KIF1A
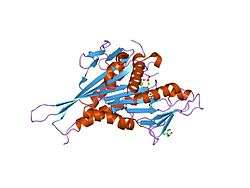
Kinesin-like protein KIF1A, also known as axonal transporter of synaptic vesicles or microtubule-based motor KIF1A, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KIF1A gene.[5][6][7]
Function
KIF1A is a member of the kinesin family. This protein is highly similar to mouse heavy-chain kinesin member 1A protein, which is an anterograde motor protein that transports membranous organelles along axonal microtubules. It is thought that this protein may play a critical role in the development of axonal neuropathies resulting from impaired axonal transport. There are multiple polyadenylation sites found in this gene.[5] Sexual orientation has been linked to the regulatory domain of the gene.[8]
Clinical significance
KIF1A is associated with hereditary spastic paraparesis.[9]
The website KIF1A.org serves as a resource for patients and care-givers, and provides links to research efforts.
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000130294 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000014602 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- 1 2 "Entrez Gene: kinesin family member 1A".
- ↑ Okada Y, Yamazaki H, Sekine-Aizawa Y, Hirokawa N (June 1995). "The neuron-specific kinesin superfamily protein KIF1A is a unique monomeric motor for anterograde axonal transport of synaptic vesicle precursors". Cell. 81 (5): 769–80. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(95)90538-3. PMID 7539720.
- ↑ Keller MP, Seifried BA, Rabin BA, Chance PF (March 1999). "Mapping of the kinesin-related gene ATSV to chromosome 2q37". Hum. Genet. 104 (3): 254–6. doi:10.1007/s004390050944. PMID 10323250.
- ↑ Ngun, Tuck (October 8, 2015). "PgmNr 95: A novel predictive model of sexual orientation using epigenetic markers". American Society of Human Genetics.
- ↑ Erlich Y, Edvardson S, Hodges E, Zenvirt S, Thekkat P, Shaag A, Dor T, Hannon GJ, Elpeleg O (April 2011). "Exome sequencing and disease-network analysis of a single family implicate a mutation in KIF1A in hereditary spastic paraparesis". Genome Res. 21 (5): 658–64. doi:10.1101/gr.117143.110. PMC 3083082. PMID 21487076.
Further reading
- Demokan S, Chang X, Chuang A, et al. (2010). "KIF1A and EDNRB are differentially methylated in primary HNSCC and salivary rinses". Int. J. Cancer. 127 (10): 2351–9. doi:10.1002/ijc.25248. PMC 2946472. PMID 20162572.
- Smith M, Escamilla JR, Filipek P, et al. (2001). "Molecular genetic delineation of 2q37.3 deletion in autism and osteodystrophy: report of a case and of new markers for deletion screening by PCR". Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 94 (1–2): 15–22. doi:10.1159/000048775. PMID 11701947.
- Kikkawa M, Hirokawa N (2006). "High-resolution cryo-EM maps show the nucleotide binding pocket of KIF1A in open and closed conformations". EMBO J. 25 (18): 4187–94. doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7601299. PMC 1570440. PMID 16946706.
- Yu W, Andersson B, Worley KC, et al. (1997). "Large-scale concatenation cDNA sequencing". Genome Res. 7 (4): 353–8. doi:10.1101/gr.7.4.353. PMC 139146. PMID 9110174.
- Albers M, Kranz H, Kober I, et al. (2005). "Automated yeast two-hybrid screening for nuclear receptor-interacting proteins". Mol. Cell. Proteomics. 4 (2): 205–13. doi:10.1074/mcp.M400169-MCP200. PMID 15604093.
- Barbe L, Lundberg E, Oksvold P, et al. (2008). "Toward a confocal subcellular atlas of the human proteome". Mol. Cell. Proteomics. 7 (3): 499–508. doi:10.1074/mcp.M700325-MCP200. PMID 18029348.
- Furlong RA, Zhou CY, Ferguson-Smith MA, Affara NA (1996). "Characterization of a kinesin-related gene ATSV, within the tuberous sclerosis locus (TSC1) candidate region on chromosome 9Q34". Genomics. 33 (3): 421–9. doi:10.1006/geno.1996.0217. PMID 8661001.
- Koshizuka T, Kawaguchi Y, Nishiyama Y (2005). "Herpes simplex virus type 2 membrane protein UL56 associates with the kinesin motor protein KIF1A". J. Gen. Virol. 86 (Pt 3): 527–33. doi:10.1099/vir.0.80633-0. PMID 15722511.
- Hillier LW, Graves TA, Fulton RS, et al. (2005). "Generation and annotation of the DNA sequences of human chromosomes 2 and 4". Nature. 434 (7034): 724–31. doi:10.1038/nature03466. PMID 15815621.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Bonaldo MF, Lennon G, Soares MB (1996). "Normalization and subtraction: two approaches to facilitate gene discovery". Genome Res. 6 (9): 791–806. doi:10.1101/gr.6.9.791. PMID 8889548.
- Andersson B, Wentland MA, Ricafrente JY, et al. (1996). "A "double adaptor" method for improved shotgun library construction". Anal. Biochem. 236 (1): 107–13. doi:10.1006/abio.1996.0138. PMID 8619474.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2002). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Shin H, Wyszynski M, Huh KH, et al. (2003). "Association of the kinesin motor KIF1A with the multimodular protein liprin-alpha". J. Biol. Chem. 278 (13): 11393–401. doi:10.1074/jbc.M211874200. PMID 12522103.
- Lee JR, Shin H, Choi J, et al. (2004). "An intramolecular interaction between the FHA domain and a coiled coil negatively regulates the kinesin motor KIF1A". EMBO J. 23 (7): 1506–15. doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7600164. PMC 391070. PMID 15014437.
- Dias Neto E, Correa RG, Verjovski-Almeida S, et al. (2000). "Shotgun sequencing of the human transcriptome with ORF expressed sequence tags". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 97 (7): 3491–6. doi:10.1073/pnas.97.7.3491. PMC 16267. PMID 10737800.
- Lee JR, Shin H, Ko J, et al. (2003). "Characterization of the movement of the kinesin motor KIF1A in living cultured neurons". J. Biol. Chem. 278 (4): 2624–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M211152200. PMID 12435738.
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.