KIF5A
Kinesin heavy chain isoform 5A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KIF5A gene.[5][6][7]
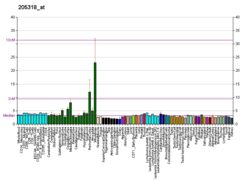
This gene encodes a member of the kinesin family of proteins. Members of this family are part of a multisubunit complex that functions as a microtubule motor in intracellular organelle transport. Mutations in this gene cause autosomal dominant spastic paraplegia 10.[7]
Interactions
See also
- Hereditary spastic paraplegia type 10
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000155980 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000074657 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ Hamlin PJ, Jones PF, Leek JP, Bransfield K, Lench NJ, Aldersley MA, Howdle PD, Markham AF, Robinson PA (Feb 1999). "Assignment of GALGT encoding beta-1, 4N-acetylgalactosaminyl-transferase (GalNAc-T) and KIF5A encoding neuronal kinesin (D12S1889) to human chromosome band 12q13 by assignment to ICI YAC 26EG10 and in situ hybridization. medjph@stjames.leeds.ac.uk". Cytogenet Cell Genet. 82 (3–4): 267–8. doi:10.1159/000015115. PMID 9858832.
- ↑ Reid E, Dearlove AM, Rhodes M, Rubinsztein DC (Oct 1999). "A new locus for autosomal dominant "pure" hereditary spastic paraplegia mapping to chromosome 12q13, and evidence for further genetic heterogeneity". Am J Hum Genet. 65 (3): 757–63. doi:10.1086/302555. PMC 1377983. PMID 10441583.
- 1 2 "Entrez Gene: KIF5A kinesin family member 5A".
- ↑ Rahman, A; Friedman D S; Goldstein L S (Jun 1998). "Two kinesin light chain genes in mice. Identification and characterization of the encoded proteins". J. Biol. Chem. 273 (25): 15395–403. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.25.15395. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 9624122.
- ↑ Rahman, A; Kamal A; Roberts E A; Goldstein L S (Sep 1999). "Defective kinesin heavy chain behavior in mouse kinesin light chain mutants". J. Cell Biol. 146 (6): 1277–88. doi:10.1083/jcb.146.6.1277. ISSN 0021-9525. PMC 2156125. PMID 10491391.
Further reading
- Fichera M, Lo Giudice M, Falco M, et al. (2005). "Evidence of kinesin heavy chain (KIF5A) involvement in pure hereditary spastic paraplegia". Neurology. 63 (6): 1108–10. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000138731.60693.d2. PMID 15452312.
- Niclas J, Navone F, Hom-Booher N, Vale RD (1994). "Cloning and localization of a conventional kinesin motor expressed exclusively in neurons". Neuron. 12 (5): 1059–72. doi:10.1016/0896-6273(94)90314-X. PMID 7514426.
- Bonaldo MF, Lennon G, Soares MB (1997). "Normalization and subtraction: two approaches to facilitate gene discovery". Genome Res. 6 (9): 791–806. doi:10.1101/gr.6.9.791. PMID 8889548.
- Rahman A, Friedman DS, Goldstein LS (1998). "Two kinesin light chain genes in mice. Identification and characterization of the encoded proteins". J. Biol. Chem. 273 (25): 15395–403. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.25.15395. PMID 9624122.
- Rahman A, Kamal A, Roberts EA, Goldstein LS (1999). "Defective kinesin heavy chain behavior in mouse kinesin light chain mutants". J. Cell Biol. 146 (6): 1277–88. doi:10.1083/jcb.146.6.1277. PMC 2156125. PMID 10491391.
- Kanai Y, Okada Y, Tanaka Y, et al. (2000). "KIF5C, a novel neuronal kinesin enriched in motor neurons". J. Neurosci. 20 (17): 6374–84. PMID 10964943.
- Setou M, Seog DH, Tanaka Y, et al. (2002). "Glutamate-receptor-interacting protein GRIP1 directly steers kinesin to dendrites". Nature. 417 (6884): 83–7. doi:10.1038/nature743. PMID 11986669.
- Reid E, Kloos M, Ashley-Koch A, et al. (2003). "A kinesin heavy chain (KIF5A) mutation in hereditary spastic paraplegia (SPG10)". Am. J. Hum. Genet. 71 (5): 1189–94. doi:10.1086/344210. PMC 385095. PMID 12355402.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Macioce P, Gambara G, Bernassola M, et al. (2004). "Beta-dystrobrevin interacts directly with kinesin heavy chain in brain". J. Cell Sci. 116 (Pt 23): 4847–56. doi:10.1242/jcs.00805. PMID 14600269.
- Amit I, Yakir L, Katz M, et al. (2004). "Tal, a Tsg101-specific E3 ubiquitin ligase, regulates receptor endocytosis and retrovirus budding". Genes Dev. 18 (14): 1737–52. doi:10.1101/gad.294904. PMC 478194. PMID 15256501.
- Stelzl U, Worm U, Lalowski M, et al. (2005). "A human protein-protein interaction network: a resource for annotating the proteome". Cell. 122 (6): 957–68. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2005.08.029. PMID 16169070.
- Blair MA, Ma S, Hedera P (2007). "Mutation in KIF5A can also cause adult-onset hereditary spastic paraplegia". Neurogenetics. 7 (1): 47–50. doi:10.1007/s10048-005-0027-8. PMID 16489470.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.