Manchester station group

The Manchester station group is a station group (for fares purposes) of four railway stations in Manchester city centre, England consisting of Manchester Piccadilly, Manchester Oxford Road, Manchester Victoria and Deansgate.[1] The station group is printed on national railway tickets as MANCHESTER STNS. For commuters in Greater Manchester the four stations are printed as MANCHESTER CTLZ which additionally permits the use of Metrolink tram services in the City Zone (between Deansgate-Castlefield, New Islington and Victoria).
The Manchester station group does not include Manchester Airport station, nor Salford Central railway stations. Prior to the opening of the Ordsall Chord in 2017, few routes stopped at multiple stations in the group, for instance the TransPennine Express Northwest route called at Deansgate, Oxford Road and Piccadilly. However there has been a sharp increase with more 'through' (as opposed to terminating) services through Manchester as part of the new May 2018 timetable – for example, the TransPennine Express from Newcastle to Manchester Airport now calls at Victoria, Oxford Road and Piccadilly.
It is permitted that rail passengers may board or disembark at any one of these four stations.[2] National visitors from outside Greater Manchester with MANCHESTER STNS as the destination are not permitted to use Metrolink in the City Zone as it is a locally funded transport scheme by the council tax payers of Greater Manchester (and subsequently funded through TfGM) and receives no national government subsidy.[3]
Note that when using the National Routeing Guide, Salford Central railway station is shown as part of the Manchester Group.[4] This means that tickets to or from Salford with Route: Any Permitted have the same validity as those to or from MANCHESTER STNS, but cannot be used interchangeably.
Use on Metrolink
Manchester Central Metrolink lines |
|---|
Greater Manchester passengers
Passengers who travel on rail services from the Greater Manchester area into one of the four Manchester stations will be issued with a ticket stating the destination as Manchester CTLZ as opposed to Manchester Picc or Manchester Vic. This allows visitors to use Metrolink trams between stops in the City Zone for free on the presentation of a Manchester CTLZ rail ticket.[5][6] The Freedom of the City scheme was introduced in 2005 by GMPTE, now Transport for Greater Manchester.[7] The City Zone includes nine Metrolink tram stops:
National Rail passengers
Passengers travelling into Manchester from outside the Greater Manchester county are not permitted to use rail tickets to travel around the city centre on the Metrolink. As a consequence the destination on the orange rail tickets is stated as Manchester STNS. The Manchester Metrolink is a locally funded transport system which receives no national subsidy from central government. National Rail passengers can alternatively use the free Metroshuttle bus situated outside stations to get around the city centre.[6]
Future
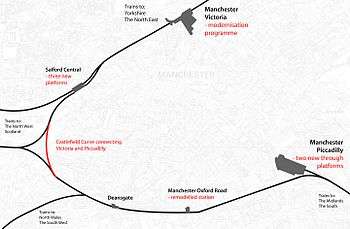
Many journeys which call at Manchester stations slow down due to the populated nature of Greater Manchester and congested routes; Network Rail have described it as a 'bottleneck'. In 2010 the Manchester hub study was released with a series of proposals to decreasing journey times.
Central to the plan is the Ordsall Chord (also known as the Castlefield Curve) which will link all four of Manchester's main stations. Two new through platforms will be built at Piccadilly and Victoria will be upgraded. The implementation of the Northern Hub proposals would reduce journey times to and from Liverpool by 15 minutes, Leeds by 15 minutes and Sheffield by 5.[8]
Stations
In use
| Station | Image | Location | Managed by | National services | Annual entry/exit (millions) 2012/13[9] |
Annual entry/exit (millions) 2013/14[9] |
Annual entry/exit (millions) 2014/15[9] |
Annual entry/exit (millions) 2015/16[9] |
Annual entry/exit (millions) 2016/17[9] |
Open date |
Terminal platforms |
Through platforms |
Category |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deansgate |  |
Deansgate | Northern | Northern TransPennine Express |
1886 | 0 | 2 | D | |||||
| Oxford Road | Oxford Road | Northern | Northern TransPennine Express Arriva Trains Wales East Midlands Trains |
1849 | 1 (none in future plans – see Northern Hub) | 4 | C1 | ||||||
| Piccadilly |  |
Piccadilly | Network Rail | Virgin Trains Northern TransPennine Express East Midlands Trains CrossCountry Arriva Trains Wales |
1842 | 12 | 2 (4 in future plans – see Northern Hub) | A | |||||
| Victoria |  |
Hunts Bank | Northern | Northern TransPennine Express |
1844 | 2 | 4 | B | |||||
| Total | 15 | 14 |
Closed
One of the first inter-city railway stations in the world was Manchester Liverpool Road station on Liverpool Street. On 15 September 1830, the Liverpool and Manchester Railway opened and services terminated at the station. Part of the station frontage remains, as does the goods warehouse. Both of these structures are Grade I protected and are part of the Museum of Science and Industry.
All four of Manchester's termini (Piccadilly, Mayfield, Exchange and Victoria) were not recommended for closure in the first Beeching Report, but the reduced rail traffic caused by the closure of other railway lines meant services were transferred to Piccadilly and Victoria.[10] Consequently, trains to Exchange and Central stations were withdrawn; the latter was granted Grade II* and later converted into an arena and exhibition centre.
| Station | Image | Location | Managed by | Open date |
Closed date |
Terminal platforms |
Through platforms |
Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Central |  |
Castlefield | London Midland Region of British Railways | 1886 | 1969 | 9 | 0 | Closed as part of the Beeching cuts in 1969. Now used as a conference and exhibition centre. Was shortlisted for High Speed 2 terminus. |
| Exchange | Salford | London, Midland and Scottish Railway | 1884 | 1969 | 0 | 5 | Had the longest platform in the world. | |
| Liverpool Road | Liverpool Street | Liverpool and Manchester Railway | 1830 | 1844 | 2 | 0 | The first urban train station in the world | |
| Mayfield |  |
Piccadilly | London and North Western Railway | 1910 | 1960 (to passengers) 1986 (closed) |
5 | 0 | Located adjacent to Piccadilly. Station remains today and can be seen on approaching Piccadilly. |
See also
References
- ↑ "Estimates of Station Usage 2015–16 -Methodological Report" (PDF). Office of Rail and Road. p. 57.
- ↑ "FAQs – I have bought a train ticket that states Manchester Stations as the destination. Can I use this on the Metrolink in the city centre?". Metrolink. Retrieved 2013-02-08.
- ↑ "Freedom of Information – Subsidies and passenger numbers for National Rail, Manchester Metrolink and London Underground" (PDF). gov.uk. 31 May 2012. Retrieved 2013-02-09.
- ↑ "National Rail Station Groups" (PDF). Retrieved 12 March 2017.
- ↑ "Free Travel on the Metrolink" (PDF). TfGM. p. 4. Retrieved 2013-02-08.
- 1 2 "Freedom of the City". TfGM. Retrieved 2013-02-08.
- ↑ "Free tram rides for train riders". BBC News. 28 October 2005. Retrieved 2013-02-08.
- ↑ "Northern Hub". Network Rail. Retrieved 2013-02-09.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Station usage". Office of Rail Regulation. Retrieved 13 December 2016.
- ↑ "Manchester Exchange". Retrieved 2013-02-09.