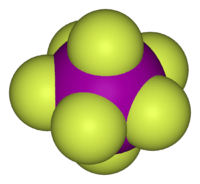
Iodine heptafluoride
 | |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Other names
Iodine(VII) fluoride Heptafluoroiodine | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.037.241 | ||
PubChem CID |
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| IF7 | |||
| Molar mass | 259.90 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | colorless gas | ||
| Density | 2.6 g/cm3 (6 °C) 2.7 g/cm3 (25 °C) | ||
| Melting point | 4.5 °C (40.1 °F; 277.6 K) (triple point) | ||
| Boiling point | 4.8 °C (40.6 °F; 277.9 K) (sublimes at 1 atm) | ||
| soluble [1] | |||
| Related compounds | |||
Related compounds |
iodine pentafluoride | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Iodine heptafluoride, also known as iodine(VII) fluoride or iodine fluoride, is an interhalogen compound with the chemical formula IF7.[2][3] It has an unusual pentagonal bipyramidal structure, as predicted by VSEPR theory.[4] The molecule can undergo a pseudorotational rearrangement called the Bartell mechanism, which is like the Berry mechanism but for a heptacoordinated system.[5] It forms colourless crystals, which melt at 4.5 °C: the liquid range is extremely narrow, with the boiling point at 4.77 °C. The dense vapor has a mouldy, acrid odour. The molecule has D5h symmetry.
Preparation
IF7 is prepared by passing F2 through liquid IF5 at 90 °C, then heating the vapours to 270 °C. Alternatively, this compound can be prepared from fluorine and dried palladium or potassium iodide to minimize the formation of IOF5, an impurity arising by hydrolysis.[6][7] Iodine heptafluoride is also produced as a by-product when dioxygenyl hexafluoroplatinate is used to prepare other platinum(V) compounds such as potassium hexafluoroplatinate(V), using potassium fluoride in iodine pentafluoride solution:[8]
- 2 O2PtF6 + 2 KF + IF5 → 2 KPtF6 + 2 O2 + IF7
Safety considerations
IF7 is highly irritating to both the skin and the mucous membranes. It also is a strong oxidizer and can cause fire on contact with organic material.
References
- ↑ Pradyot Patnaik. Handbook of Inorganic Chemicals. McGraw-Hill, 2002, ISBN 0-07-049439-8
- ↑ Macintyre, J. E. (Ed.). (1992). Dictionary of Inorganic Compounds (Vol. 3). London: Chapman & Hall.
- ↑ O'Neil, Maryadele J. (Ed.). (2001). The Merck Index (13th ed.). Whitehouse Station, NJ: Merck.
- ↑ K. O. Christe; E. C. Curtis; D. A. Dixon (1993). "On the problem of heptacoordination: vibrational spectra, structure, and fluxionality of iodine heptafluoride". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 115 (4): 1520–1526. doi:10.1021/ja00057a044.
- ↑ W. J. Adams; H. Bradford Thompson; L. S. Bartell (1970). "Structure, Pseudorotation, and Vibrational Mode Coupling in IF7: An Electron Diffraction Study". Journal of Chemical Physics. 53 (10): 4040–4046. doi:10.1063/1.1673876.
- ↑ Schumb, W. C.; Lynch, M. A. (1950). "Iodine Heptafluoride". Industrial & Engineering Chemistry. 42 (7): 1383–1386. doi:10.1021/ie50487a035.
- ↑ Ruff, O.; Keim, R. (1930). ""Das Jod-7-fluorid" (The iodine-7-fluoride)". Zeitschrift für Anorganische und Allgemeine Chemie (in German). 193 (1/2): 176–186. doi:10.1002/zaac.19301930117.
- ↑ Beveridge, A. D.; Clark, H. C. (1967). "Pentahalides of the Transition Metals". In Gutmann, Viktor. Halogen Chemistry. 3. Academic Press. pp. 179–226. ISBN 9780323148474.
External links
- WebBook page for IF7
- National Pollutant Inventory - Fluoride and compounds fact sheet
- web elements listing