Mibefradil
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Posicor |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| MedlinePlus | a607007 |
| Routes of administration | By mouth (tablets) |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 70% |
| Protein binding | >99% |
| Metabolism | Liver |
| Elimination half-life | 17–25 hours |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C29H38FN3O3 |
| Molar mass | 495.63 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 128 °C (262 °F) (dihydrochloride salt) |
| |
| |
| | |
Mibefradil (Posicor) is a drug for the treatment of hypertension and chronic angina pectoris. It belongs to a group known as calcium channel blockers.
The mechanism of action of mibefradil is characterized by the selective blockade of transient, low-voltage-activated (T-type) calcium channels over long-lasting, high-voltage-activated (L-type) calcium channels, which is probably responsible for many of its unique properties.
It is nonselective.[1]
On June 8, 1998, Roche announced the voluntary withdrawal of the drug from the market, one year after approval by the FDA, due to the potential for drug interactions, some of them deadly, which may occur when it is taken together with some other medications.[2]
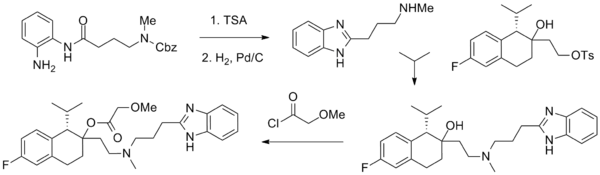
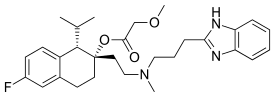
Synthesis
References
- ↑ Bezprozvanny I, Tsien RW (September 1995). "Voltage-dependent blockade of diverse types of voltage-gated Ca2+ channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes by the Ca2+ channel antagonist mibefradil (Ro 40-5967)". Mol. Pharmacol. 48 (3): 540–9. PMID 7565636.
- ↑ Heart Drug Withdrawn as Evidence Shows It Could Be Lethal: https://www.nytimes.com/1998/06/09/us/heart-drug-withdrawn-as-evidence-shows-it-could-be-lethal.html
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.