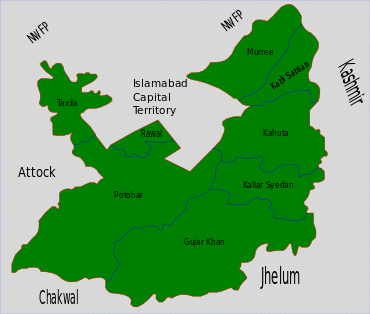
Gujar Khan Tehsil
| Gujar Khan Tehsil تحصِیل گُوجر خان | |
|---|---|
| Tehsil | |
 | |
| Country | Pakistan |
| Region | Punjab |
| District | Rawalpindi District |
| Capital | Gujar Khan |
| Union councils | 36 |
| Government | |
| • MNA | Raja Pervaiz Ashraf |
| • MPA | Chaudhary Javed Kausar |
| • MPA | Chaudhary Sajid Mehmood |
| • Mayor | Shahid Saraf |
| Area | |
| • Total | 1,466 km2 (566 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 461 m (1,512 ft) |
| Population (2017) | |
| • Total | 678,503 |
| • Density | 662.83/km2 (1,716.7/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+5 (PST) |
Gujar Khan Tehsil (Urdu: تحصِیل گُوجر خان ), headquartered at Gujar Khan, is one of the seven Tehsils (sub-divisions) of Rawalpindi District in the Punjab province of Pakistan. It is administratively subdivided into 36 Union Councils[1] and according to the 1998 census has a population of 493,000. In 2017 census Gujar Khan has a population of 678,503[2]
History
In 997 CE, Sultan Mahmud Ghaznavi, took over the Ghaznavid dynasty empire established by his father, Sultan Sebuktegin, In 1005 he conquered the Shahis in Kabul in 1005, and followed it by the conquests of Punjab region. The Delhi Sultanate and later Mughal Empire ruled the region. The Punjab region became predominantly Muslim due to missionary Sufi saints whose dargahs dot the landscape of Punjab region.
After the decline of the Mughal Empire, the Sikh Empire invaded and occupied Rawalpindi District. The Muslims faced restrictions during the Sikh rule. During the period of British rule, Gujar Khan Tehsil increased in population and importance.
The tehsil of Gujar Khan was described in the Imperial Gazetteer of India, compiled during the first decade of the twentieth century, as follows:[3]
"Southern tahsil of Rawalpindi District, Punjab, lying between 33°4′ and 33°26′ N. and 72°56′ and 73°37′ E., with an area of 567 square miles. It is bounded on the east by the Jhelum river, which cuts it off from Kashmir territory. Except for a low ridge of sandstone hills along the Jhelum, the tahsil consists of a plain intersected by numerous ravines. The population in 1901 was 150,566, compared with 152,455 in 1891. It contains 381 villages, of which Gujar Khan is the headquarters. The land revenue and cesses in 1903-4 amounted to 2-7 lakhs."
During the period of British rule, Gujar Khan Tehsil increased in population and importance. The predominantly Muslim population supported Muslim League and Pakistan Movement. After the independence of Pakistan in 1947, the minority Hindus and Sikhs migrated to India while the Muslims refugees from India settled down in the Rawalpindi District.
Administration
The tehsil of Gujar Khan is administratively subdivided into 36 Union Councils, these are:
- Bewal
- Noor Dolal
- Bhadana
- Changa Bangial
- Daultala
- Devi
- Gujar Khan-I
- Gujar Khan-II
- Gujar Khan-III
- Gulyana
- Gungrila
- Jand Mehlo
- Jarmot Kalan
- Jatli
- Jhungle
- Kalyam Awan
- Kaniat Khalil
- Karumb Ilyas
- Kauntrila
- Kuri Dolal
- Mandrah
- Manghot
- Mankiala Branmma
- Matwa
- Mohra Noori
- Narali
- Punjgran Kalan
- Qazian
- Raman
- Sahang
- Sui Cheemian
- Sukho
- Syed Kasran
- Thathi
- Kuri Hazaro
- Islampura Jabbar
Educational establishments include Punjab College, Govt. Sarwar Shaheed (N.H.) College, Indus College and the Super Wings Group of Colleges.
Sanghori
Sanghori Sarwar Shaheed is a village of Gujar Khan Tehsil, Rawalpindi District, in Punjab, Pakistan. Captain Sarwar Shaheed, the first Nishan-e-haider holder, was born in this village. A memorial to Captain Sarwar Shaheed (Nishan-E-haider) is situated in Sanghori Sarwar Shaheed. (Muhammad Zafran Malik)
Natural resources
Large reserves of oil and gas were discovered in February 2002 at Tobra, about ten kilometres from Gujar Khan. The field is being developed by the Oil and Gas Development Company. The field could produce 1,600 barrels of crude oil daily.[4]
Notable People
- Gen Ashfaq Pervez Kiyani, Ex Army Chief
- Raja Pervaiz Ashraf, Ex prime minister of Pakistan
- Captain Raja Muhammad Sarwar,recipient of Nishan i Haider
- Muhammad Hussain Janjua, first soldier to be awarded Nishan-e-Haider
- Amir Khan, Boxer
- Mohammad Amir, cricketer
- Najaf Shah, cricketer
See also
References
- ↑ Zila, Tehsil & Town Councils Membership for Punjab - Election Commission of Pakistan Archived 2009-03-04 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ District Government of Rawalpindi Archived 2008-03-13 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ Gujar Khān, v. 12, p. 353
- ↑ Asia Times Online (Holdings) Ltd. "Business in Asia". Retrieved 2007-07-02.
Coordinates: 33°24′20″N 73°14′40″E / 33.40556°N 73.24444°E