jōbōji was elevated to town status on December 25, 1940. Gohenchi, Tomai, Ishikiridokoro, and Nisattai merged with Fukuoka on March 10, 1955. The modern city was founded on April 1, 1972, with the merger of the town of Fukuoka with the village of Kindaichi. On January 1, 2006, the city of Ninohe annexed the town of Jōbōji.
Government
Ninohe has a mayor-council form of government with a directly elected mayor and a unicameral city legislature of 18 members.
Economy
The local economy of Ninohe is based on agriculture and food processing. Local produce include apples, dairy products and hops.
Education
Ninohe has eight public elementary schools and four middle schools operated by the city government, and two public high schools operated by the Iwate Prefectural Board of Education. There is also a prefectural vocational school, and a special education school operated by the prefectural government.
Transportation
Railway
Highway
Local attractions
- Site of Kunohe Castle, a National Historic Site
- Kindaichi Onsen, a popular hot spring resort
- Tendai-ji temple, founded in the Nara period
Noted people from Ninohe
- Tanakadate Aikitsu, scientist [4]
References
- ↑ City of Ninohe official home page
- ↑ Ninohe climate data
- ↑ Ninohe population statistics
- ↑ Dr. Aikitu Tanakadate: World-Renowned Geophysicist and Seismologist by Satio Tanno (President, Aikitu Tanakadate Society). August 31, 1995
External links
![]()
- Official Website (in Japanese)

