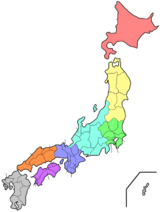
Ibaraki Prefecture
| Ibaraki Prefecture 茨城県 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Prefecture | |||
| Japanese transcription(s) | |||
| • Japanese | 茨城県 | ||
| • Rōmaji | Ibaraki-ken | ||
| |||
 | |||
| Country | Japan | ||
| Region | Kantō | ||
| Island | Honshu | ||
| Capital | Mito | ||
| Government | |||
| • Governor | Kazuhiko Ōigawa | ||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 6,095.58 km2 (2,353.52 sq mi) | ||
| Area rank | 23rd | ||
| Population (February 1, 2017) | |||
| • Total | 2,903,925 | ||
| • Rank | 11th | ||
| • Density | 476.40/km2 (1,233.9/sq mi) | ||
| ISO 3166 code | JP-08 | ||
| Districts | 7 | ||
| Municipalities | 44 | ||
| Flower | Rose (Rosa) | ||
| Tree | Ume tree (Prunus mume) | ||
| Bird | Eurasian Skylark (Alauda arvensis) | ||
| Website |
www | ||
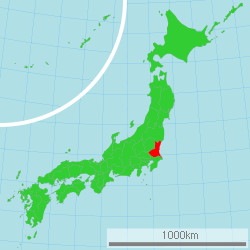
Ibaraki Prefecture (茨城県 Ibaraki-ken) is a prefecture of Japan, located in the Kantō region.[1] The capital is Mito.[2]
History
Ibaraki Prefecture was previously known as Hitachi Province. In 1871, the name of the province became Ibaraki.
Geography
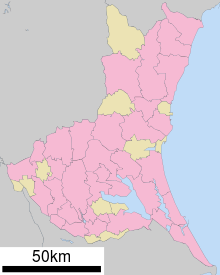
City Town




Ibaraki Prefecture is the northeastern part of the Kantō region, stretching between Tochigi Prefecture and the Pacific Ocean and bounded on the north and south by Fukushima Prefecture and Chiba Prefecture. It also has a border on the southwest with Saitama Prefecture. The northernmost part of the prefecture is mountainous, but most of the prefecture is a flat plain with many lakes.
As of 1 April 2012, 15% of the total land area of the prefecture was designated as Natural Parks, namely Suigo-Tsukuba Quasi-National Park and nine Prefectural Natural Parks.[3]
Cities
Thirty-two (32) cities are located in Ibaraki Prefecture:
- Mito (capital city of the prefecture)
- Bandō
- Chikusei
- Hitachi
- Hitachinaka
- Hitachiōmiya
- Hitachiōta
- Hokota
- Inashiki
- Ishioka
- Itako
- Jōsō
- Kamisu
- Kasama
- Kashima
- Kasumigaura
- Kitaibaraki
- Koga
- Moriya
- Naka
- Namegata
- Omitama
- Ryūgasaki
- Sakuragawa
- Shimotsuma
- Takahagi
- Toride
- Tsuchiura
- Tsukuba
- Tsukubamirai
- Ushiku
- Yūki
Towns and villages
These are the towns and villages in each district:
Mergers
Economy
Ibaraki's industries include energy production, particularly nuclear energy, as well as chemical and precision machining industries. The Hitachi company was founded in the Ibaraki city of the same name.
As of March 2011, the prefecture produced 25% of Japan's bell peppers and Chinese cabbage.[4]
Demographics
Ibaraki's population is increasing modestly as the Greater Tokyo region spreads out.
Culture
Ibaraki is known for nattō, or fermented soybeans, in Mito, watermelons in Kyōwa (recently merged into Chikusei), and chestnuts in the Nishiibaraki region.
Ibaraki is famous for the martial art of Aikido founded by Ueshiba Morihei, also known as Osensei. Ueshiba spent the latter part of his life in the town of Iwama, now part of Kasama, and the Aiki Shrine and dojo he created still remain.[5]
There are castle ruins in many cities, including Mito, Kasama, and Yūki.
Kasama is famous for Shinto, art culture and pottery.
The capital Mito is home to Kairakuen, one of Japan's three most celebrated gardens, and famous for its over 3,000 Japanese plum trees of over 100 varieties.
Education
University
- Ami
- Hitachi
- Mito
- Ibaraki University
- Tokiwa University
- Tsuchiura
- Tsukuba International University
- Tsukuba
- Ryugasaki
Sports
The sports teams listed below are based in Ibaraki.
Football (soccer)
Volleyball
Rugby
- Kashima Rugby Football Club RFC
Baseball
- Ibaraki Golden Golds (Regional club)
Wrestling
- Hitachi Pro Wrestling (Regional group)
Basketball
Tourism
- A panoramic view of Kasumigaura and Tsuchiura, from Mount Hokyo
 Fukuroda waterfalls in Daigo
Fukuroda waterfalls in Daigo- A view of Mount Tsukuba, from Tsukuba City
 A view of Suigo Itako Iris Garden
A view of Suigo Itako Iris Garden A view of Rokkakudo and Pacific Ocean in Kitaibaraki
A view of Rokkakudo and Pacific Ocean in Kitaibaraki
Transportation and access
Railways
- East Japan Railway Company
- Tsukuba Express
- Kantō Railway
- Kashima Rinkai Railway
- Minato Line (Hitachinaka Seaside Railway)
- Mooka Line (Mooka Railway)
Cable cars
Roads
Expressways
National highways
- National Route 4 (around Koga area)
- National Route 6 (Nihonbashi of Tokyo-Toride-Tsuchiura-Mito-Hitachi-Iwaki-Sendai)
- National Route 50
- National Route 51 (Mito-Kashima-Itako-Narita-Chiba)
- National Route 118
- National Route 123
- National Route 124
- National Route 125 (Katori-Tsuchiura-Tsukuba-Koga-Gyoda-Kumagaya)
- National Route 245
- National Route 293
- National Route 294
- National Route 349
- National Route 354
- National Route 355
- National Route 400 (Mito-Nakagawa-Nikko-South Aizu-West Aizu
- National Route 408
- National Route 461
Ports
- Kashima Port
Airports
Pronunciation
The prefecture is often mispronounced "Ibaragi". However, the correct pronunciation is "Ibaraki". According to the author of "Not Ibaragi, Ibaraki",[6] this is most likely due to a mishearing of the softening of the "k" sound in Ibaraki dialect.
See also
Notes
- ↑ Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005). "Ibaraki-ken" in Japan Encyclopedia, p. 367, at Google Books; "Kantō" in Japan Encyclopedia, p. 479, at Google Books.
- ↑ Nussbaum, "Mito" at Japan Encyclopedia, p. 642, at Google Books.
- ↑ "General overview of area figures for Natural Parks by prefecture" (PDF). Ministry of the Environment. 1 April 2012. Retrieved 9 November 2013.
- ↑ Schreiber, Mark, "Japan's food crisis goes beyond recent panic buying", The Japan Times, 17 April 2011, p. 9.
- ↑ Aikikai Foundation Ibaraki Branch Dojo " Founder and Iwama", Retrieved August 25 2017
- ↑ いばらぎじゃなくていばらき [Ibaragi ja Nakute Ibaraki]
References
- Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric and Käthe Roth. (2005). Japan Encyclopedia. Cambridge: Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-674-01753-5. OCLC 58053128.
External links
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Ibaraki. |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Ibaraki Prefecture. |
- Ibaraki Prefecture Official Website (in Japanese)
- Ibaraki Prefecture Official Website (in English)