County Roscommon
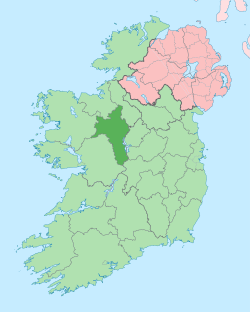
County Roscommon (Irish: Contae Ros Comáin) is a county in Ireland. In the western region, it is part of the province of Connacht. It is the 11th largest Irish county by area and 27th most populous. Its county town and largest town is Roscommon. Roscommon County Council is the local authority for the county. The population of the county was 64,544 at to the 2016 census.[4]
County Roscommon Contae Ros Comáin | |
|---|---|
 Coat of arms | |
| Motto(s): | |
 | |
| Country | Ireland |
| Province | Connacht |
| Dáil Éireann | Roscommon–Galway |
| EU Parliament | Midlands–North-West |
| Established | c. 1569[1][2] |
| County town | Roscommon |
| Government | |
| • Type | County Council |
| Area | |
| • Total | 2,548 km2 (984 sq mi) |
| Area rank | 11th |
| Highest elevation | 428 m (1,404 ft) |
| Population (2016)[4] | |
| • Total | 64,544 |
| • Rank | 27th |
| • Density | 25/km2 (66/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC±0 (WET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+1 (IST) |
| Eircode routing keys | F42, F45, F52 (primarily) |
| Telephone area codes | 071, 090 (primarily) |
| Vehicle index mark code | RN |
| Website | www |
Etymology
County Roscommon is named after the county town of Roscommon. Roscommon comes from the Irish Ros meaning a wooded, gentle height and Comán, the first abbot and bishop of Roscommon who founded the first monastery there in 550 AD.[5]
Geography
County Roscommon has an area of 2,548 square kilometres (984 sq mi).[3] Lough Key in north Roscommon is noted for having thirty-two islands. The geographical centre of Ireland is located on the western shore of Lough Ree in the south of the county.[6]
Roscommon is the third largest of Connacht's five counties by size and the second-smallest in terms of population. It ranks 11th in size of Ireland's 32 counties, but 27th in terms of population, making it the 3rd most sparsely populated county after Leitrim and Mayo. The county borders every other Connacht county: Galway, Mayo, Sligo, and Leitrim, as well as three Leinster counties: Longford, Westmeath, and Offaly. In 2008, a news report said that statistically, Roscommon has the longest life expectancy of any county on the island of Ireland.[7]
Seltannasaggart, which is located along the northern border with County Leitrim, is the tallest point in County Roscommon, measuring to a height of 428 m (1,404 ft).[8]
Baronies
There are nine historical baronies in County Roscommon.
North Roscommon
- Boyle (north Roscommon including Boyle and Arigna).
- Frenchpark (north-west, including Ballaghaderreen and Frenchpark).
- Roscommon (mid-north-east, including Tulsk).
- Castlereagh (west, including Castlerea and Ballinlough).
- Ballintober North (east including Rooskey and Tarmonbarry).
South Roscommon
- Ballymoe shared with County Galway includes Ballymoe, Creggs and Glenamaddy.
- Ballintober South (south-mid-east, including Roscommon).
- Athlone (mid-south, including Knockcroghery and part of Athlone).
- Moycarn (far-south, including part of Ballinasloe).
History

Rathcroghan (Rath Cruachán), near Tulsk, a complex of archaeological sites, the home of Queen Medb (Méadhbh, Maeve), was the seat of Kings of Connacht and then to the High Kings of Ireland. This was the starting point of the Táin Bó Cúailnge, or Cattle Raid of Cooley, an epic tale in Irish mythology. The county is home to prehistoric ringforts such as Carnagh West Ringfort and Drummin fort.
County Roscommon as an administrative division has its origins in the medieval period. With the conquest and division of the Kingdom of Connacht, those districts in the east retained by King John as "The King's Cantreds" covered County Roscommon, and parts of East Galway. These districts were leased to the native kings of Connacht and eventually became the county. In 1585 during the Tudor re-establishment of counties under the Composition of Connacht, Roscommon was established with the South-west boundary now along the River Suck.
