Hulu Perak District
| Hulu Perak District | |
|---|---|
|
| |
| Daerah Hulu Perak | |
| Other transcription(s) | |
| • Chinese | 上霹雳县 |
| • Tamil | உலு பேராக் |
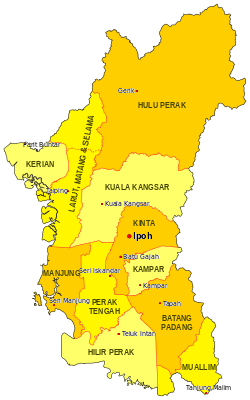 Location of Hulu Perak District in Perak | |
 Hulu Perak District Location of Hulu Perak District in Malaysia | |
| Coordinates: 5°20′N 101°15′E / 5.333°N 101.250°ECoordinates: 5°20′N 101°15′E / 5.333°N 101.250°E | |
| Country |
|
| State |
|
| Seat | Gerik |
| Local area government(s) |
Gerik District Council (Gerik) Lenggong District Council (Lenggong) Pengkalan Hulu District Council (Pengkalan Hulu) |
| Government | |
| • District officer | n/a[1] |
| Area[2] | |
| • Total | 6,560.43 km2 (2,533.00 sq mi) |
| Population (2010)[3] | |
| • Total | 89,067 |
| • Estimate (2015)[4] | 97,300 |
| • Density | 14/km2 (35/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (MST) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+8 (Not observed) |
| Postcode |
33100 (Pengkalan Hulu) 33300 (Gerik) 33400 (Lenggong) |
| Calling code | +6-05 |
| Vehicle registration plates | A |
The Hulu Perak District is a district in Perak, Malaysia. To the east of the district is the state of Kelantan, to the west is Kedah, to the south is the district of Kuala Kangsar while to the south-west is the district of Larut, Matang and Selama. Hulu Perak also shares a border with Betong District of Thailand. The seat of the district is Gerik, which is also the largest town of the district.
The highest point of the district is located at Titiwangsa Mountains, with 1,533 m high Ulu Titi Basah peak near the Thai/Malaysian border, and Temenggor Lake.[5]
History
In 1511, after the fall of the Malacca Sultanate to the Portuguese, Sultan Mahmud Shah retreated and established his government in Bentan. In 1526 the Portuguese attacked his domain again and forced him to retreat to Kampar and to establish his rule there.
At that time, Tun Saban had moved to Upper Patani and stayed at Beredung Budi. He then moved to Belum Forest in Hulu Perak, founded a village at a place called Relap Hati, and became the chief of the peoples in Belum Forest.
For sometime until the 19th century, a good part of this district was under the sovereignty of Siam, as part of the old Malay kingdom of Reman. The area then under Thai control included what is today Gerik, Pengkalan Hulu (Kroh), Kerunai, the Belum forest and the Temenggor Lakes. The capital of Reman was near Pengkalan Hulu. [6]
In 1882, the border between the then-British protected state of Perak and the Siamese vassal state of Reman was delimited at Bukit Nasha, some 5 km south of Gerik town.
An adjustment in 1899 transferred Gerik town and the surrounding commune to the Federated Malay States, which Perak was then part of.
The present-day border, part of the longer Malaysia-Thailand border, was finalised in 1909, when the districts of Pengkalan Hulu, Kerunai, Belukar Semang, Belum and the present-day Temenggor Lakes were transferred to the FMS. The British also gained control of Perlis, Kedah, Kelantan and Terengganu.
Administrative divisions
Hulu Perak District is divided into 10 mukims and three district councils, which are:[7]
- Under Pengkalan Hulu District Council
- Pengkalan Hulu (with Klian Intan)
- Belukar Semang
- Under Gerik District Council
- Gerik (with Kuala Rui)
- Belum
- Kenering (with Lawin)
- Kerunai
- Temenggor (with Banding Island)
- Under Lenggong District Council
- Lenggong
- Durian Pipit (with Tasik Raban)
- Temelong (with Kota Tampan)
Demographics
The following is based on Department of Statistics Malaysia 2010 census.[3]
| Ethnic groups in Hulu Perak , 2010 census | ||
|---|---|---|
| Ethnicity | Population | Percentage |
| Bumiputera | 77,386 | 86.9% |
| Chinese | 8,628 | 9.6% |
| Indian | 1,658 | 1.9% |
| Others | 1,395 | 1.6% |
| Total | 89,067 | 100% |
Federal Parliament and State Assembly Seats
List of Hulu Perak district representatives in the Federal Parliament (Dewan Rakyat)
| Parliament | Seat Name | Member of Parliament | Party |
|---|---|---|---|
| P.054 | Gerik | Hasbullah Osman | Barisan Nasional |
| P.055 | Lenggong | Dr. Shamsul Anuar Nasarah | Barisan Nasional |
List of Hulu Perak district representatives in the State Legislative Assembly of Perak
| Parliament | State | Seat Name | State Assemblyman | Party |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P.054 | N.01 | Pengkalan Hulu | Aznel Ibrahim | Barisan Nasional |
| P.054 | N.02 | Temengor | Salbiah Mohamed | Barisan Nasional |
| P.055 | N.03 | Kenering | Mohd Tarmizi Idris | Barisan Nasional |
| P.055 | N.04 | Kota Tampan | Saarani Mohamad | Barisan Nasional |
See also
References
- ↑ "Portal Rasmi Pejabat Daerah Dan Tanah Hulu Perak, Gerik - Pegawai Daerah". pdtgerik.perak.gov.my.
- ↑ "Rancangan Tempatan Daerah Hulu Perak 2030 (Jilid 1)" (PDF) (in Malay).
- 1 2 "Population Distribution and Basic Demographic Characteristics, 2010" (PDF). Department of Statistics, Malaysia. Archived from the original (PDF) on 22 May 2014. Retrieved 19 April 2012.
- ↑ "Rancangan Struktur Negeri Perak 2040" (PDF). p. 316.
- ↑ "Gunong Ulu Titi Basah: Thailand". Geographic.org. 1994-04-06. Retrieved 2013-04-30.
- ↑ "Perang saudara di Hulu Perak". Utusan Online. Utusan Malaysia. Retrieved 16 October 2016.
- ↑ "Portal Rasmi Pejabat Daerah Dan Tanah Hulu Perak, Gerik - Geografi Daerah". pdtgerik.perak.gov.my.
External Links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Hulu Perak. |