Chlorzoxazone
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Parafonforte |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682577 |
| Routes of administration | oral |
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | well absorbed |
| Protein binding | 13–18% |
| Metabolism | hepatic |
| Elimination half-life | 1.1 hr |
| Excretion | urine (<1%) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard |
100.002.186 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
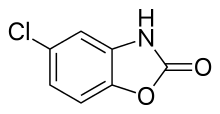
| Formula | C7H4ClNO2 |
| Molar mass | 169.565 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Chlorzoxazone (INN) is a centrally acting muscle relaxant used to treat muscle spasm and the resulting pain or discomfort. It acts on the spinal cord by depressing reflexes. It is sold under the trade names "'Lorzone'", Paraflex and Muscol and in combination form as Parafon Forte, a combination of chlorzoxazone and acetaminophen (paracetamol). Possible side effects include dizziness, lightheadedness, malaise, nausea, vomiting, and liver dysfunction. Used with acetaminophen it has added risk of hepatoxicity, which is why the combination is not recommended. It can also be administered for acute pain in general and for tension headache (muscle contraction headache).
Like metaxalone, no specific mechanism of action has been identified for chlorzoxazone, with general central nervous system depression being the only currently accepted aspect to its medical benefits. Search for the exact mechanism of action is ongoing but limited due to the existence of more-effective safe muscle relaxers (ex. diazepam, cyclobenzaprine, tizanidine) greatly limiting the potential benefit of identifying novel compounds which share chlozoxazone's mechanism of action.
As of 2015 the cost for a typical course of medication in the United States is less than 25 USD.[1]
See also
References
- D.F. Marsh, U.S. Patent 2,895,877 (1959).
- Dong DL, Luan Y, Feng TM, Fan CL, Yue P, Sun ZJ, Gu RM, Yang BF (2006). "Chlorzoxazone inhibit contraction of rat thoracic aorta". Eur J Pharmacol. 545 (2–3): 161–6. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2006.06.063. PMID 16859676.
- Park J, Kim K, Park P, Ha J (2006). "Effect of high-dose aspirin on CYP2E1 activity in healthy subjects measured using chlorzoxazone as a probe". J Clin Pharmacol. 46 (1): 109–14. doi:10.1177/0091270005282635. PMID 16397290.
- Wan J, Ernstgård L, Song B, Shoaf S (2006). "Chlorzoxazone metabolism is increased in fasted Sprague-Dawley rats". J Pharm Pharmacol. 58 (1): 51–61. doi:10.1211/jpp.58.1.0007. PMC 1388188. PMID 16393464.
- PARAFON DSC (chlorzoxazone) tablet, Daily Med, U.S. National Library of Medicine