Medieval art
A "well defined" and "original" fine metal workshop was active in County Roscommon in the 12th century. The Cross of Cong, the Aghadoe crosier, Shrine of the Book of Dimma and Shrine of Manchan of Mohill' are grouped together as having been created by Mael Isu Bratain Ui Echach et al., at the same Roscommon workshop.[9][10][11][12] The workshop has been linked to St. Assicus of Elphin.[13]
Ordnance Survey

John O'Donovan (1806–1861), historian and scholar, visited County Roscommon in 1837, while compiling information for the Ordnance Survey. Entering St Peter's parish in Athlone in June 1837, he wrote, "I have now entered upon a region totally different from Longford, and am very much pleased with the intelligence of the people." However, he had major problems with place-names. He later wrote, "I am sick to death's door of lochawns, and it pains me to the very soul to have to make these remarks, but what can I do when I cannot make the usual progress? Here I am stuck in the mud in the middle of Loughs, Turlaghs, Lahaghs and Curraghs, the names of many of which are only known to a few old men in their immediate neighbourhood and I cannot give many of them utterance from the manner in which they are spelled."[14][15]

Government and politics
Roscommon is governed locally by the 18-member Roscommon County Council.
For general elections, Roscommon forms part of the three-seat Roscommon–Galway constituency.
Rail transport
There are railway stations located in Boyle, Carrick-on-Shannon (Dublin-Sligo line), Roscommon, Castlerea (Dublin-Westport line), Ballinasloe (Dublin-Galway line) and Athlone (Dublin-Galway and Dublin-Westport lines).
Sport
Gaelic football is the dominant sport in Roscommon. Roscommon won the All-Ireland Senior Football Championships in 1943 and 1944 and the National Football League Division 1 in 1979, as well as Division 2 in 2015 and 2018. Roscommon have captured the Connacht Senior Football Championship on 23 occasions, the most recent being in 2019.
Roscommon's main hurling title was the 2007 Nicky Rackard Cup.
Soccer and Rugby are also popular sports in the county.
Notable people
In order of birth:
- Charles O'Conor (1710–1791), historian and antiquarian of the O'Conor Don family
- Matthew O'Conor Don (1773–1844) historian born in Ballinagare, Co. Roscommon
- Arthur French, 1st Baron de Freyne (1786–1856), Member of Parliament and landlord of Frenchpark House
- Sir John Scott Lillie (1790–1868) CB, decorated Peninsular War veteran, inventor and political activist in England
- William Wilde (1815–1876), surgeon, innovator and father of Oscar Wilde, born in Castlerea, Co. Roscommon
- Michael Dockry (born 1817), member of the Wisconsin State Assembly
- Thomas Curley (1825–1904), American Civil War colonel, farmer and Wisconsin legislator, born in Tremane, near Athleague, Co. Roscommon
- Henry Gore-Browne (1830–1912), Victoria Cross recipient, born in Newtown, Co. Roscommon
- Luke O'Connor (1831–1915), first soldier to receive the Victoria Cross, born in Elphin
- John Fitzgibbon (1845–1919), Member of Parliament
- William Griffiths (1841–1879), recipient of the Victoria Cross, born in Co. Roscommon
- Percy French (1854–1920), born in Tulsk, was a foremost songwriter and entertainer, and water-colour painter
- Sir Owen Lloyd (1854–1941), recipient of the Victoria Cross, born in Co. Roscommon
- Thomas Heazle Parke (1857–1893, explorer and naturalist, born at Clogher House
- Charlotte O'Conor Eccles (1860–1911) writer, journalist and translator born in the county
- Roderic O'Conor (1860–1940), impressionist artist of the O'Conor Don Family
- Douglas Hyde (1860–1949), scholar of the Irish language, first President of Ireland (1938–45), founder of the Gaelic League during the Revival of the late 19th – early 20th century, born in Castlerea and buried in the Hyde Museum, Frenchpark, Roscommon
- Margaret Cousins (née Gillespie, 1878–1954), educationist and suffragist in India, born in Boyle, Co. Roscommon
- Maureen O'Sullivan (1911–1998), Ireland's first international movie star, born in Boyle
- Brian O'Doherty (born 1928), artist and art critic in New York City, born in Ballaghaderreen
- Albert Reynolds (1932–2014), Taoiseach, born in Rooskey, Co. Roscommon
- Nuala Quinn-Barton (living), US film producer, artist and model brought up at Killerr, Ballintober, County Roscommon
- Brian Leyden (born 1960), novelist, short story writer, screenwriter and documentarian of Arigna, Co. Roscommon
- Luke 'Ming' Flanagan (born 1972), politician and MEP born in Roscommon
- Chris O'Dowd (born 1979), actor and comedian, born in Boyle
See also
- List of abbeys and priories in Ireland (County Roscommon)
- Counties of Ireland
- Earl of Roscommon
- High Sheriff of Roscommon
- Lord Lieutenant of Roscommon
- Midland Great Western Railway
- National Famine Museum
References
- MANNION, JOSEPH (20 June 2019). "ELIZABETHAN COUNTY GALWAY: THE ORIGIN AND EVOLUTION OF AN ADMINISTRATIVE UNIT OF TUDOR LOCAL GOVERNMENT". Journal of the Galway Archaeological and Historical Society. 64: 64–89. JSTOR 24612855.
