Lahore Division
| Lahore Division | |
|---|---|
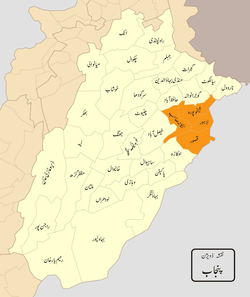 | |
| Districts |
Lahore Kasur |
| Area | |
| • Total | 5,767 km2 (2,227 sq mi) |
| Population (2017)[1] | |
| • Total | 14,581,281 |
| • Density | 2,500/km2 (6,500/sq mi) |
| National Assembly Seats (2018) |
Total (18)
|
| Punjab Assembly Seats (2018) |
Total (39)
|
Lahore Division is an administrative division of Punjab Province, Pakistan. Before 2000 it comprised four Districts - Kasur, Lahore, Nankana Sahib District and Sheikhupura. Under the reforms of 2000, this tier of government was abolished, but in 2000 divisions were restored. However, the restored Lahore Division has only comprised Kasur and Lahore Districts; a new division, Sheikhupura Division was created to comprise Nankana Sahib and Sheikhupura Districts.[2][3][4]
History
Lahore Division was originally an administrative division of the Punjab Province of British India. It extended along the right bank of the Sutlej River from the Himalaya to Multan, and comprised the six districts of Sialkot, Gujranwala, Lahore, Amritsar, Gurdaspur and Gujrat. The total area of the division was 44,430 km2 (17,154 sq mi) and the population according to the 1901 census of India was 5,598,463.[5] The commissioner for the division also exercised political control over the hill state of Chamba.
The Commissioner's headquarters were at Lahore and Dalhousie.The total population of the Division increased from 4,696,636 in 1881 to 5,321,535 in 1891, and 5,598,463 in 1901. The total area was 44,430 square kilometres (17,154 sq mi), and the density of population was 326 persons per square mile, compared with 208 for British territory in the Province as a whole. In 1901 Muslims numbered 3,332,175, or 60 percent of the total; while other religions included Hindus, 1,567,402; Sikhs, 661,320; Jains, 5,5,07; Buddhists, 6; Parsis, 228; and Christians, 31,815, of whom 25,248 were natives.[6]
The division contained six districts:[5]
| District | Area (square miles) |
Population (1901 census figures) |
Land revenue and cesses (thousands of rupees). |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gujrat | 4,771 | 497,706 | 6,90 |
| Lahore | 3,704 | 1,162,109 | 12,55 |
| Amritsar | 1,601 | 1,023,828 | 14,54 |
| Gurdaspur | 1,889 | 940,334 | 17,72 |
| Sialkot | 1,991 | 1,083,909 | 17,27 |
| Gujranwala | 3,198 | 890,557 | 12,89 |
| Total | 17,154 | 5,598,463 | 81,87 |
Gurdaspur included a few square miles of mountainous country, enclosing the hill station of Dalhousie (highest, point, 7,687 feet) ; but otherwise the Division was flat. It contained 9,869 villages and 41 towns, of which the largest are Lahore (population, 202,964, including cantonment), Amristar(162,429), Sialkot (57,956), Gujranwala (29,224), Batala (27,365), and Gujrat (22,022). In commercial importance Lahore and Amritsar dwarfed all other towns in the Division, but Sialkot and Batala were considerably more than local centres. Besides the administrative charge of six British Districts, the Commissioner of Lahore had political control over the Native State of Chamba, which had an area of 8,330 square kilometres (3,216 sq mi) and a population (1901) of 127,834.[5]
Independence
With the independence of Pakistan in 1947, Lahore Division was divided among the two countries. with the eastern half becoming Amrtisar Division.
References
- ↑ "DISTRICT WISE CENSUS RESULTS CENSUS 2017" (PDF). www.pbscensus.gov.pk. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2017-08-29.
- ↑ Divisions/Districts of Pakistan Archived 2006-09-30 at the Wayback Machine.
Note: Although divisions as an administrative structure were abolished, the Election Commission of Pakistan still grouped Districts under the Division names until the divisions were restored in 2008. - ↑ http://health.punjab.gov.pk/?q=system/files/Division_and_district_wise_facilities.pdf Archived 2015-04-16 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ "Punjab Government Plans to Carve a New District from Lahore". Archived from the original on 2010-06-03.
- 1 2 3 "Imperial Gazetteer2 of India, Volume 16, page 96 -- Imperial Gazetteer of India -- Digital South Asia Library". dsal.uchicago.edu. Archived from the original on 17 July 2014. Retrieved 27 April 2018.
- ↑ "Imperial Gazetteer2 of India, Volume 16, page 95 -- Imperial Gazetteer of India -- Digital South Asia Library". dsal.uchicago.edu. Archived from the original on 3 March 2016. Retrieved 27 April 2018.