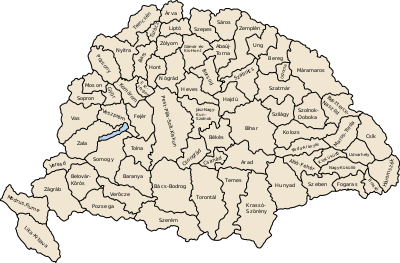
Baranya County (former)
Baranya (Hungarian: Baranya, Croatian: Baranja, Serbian: Барања / Baranja, German: Branau) was an administrative county (comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary. Its territory is now divided between present-day Baranya County of Hungary and Osijek-Baranja County of Croatia. The capital of the county was Pécs.
| Baranya County | |
|---|---|
| County of the Kingdom of Hungary (1000-1541, 1699-1946) | |
.svg.png) Coat of arms
| |
 | |
| Capital | Pécs |
| Area | |
| • Coordinates | 46°5′N 18°14′E |
• 1910 | 5,176 km2 (1,998 sq mi) |
• 1930 | 4,033 km2 (1,557 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• 1910 | 352478 |
• 1930 | 311660 |
| History | |
• Established | 1000 |
• Ottoman conquest | 1541 |
• County recreated | 1699 |
| 4 June 1920 | |
| 11 April 1941 | |
• Monarchy abolished | 1 February 1946 |
| Today part of | (4,033 km2) (1,143 km2) |

Geography
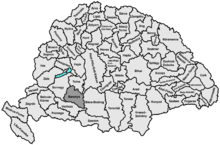
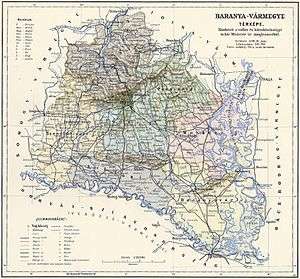
Baranya county was located in Baranya region. It shared borders with the Hungarian counties Somogy, Tolna, Bács-Bodrog and Verőce (the latter county was part of Croatia-Slavonia). The county stretched along the rivers Drava (north bank) and Danube (west bank), up to their confluence. Its area was 5,176 km² around 1910.
Historical background
Baranya county arose as one of the first counties of the Kingdom of Hungary, in the 11th century. Stephen I of Hungary founded an episcopal seat here. In the 15th century, Janus Pannonius was the Bishop of Pécs. In the 16th century, the Ottoman Empire conquered Baranya, and included it into the sanjak of Mohács, an Ottoman administrative unit, with the seat in the city of Mohács.
History
In the end of the 17th century, Baranya was captured by Habsburg Monarchy, and was included into Habsburg Kingdom of Hungary after the Battle of Mohács (1687).
In 1918, the entire Baranya was captured by Serbian troops and was administered by the newly created Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes, but as a Republic, see: Baranya-Baja Republic.
By the Treaty of Trianon of 1920, the territory of the county was divided between the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes (renamed to Yugoslavia in 1929) and Hungary. The south-east of the county was assigned to the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes, while the remainder was assigned to Hungary.
The former Yugoslav part of the pre-1920 county was occupied and annexed by Hungary during World War II and the pre-1920 borders of Baranya county were restored in 1941. The pre-1920 borders were restored again after World War II and the territory of the county reduced again.
Since 1991, when Croatia became independent from Yugoslavia, the Yugoslav part of pre-1920 Baranya county is part of Croatia. Between 1991 and 1995 it was under occupation of rebel Croatian Serbs, while from 1995 through 1998 the United Nations administered that area (United Nations Transitional Administration for Eastern Slavonia, Baranja and Western Sirmium) as a transitional body. In modern times there is a Magyar and Serb minority in Croatian Baranja and a Croatian minority in Hungarian Baranya. Roma minority is present in both parts, as well as Germans (mostly until 1945). Today, the present Hungarian county of Baranya also include some lands in the west that were not part of the historic Baranya county (after World War II most of the district of Szigetvár - previously part of Somogy county - and some other localities was transferred to Baranya county).


Demographics
In 1900, the county had a population of 334,764 people and was composed of the following linguistic communities:[1]
Total:
- Hungarian: 183,042 (54.7%)
- German: 111,051 (33.2%)
- Croatian: 15,431 (4.6%)
- Serbian: 12,856 (3.8%)
- Slovak: 482 (0.1%)
- Romanian: 47 (0.0%)
- Ruthenian: 10 (0.0%)
- Other or unknown: 11,845 (3.6%)
According to the census of 1900, the county was composed of the following religious communities:[2]
Total:
- Roman Catholic: 253,686 (75.8%)
- Calvinist: 43,014 (12.9%)
- Lutheran: 14,252 (4.3%)
- Greek Orthodox: 13,520 (4.0%)
- Jewish: 9,260 (2.8%)
- Greek Catholic: 201 (0.0%)
- Unitarian: 105 (0.0%)
- Other or unknown: 726 (0.2%)
In 1910, the county had a population of 352,478 people and was composed of the following linguistic communities:[3]
- Hungarian: 199,659 (56.6%)
- German: 112,297 (31.9%)
- Serbian: 13,048 (3.7%)
- Croatian: 10,159 (2,9)
- Slovak: 392 (0.1%)
- Romanian: 54 (0.0%)
- Ruthenian: 5 (0.0%)
- Other: 16,864 (4.8%)
According to the census of 1910, the county was composed of the following religious communities:[4]
Subdivisions
In the early 20th century, the subdivisions of Baranya county were:
References
- "KlimoTheca :: Könyvtár". Kt.lib.pte.hu. Retrieved 6 December 2012.
- "KlimoTheca :: Könyvtár". Kt.lib.pte.hu. Retrieved 6 December 2012.
- "KlimoTheca :: Könyvtár". Kt.lib.pte.hu. Retrieved 16 June 2012.
- "KlimoTheca :: Könyvtár". Kt.lib.pte.hu. Retrieved 16 June 2012.