- "County Galway, Ireland Genealogy Genealogy - FamilySearch Wiki". www.familysearch.org.
- "Students Corner – Statistical Facts About Your County – Cavan". Central Statistics Office (Ireland). Archived from the original on 26 April 2016. Retrieved 15 April 2019.
- "Census 2016 Sapmap Area: County Roscommon". Central Statistics Office (Ireland). Retrieved 18 October 2018.
- Walsh, Jane (9 September 2016). "What do Ireland's county names mean?". IrishCentral.com. Retrieved 22 November 2016.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 28 February 2012. Retrieved 7 February 2016.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "Roscommon tops life expectancy study". RTÉ News. Dublin: RTÉ Commercial Enterprises. 12 August 2008. Retrieved 19 August 2009.
- "Seltannasaggart 428m hill, Arigna Mountains Ireland at MountainViews.ie". mountainviews.ie.
- Ó Floinn 1987, pp. 179-187.
- Hourihane 2012, pp. 225.
- Edwards 2013, pp. 147.
- Karkov, Ryan & Farrell 1997, pp. 269.
- Kelly 1902, pp. 291-292.
- Hunt, Roy, "Painful progress: the slow evolution of County Roscommon society, 1850-1914". Unpublished Thesis, 2010, NUIG p. 8.
- John O' Donovan, "Letters containing information relative to the antiquities of the County of Roscommon, collected during the progress of the Ordnance Survey, 1837". p. 5. Special collections section, National University of Ireland, Galway, 2009, reproduced by Rev. Michael O'Flanagan, Bray 1927.
Secondary references
- Ó Floinn, Raghnall (1987). Michael Ryan (ed.). In Ireland and Insular Art A.D. 500–1200: Proceedings of a Conference at University College Cork, 31 October–3 November 1985 (Schools of Metalworking in Eleventh- and Twelfth-Century Ireland ed.). Dublin: Royal Irish Academy, International Specialized Book Service Incorporated. pp. 179–187. ISBN 9780901714541.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Hourihane, Colum (2012). The Grove Encyclopedia of Medieval Art and Architecture. Volume 2. OUP USA. p. 225. ISBN 9780195395365. Retrieved 12 October 2016.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Edwards, Nancy (2013). The Archaeology of Early Medieval Ireland. Routledge. p. 147. ISBN 9781135951498. Retrieved 10 October 2016.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Karkov, Catherine E.; Ryan, Michael; Farrell, Robert T. (1997). The Insular Tradition: Theory and Practice in Transpersonal Psychotherapy. SUNY Press. p. 269. ISBN 9780791434567. Retrieved 10 October 2016.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Kelly, J. J. (1902). "The Irish Ecclesiastical Record, A monthly journal, under Episcopal Sanction" (PDF) (Volume 11 XI ed.). Dublin: Browne & Nolan, Limited, Nassau-Street: 291–292. Retrieved 10 October 2016. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help)CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
External links
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for County Roscommon. |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to County Roscommon. |