Dichlorodifluoromethane
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Dichloro(difluoro)methane | |||
| Other names
Dichlorodifluoromethane Carbon dichloride difluoride Dichloro-difluoro-methane Difluorodichloromethane Freon 12 R-12 CFC-12 P-12 Propellant 12 Halon 122 Arcton 6 Arcton 12 E940 Fluorocarbon 12 Genetron 12 Refrigerant 12 | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.813 | ||
| EC Number | 200-893-9 | ||
| E number | E940 (glazing agents, ...) | ||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID |
|||
| RTECS number | PA8200000 | ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1028 | ||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| CCl2F2 | |||
| Molar mass | 120.91 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless gas with ether-like odor | ||
| Odor | ether-like at very high concentrations | ||
| Density | 1.486 g/cm3 (−29.8 °C (−21.6 °F)) | ||
| Melting point | −157.7 °C (−251.9 °F; 115.5 K) | ||
| Boiling point | −29.8 °C (−21.6 °F; 243.3 K) | ||
| 0.286 g/l at 20 °C (68 °F) | |||
| Solubility in alcohol, ether, benzene, acetic acid | Soluble | ||
| log P | 2.16 | ||
| Vapor pressure | 568 kPa (20 °C (68 °F)) | ||
Henry's law constant (kH) |
0.0025 mol kg−1 bar−1 | ||
| -52.2·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
| Structure | |||
| Tetrahedral | |||
| 0.51 D[1] | |||
| Hazards | |||
| Main hazards | Damaging to Earth's protective ozone | ||
| Safety data sheet | See: data page | ||
| R-phrases (outdated) | R44 R59[2] | ||
| S-phrases (outdated) | S9 S38[2] | ||
| NFPA 704 | |||
| Flash point | Non-flammable [3] | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LC50 (median concentration) |
760,000 ppm (mouse, 30 min) 800,000 ppm (rabbit, 30 min) 800,000 ppm (guinea pig, 30 min) 600,000 ppm (rat, 2 hr)[4] | ||
| US health exposure limits (NIOSH): | |||
PEL (Permissible) |
TWA 1000 ppm (4950 mg/m3)[3] | ||
REL (Recommended) |
TWA 1000 ppm (4950 mg/m3)[3] | ||
IDLH (Immediate danger) |
15000 ppm[3] | ||
| Supplementary data page | |||
| Refractive index (n), Dielectric constant (εr), etc. | |||
Thermodynamic data |
Phase behaviour solid–liquid–gas | ||
| UV, IR, NMR, MS | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Dichlorodifluoromethane (R-12) is a colorless gas usually sold under the brand name Freon-12, and a chlorofluorocarbon halomethane (CFC) used as a refrigerant and aerosol spray propellant. Complying with the Montreal Protocol, its manufacture was banned in developed countries (non-article 5 countries) in 1996, and developing countries (article 5 countries) in 2010 due to concerns about its damaging impact to the ozone layer.[5] Its only allowed usage is as fire retardant in submarines and aircraft. It is soluble in many organic solvents. Dichlorodifluoromethane was one of the original propellants for Silly String. R-12 cylinders are colored white.
Preparation
It can be prepared by reacting carbon tetrachloride with hydrogen fluoride in the presence of a catalytic amount of antimony pentachloride:
- CCl4 + 2HF → CCl2F2 + 2HCl
This reaction can also produce trichlorofluoromethane (CCl3F), chlorotrifluoromethane (CClF3) and tetrafluoromethane (CF4).[6]
History
Charles (Boss) Kettering, vice president of General Motors Research Corporation, was seeking a refrigerant replacement that would be colorless, odorless, tasteless, nontoxic, and nonflammable. He assembled a team that included Thomas Midgley, Jr., Albert Leon Henne, and Robert McNary. From 1930 to 1935, they developed dichlorodifluoromethane (CCl2F2 or R12), trichlorofluoromethane (CCl3F or R11), chlorodifluoromethane (CHClF2 or R22), trichlorotrifluoroethane (CCl2FCClF2 or R113), and dichlorotetrafluoroethane (CClF2CClF2 or R114), through Kinetic Chemicals which was a joint venture between DuPont and General Motors.[7]
Use as an aerosol
The use of chlorofluorocarbons as aerosols in medicine, such as USP-approved salbutamol, has been phased out by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. A different propellant known as hydrofluoroalkane, or HFA, which is not known to harm the environment, was chosen to replace it.[8]
Retrofitting
R-12 was used in most refrigeration and vehicle air conditioning applications prior to 1994 before being replaced by 1,1,1,2-tetrafluoroethane (R-134a), which has an insignificant ozone depletion potential. Automobile manufacturers started using R-134a instead of R-12 in 1992–1994. When older units leak or require repair involving removal of the refrigerant, retrofitment to a refrigerant other than R-12 (most commonly R-134a) is required in some jurisdictions. The United States does not require automobile owners to retrofit their systems; however, taxes on ozone-depleting chemicals coupled with the relative scarcity of the original refrigerants on the open market make retrofitting the only economical option. Retrofitment requires system flush and a new filter/dryer or accumulator, and may also involve the installation of new seals and/or hoses made of materials compatible with the refrigerant being installed. Mineral oil used with R-12 is not compatible with R-134a. Some oils designed for conversion to R-134a are advertised as compatible with residual R-12 mineral oil.
Gallery
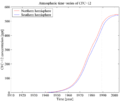 Time-series of atmospheric concentrations of CFC-12 (Walker et al., 2000)
Time-series of atmospheric concentrations of CFC-12 (Walker et al., 2000)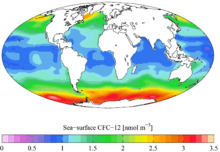 1990s sea surface CFC-12 concentration
1990s sea surface CFC-12 concentration 1990s CFC-12 oceanic vertical inventory
1990s CFC-12 oceanic vertical inventory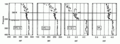 CFC-12, CFC-11, H-1211 and SF6 vertical profiles
CFC-12, CFC-11, H-1211 and SF6 vertical profiles
References
- ↑ Khristenko, Sergei V.; Maslov, Alexander I. and Viatcheslav P. Shevelko; Molecules and Their Spectroscopic Properties, p. 74 ISBN 3642719481
- 1 2 "Dichlorodifluoromethane MSDS" (PDF). Synquest Labs.
- 1 2 3 4 "NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards #0192". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ↑ "Dichlorodifluoromethane". Immediately Dangerous to Life and Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ↑ "Dichlorodifluoromethane at LearnChemistry (Royal Society of Chemistry)". rsc.org. Retrieved 2017-11-29.
- ↑ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. p. 304. ISBN 0-08-037941-9.
- ↑ Plunkett, Roy J. (1986). High Performance Polymers: Their Origin and Development. Elsevier Science Publishing Co. , Inc. pp. 261–262. ISBN 978-94-011-7073-4.
- ↑ 'Rescue' asthma inhaler replacements coming to Pa. Archived February 16, 2007, at the Wayback Machine.
External links
- NOAA/ESRL CFC-12 global measurements
- International Chemical Safety Card 0048
- Overview of Freon-12 and some of its environmental problems
- MSDS at Oxford University
- Thermochemistry data at chemnet.ru
- IR absorption spectra
- CDC - NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards