Plug-in electric vehicle

A plug-in electric vehicle (PEV) is any motor vehicle that can be recharged from an external source of electricity, such as wall sockets, and the electricity stored in the rechargeable battery packs drives or contributes to drive the wheels. PEV is a subset of electric vehicles that includes all-electric or battery electric vehicles (BEVs), plug-in hybrid vehicles (PHEVs), and electric vehicle conversions of hybrid electric vehicles and conventional internal combustion engine vehicles.[3][4][5] In China, plug-in electric vehicles are called new energy vehicles (NEVs).
Plug-in cars have several benefits compared to conventional internal combustion engine vehicles. They have lower operating and maintenance costs, and produce little or no local air pollution. They reduce dependence on petroleum and may severally reduce greenhouse gas emissions, depending on the electricity source, as motors are typically much more efficient than their engine equivalents. Plug-in hybrids capture most of these benefits when they are operating in all-electric mode. Despite their potential benefits the stock of plug-in electric cars represented just 0.15% of the 1.4 billion motor vehicles on the world's roads by the end of 2016.[6]
BYD sold the most plug-in electric cars in 2015 [7] and built more plug-in cars than any other maker in 2016. [8]
As of December 2016, there were over 60 models of highway capable plug-in electric passenger cars and light-duty utility vans available for retail sales in the world.[9] Cumulative global sales of highway legal plug-in electric passenger cars and light utility vehicles achieved the 2 million unit milestone in December 2016.[6] The 3 million milestone was achieved in November 2017.[10] The global ratio between the stock of all-electrics (BEVs) and plug-in hybrids (PHEVs) was 61:39 at the end of 2016.[11] As of January 2018, the Nissan Leaf is the world's top selling highway-capable all-electric car in history, with global sales of over 300,000 units.[1] The Tesla Model S ranks second with more than 200,000 units sold worldwide as of November 2017.[12]
BYD ranks #1 In the world for plug-in electric car sales in 2017.[13] As of December 2017, China has the world's largest stock of highway legal light-duty plug-in electric vehicles with cumulative sales of more than 1.2 million plug-in electric passenger cars.[6][14] Among country markets, the United States ranks second with almost 765,000 plug-in electric cars sold through December 2017.[6][15][16] More than 943,000 light-duty plug-in electric passenger cars have been registered in Europe up until December 2017,[6][17] with sales in the light-duty plug-in electric segment led by Norway with over 200,000 units registered.[18] China is the world's leader in the plug-in heavy-duty segment, including electric all-electric buses, and plug-in commercial and sanitation trucks, with a stock of new energy vehicles sold of more than 1,7 million units through December 2017.[19][20][21] As of December 2016, China was the world's largest plug-in electric bus market with a stock of almost 343,500 vehicles.[22]
Terminology
Plug-in electric vehicle
A plug-in electric vehicle (PEV) is any motor vehicle with rechargeable battery packs that can be charged from the electric grid, and the electricity stored on board drives or contributes to drive the wheels for propulsion.[3][4] Plug-in electric vehicles are also sometimes referred to as grid-enabled vehicles (GEV)[4] and also as electrically chargeable vehicles.[23]
PEV is a subcategory of electric vehicles that includes battery electric vehicles (BEVs), plug-in hybrid vehicles, (PHEVs), and electric vehicle conversions of hybrid electric vehicles and conventional internal combustion engine vehicles.[3][4] Even though conventional hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) have a battery that is continually recharged with power from the internal combustion engine and regenerative braking, they can not be recharged from an off-vehicle electric energy source, and therefore, they do not belong to the category of plug-in electric vehicles.[3][4]
"Plug-in electric drive vehicle" is the legal term used in U.S. federal legislation to designate the category of motor vehicles eligible for federal tax credits depending on battery size and their all-electric range.[24][25] In some European countries, particularly in France, "electrically chargeable vehicle" is the formal term used to designate the vehicles eligible for these incentives.[26] While the term "plug-in electric vehicle" most often refers to automobiles or "plug-in cars", there are several other types of plug-in electric vehicle, including electric motorcycles and scooters, neighborhood electric vehicles or microcars, city cars, vans, buses, electric trucks or lorries, and military vehicles.[27]
Battery electric vehicles
A battery electric vehicle (BEV) uses chemical energy stored in rechargeable battery packs as its only source for propulsion.[4][28] BEVs use electric motors and motor controllers instead of internal combustion engines (ICEs) for propulsion.[4]
A plug-in hybrid operates as an all-electric vehicle or BEV when operating in charge-depleting mode, but it switches to charge-sustaining mode after the battery has reached its minimum state of charge (SOC) threshold, exhausting the vehicle's all-electric range (AER).[29][30]
Plug-in hybrid electric vehicles
A plug-in hybrid electric vehicle (PHEV or PHV), also known as a plug-in hybrid, is a hybrid electric vehicle with rechargeable batteries that can be restored to full charge by connecting a plug to an external electric power source.[4][31] A plug-in hybrid shares the characteristics of both a conventional hybrid electric vehicle and an all-electric vehicle: it uses a gasoline engine and an electric motor for propulsion, but a PHEV has a larger battery pack that can be recharged, allowing operation in all-electric mode until the battery is depleted.[31][32][33]

Aftermarket conversions
An aftermarket electric vehicle conversion is the modification of a conventional internal combustion engine vehicle (ICEV) or hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) to electric propulsion, creating an all-electric or plug-in hybrid electric vehicle.[34][35][36]
There are several companies in the U.S. offering conversions. The most common conversions have been from hybrid electric cars to plug-in hybrid, but due to the different technology used in hybrids by each carmaker, the easiest conversions are for 2004–2009 Toyota Prius and for the Ford Escape/Mercury Mariner Hybrid.[34]
New energy vehicles
In China the term new energy vehicles (NEVs) refers to vehicles that are partially or fully powered by electricity, such as battery electric vehicles (BEVs) and plug-in hybrids (PHEVs). The Chinese government began implementation of its NEV program in 2009 to foster the development and introduction of new energy vehicles.[37]
Advantages
PEVs have several advantages. These include reduced greenhouse gas emissions, improved air quality, noise reduction and national security benefits. According to the Center for American Progress, PEVs are an important part of the group of technologies that will help the U.S. meet its goal under the Paris Agreement, which is a 26-28 percent reduction in greenhouse gas emissions by the year 2025.[38]
Lower operating and maintenance costs
Internal combustion engines are relatively inefficient at converting on-board fuel energy to propulsion as most of the energy is wasted as heat, and the rest while the engine is idling. Electric motors, on the other hand, are more efficient at converting stored energy into driving a vehicle. Electric drive vehicles do not consume energy while at rest or coasting, and modern plug-in cars can capture and reuse as much as one fifth of the energy normally lost during braking through regenerative braking.[39][40] Typically, conventional gasoline engines effectively use only 15% of the fuel energy content to move the vehicle or to power accessories, and diesel engines can reach on-board efficiencies of 20%, while electric drive vehicles typically have on-board efficiencies of around 80%.[39]

In the United States, as of early 2010 with a national average electricity rate of US$0.10 per kWh,[42] the cost per mile for a plug-in electric vehicle operating in all-electric mode is estimated between $0.02 to $0.04, while the cost per mile of a standard automobile varies between $0.08 to $0.20, considering a gasoline price of $3.00 per gallon.[39] As petroleum price is expected to increase in the future due to oil production decline and increases in global demand, the cost difference in favor of PEVs is expected to become even more advantageous.[39]
According to Consumer Reports, as of December 2011 the Nissan Leaf has a cost of 3.5 cents per mile and the Chevrolet Volt has a cost in electric mode of 3.8 cents per mile. The Volt cost per mile is higher because it is heavier than the Leaf. These estimates are based on the fuel economy and energy consumption measured on their tests and using a U.S. national average rate of 11 cents per kWh of electricity. When the Volt runs in range-extended mode using its premium gasoline-powered engine, the plug-in hybrid has a cost of 12.5 cents per mile. The out-of-pocket cost per mile of the three most fuel efficient gasoline-powered cars as tested by the magazine are the Toyota Prius, with a cost of 8.6 cents per miles, the Honda Civic Hybrid with 9.5 cents per mile, the Toyota Corolla with 11.9 cents per mile, and the Hyundai Elantra 13.1 cents per mile. The analysis also found that on trips up to 100 mi (160 km), the Volt is cheaper to drive than the Prius and the other three cars due to the Volt's 35 mi (56 km) driving range on electricity. The previous operating costs do not include maintenance, depreciation or other costs.[43]
All-electric and plug-in hybrid vehicles also have lower maintenance costs as compared to internal combustion vehicles, since electronic systems break down much less often than the mechanical systems in conventional vehicles, and the fewer mechanical systems on board last longer due to the better use of the electric engine. PEVs do not require oil changes and other routine maintenance checks.[39][40]
The Edison Electric Institute (EEI) conducted an analysis that demonstrated that between January 1976 and February 2012 the real price for gasoline has been much more volatile than the real price of electricity in the United States. The analysis is based on a plug-in electric vehicle with an efficiency of 3.4 miles per kW-hr (like the Mitsubishi i MiEV) and a gasoline-powered vehicle with a fuel economy rated at 30 mpg‑US (7.8 L/100 km; 36 mpg‑imp) (like the 2012 Fiat 500). The EEI estimated that operating a plug-in would have had an equivalent cost of around US$1.50 a gallon in the late 1970s and early 1980s, and around US$1.00 a gallon since the late 1990s. In contrast, the price to operate an internal combustion engine vehicle has had much ample variations, costing more than US$3.50 per gallon during the 1979 energy crisis, then had a couple of lows with prices at less than US$1.50 during 1999 and 2001, only to climb and reach a maximum of more than US$4.00 before the beginning of the 2007–2009 financial crisis, by early 2012 has fluctuated around US$3.50. The analysis found that the cost of an equivalent electric-gallon of gasoline would have been not only cheaper to operate during the entire analysis period but also that equivalent electricity prices are more stable and have been declining in terms of equivalent dollars per gallon.[44][45]
Air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions

Electric cars, as well as plug-in hybrids operating in all-electric mode, emit no harmful tailpipe pollutants from the onboard source of power, such as particulates (soot), volatile organic compounds, hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide, ozone, lead, and various oxides of nitrogen. The clean air benefit is usually local because, depending on the source of the electricity used to recharge the batteries, air pollutant emissions are shifted to the location of the generation plants.[40] In a similar manner, plug-in electric vehicles operating in all-electric mode do not emit greenhouse gases from the onboard source of power, but from the point of view of a well-to-wheel assessment, the extent of the benefit also depends on the fuel and technology used for electricity generation. This fact has been referred to as the long tailpipe of plug-in electric vehicles. From the perspective of a full life cycle analysis, the electricity used to recharge the batteries must be generated from renewable or clean sources such as wind, solar, hydroelectric, or nuclear power for PEVs to have almost none or zero well-to-wheel emissions.[3][40] On the other hand, when PEVs are recharged from coal-fired plants, they usually produce slightly more greenhouse gas emissions than internal combustion engine vehicles and higher than hybrid electric vehicles.[40][46] In the case of plug-in hybrid electric vehicles operating in hybrid mode with assistance of the internal combustion engine, tailpipe and greenhouse emissions are lower in comparison to conventional cars because of their higher fuel economy.[3]
The magnitude of the potential advantage depends on the mix of generation sources and therefore varies by country and by region. For example, France can obtain significant emission benefits from electric and plug-in hybrids because most of its electricity is generated by nuclear power plants; similarly, most regions of Canada are primarily powered with hydroelectricity, nuclear, or natural gas which have no or very low emissions at point of generation; and the state of California, where most energy comes from natural gas, hydroelectric and nuclear plants can also secure substantial emission benefits. The United Kingdom also has a significant potential to benefit from PEVs as natural gas plants dominate the generation mix. On the other hand, emission benefits in Germany, China, India, and the central regions of the United States are limited or non-existent because most electricity is generated from coal.[40][47] However these countries and regions might still obtain some air quality benefits by reducing local air pollution in urban areas. Cities with chronic air pollution problems, such as Los Angeles, México City, Santiago, Chile, São Paulo, Beijing, Bangkok and Kathmandu may also gain local clean air benefits by shifting the harmful emission to electric generation plants located outside the cities. Nevertheless, the location of the plants is not relevant when considering greenhouse gas emission because their effect is global.[40]
Carbon footprint during production
- Ricardo
A report published in June 2011, prepared by Ricardo in collaboration with experts from the UK's Low Carbon Vehicle Partnership, found that hybrid electric cars, plug-in hybrids and all-electric cars generate more carbon emissions during their production than current conventional vehicles, but still have a lower overall carbon footprint over the full life cycle. The higher carbon footprint during production of electric drive vehicles is due mainly to the production of batteries. As an example, 43 percent of production emissions for a mid-size electric car are generated from the battery production, while for standard mid-sized gasolineinternal combustion engine vehicle, around 75% of the embedded carbon emissions during production comes from the steel used in the vehicle glider.[48] The following table summarizes key results of this study for four powertrain technologies:
| Comparison of full life cycle assessment(well-to-wheels) of carbon emissions and carbon footprint during production for four different powertrain technologies[48] | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Type of vehicle (powertrain) | Estimated emissions in production (tonnes CO2e) | Estimated lifecycle emissions (tonnes CO2e) | Percentage of
emissions |
| Standard gasoline vehicle | 5.6 | 24 | 23% |
| Hybrid electric vehicle | 6.5 | 21 | 31% |
| Plug-in hybrid electric vehicle | 6.7 | 19 | 35% |
| Battery electric vehicle | 8.8 | 19 | 46% |
| Notes: Estimates based upon a 2015 model vehicle assuming 150,000 km (93,000 mi) full life travel using 10% ethanol blend and 500g/kWh grid electricity. | |||
The Ricardo study also found that the lifecycle carbon emissions for mid-sized gasoline and diesel vehicles are almost identical, and that the greater fuel efficiency of the diesel engine is offset by higher production emissions.[48]
- Volkswagen
In 2014 Volkswagen published the results of life-cycle assessment of its electric vehicles certified by TÜV NORD, and independent inspection agency. The study found that CO
2 emissions during the use phase of its all-electric VW e-Golf are 99% lower than those of the Golf 1.2 TSI when powers comes from exclusively hydroelectricity generated in Germany, Austria and Switzerland. Accounting for the full lifecycle, the e-Golf reduces emissions by 61%, offsetting higher production emissions. When the actual EU-27 electricity mix is considered, the e-Golf emissions are still 26% lower than those of the conventional Golf 1.2 TSI. Similar results were found when comparing the e-Golf with the Golf 1.6 TDI. The analysis considered recycling of the three vehicles at the end of their lifetime.[49]
Uniti
The Swedish automotive startup Uniti Sweden AB has been working on an electric city car entirely designed to be sustainable. The CEO Lewis Horne said “When people sell electric cars, the motivation is sustainability. So, why are they so heavy, and why are they the same cars? Where you just take out petrol and you put in the huge battery and you call it sustainable. But it’s not.”. The company has been designing a car that uses sustainable and recycled material such as bio-composite to reduce the footprint of the car during production.[50] In addition, the fully automated factory provided in partnership with Siemens will be able to work with the lights turned off during 22h per day to save energy.[51]
Well-to-wheel GHG emissions in the U.S.
- Environmental Protection Agency
The following table compares tailpipe and upstream CO2 emissions estimated by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency for all series production model year 2014 plug-in electric vehicles available in the U.S. market. Total emissions include the emissions associated with the production and distribution of electricity used to charge the vehicle, and for plug-in hybrid electric vehicles, it also includes emissions associated with tailpipe emissions produced from the internal combustion engine. These figures were published by the EPA in October 2014 in its annual report "Light-Duty Automotive Technology, Carbon Dioxide Emissions, and Fuel Economy Trends: 1975 Through 2014." All emissions are estimated considering average real world city and highway operation based on the EPA 5-cycle label methodology, using a weighted 55% city and 45% highway driving. For the first time, the 2014 Trends report presents an analysis of the impact of alternative fuel vehicles, with emphasis in plug-in electric vehicles because as their market share is approaching 1%, the EPA concluded that PEVs began to have a measurable impact on the U.S. overall new vehicle fuel economy and CO2 emissions.[52][53]
For purposes of an accurate estimation of emissions, the analysis took into consideration the differences in operation between plug-in hybrids. Some, like the Chevrolet Volt, can operate in all-electric mode without using gasoline, and others operate in a blended mode like the Toyota Prius PHV, which uses both energy stored in the battery and energy from the gasoline tank to propel the vehicle, but that can deliver substantial all-electric driving in blended mode. In addition, since the all-electric range of plug-in hybrids depends on the size of the battery pack, the analysis introduced a utility factor as a projection of the share of miles that will be driven using electricity by an average driver, for both, electric only and blended EV modes. Since all-electric cars do not produce tailpipe emissions, the utility factor applies only to plug-in hybrids. The following table shows the overall fuel economy expressed in terms of miles per gallon gasoline equivalent (mpg-e) and the utility factor for the ten MY2014 plug-in hybrids available in the U.S. market, and EPA's best estimate of the CO2 tailpipe emissions produced by these PHEVs.[52]
In order to account for the upstream CO2 emissions associated with the production and distribution of electricity, and since electricity production in the United States varies significantly from region to region, the EPA considered three scenarios/ranges with the low end scenario corresponding to the California powerplant emissions factor, the middle of the range represented by the national average powerplant emissions factor, and the upper end of the range corresponding to the powerplant emissions factor for the Rocky Mountains. The EPA estimates that the electricity GHG emission factors for various regions of the country vary from 346 g CO2/kWh in California to 986 g CO2/kWh in the Rockies, with a national average of 648 g CO2/kWh.[52]
| Comparison of tailpipe and upstream CO2 emissions(1) estimated by EPA for the MY 2014 plug-in electric vehicles available in the U.S. market[52] | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vehicle | Overall fuel economy (mpg-e) | Utility factor(2) (share EV miles) | Tailpipe CO2 (g/mi) | Tailpipe + Total Upstream CO2 | ||
| Low (g/mi) | Avg (g/mi) | High (g/mi) | ||||
| BMW i3 | 124 | 1 | 0 | 93 | 175 | 266 |
| Chevrolet Spark EV | 119 | 1 | 0 | 97 | 181 | 276 |
| Honda Fit EV | 118 | 1 | 0 | 99 | 185 | 281 |
| Fiat 500e | 116 | 1 | 0 | 101 | 189 | 288 |
| Nissan Leaf | 114 | 1 | 0 | 104 | 194 | 296 |
| Mitsubishi i | 112 | 1 | 0 | 104 | 195 | 296 |
| Smart electric drive | 107 | 1 | 0 | 109 | 204 | 311 |
| Ford Focus Electric | 105 | 1 | 0 | 111 | 208 | 316 |
| Tesla Model S (60 kWh) | 95 | 1 | 0 | 122 | 229 | 348 |
| Tesla Model S (85 kWh) | 89 | 1 | 0 | 131 | 246 | 374 |
| BMW i3 REx(3) | 88 | 0.83 | 40 | 134 | 207 | 288 |
| Mercedes-Benz B-Class ED | 84 | 1 | 0 | 138 | 259 | 394 |
| Toyota RAV4 EV | 76 | 1 | 0 | 153 | 287 | 436 |
| BYD e6 | 63 | 1 | 0 | 187 | 350 | 532 |
| Chevrolet Volt | 62 | 0.66 | 81 | 180 | 249 | 326 |
| Toyota Prius Plug-in Hybrid | 58 | 0.29 | 133 | 195 | 221 | 249 |
| Honda Accord Plug-in Hybrid | 57 | 0.33 | 130 | 196 | 225 | 257 |
| Cadillac ELR | 54 | 0.65 | 91 | 206 | 286 | 377 |
| Ford C-Max Energi | 51 | 0.45 | 129 | 219 | 269 | 326 |
| Ford Fusion Energi | 51 | 0.45 | 129 | 219 | 269 | 326 |
| BMW i8 | 37 | 0.37 | 198 | 303 | 351 | 404 |
| Porsche Panamera S E-Hybrid | 31 | 0.39 | 206 | 328 | 389 | 457 |
| McLaren P1 | 17 | 0.43 | 463 | 617 | 650 | 687 |
| Average MY 2014 gasoline car | 24.2 | 0 | 367 | 400 | 400 | 400 |
| Notes: (1) Based on 45% highway and 55% city driving. (2) The utility factor represents, on average, the percentage of miles that will be driven using electricity (in electric only and blended modes) by an average driver. (3) The EPA classifies the i3 REx as a series plug-in hybrid[52][54][55] | ||||||
- Union of Concerned Scientists
The Union of Concerned Scientists (UCS) published a study in 2012 that assessed average greenhouse gas emissions in the U.S. resulting from charging plug-in car batteries from the perspective of the full life-cycle (well-to-wheel analysis) and according to fuel and technology used to generate electric power by region. The study used the model year 2011 Nissan Leaf all-electric car to establish the analysis baseline, and electric-utility emissions are based on EPA's 2009 estimates. The UCS study expressed the results in terms of miles per gallon instead of the conventional unit of grams of greenhouse gases or carbon dioxide equivalent emissions per year in order to make the results more friendly for consumers. The study found that in areas where electricity is generated from natural gas, nuclear, hydroelectric or renewable sources, the potential of plug-in electric cars to reduce greenhouse emissions is significant. On the other hand, in regions where a high proportion of power is generated from coal, hybrid electric cars produce less CO2 equivalent emissions than plug-in electric cars, and the best fuel efficient gasoline-powered subcompact car produces slightly less emissions than a PEV. In the worst-case scenario, the study estimated that for a region where all energy is generated from coal, a plug-in electric car would emit greenhouse gas emissions equivalent to a gasoline car rated at a combined city/highway driving fuel economy of 30 mpg‑US (7.8 L/100 km; 36 mpg‑imp). In contrast, in a region that is completely reliant on natural gas, the PEV would be equivalent to a gasoline-powered car rated at 50 mpg‑US (4.7 L/100 km; 60 mpg‑imp).[56][57]
The study concluded that for 45% of the U.S. population, a plug-in electric car will generate lower CO2 equivalent emissions than a gasoline-powered car capable of combined 50 mpg‑US (4.7 L/100 km; 60 mpg‑imp), such as the Toyota Prius and the Prius c. The UCS also found that for 37% of the population, the electric car emissions will fall in the range of a gasoline-powered car rated at a combined fuel economy of 41 to 50 mpg‑US (5.7 to 4.7 L/100 km; 49 to 60 mpg‑imp), such as the Honda Civic Hybrid and the Lexus CT200h. Only 18% of the population lives in areas where the power-supply is more dependent on burning carbon, and the greenhouse gas emissions will be equivalent to a car rated at a combined fuel economy of 31 to 40 mpg‑US (7.6 to 5.9 L/100 km; 37 to 48 mpg‑imp), such as the Chevrolet Cruze and Ford Focus.[57][58][59] The study found that there are no regions in the U.S. where plug-in electric cars will have higher greenhouse gas emissions than the average new compact gasoline engine automobile, and the area with the dirtiest power supply produces CO2 emissions equivalent to a gasoline-powered car rated at 33 mpg‑US (7.1 L/100 km).[56]
In September 2014 the UCS published an updated analysis of its 2012 report. The 2014 analysis found that 60% of Americans, up from 45% in 2009, live in regions where an all-electric car produce fewer CO2 equivalent emissions per mile than the most efficient hybrid. The UCS study found several reasons for the improvement. First, electric utilities have adopted cleaner sources of electricity to their mix between the two analysis. The 2014 study used electric-utility emissions based on EPA's 2010 estimates, but since coal use nationwide is down by about 5% from 2010 to 2014, actual efficiency in 2014 is better than estimated in the UCS study. Second, electric vehicles have become more efficient, as the average 2013 all-electric vehicle used 0.33 kWh per mile, representing a 5% improvement over 2011 models. Also, some new models are cleaner than the average, such as the BMW i3, which is rated at 0.27 kWh by the EPA. An i3 charged with power from the Midwest grid would be as clean as a gasoline-powered car with about 50 mpg‑US (4.7 L/100 km), up from 39 mpg‑US (6.0 L/100 km) for the average electric car in the 2012 study. In states with a cleaner mix generation, the gains were larger. The average all-electric car in California went up to 95 mpg‑US (2.5 L/100 km) equivalent from 78 mpg‑US (3.0 L/100 km) in the 2012 study. States with dirtier generation that rely heavily on coal still lag, such as Colorado, where the average BEV only achieves the same emissions as a 34 mpg‑US (6.9 L/100 km; 41 mpg‑imp) gasoline-powered car. The author of the 2014 analysis noted that the benefits are not distributed evenly across the U.S. because electric car adoptions is concentrated in the states with cleaner power.[60][61]

In November 2015 the Union of Concerned Scientists published a new report comparing two battery electric vehicles (BEVs) with similar gasoline vehicles by examining their global warming emissions over their full life-cycle, cradle-to-grave analysis. The two BEVs modeled, midsize and full-size, are based on the two most popular BEV models sold in the United States in 2015, the Nissan Leaf and the Tesla Model S. The study found that all-electric cars representative of those sold today, on average produce less than half the global warming emissions of comparable gasoline-powered vehicles, despite taken into account the higher emissions associated with BEV manufacturing. Considering the regions where the two most popular electric cars are being sold, excess manufacturing emissions are offset within 6 to 16 months of average driving. The study also concluded that driving an average EV results in lower global warming emissions than driving a gasoline car that gets 50 mpg‑US (4.7 L/100 km) in regions covering two-thirds of the U.S. population, up from 45% in 2009. Based on where EVs are being sold in the United States in 2015, the average EV produces global warming emissions equal to a gasoline vehicle with a 68 mpg‑US (3.5 L/100 km) fuel economy rating. The authors identified two main reason for the fact that EV-related emissions have become even lower in many parts of the country since the first study was conducted in 2012. Electricity generation has been getting cleaner, as coal-fired generation has declined while lower-carbon alternatives have increased. In addition, electric cars are becoming more efficient. For example, the Nissan Leaf and the Chevrolet Volt, have undergone improvements to increase their efficiencies compared to the original models launched in 2010, and other even more efficient BEV models, such as the most lightweight and efficient BMW i3, have entered the market.[62][63]
- National Bureau of Economic Research
One criticism to the UCS study is that the analysis was made using average emissions rates across regions instead of marginal generation at different times of the day. The former approach does not take into account the generation mix within interconnected electricity markets and shifting load profiles throughout the day.[64][65] An analysis by three economist affiliated with the National Bureau of Economic Research (NBER), published in November 2014, developed a methodology to estimate marginal emissions of electricity demand that vary by location and time of day across the United States. The marginal analysis, applied to plug-in electric vehicles, found that the emissions of charging PEVs vary by region and hours of the day. In some regions, such as the Western U.S. and Texas, CO2 emissions per mile from driving PEVs are less than those from driving a hybrid car. However, in other regions, such as the Upper Midwest, charging during the recommended hours of midnight to 4 a.m. implies that PEVs generate more emissions per mile than the average car currently on the road. The results show a fundamental tension between electricity load management and environmental goals as the hours when electricity is the least expensive to produce tend to be the hours with the greatest emissions. This occurs because coal-fired units, which have higher emission rates, are most commonly used to meet base-level and off-peak electricity demand; while natural gas units, which have relatively low emissions rates, are often brought online to meet peak demand.[65]
Well-to-wheel GHG emissions in several countries
A study published in the UK in April 2013 assessed the carbon footprint of plug-in electric vehicles in 20 countries. As a baseline the analysis established that manufacturing emissions account for 70 g CO2/km for an electric car and 40 g CO2/km for a petrol car. The study found that in countries with coal-intensive generation, PEVs are no different from conventional petrol-powered vehicles. Among these countries are China, Indonesia, Australia, South Africa and India. A pure electric car in India generates emissions comparable to a 20 mpg‑US (12 L/100 km; 24 mpg‑imp) petrol car.[66][67]
The country ranking was led by Paraguay, where all electricity is produced from hydropower, and Iceland, where electricity production relies on renewable power, mainly hydro and geothermal power. Resulting carbon emissions from an electric car in both countries are 70 g CO2/km, which is equivalent to a 220 mpg‑US (1.1 L/100 km; 260 mpg‑imp) petrol car, and correspond to manufacturing emissions. Next in the ranking are other countries with low carbon electricity generation, including Sweden (mostly hydro and nuclear power ), Brazil (mainly hydropower) and France (predominantly nuclear power). Countries ranking in the middle include Japan, Germany, the UK and the United States.[66][67][68]
The following table shows the emissions intensity estimated in the study for those countries where electric vehicle are available, and the corresponding emissions equivalent in miles per US gallon of a petrol-powered car:
| Country comparison of full life cycle assessment of greenhouse gas emissions resulting from charging plug-in electric cars and emissions equivalent in terms of miles per US gallon of a petrol-powered car[66][68] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Country | PEV well-to-wheels carbon dioxide equivalent emissions per electric car expressed in (CO2e/km) | Power source | PEV well-to-wheels emissions equivalent in terms of mpg US of petrol-powered car | Equivalent petrol car |
| 81 | Low carbon | 159 mpg‑US (1.48 L/100 km) | Hybrid multiples | |
| 93 | 123 mpg‑US (1.91 L/100 km) | |||
| 115 | Fossil light | 87 mpg‑US (2.7 L/100 km) | Beyond hybrid | |
| 146 | 61 mpg‑US (3.9 L/100 km) | |||
| 175 | Broad mix | 48 mpg‑US (4.9 L/100 km) | New hybrid | |
| 179 | 47 mpg‑US (5.0 L/100 km) | |||
| 189 | 44 mpg‑US (5.3 L/100 km) | |||
| 202 | Fossil heavy | 40 mpg‑US (5.9 L/100 km) | Efficient petrol | |
| 203 | 40 mpg‑US (5.9 L/100 km) | |||
| 258 | Coal-based | 30 mpg‑US (7.8 L/100 km) | Average petrol | |
| 292 | 26 mpg‑US (9.0 L/100 km) | |||
| 370 | 20 mpg‑US (12 L/100 km) | |||
| Note: Electric car manufacturing emissions account for 70 g CO2/km Source: Shades of Green: Electric Cars’ Carbon Emissions Around the Globe, Shrink That Footprint, February 2013.[68] | ||||
Less dependence on imported oil
For many net oil importing countries the 2000s energy crisis brought back concerns first raised during the 1973 oil crisis. For the United States, the other developed countries and emerging countries their dependence on foreign oil has revived concerns about their vulnerability to price shocks and supply disruption. Also, there have been concerns about the uncertainty surrounding peak oil production and the higher cost of extracting unconventional oil. A third issue that has been raised is the threat to national security because most proven oil reserves are concentrated in relatively few geographic locations, including some countries with strong resource nationalism, unstable governments or hostile to U.S. interests.[40][69][70] In addition, for many developing countries, and particularly for the poorest African countries, high oil prices have an adverse impact on the government budget and deteriorate their terms of trade thus jeopardizing their balance of payments, all leading to lower economic growth.[71][72]
Through the gradual replacement of internal combustion engine vehicles for electric cars and plug-in hybrids, electric drive vehicles can contribute significantly to lessen the dependence of the transport sector on imported oil as well as contributing to the development of a more resilient energy supply.[40][69][70][73]
Vehicle-to-grid
Plug-in electric vehicles offer users the opportunity to sell electricity stored in their batteries back to the power grid, thereby helping utilities to operate more efficiently in the management of their demand peaks.[74] A vehicle-to-grid (V2G) system would take advantage of the fact that most vehicles are parked an average of 95 percent of the time. During such idle times the electricity stored in the batteries could be transferred from the PEV to the power lines and back to the grid. In the U.S. this transfer back to the grid have an estimated value to the utilities of up to $4,000 per year per car.[75] In a V2G system it would also be expected that battery electric (BEVs) and plug-in hybrids (PHEVs) would have the capability to communicate automatically with the power grid to sell demand response services by either delivering electricity into the grid or by throttling their charging rate.[74][76][77]
Disadvantages

Cost of batteries and cost of ownership
- Cost of batteries
As of 2015, plug-in electric vehicles are significantly more expensive as compared to conventional internal combustion engine vehicles and hybrid electric vehicles due to the additional cost of their lithium-ion battery pack. According to a 2010 study by the National Research Council, the cost of a lithium-ion battery pack was about US$1,700/kWh of usable energy, and considering that a PHEV-10 requires about 2.0 kWh and a PHEV-40 about 8 kWh, the manufacturer cost of the battery pack for a PHEV-10 is around US$3,000 and it goes up to US$14,000 for a PHEV-40.[78][79] As of June 2012, and based on the three battery size options offered for the Tesla Model S, the New York Times estimated the cost of automotive battery packs between US$400 to US$500 per kilowatt-hour.[80] A 2013 study by the American Council for an Energy-Efficient Economy reported that battery costs came down from US$1,300 per kWh in 2007 to US$500 per kWh in 2012. The U.S. Department of Energy has set cost targets for its sponsored battery research of US$300 per kWh in 2015 and US$125 per kWh by 2022. Cost reductions through advances in battery technology and higher production volumes will allow plug-in electric vehicles to be more competitive with conventional internal combustion engine vehicles.[81]
According to a study published in February 2016 by Bloomberg New Energy Finance (BNEF), battery prices fell 65% since 2010, and 35% just in 2015, reaching US$350 per kWh. The study concludes that battery costs are on a trajectory to make electric vehicles without government subsidies as affordable as internal combustion engine cars in most countries by 2022. BNEF projects that by 2040, long-range electric cars will cost less than US$22,000 expressed in 2016 dollars. BNEF expects electric car battery costs to be well below US$120 per kWh by 2030, and to fall further thereafter as new chemistries become available.[82]
- Cost of ownership
A study published in 2011 by the Belfer Center, Harvard University, found that the gasoline costs savings of plug-in electric cars do not offset their higher purchase prices when comparing their lifetime net present value of purchase and operating costs for the U.S. market at 2010 prices, and assuming no government subidies. According to the study estimates, a PHEV-40 is US$5,377 more expensive than a conventional internal combustion engine, while a battery electric vehicles is US$4,819 more expensive.[83] These findings assumed a battery cost of US$600 per kWh, which means that the Chevrolet Volt battery pack cost around US$10,000 and the Nissan Leaf pack costs US$14,400. The study also assumed a gasoline price of US$3.75 per gallon (as of mid June 2011), that vehicles are driven 12,000 miles (19,000 km) per year, an average price of electricity of US$0.12 per kWh, that the plug-in hybrid is driven in all-electric mode 85% of the time, and that the owner of PEVs pay US$1,500 to install a Level II 220/240 volt charger at home.[84]
The study also include hybrid electric vehicles in the comparison, and analyzed several scenarios to determine how the comparative net savings will change over the next 10 to 20 years, assuming that battery costs will decrease while gasoline prices increase, and also assuming higher fuel efficiency of conventional cars, among other scenarios. Under the future scenarios considered, the study found that BEVs will be significantly less expensive than conventional cars (US$1,155 to US$7,181 cheaper), while PHEVs, will be more expensive than BEVs in almost all comparison scenarios, and only less expensive than conventional cars in a scenario with very low battery costs and high gasoline prices. The reason for the different savings among PEVs is because BEVs are simpler to build and do not use liquid fuel, while PHEVs have more complicated powertrains and still have gasoline-powered engines. The following table summarizes the results of four of the seven scenarios analyzed by the study.[84]
| Comparison of net lifetime savings among conventional gasoline-powered cars, hybrids and plug-in electric cars for several scenarios (U.S. market at 2010 prices)[84] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Description | Conventional ICE | Hybrid electric (HEV) | Plug-in hybrid (PHEV) | Battery electric (BEV) |
| Scenario: 2010 costs (battery US$600 per kWh, gasoline US$3.75 per gallon, and electricity US$0.12 per kWh) | ||||
| Purchase price | US$21,390 | US$22,930 | US$30,235 | US$33,565 |
| Total net present cost | US$32,861 | US$33,059 | US$38,239 | US$37,680 |
| Cost differential with conventional car | - | US$197 | US$5,377 | US$4,819 |
| Scenario: Future Costs – Lower battery cost and higher gasoline and electricity prices (battery US$300 per kWh, gasoline US$4.50 per gallon, and electricity US$0.15 per kWh) | ||||
| Total net present cost | US$34,152 | US$32,680 | US$34,601 | US$30,674 |
| Cost differential with conventional car | - | (US$1,472) | US$449 | (US$3,478) |
| Scenario: Future Costs – Low battery cost and higher gasoline and electricity prices (battery US$150 per kWh, gasoline US$4.50 per gallon, and electricity US$0.15 per kWh) | ||||
| Total net present cost | US$34,152 | US$32,080 | US$32,549 | US$26,971 |
| Cost differential with conventional car | - | (US$2,072) | (US$1,603) | (US$7,181) |
| Scenario: Higher fuel efficiency ICEs:50 miles per US gallon (4.7 L/100 km; 60 mpg‑imp) HEVs and PHEVs: 75 miles per US gallon (3.1 L/100 km; 90 mpg‑imp) (battery US$300 per kWh, gasoline US$4.50 per gallon, and electricity US$0.15 per kWh) | ||||
| Total net present cost | US$32,829 | US$31,366 | US$34,403 | US$30,674 |
| Cost differential with conventional car | - | (US$463) | US$2,574 | (US$1,155) |
| Note: Assumes vehicles are driven 12,000 miles (19,000 km) per year and plug-in hybrid is driven in all-electric mode 85% of the time. Does not take into account other differences in cost of ownership. | ||||
According to a study by the Electric Power Research Institute published in June 2013, the total cost of ownership of the 2013 Nissan Leaf SV is substantially lower than that of comparable conventional and hybrid vehicles. For comparison, the study constructed average hybrid and conventional vehicles and assumed an average US distance per trip distribution. The study took into account the manufacturer's suggested retail price, taxes, credits, destination charge, electric charging station, fuel cost, maintenance cost, and additional cost due to the use of a gasoline vehicle for trips beyond the range of the Leaf.[85]
| Electric Power Research Institute comparison of the Leaf versus average conventional and hybrid cars. | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vehicle | Operating mode (powertrain) | Total ownership cost | |||||||
| US Average | California | ||||||||
| Nissan Leaf SV | All-electric | $37,288 | $35,596 | ||||||
| Chevrolet Volt | Plug-in hybrid | $44,176 | $40,800 | ||||||
| Average Conventional | Gasoline | $44,949 | $46,561 | ||||||
| Average Hybrid | Gasoline-electric hybrid | $44,325 | $45,416 | ||||||
| Notes: Costs are based on a gasoline price of $3.64 per gallon, an electricity rate of $0.12/kWh, and a vehicle lifetime of 150,000 miles. The average conventional car was constructed by averaging of Honda Civic EX, Chevrolet Cruze LTZ, Ford Focus Titanium, and Volkswagen Passat. The average hybrid car was constructed from Ford Fusion Hybrid, Honda Civic Hybrid, Toyota Camry Hybrid XLE, and Toyota Prius trim IV. | |||||||||
Availability of recharging infrastructure

Despite the widespread assumption that plug-in recharging will take place overnight at home, residents of cities, apartments, dormitories, and townhouses do not have garages or driveways with available power outlets, and they might be less likely to buy plug-in electric vehicles unless recharging infrastructure is developed.[86][87] Electrical outlets or charging stations near their places of residence, in commercial or public parking lots, streets and workplaces are required for these potential users to gain the full advantage of PHEVs, and in the case of EVs, to avoid the fear of the batteries running out energy before reaching their destination, commonly called range anxiety.[87][88] Even house dwellers might need to charge at the office or to take advantage of opportunity charging at shopping centers.[89] However, this infrastructure is not in place and it will require investments by both the private and public sectors.[88]
Several cities in California and Oregon, and particularly San Francisco and other cities in the San Francisco Bay Area and Silicon Valley, already have deployed public charging stations and have expansion plans to attend both plug-ins and all-electric cars.[88] Some local private firms such as Google and Adobe Systems have also deployed charging infrastructure. In Google's case, its Mountain View campus has 100 available charging stations for its share-use fleet of converted plug-ins available to its employees.[88][90] Solar panels are used to generate the electricity, and this pilot program is being monitored on a daily basis and performance results are published on the RechargeIT website.[90] As of December 2013, Estonia is the first and only country that had deployed an EV charging network with nationwide coverage, with 165 fast chargers available along highways at a minimum distance of between 40 to 60 km (25 to 37 mi), and a higher density in urban areas.[91][92][93]
The importance to build the infrastructure necessary to support electric vehicles is illustrated by the decision of Car2Go in San Diego, California, that due to insufficient charging infrastructure decided to replace all of its all-electric car fleet with gasoline-powered cars starting on 1 May 2016. When the carsharing service started in 2011, Car2Go expected 1,000 charging stations to be deployed around the city, but only 400 were in place by early 2016. As a result, an average of 20% of the carsharing fleet is unavailable at any given time because the cars are either being charged or because they don’t have enough electricity in them to be driven. Also, many of the company’s 40,000 San Diego members say they often worry their Car2Go will run out of charge before they finish their trip.[94]
Battery swapping

A different approach to resolve the problems of range anxiety and lack of recharging infrastructure for electric vehicles was developed by Better Place. Its business model considers that electric cars are built and sold separately from the battery pack. As customers are not allowed to purchase battery packs, they must lease them from Better Place which will deploy a network of battery swapping stations thus expanding EVs range and allowing long distance trips. Subscribed users pay a per-distance fee to cover battery pack leasing, charging and swap infrastructure, the cost of sustainable electricity, and other costs.[95][96] Better Place signed agreement for deployment in Australia, Denmark, Israel, Canada, California, and Hawaii.[97] The Renault Fluence Z.E. was the electric car built with switchable battery technology sold for the Better Place network.[98] The robotic battery-switching operation was completed in about five minutes.[99]
After implementing the first modern commercial deployment of the battery swapping model in Israel and Denmark, Better Place filed for bankruptcy in Israel in May 2013. The company's financial difficulties were caused by the high investment required to develop the charging and swapping infrastructure, about US$850 million in private capital, and a market penetration significantly lower than originally predicted by Shai Agassi. Less than 1,000 Fluence Z.E. cars were deployed in Israel and around 400 units in Denmark.[100][101]
Tesla Motors designed its Model S to allow fast battery swapping.[102] In June 2013, Tesla announced their goal to deploy a battery swapping station in each of its supercharging stations. At a demonstration event Tesla showed that a battery swap operation with the Model S takes just over 90 seconds, about half the time it takes to refill a gasoline-powered car used for comparison purposes during the event.[103][104] The first stations are planned to be deployed along Interstate 5 in California where, according to Tesla, a large number of Model S sedans make the San Francisco-Los Angeles trip regularly. These will be followed by the Washington, DC to Boston corridor.[103]
Other charging solutions


The REVA NXR exhibited in the 2009 Frankfurt Motor Show and the Nissan Leaf SV trim both have roof-mounted solar panels. These solar panels are designed to trickle charge the batteries when the car is moving or parked.[105][106][107] Another proposed technology is REVive, by Reva. When the REVA NXR's batteries are running low or are fully depleted, the driver is able to send an SMS to REVive and unlock a hidden reserve in the battery pack. Reva has not provided details on how the system will work.[108][109] The Fisker Karma uses solar panel in the roof to recharge the 12-volt lead-acid accessory battery.[110] The Nissan Leaf SL trim also has a small solar panel at the rear of the roof/spoiler that can trickle charge the auxiliary 12-volt lead-acid battery.[111]
Potential overload of the electrical grid
The existing electrical grid, and local transformers in particular, may not have enough capacity to handle the additional power load that might be required in certain areas with high plug-in electric car concentrations. As recharging a single electric-drive car could consume three times as much electricity as a typical home, overloading problems may arise when several vehicles in the same neighborhood recharge at the same time, or during the normal summer peak loads. To avoid such problems, utility executives recommend owners to charge their vehicles overnight when the grid load is lower or to use smarter electric meters that help control demand. When market penetration of plug-in electric vehicles begins to reach significant levels, utilities will have to invest in improvements for local electrical grids in order to handle the additional loads related to recharging to avoid blackouts due to grid overload. Also, some experts have suggested that by implementing variable time-of-day rates, utilities can provide an incentive for plug-in owners to recharge mostly overnight, when rates are lower.[88][112]
General Motors is sponsoring the Pecan Street demonstration project in Austin, Texas. The project objective is to learn the charging patterns of plug-in electric car owners, and to study how a residential fleet of electric vehicles might strain the electric grid if all owners try to charge them at the same, which is what the preliminary monitoring found when the plug-in cars return home in the evening. The Mueller neighborhood is the test ground, and as of June 2013, the community has nearly 60 Chevrolet Volt owners alone. This cluster of Volts was achieved thanks to GM's commitment to match the federal government's $7,500 rebate incentive, which effectively halves the purchase price of the plug-hybrid electric cars.[113]
Risks associated with noise reduction

Electric cars and plug-in hybrids when operating in all-electric mode at low speeds produce less roadway noise as compared to vehicles propelled by an internal combustion engine, thereby reducing harmful noise health effects. However, blind people or the visually impaired consider the noise of combustion engines a helpful aid while crossing streets, hence plug-in electric cars and conventional hybrids could pose an unexpected hazard when operating at low speeds.[114][115] Several tests conducted in the U.S. have shown that this is a valid concern, as vehicles operating in electric mode can be particularly hard to hear below 20 mph (30 km/h) for all types of road users and not only the visually impaired.[116][117][118] At higher speeds the sound created by tire friction and the air displaced by the vehicle start to make sufficient audible noise.[115]
Some carmakers announced they have decided to address this safety issue, and as a result, the Nissan Leaf electric car and Chevrolet Volt plug-in hybrid, both launched in December 2010, as well as the Fisker Karma plug-in hybrid launched in 2011 launched in 2012, include electric warning sounds to alert pedestrians, the blind and others to their presence.[119][120][121][122][123] As of January 2014, most of the hybrids and plug-in electric and hybrids available in the United States, Japan and Europe make warning noises using a speaker system.[124]
The Japanese Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism issued guidelines for hybrid and other near-silent vehicles in January 2010.[125] In the United States the Pedestrian Safety Enhancement Act of 2010 was approved by the U.S. Senate and the House of Representatives in December 2010.[126][127][128] After several delays, the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) issued its ruling in February 2018. It requires hybrids and electric vehicles traveling at less than 18.6 mph (30 km/h) to emit warning sounds that pedestrians must be able to hear over background noises. The regulation requires full compliance in September 2020, but 50% of "quiet" vehicles must have the warning sounds by September 2019.[129]
In April 2014 the European Parliament approved legislation that requires the mandatory use of the AVAS for all new electric and hybrid electric vehicles and car manufacturers have to comply within 5 years.[130][131]
Risks of battery fire
Lithium-ion batteries may suffer thermal runaway and cell rupture if overheated or overcharged, and in extreme cases this can lead to combustion.[132] To reduce these risks, lithium-ion battery packs contain fail-safe circuitry that shuts down the battery when its voltage is outside the safe range.[133][134] When handled improperly, or if manufactured defectively, some rechargeable batteries can experience thermal runaway resulting in overheating. Especially prone to thermal runaway are lithium-ion batteries. Reports of exploding cellphones have been reported in newspapers. In 2006, batteries from Apple, HP, Toshiba, Lenovo, Dell and other notebook manufacturers were recalled because of fire and explosions.[135][136][137][138] Also, during the Boeing 787 Dreamliner's first year of service, at least four aircraft suffered from electrical system problems stemming from its lithium-ion batteries, resulting in the whole Dreamliner fleet being voluntarily grounded in January 2013.[139][140]
Several plug-in electric vehicle fire incidents have taken place since the introduction of mass-production plug-in electric vehicles in 2008. Most of them have been thermal runaway incidents related to the lithium-ion batteries and have involved the Zotye M300 EV, Chevrolet Volt, Fisker Karma, BYD e6, Dodge Ram 1500 Plug-in Hybrid, Toyota Prius Plug-in Hybrid, Mitsubishi i-MiEV and Outlander P-HEV. As of November 2013, four fires after a crash have been reported associated with the batteries of all-electric cars involving a BYD e6 and three Tesla Model S cars.
The first modern crash-related fire was reported in China in May 2012, after a high-speed car crashed into a BYD e6 taxi in Shenzhen.[141] The second reported incident occurred in the United States on October 1, 2013, when a Tesla Model S caught fire after the electric car hit metal debris on a highway in Kent, Washington state, and the debris punctured one of 16 modules within the battery pack.[142][143] A second reported fire occurred on October 18, 2013, in Merida, Mexico. In this case the vehicle was being driven at high speed through a roundabout and crashed through a wall and into a tree. On November 6, 2013, a Tesla Model S being driven on Interstate 24 near Murfreesboro, Tennessee caught fire after it struck a tow hitch on the roadway, causing damage beneath the vehicle.[144]
The U.S. National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) is conducting a study due in 2014 to establish whether lithium-ion batteries in plug-electric vehicles pose a potential fire hazard. The research is looking at whether the high-voltage batteries can cause fires when they are being charged and when the vehicles are involved in an accident.[145] Both General Motors and Nissan have published a guide for firefighters and first responders to properly handle a crashed plug-in electric-drive vehicle and safely disable its battery and other high voltage systems.[146][147]
Rare-earth metals availability and supply security
Common technology for plug-ins and electric cars is based on the lithium-ion battery and an electric motor which uses rare-earth elements. The demand for lithium, heavy metals, and other specific elements (such as neodymium, boron and cobalt) required for the batteries and powertrain is expected to grow significantly due to the future sales increase of plug-in electric vehicles in the mid and long term.[148][149] As of 2011, the Toyota Prius battery contains more than 20 lb (9.1 kg) of the rare-earth element lanthanum,[150] and its motor magnets use neodymium and dysprosium.[151] While only 0.25 oz (7 g) of lithium carbonate equivalent (LCE) are required in a smartphone and 1.1 oz (30 g) in a tablet computer, electric vehicles and stationary energy storage systems for homes, businesses or industry use much more lithium in their batteries. As of 2016 a hybrid electric passenger car might use 11 lb (5 kg) of LCE, while one of Tesla's high performance electric cars could use as much as 180 lb (80 kg).[152]
Some of the largest world reserves of lithium and other rare metals are located in countries with strong resource nationalism, unstable governments or hostility to U.S. interests, raising concerns about the risk of replacing dependence on foreign oil with a new dependence on hostile countries to supply strategic materials.[148][149][153][154]
- Lithium

The main deposits of lithium are found in China and throughout the Andes mountain chain in South America. In 2008 Chile was the leading lithium metal producer with almost 30%, followed by China, Argentina, and Australia.[149][156] In the United States lithium is recovered from brine pools in Nevada.[157][158]
Nearly half the world's known reserves are located in Bolivia,[149][153] and according to the US Geological Survey, Bolivia's Salar de Uyuni desert has 5.4 million tons of lithium.[153][157] Other important reserves are located in Chile, China, and Brazil.[149][157] Since 2006 the Bolivian government have nationalized oil and gas projects and is keeping a tight control over mining its lithium reserves. Already the Japanese and South Korean governments, as well as companies from these two countries and France, have offered technical assistance to develop Bolivia's lithium reserves and are seeking to gain access to the lithium resources through a mining and industrialization model suitable to Bolivian interests.[153][159][160]
According to a 2011 study conducted at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory and the University of California Berkeley, the currently estimated reserve base of lithium should not be a limiting factor for large-scale battery production for electric vehicles, as the study estimated that on the order of 1 billion 40 kWh Li-based batteries (about 10 kg of lithium per car)[161] could be built with current reserves, as estimated by the U.S. Geological Survey.[162] Another 2011 study by researchers from the University of Michigan and Ford Motor Company found that there are sufficient lithium resources to support global demand until 2100, including the lithium required for the potential widespread use of hybrid electric, plug-in hybrid electric and battery electric vehicles. The study estimated global lithium reserves at 39 million tons, and total demand for lithium during the 90-year period analyzed at 12–20 million tons, depending on the scenarios regarding economic growth and recycling rates.[163]
A 2016 study by Bloomberg New Energy Finance (BNEF) found that availability of lithium and other finite materials used in the battery packs will not be a limiting factor for the adoption of electric vehicles. BNEF estimated that battery packs will require less than 1% of the known reserves of lithium, nickel, manganese, and copper through 2030, and 4% of the world’s cobalt. After 2030, the study states that new battery chemistries will probably shift to other source materials, making packs lighter, smaller, and cheaper.[82]
- Rare-earth elements
China has 48% of the world's reserves of rare-earth elements, the United States has 13%, and Russia, Australia, and Canada have significant deposits. Until the 1980s, the U.S. led the world in rare-earth production, but since the mid-1990s China has controlled the world market for these elements. The mines in Bayan Obo near Baotou, Inner Mongolia, are currently the largest source of rare-earth metals and are 80% of China's production. In 2010 China accounted for 97% of the global production of 17 rare-earth elements.[150] Since 2006 the Chinese government has been imposing export quotas reducing supply at a rate of 5% to 10% a year.[154][164][165]
Prices of several rare-earth elements increased sharply by mid-2010 as China imposed a 40% export reduction, citing environmental concerns as the reason for the export restrictions. These quotas have been interpreted as an attempt to control the supply of rare earths. However, the high prices have provided an incentive to begin or reactivate several rare-earth mining projects around the world, including the United States, Australia, Vietnam, and Kazakhstan.[164][165][166][167]
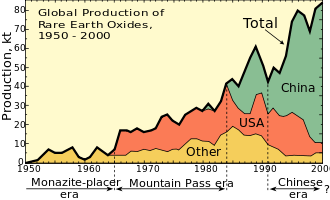
In September 2010, China temporarily blocked all exports of rare earths to Japan in the midst of a diplomatic dispute between the two countries. These minerals are used in hybrid cars and other products such wind turbines and guided missiles, thereby augmenting the worries about the dependence on Chinese rare-earth elements and the need for geographic diversity of supply.[165][168] A December 2010 report published by the US DoE found that the American economy vulnerable to rare-earth shortages and estimates that it could take 15 years to overcome dependence on Chinese supplies.[169][170] China raised export taxes for some rare earths from 15 to 25%, and also extended taxes to exports of some rare-earth alloys that were not taxed before. The Chinese government also announced further reductions on its export quotas for the first months of 2011, which represent a 35% reduction in tonnage as compared to exports during the first half of 2010.[171]
On September 29, 2010, the U.S. House of Representatives approved the Rare Earths and Critical Materials Revitalization Act of 2010 (H.R.6160).[172][173] The approved legislation is aimed at restoring the U.S. as a leading producer of rare-earth elements, and would support activities in the U.S. Department of Energy (US DoE) to discover and develop rare-earth sites inside of the U.S. in an effort to reduce the auto industry's near-complete dependence on China for the minerals.[173][174] A similar bill, the Rare Earths Supply Technology and Resources Transformation Act of 2010 (S. 3521), is being discussed in the U.S. Senate.[173][175]
In order to avoid its dependence on rare-earth minerals, Toyota Motor Corporation announced in January 2011 that it is developing an alternative motor for future hybrid and electric cars that does not need rare-earth materials. Toyota engineers in Japan and the U.S. are developing an induction motor that is lighter and more efficient than the magnet-type motor used in the Prius, which uses two rare earths in its motor magnets. Other popular hybrids and plug-in electric cars in the market that use these rare-earth elements are the Nissan Leaf, the Chevrolet Volt and Honda Insight. For its second generation RAV4 EV due in 2012, Toyota is using an induction motor supplied by Tesla Motors that does not require rare-earth materials. The Tesla Roadster and the Tesla Model S use a similar motor.[151]
Car dealers reluctance to sell
With the exception of Tesla Motors, almost all new cars in the United States are sold through dealerships, so they play a crucial role in the sales of electric vehicles, and negative attitudes can hinder early adoption of plug-in electric vehicles.[176][177] Dealers decide which cars they want to stock, and a salesperson can have a big impact on how someone feels about a prospective purchase. Sales people have ample knowledge of internal combustion cars while they do not have time to learn about a technology that represents a fraction of overall sales.[176] As with any new technology, and in the particular case of advanced technology vehicles, retailers are central to ensuring that buyers, especially those switching to a new technology, have the information and support they need to gain the full benefits of adopting this new technology.[177]
There are several reasons for the reluctance of some dealers to sell plug-in electric vehicles. PEVs do not offer car dealers the same profits as gasoline-powered car. Plug-in electric vehicles take more time to sell because of the explaining required, which hurts overall sales and sales people commissions. Electric vehicles also may require less maintenance, resulting in loss of service revenue, and thus undermining the biggest source of dealer profits, their service departments. According to the National Automobile Dealers Association (NADS), dealers on average make three times as much profit from service as they do from new car sales. However, a NADS spokesman said there was not sufficient data to prove that electric cars would require less maintenance.[176] According to the New York Times, BMW and Nissan are among the companies whose dealers tend to be more enthusiastic and informed, but only about 10% of dealers are knowledgeable on the new technology.[176]
A study conducted at the Institute of Transportation Studies (ITS), at the University of California, Davis (UC Davis) published in 2014 found that many car dealers are less than enthusiastic about plug-in vehicles. ITS conducted 43 interviews with six automakers and 20 new car dealers selling plug-in vehicles in California’s major metro markets. The study also analyzed national and state-level J.D. Power 2013 Sales Satisfaction Index (SSI) study data on customer satisfaction with new car dealerships and Tesla retail stores. The researchers found that buyers of plug-in electric vehicles were significantly less satisfied and rated the dealer purchase experience much lower than buyers of non-premium conventional cars, while Tesla Motors earned industry-high scores. According to the findings, plug-in buyers expect more from dealers than conventional buyers, including product knowledge and support that extends beyond traditional offerings.[177][178]
In 2014 Consumer Reports published results from a survey conducted with 19 secret shoppers that went to 85 dealerships in four states, making anonymous visits between December 2013 and March 2014. The secret shoppers asked a number of specific questions about cars to test the salespeople’s knowledge about electric cars. The consumer magazine decided to conduct the survey after several consumers who wanted to buy a plug-in car reported to the organization that some dealerships were steering them toward gasoline-powered models. The survey found that not all sales people seemed enthusiastic about making PEV sales; a few outright discouraged it, and even one dealer was reluctant to even show a plug-in model despite having one in stock. And many sales people seemed not to have a good understanding of electric-car tax breaks and other incentives or of charging needs and costs. Consumer Reports also found that when it came to answering basic questions, sales people at Chevrolet, Ford, and Nissan dealerships tended to be better informed than those at Honda and Toyota. The survey found that most of the Toyota dealerships visited recommended against buying a Prius Plug-in and suggested buying a standard Prius hybrid instead. Overall, the secret shoppers reported that only 13 dealers “discouraged sale of EV,” with seven of them being in New York. However, at 35 of the 85 dealerships visited, the secret shoppers said sales people recommended buying a gasoline-powered car instead.[179]
The ITS-Davis study also found that a small but influential minority of dealers have introduced new approaches to better meet the needs of plug-in customers. Examples include marketing carpool lane stickers, enrolling buyers in charging networks, and preparing incentive paperwork for customers. Some dealers assign seasoned sales people as plug-in experts, many of whom drive plug-ins themselves to learn and be familiar with the technology and relate the car’s benefits to potential buyers. The study concluded also that carmakers could do much more to support dealers selling PEVs.[177]
Government incentives
Several national and local governments around the world have established tax credits, grants and other financial and non-financial incentives for consumers to purchase a plug-in electric vehicle as a policy to promote the introduction and mass market adoption of this type of vehicles.
As of 2010, 17 of the 27 European Union member states provide tax incentives for electrically chargeable vehicles. The incentives consist of tax reductions and exemptions, as well as of bonus payments for buyers of plug-in and hybrid vehicles.[26][180] Other countries offering subsidies and tax incentives include China, the United States, Japan, South Korea, India, some provinces in Canada, and Costa Rica.[181][182]
Production plug-in electric vehicles available
_cropped.jpg)
During the 1990s several highway-capable plug-in electric cars were produced in limited quantities, all were battery electric vehicles. PSA Peugeot Citroën launched several electric "Électrique" versions of its models starting in 1991, notably the Citroën C15, C25 and Berlingo and Peugeot J5 and Partner panel vans and the Citroën AX and Saxo and Peugeot 106 superminis. The Saxo was the best-selling and most produced ever electric car at the time. Other models were available through leasing mainly in California. Popular models included the General Motors EV1 and the Toyota RAV4 EV. Some of the latter were sold to the public and are in use still today.[183] In the late 2000s began a new wave of mass production plug-in electric cars, motorcycles and light trucks. However, as of 2011, most electric vehicles in the world roads were low-speed, low-range neighborhood electric vehicles (NEVs) or electric quadricycles. Pike Research estimated there were almost 479,000 NEVs on the world roads in 2011.[184] As of October 2015, the GEM neighborhood electric vehicle is the market leader in North America, with global sales of more than 50,000 units since 1998.[185] Sales of low-speed electric vehicles experienced considerable growth in China between 2012 and 2016. As of December 2016, the Chinese stock of NEVs was estimated to be between 3 million and 4 million units, with most powered by lead-acid batteries.[22]
As of December 2016, there were over 60 models of highway-capable plug-in electric passenger cars and light-utility vans available in the world.[9] As of August 2015, there were 45 different plug-in electric passenger car models offered in Europe, 20 available in North America, 19 in China, 14 in Japan, and 7 in Australia.[186] There are also available several commercial models of plug-in motorcycles, all-electric buses, and heavy-duty trucks.
Cumulative global sales of highway legal plug-in electric passenger cars and light utility vehicles passed the one million unit milestone in September 2015,[187] the two million mark in December 2016,[6] and the three million milestone was achieved in November 2017.[10] The Renault-Nissan-Mitsubishi Alliance is the world's leading electric vehicle manufacturer. The Alliance reached sales of 500,000 electric vehicles delivered globally in October 2017, including the models manufactured by Mitsubishi Motors, now part of the Alliance.[188]
_trimmed.jpg)
BYD Auto is the world's second largest plug-in electric car manufacturer with more than 300,000 units delivered in China through December 2017.[6][191][192] Its Qin plug-in hybrid is the company's top selling model with over 89,000 units sold in China through December 2017, making it the all-time best-selling plug-in electric car in the country.[189][193] As of September 2017, Tesla ranked as the world's third largest plug-in electric vehicle manufacturer with global sales of over 250,000 units in September 2017.[194][195][191] Its Model S was the world's top selling plug-in car for two years running, 2015 and 2016,[189][190] and Model S global sales passed the 200,000 unit mark in the fourth quarter of 2017.[12] As of April 2018, the BMW Group had sold over 250,000 plug-in cars, accounting for global sales its BMW i cars, BMW iPerformance plug-in hybrid models, and MINI brand plug-ins.[196]
BYD Auto ended 2015 as the world's best selling manufacturer of highway legal light-duty plug-in electric vehicles, with 61,722 units sold, mostly plug-in hybrids, followed by Tesla, with 50,580 units sold in 2015.[197][198][199] BYD was the world's top selling plug-in car manufacturer for a second year running, with 101,183 units sold in 2016, one more time followed again by Tesla with 76,243 units delivered.[6][200] In 2017 BYD ranked for the third year in a row as the global top plug-in car manufacturer with 113,669 units delivered.[193][192] The Renault-Nissan-Mitsubishi Alliance was the top selling automotive group with 119,995 units sold worldwide in 2017.[201]
Sales and main markets

The global stock of plug-in electric vehicles between 2005 and 2009 consisted exclusively of all-electric cars, totaling about 1,700 units in 2005, and almost 6,000 in 2009. The plug-in stock rose to about 12,500 units in 2010, of which, only 350 vehicles were plug-in hybrids.[203][204] By comparison, during the Golden Age of the electric car at the beginning of the 20th century, the EV stock peaked at approximately 30,000 vehicles.[202] After the introduction of the Nissan Leaf and the Chevrolet Volt in late December 2010, the first mass-production plug-in cars by major carmakers, plug-in car sales grew to about 50,000 units in 2011, jumped to 125,000 in 2012, and rose to almost 213,000 plug-in electric cars and utility vans in 2013. Sales totaled over 315,000 units in 2014, up 48% from 2013,[205] By mid-September 2015, the global stock of highway legal plug-in electric passenger cars and utility vans reached the one million sales milestone.[187][206] Sales of plug-in electric vehicles achieved the one million milestone almost twice as fast as hybrid electric vehicles (HEV). While it took four years and 10 months to reach one-million PEV sales, it took more than around nine years and a few months for HEVs to reach its first million sales.[187][206] A 2016 analysis by the Consumer Federation of America (CFA) found that five years after its introduction, sales of plug-in electric cars in the American market outsold conventional hybrids during the same period.[207]
The global ratio between all-electrics (BEVs) and plug-in hybrids (PHEVs) was 60:40 between 2014 and the first half of 2016, mainly due to the large all-electric market in China. In the U.S. and Europe, the ratio approached a 50:50 split.[208] All-electric cars oversold plug-in hybrids in 2016, with pure electrics representing about 61% of the global stock,[11] up from 58.9% at the end of 2015.[203] The global ratio between battery BEVs and PHEVs was 66:34 in 2017.[209] Cumulative global sales of highway-capable light-duty pure electric vehicles since 2010 achieved the one million unit milestone in September 2016.[210]
In five years, global sales of highway legal light-duty plug-in electric vehicles have increased more than ten-fold, totaling more than 565,000 units in 2015. Plug-in sales in 2015 increased about 80% from 2014, driven mainly by China and Europe.[205] Both markets passed in 2015 the U.S. as the largest plug-in electric car markets in terms of total annual sales, with China ranking as the world's best-selling plug-in electric passenger car country market in 2015.[212][213] About 775,000 plug-in cars and vans were sold in 2016, and cumulative global sales totaled an estimated 2.032 million plug-in cars and utility vans by the end of 2016.[6] The global market share of the light-duty plug-in vehicle segment achieved a record 0.86% of total new car sales in 2016, up from 0.62% in 2015 and 0.38% in 2014.[11] Despite the rapid growth experienced, the plug-in electric car segment represented just 0.15% of the 1.4 billion motor vehicles on the world's roads by the end of 2016, up from 0.1% in 2015.[6][82] Global light-duty plug-in vehicle sales passed the 3 million milestone in November 2017.[10] About 1.2 million plug-ins cars and vans were sold worldwide in 2017, with China accounting for about half of global sales in 2017.[14]
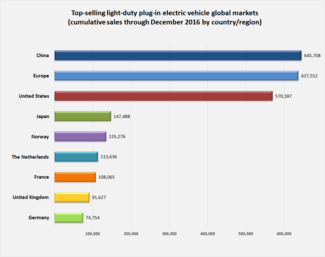
As of December 2016, with cumulative sales of more than 645,000 plug-in electric passenger cars, China has the world's largest fleet of light-duty plug-in electric vehicles, after having overtook during 2016 both the U.S. and Europe in terms of cumulative sales. This figure accounts for both, domestically produced new energy passenger cars and imports.[6][19][214] The fleet of Chinese plug-in cars represents 43.0% of the global stock of light-duty plug-in vehicles at the end of 2016.[211] Among country markets, the U.S. ranks second, with over 570,000 plug-in passenger cars sold through December 2016,[15] representing 28.1% of the global stock of plug-ins.[211] Japan has the world's third largest plug-in stock, with about 147,500 highway legal plug-in electric vehicles sold in the country between July 2009 and December 2016.[211] As of December 2016, about 637,500 plug-in electric passenger cars and vans have been registered in Europe, representing 31.4% of the global stock, the second largest after China.[6][211] The region was the world's largest light-duty plug-in market until October 2016.[19]
As of December 2016, more than 951,000 new energy vehicles have been sold in China since 2011, making the country the world's leader when all plug-in automotive segments are considered, including passenger cars, electric buses, and commercial plug-in heavy-duty trucks.[19][20] The stock of new energy vehicles in China achieved the 500,000 unit milestone in March 2016.[215] As of December 2016, China had the world's largest electric bus stock with about 343,500 vehicles, up from 173,000 plug-in electric buses in 2015, both representing almost the entire global stock of plug-in buses.[22][203][216] The European market account for 1,273 plug-in electric buses and the U.S. for only 200.[22]
| Top 10 countries or autonomous territories by plug-in electric passenger car market share of total new car sales between 2013 and 2017 | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Country or territory |
Market share (%) 2017 |
Rank | Country or territory |
Market share (%) 2016[211][217] |
Rank | Country or territory |
Market share (%) 2015[212][218] |
Rank | Country or territory |
Market share (%) 2014[219] |
Rank | Country or territory |
Market share (%) 2013[220] |
| 1 | 39.2%[221] | 1 | 29.1 % | 1 | 22.39 % | 1 | 13.84 % | 1 | 6.10 % | |||||
| 2 | 14%[222] | 2 | 6.4 % | 2 | 9.74 % | 2 | 3.87 % | 2 | 5.55 % | |||||
| 3 | 5.2%[223] | 3 | ~5 % | 3 | 4.84 % | 3 | 2.71 % | 3 | 0.94 % | |||||
| 4 | 2.6%[225] | 4 | 4.6 % | 4 | 2.93 % | 4 | 1.57 % | 4 | 0.91 % | |||||
| 5 | 2.6%[227] | 5 | 3.5 % | 5 | 2.62 % | 5 | 1.53 % | 5 | 0.83 % | |||||
| 6 | 2.6 %[229] | 6 | 1.8 % | 6 | 2.29 % | 6 | 1.06 % | 6 | 0.73 % | |||||
| 7 | 2.6 %[230] | 7 | 1.8 % | 7 | 1.98 % | 7 | 0.88 % | 7 | 0.71 % | |||||
| 8 | 2.1%[14] | 8 | 1.6 % | 8 | 1.19 % | 8 | 0.75 % | 8 | 0.60 % | |||||
| 9 | 2.1%[233] | 9 | 1.4 % | 9 | 1.07 % | 9 | 0.72 % | 9 | 0.44 % | |||||
| 10 | 1.98%[234] | 10 | 1.37 % | 10 | 0.90 % | 10 | 0.70 % | 10 | 0.29 % | |||||
| Selected regional markets Plug-in electric passenger car market share between 2013 and 2017 | ||||||||||||||
| 4.8% % | 3.6 % | 3.1 % | 3.2 % | 2.5 % | ||||||||||
| 2% | 1.3 % | 1.41 % | 0.66 % | 0.49 % | ||||||||||
| Notes: (1) European figures correspond to European Union member countries plus EFTA countries (Norway and Switzerland) 2) The French market share corresponds to combined sales all-electric passenger cars and utility vans only (plug-in hybrids not included). | ||||||||||||||
China
Domestically built new energy vehicle sales in China totaled 1,728,447 units between 2011 and 2017. These figures include heavy-duty commercial vehicles such buses and sanitation trucks,[19][20][21] and only include vehicles manufactured in the country as imports are not subject to government subsidies.[246] China is the world's largest electric bus market, and its electric bus stock grew nearly sixfold between 2014 and 2015,[203] reaching 343,500 units in 2016, doubling the 2015 stock.[22]
As of December 2017, cumulative sales of domestically produced highway legal plug-in electric passenger cars totaled over 1,2 million units since 2005, of which, a total of 579,000 were sold in 2017, representing about half of global plug-in car sales in 2017.[203][14][21][247] Domestically produced cars account for about 96% of new energy car sales in China.[14][248] A particular feature of the Chinese passenger plug-in market is the dominance of small entry level vehicles.[249]
In September 2016, the Chinese stock of plug-in passenger cars reached the same level of the American stock,[250] and by November 2016, China’s cumulative total plug-in passenger vehicles sales had surpassed those of Europe, allowing China to become the market with the world's largest stock of light-duty plug-in electric vehicles, with almost 600,000 plug-in passenger cars.[19][214] China also surpassed the U.S. and Europe in terms of annual sales of light-duty plug-in electric vehicles, both in calendar years 2015 and current-year-to-date through November.[19][214]
The stock of new energy vehicles sold in China since 2011 achieved the 500,000 unit milestone in March 2016, making the country the world's leader in the plug-in heavy-duty segment, including electric buses and plug-in trucks.[215] Cumulative sales of new energy passenger cars achieved the 500,000 unit milestone in September 2016, excluding imports.[246] As of December 2017, the BYD Qin plug-in hybrid, with 89,393 units sold since its inception, continued to rank as the all-time top selling plug-in electric car in the country.[189][193] The BAIC EC-Series all-electric city car was Chinese the top selling plug-in car in 2017 with 78,079 units sold in China, making also the city car the world's top selling plug-in car in 2017. BYD Auto was again the top selling Chinese car manufacturer in 2017.[192][193][14][251]
United States
As of December 2017, cumulative sales totaled 764,666 highway legal plug-in electric cars in the U.S. since the market launch of the Tesla Roadster in 2008.[15][16] As of December 2016, the American stock represented 28.1% of the global light-duty plug-in stock, down from about 40% in 2014.[211][6] As of December 2016, the U.S. has the world's third largest stock of plug-in passenger cars, after having being overtook by Europe in 2015 and China during 2016.[19][214] California is the largest U.S. car market, and accounts for approximately 48% percent of cumulative plug-in sales in the American market from 2011 to June 2016, and also accounts for about 50% of nationwide all-electric car sales and 47% of total plug-in hybrid sales. The other nine states that follow California's Zero Emission Vehicle (ZEV) regulations have accounted for another 10% of cumulative plug-in car sales in the U.S. during the same period.[255] California's plug-in stock totaled almost 270,000 units at the end of 2016.[211]

Nationwide sales climbed from 17,800 units delivered in 2011 to 53,200 during 2012, and reached 97,100 in 2013.[256] In 2014 plug-in electric car sales totaled 123,248 units, and fell to 114,248 in 2015.[257] A total of 157,181 plug-in cars were sold in 2016, up 37.6% from 2015,[258] and rose to 194,479 in 2017, up 23.7% from 2016.[16] The market share of plug-in electric passenger cars increased from 0.14% of new car sales in 2011 to 0.37% in 2012, 0.62% in 2013, and reached 0.75% of new car sales in 2014.[257][259][260] As plug-in car sales slowed down during 2015, the segment's market share fell to 0.66% of new car sales,[257] but increased to 0.90% in 2016.[258] The plug-in segment passed the 1% market share for the first time in 2017, with 1.13% of the country's total annual new car sales.[16] The highest-ever monthly market share for plug-in electric vehicles was achieved in December 2017 with 1.58% of new car sales. The previous record was achieved in September 2017.[16][261] Monthly sales of plug-in cars in the American market passed the 1% mark for the first time in September 2016 (1.12%).[262] December 2017 is also the best monthly plug-in sales volume on record ever, with 25,149 units delivered.[16][261]
Japan
As of December 2017, Japan had a stock of light-duty plug-in vehicles of about 207,200.[22][264] As of 2016, the Japanese stock consisted of 86,390 all-electric cars (57.1%) and 64,860 plug-in hybrids (42.9%).[22] Plug-in segment sales climbed from 1,080 units in 2009 to 12,630 in 2011, and reached 24,440 in 2012.[203] Global sales of pure electric cars in 2012 were led by Japan with a 28% market share of the segment sales. Japan ranked second after the U.S. in terms of its share of plug-in hybrid sales in 2012,[265] and until 2016, the country ranked third.[6]
The plug-in segment sales remained flat in 2014 with 30,390 units sold, and a market share of 1.06% of total new car sales in the country (kei cars not included).[219] Sales totaled 24,660 units in 2015 and 24,851 units in 2016.[22] The rate of growth of the Japanese plug-in segment slowed down from 2013, with annual sales falling behind Europe, the U.S. and China during 2014 and 2015.[212][266] The segment market share fell from 0.68% in 2014 to 0.59% in 2016.[22] The decline in plug-in car sales reflects the Japanese government and the major domestic carmakers decision to adopt and promote hydrogen fuel cell vehicles instead of plug-in electric vehicles.[267][268] Sales recovered in 2017, with almost 56,000 plug-in cars sold, and the segment's market share reached 1.1%.[264] Since December 2010, Nissan has sold 72,494 Leafs through December 2016, making the Leaf the all-time best-selling plug-in car in the country.[263]
Europe
As of December 2017, about 943,600 plug-in electric passenger cars and vans have been registered in Europe, making the region the world's second largest after China.[6][211][17] As of December 2017, European sales of plug-in cars and vans are led by Norway with over 200,000 units registered, followed by France with almost 158,000, and the UK with over 137,000 units.[6][18][234][271] Norway was the top selling plug-in country market in Europe in 2016 and 2017.[211][221] The other top selling European markets in terms of cumulative registrations are Germany, the Netherlands and Sweden.[211]
Cumulative sales of light-duty plug-in electric vehicles in Europe passed the 500,000 unit milestone in May 2016.[272] Norway passed the 100,000th registered plug-in unit milestone in April 2016,[273] France passed the same milestone in September 2016,[274] and the Netherlands in November 2016.[275] The UK achieved the 100,000 unit mark in March 2017.[211][276]
As of December 2015, France ranked as the largest European market for light-duty electric commercial vehicles or utility vans, accounting for nearly half of all vans sold in the European Union.[277] The French market share of all-electric utility vans reached a market share of 1.22% of new vans registered in 2014, and 1.30% in 2015.[278] Denmark is the second largest European market, with over 2,600 plug-in electric vans sold in 2015, with an 8.5% market share of all vans sold in the country. Most of the van sold in the Danish market are plug-in hybrids, accounting for almost all of the plug-in hybrid van sales across the EU.[277] European sales of plug-in electric cars passed 200,000 units for the first time in 2016, and the plug-in segment achieved a market share of 1.3%.[237] Sales in 2017 exceeded 300,000 units with a market share of 2%.[17]
Norway
As of December 2017, the stock of light-duty plug-in electric vehicles registered in Norway totaled more than 200,000 units,[18] making Norway the European country with the largest stock of plug-in cars and vans, and the fourth largest in the world.[6][211] As of 31 December 2017, and accounting for both new and used imports registrations, the Norwegian light-duty plug-in electric fleet consisted of 141,951 all-electric passenger cars and vans, and 67,171 plug-in hybrids.[279] The registered plug-in stock includes almost 2,700 all-electric vans and about 24,500 used imported electric cars from neighboring countries as of December 2017.[221][280][281][282] The government's target of 50,000 all-electric cars on Norwegian roads was reached in April 2015, more than two years earlier than expected, thanks to the successful policies implemented to promote electric vehicle adoption that include fiscal and non-monetary incentives.[283][284] The milestone of 100,000 light-duty plug-in electric vehicles registered was achieved in April 2016,[273][285] and 100,000 all-electric vehicles in December 2016, representing about 10% of all pure electric cars that have been sold worldwide.[286][287]
The Norwegian fleet of plug-in electric cars is one of the cleanest in the world because 98% of the electricity generated in the country comes from hydropower.[288][289] Norway, with about 5.2 million people, is the country with the largest EV ownership per capita in the world.[290][291][292] In March 2014, Norway became the first country where over one in every 100 registered passenger cars is plug-in electric.[293] The plug-in car market penetration reached 2% in March 2015,[294] passed 3% in December 2015,[295][296] and achieved 5% at the end of 2016.[211]
France
As of December 2017, the stock of light-duty plug-in electric vehicles registered in France totaled 149,797 plug-in cars and electric utility vans delivered since 2010,[211][234] As of December 2016, the country ranked as the third largest plug-in market in Europe after Norway and the Netherlands, and the world's sixth.[6] As of December 2017, and accounting for registrations since 2010, the plug-in electric stock consisted consisted of 92,256 all-electric passenger cars, 25,269 all-electric utility vans, and 32,272 plug-in hybrids.[305][234][274] The stock of light-duty plug-in electric vehicles registered in France passed the 100,000 unit milestone in October 2016.[274][306]As of December 2015, France is the country with the world's largest market for light-duty electric commercial vehicles or utility vans. Nearly half of the vans sold in the European Union are sold in France as a result of a national purchase incentive scheme, which French companies have embraced.[277] The market share of all-electric utility vans reached a market share of 1.22% of new vans registered in 2014, and 1.30% in 2015.[278]
United Kingdom
More than 137,000 light-duty plug-in electric vehicles have been registered in the UK up until December 2017, including about 5,100 plug-in commercial vans.[271] Since the launch of the Plug-In Car Grant in January 2011, a total of 127,509 eligible cars have been registered through December 2017,[313] and, as of December 2016, the number of claims made through the Plug-in Van Grant scheme totaled 2,938 units since the launch of the scheme in 2012.[314] Before the introduction of series production plug-in vehicles, a total of 1,096 all-electric vehicles were registered in the UK between 2006 and December 2010.[315] Before 2011, the G-Wiz, a heavy quadricycle, listed as the top-selling EV for several years.[316] As of December 2016, the UK had the fourth largest European stock of light-duty plug-in vehicles,[6] and with 36,907 plug-in passenger cars registered in 2016, ranked as the second best selling European market that year after Norway.[211]
Germany
As of December 2017, a total of 129,246 plug-in electric cars have been registered in Germany since 2010.[211][323] The country is the largest passenger car market in Europe, however, as of December 2016, ranked as the fifth largest plug-in market in Europe.[272][211] About 80% of the plug-in cars registered in the country through September 2016 were registered since January 2014.[317][321][324] The official German definition of electric vehicles changed at the beginning of 2013, before that, official statistics only registered all-electric vehicles because plug-in hybrids were accounted together with conventional hybrids. As a result, the registrations figures for 2012 and older do not account for total new plug-in electric car registrations.[325]
A record of 54,492 plug-in cars were registered in 2017, up 217% the previous year, and consisting of 29,436 plug-in hybrids and 25,056 all-electric cars.[323] Registrations in 2017 achieved a market share of 1.58%.[323] The top selling models in 2017 were the Audi A3 e-tron (4,454), Renault Zoe (4,322), and BMW i3 (4,319).[326]
Netherlands
As of 31 December 2017, there were 121,542 highway legal light-duty plug-in electric vehicles registered in the Netherlands, consisting of 98,217 range-extended and plug-in hybrids, 21,115 pure electric cars, and 2,210 all-electric light utility vans. When buses, trucks, motorcycles, quadricycles and tricycles are accounted for, the Dutch plug-in electric-drive fleet climbs to 123,499 units.[225] The country's electric vehicle stock reaches 165,886 units when fuel cell electric vehicles (43), mopeds (4,376), electric bicycles (37,652), and microcars (316) are accounted for.[225] A distinct feature of the Dutch plug-in market is dominance of plug-in hybrids, which represented 81% of the country's stock of passenger plug-in electric cars and vans registered at the end of December 2017.[225]
The Netherlands listed as the world's third best-selling country market for light-duty plug-in vehicles in 2015, with 43,971 units registered that year.[212] Until December 2015, the Netherlands had Europe's largest fleet light-duty plug-in vehicles.[212] Plug-in sales fell sharply during 2016, and as a result, by early October 2016, the Netherlands listed as the third largest European plug-in market, after being surpassed during the year by both Norway and France.[274][273] As of July 2016, the Netherlands had the second largest plug-in market concentration per capita in the world after Norway.[333] The stock of light-duty plug-in electric vehicles registered in the Netherlands achieved the 100,000 unit milestone in November 2016.[275][334] However, due to changes in tax rules, the plug-in market share declined from 9.9% in 2015, to 6.7% in 2016, and fell to 2.6% in 2017.[225]
Top selling PEV models
All-electric cars and vans
The world's top selling highway-capable all-electric car ever is the Nissan Leaf with global sales of more than 300,000 units through early January 2018.[1] The United States is the world's largest Leaf market with 114,827 units sold through December 2017.[2][16] The other two top markets are Japan with 74,494 units delivered up until December 2016,[263] and Europe with about 66,000 units through November 2016.[2] The European market is led by Norway with 19,407 new units registered up until December 2016,[9][335] and the UK with 15,000 September 2016.[9]
Ranking second is the all-electric Tesla Model S, with global deliveries of more than 200,000 cars as of November 2017,[12] with the United States as its leading market with about 118,817 units delivered through December 2017.[336][258][16] As of September 2016, Norway ranked as the Model S largest overseas market, with 11,763 new units registered,[337][338][339][340] followed by China with 5,524 units registered through September 2015.[341][342] The Tesla Model S was the world's top selling plug-in car for two years in a row, 2015 and 2016.[189][190] The BAIC EC-Series all-electric city car ranked as the world's top selling plug-in car in 2017 with 78,079 units sold in China.[14] The world's all-time top selling all-electric light utility vehicle is the Renault Kangoo Z.E., with global sales of 29,523 electric vans delivered since inception through December 2017.[343][344]
The following table presents global sales of the top selling highway-capable electric cars and light utility vehicles produced between 2008 and December 2016. The table includes all-electric passenger cars and utility vans with cumulative sales of about or over 20,000 units since the introduction of the first modern production all-electric car in 2008, the Tesla Roadster.
| Top selling highway legal electric cars and light utility vehicles produced between 2008 and December 2016(1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Market launch | Global sales | Sales through |
| Nissan Leaf | Dec 2010 | + 250,000 | Dec 2016[345] |
| Tesla Model S | Jun 2012 | 158,159 | Dec 2016[346][336] |
| BMW i3 | Nov 2013 | ~ 65,500 | Dec 2016[189] |
| Renault Zoe | Dec 2012 | 61,205 | Dec 2016[343] |
| BAIC EV series | 2012 | 42,626(3) | Dec 2016[347][348][349][350] |
| Mitsubishi i-MiEV family | Jul 2009 | ~ 37,600 | Jun 2016[351] |
| BYD e6 | Oct 2011 | 34,862(3) | Dec 2016[348][347][352][353][350] |
| Tesla Model X | Sep 2015 | 25,524 | Dec 2016[189] |
| Renault Kangoo Z.E. | Oct 2011 | 25,205 | Dec 2016.[343] |
| Volkswagen e-Golf | May 2014 | 24,498(4) | Jun 2016[257][354][355][356][357] |
| JAC J3/iEV family | 2010 | 23,241(3) | Jun 2016[347][348][349][358][359][360] |
| Cumulative global sales 2008 – Dec 2016 | 0ver 1,230,000 | Dec 2016[11] | |
| Notes: (1) Vehicles are considered highway-capable if able to achieve at least a top speed of 100 km/h (62 mph). Several models, such as the Chery QQ3 EV/eQ EV, Kandi EV and the Zotye Zhidou E20, are highway legal in China but do not meet this requirement. (2) BMW i3 sales includes the REx variant. (3) Sales in main China only. (4) Sales in Europe and the U.S. only. | |||
Plug-in hybrids

As of December 2016, the Volt/Ampera family is the world's best selling plug-in hybrid and the third best selling plug-in electric car after the Nissan Leaf and the Model S.[2] Chevrolet Volt and Opel/Vauxhaul Ampera combined sales totaled about 134,500 units worldwide through December 2016, including just over 10,000 Opel/Vauxhall Amperas sold in Europe through June 2016.[2][9] Volt sales are led by the United States with 113,489 units delivered, followed by Canada with 8,884 units, both through December 2016.[15][362] The Netherlands is the leading European market with about 6,000 Amperas and Volts registered as of December 2015.[9]
Ranking next is the Mitsubishi Outlander P-HEV with around 119,500 units sold worldwide as of December 2016.[189] As of March 2016, Europe ranked as the Outlander P-HEV leading market with 65,529 units sold, followed by Japan with 33,730 units.[363] European sales are led by the UK with 26,600 units sold through December 2016,[364] followed by the Netherlands with 25,984 units registered by the end of 2016.[327]
Ranking third is the first generation Toyota Prius Plug-in Hybrid with 75,400 units sold worldwide through April 2016.[365] The United States is the market leader with 44,767 units delivered through December 2016.[366][252][258][367] Japan ranks next with about 22,100 units, followed by Europe with 10,500 units, both, through April 2016.[365] The leading European market is the Netherlands with 4,134 units registered as of 30 November 2015.[368] Production of the first generation Prius Plug-in ended in June 2015.[369] The second generation Prius plug-in hybrid, the Toyota Prius Prime, was released in the United States in November 2016.[370]
The following table presents cumulative sales through December 2016 of those plug-in hybrid models that have sold about 10,000 units since the introduction of the first modern production plug-in hybrid vehicle in December 2008, the BYD F3DM.
| Top selling highway legal plug-in hybrid electric cars between 2008 and December 2016 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Market launch | Global sales | Sales through |
| Chevrolet Volt(1) | Dec 2010 | ~134,500 | Dec 2016[2] |
| Mitsubishi Outlander P-HEV | Jan 2013 | ~119,500 | Dec 2016[189] |
| Toyota Prius PHV | Jan 2012 | ~77,850 | Dec 2016[189] |
| BYD Qin(2) | Dec 2013 | 68,655 | Dec 2016[189] |
| BYD Tang(2) | Jun 2015 | 49,780 | Dec 2016[350][371] |
| Ford Fusion Energi(3) | Feb 2013 | 43,713 | Dec 2016[257][372][373][258][260] |
| Ford C-Max Energi(4) | Oct 2012 | 35,705 | Dec 2016[257][373][374][258][355] |
| SAIC Roewe 550 PHEV(2) | Nov 2013 | 26,856 | Dec 2016[347][375][350] |
| Volkswagen Golf GTE | Aug 2014 | 24,089 | Jun 2016[376][357] |
| Volvo V60 Plug-in Hybrid | Nov 2012 | 21,185 | Jun 2016[376][377][378][379] |
| Audi A3 Sportback e-tron(5) | Aug 2014 | 18,467 | Jun 2016[373][376][354][357][380] |
| BMW i8 | Aug 2014 | 10,000 | Nov 2016[381] |
| Volvo XC90 T8(5) | Aug 2015 | 9,044 | Jun 2016[257][373][354][355][357] |
| Cumulative global sales Dec 2008 – Dec 2016 | ~800,000 | Dec 2016[11] | |
| Notes: (1) Includes Vauxhall/Opel Ampera sales in Europe, and Holden Volt in Australia and New Zealand. This figure includes over 10,000 Opel/Vauxhall Amperas sold in Europe through December 2016.[9] (2) Sales in China only. (3) Sales in the U.S. and Canada only. (4) Only includes European sales for 2015. (5) Only accounts for CYTD 2016 sales in Europe, U.S. and Canada. | |||
See also
- All-electric vehicle (EV) or battery electric vehicle (BEV)
- Electric car
- Electric car use by country
- Electric vehicle battery
- Electric vehicle warning sounds
- Hybrid tax credit (U.S.)
- List of electric cars currently available
- List of modern production plug-in electric vehicles
- Neighborhood electric car
- New energy vehicles in China
- Plug In America
- Plug-in hybrid vehicle, (PHEV)
- RechargeIT (Google.org PHEV program)
- Renewable energy by country
References
- 1 2 3 4 "Nissan delivers 300,000th Nissan LEAF" (Press release). Yokohama: Nissan. 2018-01-08. Retrieved 2018-01-14.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Cobb, Jeff (2017-01-09). "Nissan's Quarter-Millionth Leaf Means It's The Best-Selling Plug-in Car In History". HybridCars.com. Retrieved 2017-01-10. As of December 2016, the Nissan Leaf is the world's best-selling plug-in car in history with more than 250,000 units delivered, followed by the Tesla Model S with over 158,000 sales, the Volt/Ampera family of vehicles with 134,500 vehicles sold, and the Mitsubishi Outlander PHEV with about 116,500 units sold through November 2016. These are the only plug-in electric cars so far with over 100,000 global sales.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 David B. Sandalow, ed. (2009). Plug-In Electric Vehicles: What Role for Washington? (1st. ed.). The Brookings Institution. pp. 2–5. ISBN 978-0-8157-0305-1. See definition on pp. 2.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 "Plug-in Electric Vehicles (PEVs)". Center for Sustainable Energy, California. Retrieved 2010-03-31.
- ↑ "PEV Frequently Asked Questions". Duke Energy. Archived from the original on 2012-03-27. Retrieved 2010-12-24.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Cobb, Jeff (2017-01-16). "The World Just Bought Its Two-Millionth Plug-in Car". HybridCars.com. Retrieved 2017-01-17. An estimated 2,032,000 highway-legal plug-in passenger cars and vans have been sold worldwide at the end of 2016. The top selling markets are China (645,708 new energy cars, including imports), Europe (638,000 plug-in cars and vans), and the United States (570,187 plug-in cars). The top European country markets are Norway (135,276), the Netherlands (113,636), France (108,065), and the UK (91,000). Total Chinese sales of domestically produced new energy vehicles, including buses and truck, totaled 951,447 vehicles. China was the top selling plug-in car market in 2016, and also has the world's largest stock of plug-in electric cars.
- ↑ John Voelcker (January 15, 2016). "Who Sold The Most Plug-In Electric Cars In 2015? (It's Not Tesla Or Nissan)". Green Car Reports.
- ↑ John Voelcker (February 10, 2017). "China's BYD built more plug-in cars than any other maker last year". Green Car Reports.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Cobb, Jeff (2016-12-12). "Chevy Volt and Nissan Leaf Celebrate Their Sixth-Year Anniversary". HybridCars.com. Retrieved 2016-12-14. Global cumulative sales of plug-in electric vehicles totaled about 1.9 million units through November 2016. The Nissan Leaf is the world's leading plug-in car with more than 240,000 units delivered. As of November 2016, the Tesla Model S ranks next with over 151,000, followed by the Vollt/Ampera family of vehicles with 130,500 vehicles sold including over 10,000 Opel/Vauxhall Amperas sold in Europe, the Mitsubishi Outlander PHEV with about 116,500 units, and the Toyota Prius PHV with about 76,200.
- 1 2 3 Vaughan, Adam (2017-12-25). "Electric and plug-in hybrid cars whiz past 3m mark worldwide". The Guardian. Retrieved 2018-01-20. "The number of fully electric and plug-in hybrid cars on the world’s roads passed the 3 million mark in November 2017."
- 1 2 3 4 5 Staff (February 2017). "Global Plug-in Sales for 2016". EV-Volumes.com. Retrieved 2017-02-05.
- 1 2 3 Cobb, Jeff (2018-01-22). "Tesla Quietly Sold 200,000th Model S Last Year". HybridCars.com. Retrieved 2018-01-22. "Tesla sold its 200,000 Model S in the fourth quarter of 2017, in October or early November, becoming the second plug-in car to cross this sales threshold after the Nissan Leaf (300,000 units by early 2017). As of December 2017, Tesla reported global sales of 212,874 Model S cars."
- ↑ Mark Kane (January 26, 2018). "BYD #1 In World For Plug-In Electric Car Sales In 2017, Beats Tesla Again". INSIDEEVs.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Jose Pontes (2018-01-18). "China December 2017". EV Sales. Retrieved 2018-01-19. Sales of plug-in electric cars in China, including imports, totaled 600,174 units in 2017. The BAIC EC-Series was the top selling plug-in with 78,079 units sold in China, making the city car the world's top selling plug-in car in 2017. The top selling plug-in hybrid was the BYD Song PHEV with 30,920 units. BYD Auto was the top selling car manufacturer. Foreign brands captured only about 4% of plug-in sales in 2017, with about half by Tesla. The Chinese plug-in car market represented roughly half of the 1.2 million plug-ins sold worldwide in 2017.
- 1 2 3 4 Cobb, Jeff (2017-01-11). "America's Plug-in Car Sales Were Their Best Ever in 2016". HybridCars.com and Baum & Associates. Retrieved 2017-01-12. Plug-in electric car sales in the U.S. totaled 157,181 units, up 37.6% from 2015 (114,248). The plug-in car segment achieved an all-time high market share of 0.90% of new car sales in 2016. December sales totaled a record monthly volume of 23,288 units and also achieved a record monthly market share of 1.39% of new car sales. The top selling model for the second year in a row was the Tesla Model S with 29,156 units sold in 2016, followed by the Chevrolet Volt (24,739), Tesla Model X (18,028), Ford Energi Fusion (15,938), and the Nissan Leaf (14,006). As of December 2016, cumulative sales totaled 570,187 plug-in cars since 2008, with the Chevrolet Volt as the all-time best selling plug-in car with 113,489 units. The Tesla Model S ranks third with an estimated 92,317 units since its inception in 2012.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Cobb, Jeff (2018-01-04). "December 2017 Dashboard". HybridCars.com and Baum & Associates. Retrieved 2018-01-21. Plug-in electric car sales in the U.S. totaled 194,479 units in 2017, consisting of 104,487 all-electric cars and 89,992 plug-in hybrids. The plug-in car segment achieved a market share of 1.13% of new car sales.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Jose, Pontes (2018-01-28). "Europe December 2017". EVSales.com. Retrieved 2018-01-29. "European sales totaled 306,143 plug-in cars in 2017. The Renault Zoe was the top selling plug-in car with 31,410 units delivered, followed by the BMW i3 with 20,855 and the Mitsubishi Outlander PHEV with 19,189."
- 1 2 3 Ayre, James (2018-01-04). "Over 50% Of New Car Registrations In Norway In 2017 = Plug-In Vehicles Or Hybrids". CleanTechnica.com. Retrieved 2018-01-11.
There are now more than 140,000 fully electric cars (BEVs) on Norwegian roads. When plug-in hybrids (PHEVs) are added, the number of electric cars surpasses 200,000.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Cobb, Jeff (2016-12-27). "China Takes Lead As Number One In Plug-in Vehicle Sales". HybridCars.com. Retrieved 2017-01-06. As of November 2016, cumulative sales of plug-in electric vehicles in China totaled 846,447 units, including passenger and commercial vehicles, making the country the world's leader in overall plug-in electric vehicle sales. With cumulative sales of about 600,000 plug-in electric passenger cars through November 2016, China is also the global leader in the plug-in passenger vehicle segment, ahead of Europe and the U.S.
- 1 2 3 4 Liu Wanxiang (2017-01-12). "中汽协:2016年新能源汽车产销量均超50万辆,同比增速约50%" [China Auto Association: 2016 new energy vehicle production and sales were over 500,000, an increase of about 50%] (in Chinese). D1EV.com. Retrieved 2017-01-12. Chinese sales of new energy vehicles in 2016 totaled 507,000, consisting of 409,000 all-electric vehicles and 98,000 plug-in hybrid vehicles.
- 1 2 3 4 Automotive News China (2018-01-16). "Electrified vehicle sales surge 53% in 2017". Automotive News China. Retrieved 2018-01-19. Chinese sales of domestically-built new energy vehicles in 2017 totaled 777,000, consisting of 652,000 all-electric vehicles and 125,000 plug-in hybrid vehicles. Sales of domestically-produced new energy passenger vehicles totalled 579,000 units, consisting of 468,000 all-electric cars and 111,000 plug-in hybrids. Only domestically built all-electric vehicles, plug-in hybrids and fuel cell vehicles qualify for government subsidies in China.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 International Energy Agency (IEA), Clean Energy Ministerial, and Electric Vehicles Initiative (EVI) (June 2017). "Global EV Outlook 2017: Two million and counting" (PDF). IEA Publications. Retrieved 2018-01-20. See pp. 5–7, 12–22, 27–28, and Statistical annex, pp. 49–51.
- ↑ "Electric Vehicles: Turning Buzz into Reality". European Automobile Manufacturers Association. 2010-02-09. Retrieved 2010-04-23.
- ↑ "Notice 2009–89: New Qualified Plug-in Electric Drive Motor Vehicle Credit". Internal Revenue Service. 2009-11-30. Retrieved 2010-04-01.
- ↑ "Consumer Energy Tax Incentives: Plug-In Hybrid Conversion Kits". U.S. Department of Energy. Retrieved 2010-04-01.
- 1 2 "An Increasing Number of Member States Levy CO2-Based Taxation or Incentivise Electric Vehicles". European Automobile Manufacturers Association. 2010-04-21. Retrieved 2010-04-23.
- ↑ "Plug-in Vehicle Tracker: What's Coming, When". Plug In America. Retrieved 2012-01-15.
- ↑ "All-Electric Vehicle Basics". Alternative Fuels & Advanced Vehicles Data Center, US DoE. Retrieved 2010-12-29.
- ↑ Kurani; et al. (2007-10-16). "Driving Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicles: Reports from U.S. Drivers of HEVs converted to PHEVs, circa 2006–07" (PDF). Institute of Transportation Studies, University of California, Davis. Retrieved 2010-12-29. See definitions in pp. 1–2.
- ↑ Matthew A. Kromer & John B. Heywood (May 2007). "Electric Powertrains: Opportunities and Challenges in the U.S. Light-Duty Vehicle Fleet" (PDF). Sloan Automotive Laboratory, Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Retrieved 2010-12-29. See definitions in pp. 30–31.
- 1 2 "Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle Basics". Alternative Fuels & Advanced Vehicles Data Center, US DoE. Retrieved 2010-12-29.
- ↑ "Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV)". Center for Energy and the Global Environment, Virginia Tech. Archived from the original on 2011-07-20. Retrieved 2010-12-29.
- ↑ "What Is A Plug-in Hybrid Car?". HybridCars.com. Retrieved 2010-12-29.
- 1 2 "How to Get a Plug-In Hybrid". CalCars. Retrieved 2010-12-29.
- ↑ "Plug-in Hybrid Conversions". HybridCars.com. Retrieved 2010-12-29.
- ↑ "Top 7 Issues for an Electric Car Conversion". HybridCars.com. 2009-06-02. Archived from the original on 2011-05-27. Retrieved 2010-12-29.
- ↑ PRTM Management Consultants, Inc. (April 2011). "The China New Energy Vehicles Program – Challenges and Opportunities" (PDF). World Bank. Retrieved 2013-04-22. See Acronyms and Key Terms, pp. v
- ↑ "Investing in Charging Infrastructure for Plug-In Electric Vehicles - Center for American Progress". Center for American Progress. Retrieved 2018-08-30.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Saurin D. Shah (2009). David B. Sandalow, ed. Chapter 2: Electrification of Transport and Oil Displacement (1st ed.). The Brookings Institution. pp. 29, 37 and 43. ISBN 978-0-8157-0305-1. in "Plug-in Electric Vehicles: What Role for Washington?"
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Sperling, Daniel and Deborah Gordon (2009). Two billion cars: driving toward sustainability. Oxford University Press, New York. pp. 22–26 and 114–139. ISBN 978-0-19-537664-7.
- ↑ Emily Masamitsu (2009-10-01). "How Much Is That Hybrid Electric Really Saving You?". Popular Mechanics. Retrieved 2010-07-11.
- ↑ "Electric Power Monthly: June 2010 Edition". U.S. Energy Information Administration. June 2010. Retrieved 2010-07-11. Prices correspond to average for March 2010 for the U.S. energy generation mix that month.
- ↑ Eric Evarts (2011-12-08). "Leaf, Volt tests show electric cars cost less per mile to operate". Consumer Reports. Retrieved 2011-12-10.
- ↑ Edison Electric Institute (EEI) (April 2012). "Plug-In Electric Vehicles: Fueled by Affordable, Diverse, Domestic Energy" (PDF). EEI. Retrieved 2012-05-26.
- ↑ Edison Electric Institute(EEI) (April 2012). "National Average Monthly Gasoline Retail Price v. Monthly Residential Electricity Price 1976–2012" (PDF). EEI. Retrieved 2012-05-26.
- ↑ "The Dirty Truth about Plug-in Hybrids, Made Interactive". Scientific American. July 2010. Retrieved 2010-10-16. Click on the map to see the results for each region.
- ↑ Palm, Erik (2009-05-01). "Study: Electric cars not as green as you think | Green Tech – CNET News". News.cnet.com. Retrieved 2010-04-18.
- 1 2 3 "Ricardo study finds electric and hybrid cars have a higher carbon footprint during production than conventional vehicles, but still offer a lower footprint over the full life cycle". Green Car Congress. 2011-06-08. Retrieved 2011-06-11.
- ↑ Mike Millikin (2014-03-13). "Volkswagen: e-mobility and sustainability; Part 1, the e-Golf and Golf GTE". Green Car Congress. Retrieved 2014-03-13. See the infograph CO2 emissions over the full life-cycle (t CO2e).
- ↑ "Uniti Sweden: the diversity behind the electric car of the future". euronews. 2017-04-08. Retrieved 2017-06-12.
- ↑ "Partnership with Siemens for fully-automated car factory". Uniti. 2017-03-16. Retrieved 2017-06-12.
- 1 2 3 4 5 U. S. Environmental Protection Agency (October 2014). "Light-Duty Automotive Technology, Carbon Dioxide Emissions, and Fuel Economy Trends: 1975 Through 2014" (PDF). EPA. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-10-18. Retrieved 2014-10-11. See Table 7.2 – MY 2014 Alternative Fuel Vehicle Powertrain and Range; pp. 98; Table 7.3 for overall fuel economy (mpg-e), pp. 100; Table 7.4 for tailpipe CO2 emissions, pp. 102; and Table 7.5 for upstream CO2 Emission, pp. 105.
- ↑ Mike Millikin (2014-10-11). "EPA Trends on EVs and PHEVs; beginning of a "measurable and meaningful impact" on new vehicle fuel economy and emissions". Green Car Congress. Retrieved 2014-10-11.
- ↑ United States Environmental Protection Agency and U.S. Department of Energy (2015-12-18). "Model Year 2016 Fuel Economy Guide - Electric vehicles & Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles" (PDF). fueleconomy.gov. Retrieved 2015-12-18. See pp. 27–28 for all-electric vehicles and pp. 30–31 for plug-in hybrid electric vehicles. The average 2016 vehicle gets 25 mpg
- ↑ United States Environmental Protection Agency and U.S. Department of Energy (2016-11-16). "Model Year 2017 Fuel Economy Guide - Electric vehicles & Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles" (PDF). fueleconomy.gov. Retrieved 2016-11-19. pp. 32–36.
- 1 2 Don Anair & Amine Mahmassani (April 2012). "State of Charge: Electric Vehicles' Global Warming Emissions and Fuel-Cost Savings across the United States" (PDF). Union of Concerned Scientists. Retrieved 2012-04-16. pp. 16–20.
- 1 2 Paul Stenquist (2012-04-13). "How Green Are Electric Cars? Depends on Where You Plug In". The New York Times. Retrieved 2012-04-14.
- ↑ Paul Stenquist (2012-04-13). "Carbon In, Carbon Out: Sorting Out the Power Grid". The New York Times. Retrieved 2012-04-14. See map for regional results
- ↑ Paul Stenquist (2012-04-13). "When it Comes to Carbon Dioxide, Lower is Better and Zero is Perfect". The New York Times. Retrieved 2012-04-14.
- ↑ Paul Stenquist (2014-09-19). "Coal Fades, So Electrics Get Cleaner". The New York Times. Retrieved 2014-10-12.
- ↑ Don Anair (2014-09-16). "How do EVs Compare with Gas-Powered Vehicles? Better Every Year…". Union of Concerned Scientists (UCS). Retrieved 2014-10-12.
- 1 2 Nealer, Rachael; Reichmuth, David; Anair, Don (November 2015). "Cleaner Cars from Cradle to Grave: How Electric Cars Beat Gasoline Cars on Lifetime Global Warming Emissions" (PDF). Union of Concerned Scientists (UCS). Retrieved 2014-11-22.
- ↑ Sebastian Blanco (2015-11-17). "UCS: Well-to-wheel, EVs cleaner than pretty much all gas cars". Autoblog (website). Retrieved 2015-11-22.
- ↑ "The ZEV's invisible tailpipe – Are zero-emission vehicles cleaner than petrol cars? It all depends..." The Economist. 2014-11-24. Retrieved 2014-12-08.
- 1 2 Graff Zivina, Joshua S.; Kotchenb, Matthew J.; Mansur, Erin T. (November 2014). "Spatial and temporal heterogeneity of marginal emissions: Implications for electric cars and other electricity-shifting policies". Journal of Economic Behavior and Organization. 107 (Part A): 248–268. doi:10.1016/j.jebo.2014.03.010. Published on line 2014-03-24. See pp. 251
- 1 2 3 "India named least green country for electric cars". The Guardian. 2013-02-07. Retrieved 2013-07-08.
- 1 2 Michaël Torregrossa (2013-03-21). "Véhicules électriques et émissions de CO2 – de 70 à 370 g CO2/km selon les pays" [Electric Vehicles and CO2 emissions – 70 to 370 g CO2/km by country] (in French). Association pour l'Avenir du Véhicule Electrique Méditerranéen (AVEM). Retrieved 2013-07-08.
- 1 2 3 Lindsay Wilson (February 2013). "Shades of Green: Electric Cars' Carbon Emissions Around the Globe". Shrink That Footprint. Retrieved 2013-07-08.
- 1 2 Mitchell, William J.; Borroni-Bird, Christopher; Burns, Lawrence D. (2010). Reinventing the Automobile: Personal Urban Mobility for the 21st Century (1st. ed.). The MIT Press. pp. 85–95. ISBN 978-0-262-01382-6. See Chapter 5: Clean Smart Energy Supply.
- 1 2 R. James Woolsey and Chelsea Sexton (2009). David B. Sandalow, ed. Chapter 1: Geopolitical Implications of Plug-in Vehicles (1st ed.). The Brookings Institution. pp. 11–21. ISBN 978-0-8157-0305-1. in "Plug-in Electric Vehicles: What Role for Washington?"
- ↑ "High oil prices disastrous for developing countries". Mongabay. 2007-09-12. Retrieved 2010-07-20.
- ↑ "Impact of High Oil Prices on African Economies" (PDF). African Development Bank. 2009-07-29. Retrieved 2010-07-20.
- ↑ Andrew Grove and Robert Burgelman (December 2008). "An Electric Plan for Energy Resilience". McKinsey Quarterly. Archived from the original on 2014-08-25. Retrieved 2010-07-20.
- 1 2 Jon Wellinhoff (2009). David B. Sandalow, ed. Chapter 4: The CashBack Car (1st ed.). The Brookings Institution. pp. 65–82. ISBN 978-0-8157-0305-1. in "Plug-in Electric Vehicles: What Role for Washington?"
- ↑ "Car Prototype Generates Electricity, And Cash". Science Daily. December 9, 2007. Retrieved 2010-07-17.
- ↑ Cleveland, Cutler J.; Morris, Christopher (2006). Dictionary of Energy. Amsterdam: Elsevier. p. 473. ISBN 0-08-044578-0.
- ↑ "Pacific Gas and Electric Company Energizes Silicon Valley With Vehicle-to-Grid Technology". Pacific Gas & Electric. 2007-04-07. Archived from the original on 2009-12-09. Retrieved 2011-01-12.
- ↑ National Research Council (2010). "Transitions to Alternative Transportation Technologies—Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles". The National Academies Press. Retrieved 2010-03-03.
- ↑ Jad Mouawad & Kate Galbraith (2009-12-14). "Study Says Big Impact of the Plug-In Hybrid Will Be Decades Away". New York Times. Retrieved 2010-03-04.
- ↑ Paul Stenquist (2012-06-25). "Tesla Model S Offers a Lesson in Electric-Vehicle Economics". The New York Times. Retrieved 2012-06-25.
- ↑ Siddiq Khan & Martin Kushler (June 2013). "Plug-in Electric Vehicles: Challenges and Opportunities" (PDF). American Council for an Energy-Efficient Economy. Retrieved 2013-07-09. ACEEE Report Number T133.
- 1 2 3 Randall, Tom (2016-02-25). "Here's How Electric Cars Will Cause the Next Oil Crisis". Bloomberg News. Retrieved 2016-02-25. See embedded video.
- ↑ Henry Lee & Grant Lovellette (July 2011). "Will Electric Cars Transform the U.S. Vehicle Market?". Belfer Center for Science and International Affairs, Kennedy School of Government. Retrieved 2011-08-07.
- 1 2 3 Henry Lee & Grant Lovellette (July 2011). "WillElectric Cars Transform the U.S. Vehicle Market?" (PDF). Belfer Center for Science and International Affairs, Kennedy School of Government. Retrieved 2011-08-07. Discussion Paper #2011-08, pages 9–18.
- ↑ Nikki Gordon-Bloomfield (2013-06-13). "Power Institute Study: Total Cost of Ownership Cheaper for Electric Cars". Retrieved 2013-06-13.
- ↑ Alan L. Madian; et al. (2009). David B. Sandalow, ed. Chapter 5: The Impact of Plug-in Hybrids on U.S. Oil Use and Greenhouse Gas Emissions. The Brookings Institution. p. 96. ISBN 978-0-8157-0305-1. in "Plug-in Electric Vehicles: What Role for Washington?"
- 1 2 Kevin Morrow; et al. (November 2008). "Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure Review. Final Report" (PDF). U.S. Department of Energy Vehicle Technologies Program. Retrieved 2010-03-07.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Todd Woody & Clifford Krauss (2010-02-14). "Cities Prepare for Life With the Electric Car". New York Times. Retrieved 2010-03-07.
- ↑ "Moving Forward in Raleigh PGR Plan". Project Get Ready. Archived from the original on 2009-03-07. Retrieved 2010-03-07.
- 1 2 RechargeIT Driving Experiment – RechargeIT is a program sponsored by Google.org, a non-profit created by Google. Archived 2010-12-09 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ Adam Palin (2013-11-19). "Infrastructure: Shortage of electric points puts the brake on sales". Financial Times. Retrieved 2013-12-28.
- ↑ KredEx (2013-02-20). "Estonia becomes the first in the world to open a nationwide electric vehicle fast-charging network". Estonian World. Retrieved 2013-12-28.
- ↑ Adam Vaughan (2013-02-20). "Estonia launches national electric car charging network". The Guardian. Retrieved 2013-12-28.
- ↑ Garrick, David (2016-03-16). "Car2Go switching electric cars to gas". The San Diego Union-Tribune. Retrieved 2016-03-25.
- ↑ "Renault-Nissan and Project Better Place Sign MoU for Mass Marketed EVs in Israel; Implementing New Ownership Model". Green Car Congress. 2008-01-28. Retrieved 2010-05-16.
- ↑ Shai Agassi, David Pogue, Gavin Newsom (2009-03-19). Making The World A 'Better Place' (YouTube). San Francisco, CA: CBS News Sunday Morning; CBS Interactive, Inc. Event occurs at 3:45.
Shai Agassi: "We [Better Place] don't let you [the customer] buy a battery; we [Better Place] buy the battery.
- ↑ Woody, Todd (2009-09-15). "Better Place Unveils Electric-Car Software". New York Times. Retrieved 2010-05-16.
- ↑ "Better Place. The Renault Fluence ZE". Better Place. 2010-10-22. Archived from the original on 2010-09-12. Retrieved 2010-10-22.
- ↑ Jim Motavalli (2011-07-29). "Plug-and-Play Batteries: Trying Out a Quick-Swap Station for E.V.'s". The New York Times. Retrieved 2013-06-23.
- ↑ Isabel Kershner (2013-05-26). "Israeli Venture Meant to Serve Electric Cars Is Ending Its Run". The New York Times. Retrieved 2013-05-27.
- ↑ Niv Elis (2013-05-26). "Death of Better Place: Electric car co. to dissolve". The Jerusalem Post. Retrieved 2013-05-30.
- ↑ Sebastian Blanco (2009-09-27). "REPORT: Tesla Model S was designed with battery swaps in mind". Autoblog Green. Retrieved 2013-06-22.
- 1 2 Mark Rogowsky (2013-06-21). "Tesla 90-Second Battery Swap Tech Coming This Year". Forbes. Retrieved 2013-06-22.
- ↑ "Tesla Motors demonstrates battery swap in the Model S". Green Car Congress. 2013-06-21. Retrieved 2013-06-22.
- ↑ "Sunny days ahead for plastic solar modules". Automotive Engineering International. 2009-10-14. Retrieved 2010-07-15.
- ↑ Carpenter, Susan (2010-03-30). "Nissan Leaf's promise: An affordable electric". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved 2010-07-15.
- ↑ YouTube (2009-11-30). "Nissan Leaf electric vehicle – CNET". YouTube. Retrieved 2010-07-15.
- ↑ "Reva Revs Phone-Controlled Charging for Electric Cars". Earth2tech.com. 2009-08-09. Retrieved 2010-07-15.
- ↑ "Reva remote charge to be unlocking battery reserve remotely". AutoblogGreen. 2009-09-10. Retrieved 2010-07-15.
- ↑ Csere, Csaba (2012-10-31). Car and Driver: Tested : 2012 Fisker Karma – Review – CAR and DRIVER. Beverly Hills, CA: Car and Driver magazine. Event occurs at 13m30s.
- ↑ Brian Cooley. "2011 Nissan Leaf – CNET". CNET CNET Car Tech. Retrieved 2011-01-09.
- ↑ Jim Motavalli (2010-07-08). "Will Electric Cars Cause More Summer Power Outages?". New York Times. Retrieved 2010-07-11.
- ↑ David Biello (2013-06-18). "Will You or the Grid Control Your Electric Car?". Scientific America. Retrieved 2013-06-23.
- ↑ Nuckols, Ben (3 March 2007). "Blind people: Hybrid cars pose hazard". USA Today. Retrieved 2009-05-08.
- 1 2 "Electric cars and noise: The sound of silence". Economist. 7 May 2009. Retrieved 2009-05-08.
- ↑ "Incidence of Pedestrian and Bicyclist Crashes by Hybrid Electric Passenger Vehicles" (PDF). National Highway Traffic Safety Administration. September 2009. Retrieved 2009-10-05. Technical Report DOT HS 811 204
- ↑ "Hybrid Cars Are Harder to Hear". University of California, Riverside. 2008-04-28. Retrieved 2010-07-03.
- ↑ Sarah Simpson (August 2009). "Are Hybrid Cars Too Quiet to Be Safe for Pedestrians?". Scientific American. Retrieved 2010-07-03.
- ↑ "Nissan demonstrates the affordable, 100% electric, zero-emission Nissan LEAF". Nissan. 2010-06-11. Archived from the original on 2010-06-14. Retrieved 2010-06-15.
- ↑ "Nissan Leaf will break the EV silence with a digital whistle [w/video]". Autoblog.com. 2010-06-14. Retrieved 2010-06-15. The article has a video with the Leaf warning sounds.
- ↑ "GM Says Volt Crew Working to Resolve 'Silent EV' Sound Safety Issue". Edmunds.com. 2009-11-25. Archived from the original on 2009-11-29. Retrieved 2010-06-15.
- ↑ Jim Motavalli (2009-10-13). "Hybrid Cars May Include Fake Vroom for Safety". New York Times. Retrieved 2010-07-02.
- ↑ Anthony Faccenda (2013-01-07). "NHTSA proposes minimum sound requirements for electric and hybrid vehicles". Torque News. Retrieved 2013-03-16.
- ↑ Gabe Nelson (2013-03-01). "Louder EVs may turn off drivers, automakers say". Automotive News. Retrieved 2013-03-21.
- ↑ "TMC to Sell Approaching Vehicle Audible System for 'Prius'". Toyota Motor Company News Release. 2010-08-24. Retrieved 2010-08-25.
- ↑ American Council of the Blind Press Release (2010-12-16). "Critical Pedestrian Safety Legislation Moves to White House for President's Signature". PR Newswire. Retrieved 2010-12-17.
- ↑ "S. 841 Pedestrian Safety Enhancement Act of 2010". Legislative Digest. 2010-12-15. Archived from the original on 2010-12-22. Retrieved 2010-12-17.
- ↑ Larry Dignan (2010-12-16). "Hybrid, electric vehicles to become louder for pedestrian safety". SmartPlanet.com. Archived from the original on 2010-12-19. Retrieved 2010-12-17.
- ↑ Shepardson, David (2018-02-26). "U.S. finalizes long-delayed 'quiet cars' rule, extending deadline". Reuters. Retrieved 2018-03-04.
- ↑ Ray Massey (2014-04-02). "Silent but deadly: EU rules all electric cars must make artificial engine noise". Daily Mail. Retrieved 2014-04-03.
- ↑ European Commission Press Release (2014-04-02). "Commission welcomes Parliament vote on decreasing vehicle noise". European Commission. Retrieved 2014-04-03.
- ↑ Spotnitz, R.; Franklin, J. (2003). "Abuse behavior of high-power, lithium-ion cells". Journal of Power Sources. 113: 81–100. doi:10.1016/S0378-7753(02)00488-3.
- ↑ "Lithium Ion technical handbook" (PDF). Gold Peak Industries Ltd. November 2003. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2007-10-07.
- ↑ Winter, M.; Brodd, J. (2004). "What Are Batteries, Fuel Cells, and Supercapacitors?". Chemical Reviews (PDF)
|format=requires|url=(help). 104 (10): 4245–69. doi:10.1021/cr020730k. PMID 15669155. - ↑ "Apple to recall 1.8 million notebook batteries – Aug. 24, 2006". cnn.com.
- ↑ "PC Notebook Computer Batteries Recalled Due to Fire and Burn Hazard". Archived from the original on 2013-01-08.
- ↑ "Lenovo and IBM Announce Recall of ThinkPad Notebook Computer Batteries Due to Fire Hazard". Archived from the original on 2013-01-08.
- ↑ "THE INQUIRER – News, reviews and opinion for tech buffs". theinquirer.net.
- ↑ "Dreamliner: Boeing 787 planes grounded on safety fears". BBC News. Retrieved 2013-06-23.
- ↑ "Japanese airlines ground Boeing 787s after emergency landing". Reuters. 2013-01-16. Retrieved 2013-06-23.
- ↑ China Autoweb (2012-05-28). "Initial details on fiery crash involving BYD e6 that killed 3". Green Car Congress. Retrieved 2012-08-13.
- ↑ Christopher Jensen (2013-10-02). "Tesla Says Car Fire Started in Battery". The New York Times. Retrieved 2013-10-05.
- ↑ Steven Russolillo (2013-10-04). "Musk Explains Why Tesla Model S Caught on Fire". The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved 2013-10-05.
- ↑ Jaclyn Trop (2013-11-07). "Another Fire Raises Questions for Tesla". The New York Times. Retrieved 2013-11-10.
- ↑ Neil Roland (2012-08-09). "Feds Researching Fire Risks from EV Batteries". MSN Autos. Retrieved 2013-06-23.
- ↑ General Motors (2011-01-19). "Detroit First Responders Get Electric Vehicle Safety Training". General Motors News. Retrieved 2011-11-12.
- ↑ Nissan (2010). "2011 LEAF First Responder's Guide" (PDF). Nissan North America. Retrieved 2011-12-20.
- 1 2 Irving Mintzer (2009). David B. Sandalow, ed. Chapter 6: Look Before You Leap: Exploring the Implications of Advanced Vehicles for Import Dependence and Passerger Safety (PDF). The Brookings Institution. pp. 107–126. ISBN 978-0-8157-0305-1. in "Plug-in Electric Vehicles: What Role for Washington?"
- 1 2 3 4 5 Clifford Krauss (2009-03-09). "The Lithium Chase". New York Times. Retrieved 2010-03-10.
- 1 2 Tim Folger (June 2011). "Rare Earth Elements: The Secret Ingredients of Everything". National Geographic. Retrieved 2011-06-12.
- 1 2 Alan Ohnsman (2011-01-14). "Toyota Readying Motors That Don't Use Rare Earths". Bloomberg. Retrieved 2011-01-19.
- ↑ Hiscock, Geoff (2015-11-18). "Electric vehicles, storage units drive prices up". The Nikkei. Retrieved 2016-02-29.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Simon Romero (2009-02-02). "In Bolivia, Untapped Bounty Meets Nationalism". New York Times. Retrieved 2010-02-28.
- 1 2 Jerry Garret (2010-04-15). "A Case for and Against Electric Cars". New York Times. Retrieved 2010-04-17.
- ↑ "Página sobre el Salar (Spanish)". Evaporiticosbolivia.org. Archived from the original on 2011-03-23. Retrieved 2010-11-27.
- ↑ Brendan I. Koerner (2008-10-30). "The Saudi Arabia of Lithium". Forbes. Retrieved 2011-05-12. Published on Forbes Magazine dated November 24, 2008.
- 1 2 3 "USGS Mineral Commodities Summaries 2009" (PDF). U. S. Geological Survey. January 2009. Retrieved 2010-03-07. See page 95.
- ↑ Hammond, C. R. (2000). The Elements, in Handbook of Chemistry and Physics 81st edition. CRC press. ISBN 0-8493-0481-4.
- ↑ "Japan To Offer Technical Aid On Lithium To Bolivia". Green Car Congress. 2010-09-12. Retrieved 2010-09-12.
- ↑ "S. Korean companies to help Bolivia develop lithium industries". Trading Markets. 2010-04-23. Retrieved 2010-09-12.
- ↑ Gaines, LL. Nelson, P. (2010). "Lithium-Ion Batteries: Examining Material Demand and Recycling Issues". Argonne National Laboratory. Retrieved 11 June 2016.
- ↑ "Study finds resource constraints should not be a limiting factor for large-scale EV battery production". Green Car Congress. 2011-06-17. Retrieved 2011-06-17.
- ↑ "University of Michigan and Ford researchers see plentiful lithium resources for electric vehicles". Green Car Congress. 2011-08-03. Retrieved 2011-08-11.
- 1 2 Keith Bradsher (2009-08-31). "China Tightens Grip on Rare Minerals". New York Times. Retrieved 2010-09-27.
- 1 2 3 "Rare earths and China – Dirty business". The Economist. 2010-09-30. Retrieved 2010-09-30.
- ↑ "Rare earths – Digging in". The Economist. 2010-09-02. Retrieved 2010-09-11.
- ↑ "Worries mount over China's 'rare earth' export ban". EurActiv.com. 2010-06-11. Retrieved 2010-09-11.
- ↑ Keith Bradsher (2010-09-23). "Amid Tension, China Blocks Crucial Exports to Japan". New York Times. Retrieved 2010-09-23.
- ↑ "Critical Materials Strategy" (PDF). U.S. Department of Energy. December 2010. Retrieved 2010-12-15.
- ↑ Keith Bradsher (2010-12-15). "U.S. Called Vulnerable to Rare Earth Shortages". New York Times. Retrieved 2010-12-15.
- ↑ Keith Bradsher (2010-12-28). "China to Tighten Limits on Rare Earth Exports". New York Times. Retrieved 2010-12-29.
- ↑ "H.R.6160 – Rare Earths and Critical Materials Revitalization Act of 2010". Open Congress. 2010-09-29. Archived from the original on 2010-10-15. Retrieved 2010-10-16.
- 1 2 3 James T. Areddy (2010-10-01). "U.S. Congress Spurs Rare Earth Race". Wall Street Journal. Retrieved 2010-10-16.
- ↑ "As Tensions Over Rare Earth Supplies Rise, New Solutions Are Beginning to Emerge". HybridCars.com. 2010-10-12. Retrieved 2010-10-16.
- ↑ "S. 3521: Rare Earths Supply Technology and Resources Transformation Act of 2010". Govtrack.us. Retrieved 2010-10-16.
- 1 2 3 4 Matt Ritchel (2015-11-24). "A Car Dealers Won't Sell: It's Electric". The New York Times. Retrieved 2015-11-28.
- 1 2 3 4 Eric Cahill & Dan Sperling (2014-11-03). "The Future Of Electric Vehicles Part 1: Car Dealers Hold The Key". Institute of Transportation Studies (ITS), at the University of California, Davis. Retrieved 2015-11-28.
- ↑ Cahill, Eric; Davies-Shawhyde, Jamie; Turrentine, Thomas S. (October 2014). "New Car Dealers and Retail Innovation in California's Plug-In Electric Vehicle Market". Institute of Transportation Studies (ITS), at the University of California, Davis. Retrieved 2015-11-29. Working Paper – UCD-ITS-WP-14-04. Click on the bar "Download PDF"
- ↑ Eric Evarts (2014-04-22). "Dealers not always plugged in about electric cars, Consumer Reports' study reveals". Consumer Reports. Retrieved 2015-11-29.
- ↑ "Growing Number of EU Countries Levying CO2 Taxes on Cars and Incentivizing Plug-ins". Green Car Congress. 2010-04-21. Retrieved 2010-04-23.
- ↑ "Global Incentives for EVs". My electric car Australia. Retrieved 2018-01-29.
- ↑ Patricia Leitón (2018-01-25). "Cuatro agencias están listas para ofrecer autos eléctricos exonerados apenas rija ley" [Four dealerships are ready to offer exempted electric cars as soon as the law goes into effect]. La Nación (San José) (in Spanish). Retrieved 2018-01-22.
- ↑ Sherry Boschert (2006). Plug-in Hybrids: The Cars that will Recharge America. New Society Publishers, Gabriola Island, Canada. ISBN 978-0-86571-571-4.
- ↑ Danny King (2011-06-20). "Neighborhood Electric Vehicle Sales To Climb". Edmunds.com Auto Observer. Retrieved 2012-02-05.
- ↑ Stephen Edelstein (2015-11-03). "Polaris Updates GEM Low-Speed Electric Vehicles". Green Car Reports. Retrieved 2015-11-22.
- ↑ JATO Dynamics (November 2015). "From Fiction to Reality: The Evolution of Electric Vehicles 2013 – 2015" (PDF). Valencia News. Retrieved 2015-11-21. pp. 5–7 and 13.
- 1 2 3 Jeff Cobb (2015-09-16). "One Million Global Plug-In Sales Milestone Reached". HybridCars.com. Retrieved 2015-09-16. Cumulative global sales totaled about 1,004,000 highway legal plug-in electric passenger cars and light-duty vehicles by mid-September 2015.
- ↑ Caroline Sasia (2017-10-17). "RENAULT-NISSAN-MITSUBISHI SPONSORS WOMEN'S FORUM GLOBAL MEETING". Alliance Renault-Nissan-Mitsubishi. Retrieved 2018-01-23.
During the Global Meeting, the Alliance, which recently reached the historic milestone of aggregate sales of 500,000 electric vehicles worldwide (Renault-Nissan-Mitsubishi).
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Cobb, Jeff (2017-01-26). "Tesla Model S Is World's Best-Selling Plug-in Car For Second Year In A Row". HybridCars.com. Retrieved 2017-01-26. See also detailed 2016 sales and cumulative global sales in the two graphs.
- 1 2 3 Sharan, Zachary (2017-02-04). "Tesla Model S & Nissan LEAF Clocked As World's Best-Selling Electric Cars In 2016". EV Volumes. CleanTechnica.com. Retrieved 2017-02-04.
- 1 2 Cobb, Jeff (2016-11-07). "China's BYD Becomes World's Third-Largest Plug-in Car Maker". HybridCars.com. Retrieved 2016-11-07.
- 1 2 3 "Top 10 Automakers by 2017 NEV Sales". Gasgoo China Automotive News. 2018-01-18. Retrieved 2018-01-29. "According to the data released by China Passenger Car Association (CPCA), BYD topped the rank with annual NEV delivery of 113,669 units, increasing 11% year on year. With NEV deliveries soaring 125% on an annual basis to 104,520 units, BAIC BJEV took the second place among the top ten automakers."
- 1 2 3 4 5 Kane, Mark (2018-01-26). "BYD #1 In World For Plug-In Electric Car Sales In 2017, Beats Tesla Again". InsideEVs.com. Retrieved 2018-01-29. "BYD sold 108,612 passenger plug-in cars in China in 2017, enough to make it the world's top selling plug-in car manufacturer for the third year in a row."
- ↑ Kane, Mark (2017-10-04). "Tesla Has Delivered More Than 250,000 EVs, ~55% In The U.S." InsideEVs.com. Retrieved 2017-10-06.
- ↑ "_Update_Letter_2017-3Q.pdf Tesla Third Quarter 2017 Update". Tesla. 2017-11-01. Retrieved 2018-01-10.
- ↑ "More than a quarter of a million electrified BMW Group vehicles on the roads after strong April sales growth" (Press release). Munich: BMW Group. 2018-05-15. Retrieved 2018-05-26.
- ↑ Cobb, Jeff (2016-01-12). "Tesla Model S Was World's Best-Selling Plug-in Car in 2015". HybridCars.com. Retrieved 2016-02-06. The Tesla Model S was the top selling plug-in electric car in 2015 with 50,366 units sold, followed by the Nissan Leaf (about 43,000), the Mitsubishi Outlander P-HEV (over 40,000), the BYD Qin (31,898) and the BMW i3 (24,057). The Model S is also the second-best seller ever with 107,148 sales since its mid-2012 launch, behind the Nissan Leaf and ahead of GM’s Volt/Ampera family, credited with 106,000 sales.
- ↑ John Voelcker (2016-01-15). "Who Sold The Most Plug-In Electric Cars In 2015? (It's Not Tesla Or Nissan)". Green Car Reports. Retrieved 2016-01-17. BYD Auto delivered 31,898 Qins, 18,375 Tangs, and 7,029 e6s during 2015. Added to that are small numbers of the T3 small commercial van and e5 battery-electric compact sedan, along with 2,888 Denza EV compact hatchbacks built by its joint venture with Daimler. Altogether, BYD sold a total of 61,722 light-duty plug-in electric vehicles in China in 2015.
- ↑ Natasha Li (2016-03-04). "Alternative Energy Vehicles Account HALF of BYD's Profits for the Very First Time in 2015". Gasgoo Automotive News. Retrieved 2016-03-07. BYD Auto delivered 69,222 new energy vehicles in China in 2015, including buses, of which, a total of 61,722 were passenger vehicles, mostly plug-in hybrids, led by the Qin and Tang.
- ↑ Jin Peiling (2017-01-10). "谁是2016年电动汽车市场的霸主?" [Who is the dominant electric vehicle market in 2016?] (in Chinese). Daily Observation Car. Archived from the original on 2017-01-16. Retrieved 2017-01-15. BYD sold more than 100,000 new energy passenger cars in China in 2016, about 30,000 more units than Tesla Motors. The BYD Tang was the top selling plug-in car in China in 2016 with 31,405 units delivered.
- ↑ Jose, Pontes (2018-01-29). "2017 Global Sales by OEM". EVSales.com. Retrieved 2018-01-29.
- 1 2 Justin Gerdes (2012-05-11). "The Global Electric Vehicle Movement: Best Practices From 16 Cities". Forbes. Retrieved 2014-10-20.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 International Energy Agency (IEA), Clean Energy Ministerial, and Electric Vehicles Initiative (EVI) (May 2016). "Global EV Outlook 2016: Beyond one million electric cars" (PDF). IEA Publications. Retrieved 2016-09-07. See pp. 4–5, and 24–25 and Statistical annex, pp. 34–37.
- ↑ Clark, Pilita; Campbell, Peter (2016-08-31). "Motor Industry: Pressure on the Pump". Financial Times. Retrieved 2016-09-01.
- 1 2 3 Argonne National Laboratory, United States Department of Energy (2016-03-28). "Fact #918: March 28, 2016 – Global Plug-in Light Vehicles Sales Increased By About 80% in 2015". Office of Energy Efficiency & Renewable Energy. Retrieved 2016-03-29.
- 1 2 Nic Lutsey (2015-09-29). "Global milestone: The first million electric vehicles". International Council on Clean Transportation (ICCT). Retrieved 2015-10-10.
- ↑ Voelcker, John (2016-11-02). "Electric car sales remain ahead of hybrids after five years". Green Car Reports. Retrieved 2016-11-05.
- ↑ "The Electric Vehicle World Sales Database: Stable 60:40 Ratio". EV-Volumes. Archived from the original on 2016-10-17. Retrieved 2016-10-17.
- ↑ EVvolumes.com (January 2018). "Global Plug-in Sales for 2017-Q4 and the Full Year (prelim.)". EVvolumes.com. Retrieved 2018-02-17. Global registrations totaled around 1.2 million units in 2017, 57 % higher than 2016. These include all global BEV and PHEV passenger cars sales, light trucks in USA/Canada and light commercial vehicle in Europe. In 2017, 66 % of sales were pure electric (BEV) and 34 % were plug-in hybrids (PHEV). The segment market share was 1.3%, and in December the global plug-in share touched the 2 % mark for the first time.
- ↑ Shahan, Zachary (2016-11-22). "1 Million Pure EVs Worldwide: EV Revolution Begins!". Clean Technica. Retrieved 2016-11-24.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 Cobb, Jeff (2017-01-17). "Top 10 Plug-in Vehicle Adopting Countries of 2016". HybridCars.com. Retrieved 2017-01-18.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Cobb, Jeff (2016-01-18). "Top Six Plug-in Vehicle Adopting Countries – 2015". HybridCars.com. Retrieved 2016-02-12. About 520,000 highway legal light-duty plug-in electric vehicles were sold worldwide in 2015, with cumulative global sales reaching 1,235,000. The United States was the leading market with 411,120 units sold since 2008, followed by China with 258,328 units sold since 2011. Japan ranks third, followed by the Netherlands (88,991), Norway (77,897), France (74,291), and the UK (53,254). Over 21,000 units were sold in Japan in 2015.
- ↑ Berman, Brad (2016-02-13). "US Falls Behind Europe and China in Global Plug-in Vehicle Market". Plugincars.com. Retrieved 2016-02-16.
- 1 2 3 4 King, Danny (2016-12-29). "China far ahead of US, Europe in total electric vehicle sales". Autoblog.com. Retrieved 2017-01-08.
Last year, China overtook both the US and Europe in annual sales of electric vehicles and plug-in hybrids. This year, it will move ahead of both the US and Europe in cumulative plug-in vehicle sales.
- 1 2 Cobb, Jeff (2016-05-11). "China Reports 500,000th Plug-in Vehicle Sold". HybridCars.com. Retrieved 2016-05-12. The stock of new energy vehicles sold in China since 2011 passed the 500,000 unit milestone in March 2016, consisting of 366,219 all-electric vehicles (72.9%) and 136,353 plug-in hybrids (27.1%). With 31,772 NEVs sold in April 2016, cumulative sales totaled 534,344 NEVs between January 2011 and April 2016.
- ↑ "Global Electric Bus Market 2015 – Size, Share, Development, Growth and Demand Forecast to 2020". Research and Markets (Press release). Dublin: Reuters. 2016-02-03. Archived from the original on 2016-02-16. Retrieved 2016-02-10.
- ↑ Jose, Pontes (2017-01-31). "Markets Roundup December 2016 (Special Edition)". EVSales.com. Retrieved 2017-02-08. For countries with top PEV market share in 2016 see "II. Engines of Growth: By EV share - Hong Kong ~5%, Iceland 4.6%, Switzerland 1.8%, Belgium 1.8, and 1.6% Austria.
- ↑ Jose, Pontes (2016-02-03). "Markets Roundup December 2015 (Special Edition)". EVSales.com. Retrieved 2016-02-17. For countries with top PEV market share in 2015 see "Engines of Growth:" Hong Kong 4.84%, Denmark 2.29%, Sweden 2.62%, and Switzerland 1.98%.
- 1 2 Jeff Cobb (2015-02-18). "Top 6 Plug-In Vehicle Adopting Countries – 2014". HybridCars.com. Retrieved 2015-02-18. </ref ''>A total of 303,866 new passenger vehicles were registered in 2014, and a total of 4,656 super clean cars, resulting in a PEV market share of 1.53% of new car sales.
- 1 2 3 Opplysningsrådet for Veitrafikken AS (OFV). "Bilsalget i 2017" [Car sales in 2017] (in Norwegian). OFV. Retrieved 2017-01-10.
- ↑ Jose, Pontes (2018-01-23). "Iceland December 2017". EVSales.com. Retrieved 2018-02-18.
- ↑ Bil Sweden (2018-01-08). "Definitiva nyregistreringar under 2017" [Definitive new registrations in 2017] (in Swedish). Bil Sweden. Retrieved 2018-01-31. Download the pdf file "PressRel1712_DEF.pdf" See tables: "Nyregistrerade supermiljöbilar december 2017", "Nyregistrerade miljöbilar per typ december 2017" and "Nyregistrerade eldrivna lätta lastbilar (högst 3,5 ton) per modell"
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "Statistics Electric Vehicles in the Netherlands" (PDF). Rijksdienst voor Ondernemend Nederland (RVO) - Dutch National Office for Enterprising -. RVO. January 2018. Retrieved 2018-01-16. With a total of 25,134 Mitsubishi Outlander P-HEVs registered by the end of December 2017, the plug-in hybrid is the all-time top selling plug-in electric vehicle in the Netherlands. The Tesla Model S is the best selling all-electric car with 8,028 units registered.
- ↑ Jose, Pontes (2016-01-29). "Iceland December 2015". EVSales.com. Retrieved 2016-02-17. Plug-in electric car sales in Iceland reached a market share of 2.93%f of new car sales in 2015.
- ↑ Jose Pontes (2018-01-09). "Switzerland December 2017". EV Sales. Retrieved 2018-02-18.
- 1 2 Bil Sweden (2015-01-02). "Nyregistreringar december 2014 (prel)" [New registrations in December 2014 (preliminar)] (in Swedish). Bil Sweden. Retrieved 2015-01-04. Download file "Nyregistreringar december 2014 (prel)" see tables: "Nyregistrerade supermiljöbilar december 2014" with summary of plug-in passenger car registrations by model for 2013 (revised) and 2014, and table "Nyregistrerade eldrivna lätta lastbilar (högst 3,5 ton) per modell:" for plug-in utility vans registrations for the same two years.
- ↑ Jose Pontes (2018-01-04). "Belgium December 2017". EV Sales. Retrieved 2018-02-18.
- ↑ Jose Pontes (2018-01-23). "Finland December 2017". EV Sales. Retrieved 2018-02-18.
- ↑ Jose Pontes (2015-01-10). "Denmark December 2014". EVSales.com. Retrieved 2015-03-15.
Denmark's PEV market shared in 2014 was 0.88% of total new car sales.
- ↑ Jose Pontes (2015-01-18). "Switzerland December 2014". EVSales.com. Retrieved 2015-03-15.
Switzerland's PEV market shared in 2014 was 0.75% of total new car sales.
- ↑ Jose Pontes (2018-01-17). "Austria December 2017". EV Sales. Retrieved 2018-02-18.
- 1 2 3 4 5 France Mobilité Électrique - AVERE France (2018-01-09). "Près de 31 000 véhicules électriques immatriculés en France en 2017 !" [Nearly 31,000 electric vehicles registered in France in 2017!] (in French). AVERE. Retrieved 2018-01-17. A total of 41,724 light-duty plug-in electric vehicles were registered in France in 2017 consisting of 24,910 all-electric cars, 6,011 electric utility vans and 10,803 plug-in hybrid cars. The plug-in car segment achieved a market share of 1.98% of new car registrations in the country in 2017.
- ↑ Statistik Austria (2016-03-16). "Kraftfahrzeuge – Neuzulassungen: Neuzulassungen nach Jahren" [Motor vehicles – registrations: Registrations by year] (in German). Statistik Austria. Retrieved 2016-03-20. Download the file "Kfz-Neuzulassungen Jänner bis Dezember 2015." A total of 2,778 passenger plug-in electric cars were sold in Austria in 2015 (consisting of 1,677 all-electrics, 931 gasoline-powered plug-in hybrids, and 170 diesel-powered plug-in hybrids) out of 308,555 passenger cars, resulting in a market share of 0.90% (see pp. 78 PDF version).
- 1 2 3 4 5 California New Car Dealers Association (CNCDA) (February 2018). "New Vehicle Registrations in State Predicted to Exceed 2 Million Units Again in 2018" (PDF). CNCDA. Retrieved 2018-02-17. Registrations through December 2017 since 2013.
- 1 2 LeSage, Jon (2016-02-06). "Renault Zoe Ekes By Mitsubishi Outlander in 2016 European Plug-in Sales". HybridCars.com. Retrieved 2017-02-06.
- ↑ Automotive Industry Data (AID) (2016-02-15). "PHEVs – Take off or transitory blip?". AID Newsletter. Retrieved 2016-02-19. Market share only includes Western European countries. A total of 95,140 plug-in hybrid cars were sold in Europe in 2015.
- ↑ Jiang Xueqing (2014-01-11). "New-energy vehicles 'turning the corner'". China Daily. Retrieved 2014-01-12.
- ↑ China Association of Automobile Manufacturers (CAAM) (2016-01-20). "New energy vehicles enjoyed a high-speed growth". CAAM. Retrieved 2016-01-21.
- ↑ China Association of Automobile Manufacturers (CAAM) (2015-01-14). "The sales and production of new energy vehicles boomed". CAAM. Retrieved 2015-01-14.
- ↑ China Association of Automobile Manufacturers (2012-01-16). "5,579 electric cars sold in China in 2011". Wind Energy and Electric Vehicle Review. Retrieved 2014-01-12.
- ↑ Cars21.com (2013-02-13). "EV sales increase 103.9% in China in 2012– Electric China Weekly No 17". Cars21.com. Retrieved 2014-01-12.
- 1 2 Cobb, Jeff (2016-09-28). "China Buys Half-Millionth Passenger Plug-in Car; On Track To Surpass US". HybridCars.com. Retrieved 2016-09-28. Sales of new energy vehicles totaled 689,447 units between 2011 and August 2016. Cumulative sales of new energy passenger cars totaled 493,290 units between 2010 and August 2016.
- ↑ Liu Wanxiang (2017-01-11). "乘联会:新能源乘用车2016年销量32万辆 比亚迪\吉利\北汽稳居前三" [By the Federation: new energy passenger car sales in 2016 totaled 320,000 units. BYD, Geely and BAIC were the top three manufacturers] (in Chinese). D1EV.com. Retrieved 2017-01-12. Sales of new energy vehicles in China totaled 320,081 units, consisting of 239,830 all-electric cars and 80,251 plug-in hybrid vehicless.
- ↑ Dune, Michael J. (2016-12-14). "China's Automotive 2030 Blueprint: No. 1 Globally In EVs, Autonomous Cars". Forbes. Retrieved 2016-12-14.
- ↑ Majeed, Abdul (2016-09-29). "China faces acid test in vehicle emissions". Business Line. Retrieved 2016-09-29.
- ↑ Cobb, Jeff (2016-10-17). "China Now Ties US For Leadership In Cumulative Global Plug-In Sales". HybridCars.com. Retrieved 2016-10-17. As of September 2016, the U.S. and China are technically tied for first place as the world's largest plug-in passenger car market. The U.S. has cumulative plug-in car sales of 522,519 units while China has 521,649 domestically produced plug-in cars. Europe is still the world's largest regional market with almost 50,000 more units sold that both countries, totaling about 570,000 light-duty plug-in vehicles.
- ↑ "Top 10 NEV Models by 2017 Sales". Gasgoo China Automotive News. 2018-01-18. Retrieved 2018-01-29.
- 1 2 Cobb, Jeff (2016-09-01). "Americans Buy Their Half-Millionth Plug-in Car". HybridCars.com. Retrieved 2016-09-02. See other figures in graphs.
- ↑ Electric Drive Transportation Association (EDTA) (January 2018). "Electric Drive Sales Dashboard". EDTA. Retrieved 2018-01-13. Sales figures sourced from HybridCars.com and direct reports submitted by EDTA member companies
- ↑ HybridCars.com and Baum & Associates. "HybridCars Dashboard". HybridCars.com. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ↑ California Air Resources Board (CARB) (2017-01-18). "California's Advanced Clean Cars Midterm Review: Summary Report for the Technical Analysis of the Light Duty Vehicle Standards" (PDF). CARB. Retrieved 2017-01-19. See pp. ES 44.
- ↑ Stacy C. Davis; Susan W. Diegel & Robert G. Boundy (July 2014). "Transportation Energy Data Book Edition 33" (PDF). Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy, U.S. Department of Energy. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2015-06-30. Retrieved 2014-09-02. See Table 6.5: Hybrid and Plug-in Vehicle Sales, 1999–2013, pp. 6–9.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Cobb, Jeff (2016-01-06). "December 2015 Dashboard". HybridCars.com and Baum & Associates. Retrieved 2016-02-13. Plug-in electric car sales in the U.S. totaled 114,248 units in 2015, consisting of 71,105 all-electric cars and 43,143 plug-in hybrids, with corresponding market shares of 0.25% and 0.41%. Sales in 2014 totaled 123,347 units.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Cobb, Jeff (2017-01-05). "December 2016 Dashboard". HybridCars.com and Baum & Associates. Retrieved 2016-12-06. Plug-in electric car sales in the U.S. totaled 157,181 units, consisting of 84,246 all-electric cars and 72,935 plug-in hybrids. The plug-in car segment achieved a market share of 0.90% of new car sales. December sales totaled 23,288 units with a market share of 1.39%. The top selling model in 2016 was the Tesla Model S with 29,156 units sold, followed by the Chevrolet Volt(24,739) and the Tesla Model X (18,028).
- ↑ Jeff Cobb (2013-01-08). "December 2012 Dashboard". HybridCars.com and Baum & Associates. Retrieved 2013-01-14. See the section: December 2012 Plug-in Electric Car Sales Numbers. A total of 53,172 plug-in electric vehicles were sold during 2012. Sales of the Fisker Karma, Coda and Wheego are not included, as these carmakers do not report monthly sales on a regular basis.
- 1 2 Jeff Cobb (2014-01-06). "December 2013 Dashboard". HybridCars.com and Baum & Associates. Retrieved 2015-03-21. Shows U.S. total sales for 2012 and 2013.
- 1 2 Kane, Mark (2018-01-11). "2017 US Plug-In EV Sales Charted: Market Grows 26%, Record 1.6% Share In December". InsideEVs.com. Retrieved 2018-01-22.
- ↑ Cobb, Jeff (2016-10-04). "Plug-in Cars Have Their Best-Ever US Sales in September". HybridCars.com and Baum & Associates. Retrieved 2016-10-04.
- 1 2 3 Kane, Mark (2017-01-25). "Nissan LEAF Sets Sales Record In Japan For 2016". InsideEVs.com. Retrieved 2017-01-26. A total of 14,795 Leafs were sold in Japan in 2016, and a total of 72,494 units since its inception.
- 1 2 Jose Pontes (2018-02-02). "Japan December 2017". EV Sales. Retrieved 2018-02-17. About 56,000 plug-in electric cars were sold in Japan in 2017.
- ↑ International Energy Agency, Clean Energy Ministerial, and Electric Vehicles Initiative (April 2013). "Global EV Outlook 2013 – Understanding the Electric Vehicle Landscape to 2020" (PDF). International Energy Agency. Retrieved 2013-04-20. See pp. 4, 6–8, and 11–12.
- ↑ Kane, Mark (2016-04-02). "Plug-In Electric Car Sales Visualized From 2011 to 2015". InsideEVs.com. Retrieved 2016-06-19.
- ↑ Shirouzu, Norihiko; Lienert, Paul (2015-10-28). "Auto power play: Japan's hydrogen car vs China's battery drive". Reuters. Retrieved 2016-06-19.
- ↑ Deign, Jason (2015-02-10). "Japan Makes a Big Bet on the Hydrogen Economy". Green Tech Media. Retrieved 2016-06-19.
- ↑ France Mobilité Électrique - AVERE France (2017-01-30). "La France s'impose comme le leader des ventes de véhicules 100% électriques en Europe en 2016" [France has emerged as the leader in vehicle sales 100% electric in Europe in 2016] (in French). AVERE. Retrieved 2017-02-05. Sales in the European light-duty all-electric vehicle market reached a record of 102,625 registrations in 2016 (includes passenger cars and utility vans).
- ↑ Pontes, Jose (2017-02-03). "Europe's Best-Selling Electric Car = Renault Zoe". EV-Sales.blogspot.com. CleanTechnica.com. Retrieved 2017-02-25.
- 1 2 Lane, Ben (January 2018). "Electric car market statistics". UK: Next Green Car. Retrieved 2018-01-11. As of 31 December 2017, the total UK light-duty electric fleet totals 137,100 plug-in electric vehicles, consisting of about 132,000 plug-in cars and 5,100 plug-in electric commercial vans. This figure includes a significant number of registered plug-in electric cars and vans which were not eligible for the grant schemes.
- 1 2 Cobb, Jeff (2016-06-15). "Europe Buys Its 500,000th Plug-in Vehicle". HybridCars.com. Retrieved 2016-06-15.
- 1 2 3 Cobb, Jeff (2016-05-09). "Norway Is Fourth Country To Register 100,000 Plug-in Cars". HybridCars.com. Retrieved 2016-05-09. As of April 2016, the United States is the leading country market with a stock of about 450,000 highway legal light-duty plug-in electric vehicles delivered since 2008. China ranks second with around 300,000 units sold since 2011, followed by Japan with about 150,000 plug-in units sold since 2009, both through March 2016. European sales are led by Norway with over 100,000 units registered by the end of April 2016.
- 1 2 3 4 Cobb, Jeff (2016-10-10). "France Becomes Fifth Nation To Buy 100,000 Plug-in Vehicles". HybridCars.com. Retrieved 2016-10-10.
- 1 2 Cobb, Jeff (2016-11-17). "The Netherlands Becomes Sixth Country To Buy 100,000 Plug-in Vehicles". HybridCars.com. Retrieved 2016-11-18.
- ↑ Society of Motor Manufacturers and Traders (SMMT) (2017-04-05). "March 2017 – EV registrations". SMMT. Retrieved 2017-04-16.
- 1 2 3 Fergusson, Malcolm (October 2016). "Electric Vehicles in Europe - 2016: Approaching adolescence" (PDF). Transport & Environment. Retrieved 2016-10-13. See pp. 15-16.
- 1 2 Automobile Propre (August 2016). "Chiffres de vente & immatriculations d'utilitaires électriques en France" [Sales figures & electric utility van registrations in France] (in French). Automobile Propre. Retrieved 2016-10-02. See "Ventes d’utilitaires électriques en 2016/2015/2014 for all-electric utility van registrations. Light-duty electric vehicles reached a 1.22% market share of new van sales in the country in 2014, and rose to 1.30% in 2015.
- ↑ Norsk Elbilforening (Norwegian Electric Vehicle Association) (January 2018). "Norwegian EV market". Norsk Elbilforening. Retrieved 2017-01-11. Place the pointing device over the graph to show the cumulative number of electric vehicles and plug-in hybrids in Norway at the end of each year. As of 31 December 2017, the registered light-duty plug-in electric stock totaled 209,122 units, consisting of 141,951 all-electric battery electric vehicles and 67,171 plug-in hybrids.
- ↑ Cobb, Jeff (2016-10-11). "Almost Half The Cars Bought In Norway Last Month Were Electrified". HybridCars.com. Retrieved 2016-10-11.
- ↑ Norwegian Road Federation (OFV) (2016-12-01). "Bilsalget i november" [Car sales in November] (in Norwegian). OFV. Archived from the original on 2016-12-10. Retrieved 2016-12-03.
- ↑ Norwegian Road Federation (OFV) (2017-01-02). "Bilsalget i desember" [Car sales in December] (in Norwegian). OFV. Archived from the original on 2017-02-02. Retrieved 2017-01-21.
- ↑ Petter Haugneland (2015-04-20). "50.000 elbiler på norske veier!" [50,000 electric cars on Norwegian roads!] (in Norwegian). Norsk elbilforening (Norwegian Electric Vehicle Association). Archived from the original on 2015-04-25. Retrieved 2015-04-21.
- ↑ Jeff Cobb (2015-04-20). "Norway Celebrates 50,000th Plug-in Car Sold; Will EV Incentives Continue?". HybridCars.com. Retrieved 2015-04-20.
- ↑ France Mobilité Électrique – AVERE France (2016-05-17). "Dossier : A la découverte du véhicule électrique en Norvège" [Dossier: Discovering the electric vehicle in Norway] (in French). AVERE. Retrieved 2016-05-19. In April 2016 Norway just exceeded the threshold of 100 000th registered electric vehicles, plug-in hybrids included.
- ↑ Frydenlund, Ståle (2016-12-13). "Norway now has 100,000 electric cars". Norsk Elbilforening (Norwegian Electric Vehicle Association). Retrieved 2016-12-13.
- ↑ Cobb, Jeff (2015-12-19). "Norway's 100,000th EV Constitutes 10-Percent Of The World's Total". HybridCars.com. Retrieved 2015-12-19.
- ↑ Figenbaum, Erik; Kolbenstvedt, Marika (June 2016). "Learning from Norwegian Battery Electric and Plug-in Hybrid Vehicle users". Institute of Transport Economics (TØI), Norwegian Centre for Transport Research. Retrieved 2016-08-17. TØI report 1492/2016. See pp. 1.
- ↑ Alister Doyle & Nerijus Adomaitis (2013-03-13). "Norway shows the way with electric cars, but at what cost?". Reuters. Retrieved 2013-03-15.
- ↑ Joly, David (2015-10-16). "Norway is A Model For Encouraging Electric Car Sales". The New York Times. Retrieved 2016-02-16.
- ↑ Agence France-Presse (2011-05-15). "Electric cars take off in Norway". The Independent. Retrieved 2011-10-09.
- ↑ AVERE (2012-06-07). "Norwegian Parliament extends electric car initiatives until 2018". AVERE. Archived from the original on 2013-10-24. Retrieved 2012-07-20.
- ↑ Klippenstein, Matthew (2014-04-08). "One Percent Of Norway's Cars Are Already Plug-In Electrics". Green Car Reports.
- ↑ Jeff Cobb (2015-04-17). "Norway Electric Car Incentives Will Hit Sales Cap Next Week". HybridCars.com. Retrieved 2015-04-21.
- ↑ Petter Haugneland (2016-02-29). "Nasjonal transportplan: Elbil er klimaløsningen" [National Transport: EV is the climate solution] (in Norwegian). Norsk Elbilforening (Norwegian Electric Vehicle Association). Archived from the original on 2016-03-05. Retrieved 2016-03-04.
- ↑ "Number of electric cars worldwide climbs to 1.3 million" (PDF) (Press release). Stuttgart: Zentrum für Sonnenenergieund Wasserstoff-Forschung Baden-Württemberg (ZSW). 2016-02-26. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-03-06. Retrieved 2016-03-04. Around 3% of some 2.64 million cars in Norway run on electricity by the end of 2015 (includes all-electric cars and plug-in hybrids).
- ↑ Autoactu.com (May 2016). "Chiffres de vente & immatriculations de voitures électriques en France" [Sales figures & electric car registrations in France] (in French). Automobile Propre. Retrieved 2016-05-14. See "Ventes de voitures électriques en 2016/2015, 2014, 2013, 2012, 2011 and 2010" It shows all electric car registrations between 2010 and 2016.
- ↑ AVERE-France (2014-01-08). "Baromètre AVERE-France Janvier 2014" [Barometer AVERE-France January 2014] (in French). France Mobilité Électrique – AVERE France. Retrieved 2014-01-14.
- ↑ Justin Aschard (2012-11-07). "Novembre 2012 – Ventes de véhicules électriques (CCFA)" [November 2012 – Sales of electric vehicles (CCFA)] (in French). France Mobilité Électrique. Retrieved 2013-02-16. See table Bilan annuel des ventes de véhicules électriques (Annual sales of electric vehicles) for detailed sales by category during 2010 and 2011.
- ↑ France Mobilité Électrique – AVERE France (2013-01-07). "Bilan des Immatriculations pour l'Année 2012" [Record Registrations for 2012] (in French). AVERE. Archived from the original on October 20, 2013. Retrieved 2013-02-16. A total of 5,663 electric cars and 3,651 electric vans were registered in France in 2012.
- ↑ AVERE-France (2015-01-05). "Le marché du véhicule électrique maintient sa progression en 2014" [The electric vehicle market continues to grow in 2014] (in French). AVERE France. Retrieved 2015-01-14.
- ↑ France Mobilité Électrique – AVERE France (2016-01-07). "Immatriculations des voitures électriques : + 62,1% en 2015" [All-electric car registrations: + 62.1% in 2015] (in French). AVERE. Retrieved 2016-05-14. A total of 17,779 all-electric cars were registered in France in 2015.
- ↑ France Mobilité Électrique – AVERE France (2016-01-08). "Immatriculations des hybrides rechargeables : La barre des 5.000 est franchie !" [Plug-in hybrid registrations: The 5,000 barrier is achieved!] (in French). AVERE. Retrieved 2016-05-14. A total of 5,006 plug-in hybrids were registered in France in 2015.
- ↑ France Mobilité Électrique – AVERE France (2016-01-12). "Immatriculations des utilitaires électriques : + 9,6% en 2015" [All-electric utility vehicle registrations: + 9.6% in 2015] (in French). AVERE. Retrieved 2016-05-14. A total of 4,916 all-electric utility vans were registered in France in 2015.
- 1 2 France Mobilité Électrique - AVERE France (2017-01-09). "Plus de 27 000 véhicules électriques immatriculés en 2016, après un mois de décembre record" [More than 27,000 electric vehicles registered in 2016, after a record month of December] (in French). AVERE. Retrieved 2017-01-09. A total of 33,774 light-duty plug-in electric vehicles were registered in France in 2016 consisting of 27,751 all-electric cars, 5,556 electric utility vans and 6,467 plug-in hybrid cars. The plug-in car segment achieved a market share of 1.40% of new car registrations in the country in 2016.
- ↑ Foucaud, Isabelle (2016-10-01). "Plus de 100.000 véhicules électriques circulent aujourd'hui en France" [More than 100,000 electric vehicles currently on the road in France]. Le Figaro (in French). Retrieved 2016-10-10. Environment Minister, Ségolène Royal, said there are more than 100,000 electric vehicles currently on the road in France.
- ↑ Society of Motor Manufacturers and Traders(SMMT) (2015-01-07). "December 2014 – EV registrations". SMT. Retrieved 2015-01-08. A total of 14,518 plug-in electric cars were registered during 2014, consisting of 6,697 pure electrics and 7,821 plug-in hybrids, up from 3,586 plug-in electric cars were registered in 2013. A total of 2,476,435 new cars were registered in 2014.
- ↑ Society of Motor Manufacturers and Traders(SMMT) (2016-01-07). "December 2015 – EV registrations". SMT. Retrieved 2016-01-21. A total of 28,188 plug-in electric cars were registered during 2015, consisting of 9,934 pure electrics and 18,254 plug-in hybrids. A total of 2,633,503 new cars were registered in 2015.
- ↑ Society of Motor Manufacturers and Traders(SMMT) (2012-01-06). "December 2011 – EV and AFV registrations". SMMT. Retrieved 2012-01-14.
- ↑ Society of Motor Manufacturers and Traders(SMMT) (2013-01-07). "December 2012 – EV and AFV registrations". SMMT. Retrieved 2013-02-16.
- ↑ Society of Motor Manufacturers and Traders(SMMT) (2014-01-07). "December 2013 – EV registrations". SMT. Retrieved 2014-01-12. A total of 2,254 plug-in electric cars were registered in 2013.
- ↑ Society of Motor Manufacturers and Traders(SMMT) (2017-01-05). "December 2016 – EV registrations". SMT. Retrieved 2017-01-09. Registrations in 2016 totaled 36,907 plug-in electric vehicles consisting of 10,264 all-electric cars and 26,643 plug-in hybrids. Of these, a total of 35,447 cars were eligible for the Plug-in Car Grant. Since its launch in 2011, a total of 83,052 cars eligible for the PICG have been registered through December 2016. A total of 2,692,786 new cars were registered in 2016, resulting in a plug-in electric car market share of 1.37% of new car sales.
- 1 2 Society of Motor Manufacturers and Traders (SMMT) (2018-01-05). "December – EV registrations". SMMT. Retrieved 2018-01-11. Registrations in 2017 totaled 47,263 plug-in electric vehicles consisting of 13,597 all-electric cars and 33,6663 plug-in hybrids. Of these, a total of 45,187 cars were eligible for the Plug-in Car Grant. Since its launch in 2011, a total of 127,509 cars eligible for the PICG have been registered through December 2017. A total of 2,540,617 new cars were registered in 2017, resulting in a plug-in electric car market share of 1.86% of new car sales.
- ↑ RAC Foundation (February 2017). "Claims made through the Plug-in Van Grant scheme". UK: RAC Foundation. Retrieved 2017-02-24. See graph with PIVG cumulative claims and claims by quarter.
- ↑ Society of Motor Manufacturers and Traders (SMMT) (April 2011). "Motor Industry Facts 2011" (PDF). SMMT. Retrieved 2012-01-14. Download the pdf report. Data available by year in Table: AFV Registrations, pp.15. Data shows all type of EVs, including quadricycles. A total of 1,096 electric vehicles were registered in the UK between 2006 and December 2010
- ↑ Nikki Gordon-Bloomfield (2013-08-30). "TLC needed: Can cars like the G-Wiz still have a purpose in life?". The Green Car Website. Retrieved 2013-10-10.
- 1 2 Kraftfahrt-Bundesamtes (KBA) (January 2015). "Neuzulassungsbarometer im Dezember 2014" [New Registrations Barometer December 2014] (in German). KBA. Retrieved 2015-01-27. A total of 13,049 plug-in electric cars registered in Germany during 2014, consisting of 8,522 all-electric cars and 4,527 plug-in hybrids.
- ↑ Autobild (2012-01-12). "2011 Full Year Best-Selling Electric Cars in Germany in 2011". BestSellingCars.com. Retrieved 2012-10-31. Cumulative number of registered electric cars was 4,541 as of January 1, 2012. All-electric car and van registrations in 2010 totaled 541 units and 2,154 in 2011..
- ↑ Kraftfahrt-Bundesamtes (KBA) (2013-01-31). "Neuzulassungen E-Mobilität 2012-Kaum Zuwachs wegen Twizy" [Registrations E-mobility – Low growth due to Twizy]. Auto Bild (in German). Retrieved 2013-02-14. A total of 2,956 all-electric cars were registered in Germany during 2012.
- ↑ Kraftfahrt-Bundesamtes (KBA). "Monatliche Neuzulassungen – Neuzulassungsbarometer im Dezember 2013" [Monthly registrations – New registrations Barometer in December 2013] (in German). KBA. Retrieved 2014-09-06. A total of 1,385 plug-in hybrids and 6,051 all-electric cars were registered during 2013.
- 1 2 Kraftfahrt-Bundesamtes (KBA) (January 2016). "Neuzulassungsbarometer im Dezember 2015" [New Registrations Barometer December 2015] (in German). KBA. Retrieved 2015-01-21. A total of 23,464 plug-in electric cars were registered in Germany during 2015, consisting of 12,363 all-electric cars and 11,101 plug-in hybrids.
- ↑ Kraftfahrt-Bundesamtes (KBA) (January 2017). "Neuzulassungsbarometer im Dezember 2016" [New Registrations Barometer December 2015] (in German). KBA. Retrieved 2017-01-11. A total of 25,154 plug-in electric cars were registered in Germany in 2016, consisting of 11,410 all-electric cars and 13,744 plug-in hybrids.
- 1 2 3 4 Kraftfahrt-Bundesamtes (KBA) (2018-01-12). "Neuzulassungsbarometer im Dezember 2017" [New Registrations Barometer December 2017] (in German). KBA. Retrieved 2018-01-12. A total of 29,436 plug-in hybrids and 25,056 all-electrric cars were registered in Germany in 2017.
- ↑ Kraftfahrt-Bundesamtes (KBA) (October 2016). "Neuzulassungsbarometer im September 2016" [New Registrations Barometer September 2016] (in German). KBA. Retrieved 2016-10-07. A total of 17,074 plug-in electric cars were registered in Germany between January and September 2016, consisting of 7,678 all-electric cars and 9,396 plug-in hybrids.
- ↑ Kraftfahrt-Bundesamtes (KBA). "Monatliche Neuzulassungen – Neuzulassungsbarometer im Juni 2014" [Monthly registrations – New registrations Barometer in June 2014] (in German). KBA. Retrieved 2014-09-06. A total of 1,575 plug-in hybrids and 4,188 electric cars were registered during the first six months of 2014.
- ↑ Kraftfahrt-Bundesamt (KBA) (January 2018). "Neuzulassungen von Personenkraftwagen nach Marken und Modellreihen im Dezember 2017 (FZ 10) (XLS, 153 KB, Datei ist nicht barrierefrei)" [New registrations of passenger cars by segments and models in December 2016] (in German). KBA. Retrieved 2018-01-13. Click on the link Neuzulassungen von Personenkraftwagen nach Marken und Modellreihen im Dezember 2017 (FZ 10) (XLS, 153 KB, Datei ist nicht barrierefrei) to download the file with registrations figures.
- 1 2 "Cijfers elektrisch vervoer – Top 5 geregistreerde modellen plug-in hybride elektrische auto – Top 10 geregistreerde modellen volledig elektrische auto" [Figures electric transport – Top 5 registered plug-in hybrids – Top 10 registered fully electric vehicle models] (PDF). Rijksdienst voor Ondernemend Nederland (RVO) - Dutch National Office for Enterprising - (in Dutch). BovagWebsite. January 2017. Retrieved 2017-01-13. With a total of 25,984 Mitsubishi Outlander P-HEVs registered by the end of December 2016, the plug-in hybrid is the all-time top registered plug-in electric vehicle in the Netherlands.
- ↑ Rijksdienst voor Ondernemend Nederland (RVO) (January 2015). "Special: Analyse over 2014" [Special: Analysis over 2014] (PDF) (in Dutch). RVO (Dutch National Office for Enterprising). Retrieved 2015-02-24. See total 2014 registration by type of PEV under the heading "31-12-2014". The market share of the plug-in electric passenger car segment in 2014 was 3.86% of total new passenger car registrations.
- ↑ Rijksdienst voor Ondernemend Nederland (RVO) (December 2015). "Cijfers elektrisch vervoer – Top 10 geregistreerde modellen volledig elektrische auto (31-12-2015)" [Figures electric transport – Aantal geregistreerde elektrische voertuigen in Nederland – Top 10 registered fully electric vehicle models (31-12-2015)] (PDF) (in Dutch). BOVBAG. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2015-09-23. Retrieved 2016-02-07.
- ↑ Rijksdienst voor Ondernemend Nederland (RVO) (January 2015). "Cijfers elektrisch vervoer – Aantal geregistreerde elektrische voertuigen in Nederland – Top 5 geregistreerde modellen plug-in hybride elektrische voertuigen (31-12-2014) – Top 6 geregistreerde modellen volledig elektrische voertuigen (31-12-2014)" [Figures electric transport – Number of registered electric vehicles in Netherlands, Top 5 registered plug-in electric hybrid vehicle models (12-31-2014) and Top 6 registered all-electric vehicle models (12-31-2014)] (PDF) (in Dutch). RVO (Dutch National Office for Enterprising). Retrieved 2015-04-27. Click the url to download the file "2014-cijfers-elektrisch-vervoer-tm-december-2014.pdf.pdf" See under the heading "31-12-2014" for total registrations figures at the end of December 2014. A total of 2,645 Model S sedans were registered in the Netherlands as of December 2014, and it ranks as the top registered all-electric vehicles in the country.
- ↑ Rijksdienst voor Ondernemend Nederland (RVO) (January 2013). "Cijfers elektrisch vervoer (30-12-2013)" [Figures electric transport (30-12-2013)] (PDF) (in Dutch). RVO (Dutch National Office for Enterprising). Retrieved 2014-08-23.
- ↑ RAI. "Verkoopstatistieken -nieuwverkoop personenautos" [Sales Statistics – New passenger car sales] (in Dutch). RAI Vereniging. Archived from the original on 2014-03-28. Retrieved 2013-02-02. Download pdf file for detailed sales in 2011 ("Download nieuwverkoop personenautos 201112") and 2012 ("Download nieuwverkoop personenautos 201212").
- ↑ Cobb, Jeff (2016-09-01). "Americans Buy Their Half-Millionth Plug-in Car: Concentration of plug-in electrified car registrations per 1,000 people". HybridCars.com. Retrieved 2016-09-04. As of July 2016, Norway had a concentration of registered plug-in cars per 1,000 people of 21.52, the Netherlands of 5.63, California of 5.83, and the United States national average was 1.52.
- ↑ "Nederland registreert meer dan 100.000 elektrische voertuigen" [Netherlands registers more than 100,000 electric vehicles] (in Dutch). Engineering Ring Net. 2016-11-18. Retrieved 2016-12-16.
- ↑ Norsk Elbilforening (Norwegian Electric Vehicle Association) (2017-01-05). "Elbilsalget: Ned i fjor – venter ny vekst i år" [EV Sales: Down from last year - awaiting new growth this year] (in Norwegian). Norsk Elbilforening. Retrieved 2017-01-21.
- 1 2 Cobb, Jeff (2016-12-05). "Tesla Model S Is Second Plug-in Car To Cross 150,000 Sales Milestone". HybridCars.com. Retrieved 2016-12-05. The Volt/Ampera family of vehicles is the world's all-time third best selling plug-in electric car after the Nissan Leaf (240,000), and the Tesla Model S (over 150,000), with 130,500 vehicles sold globally through November 2016.
- ↑ Norwegian Road Federation (OFV) (January 2015). "Bilsalget i 2014" [Car sales in 2014] (in Norwegian). OFV. Retrieved 2015-01-14. A total of 10,639 plug-in electric vehicles were registered in Norway in 2013, consisting of: 7,885 new electric cars, 2,086 used imported all-electric cars, 328 new plug-in hybrid cars and 340 new all-electric vans. A total of 23,390 plug-in electric vehicles were registered in Norway in 2014, consisting of: 18,094 new electric cars, 3,063 used imported all-electric cars, 1,678 new plug-in hybrid cars and 555 new all-electric vans.
- ↑ Norwegian Road Federation (OFV) (January 2015). "Bilsalget i 2015" [Car sales in 2015] (in Norwegian). OFV. Archived from the original on 2016-02-09. Retrieved 2016-03-05. Registrations of new plug-in electric vehicles totaled 25,779 electric cars (zero emission vehicles totaled 25,788 accounting for 9 hydrogen vehicles), 7,964 plug-in hybrids and 712 all-electric vans in 2015. In addition, registrations of used imports totaled 5,122 electric cars and 55 electric vans. Plug-in electric vehicle registrations totaled 39,632 units.
- ↑ Norwegian Road Federation (OFV) (October 2016). "Bilsalget i september" [Car sales in September] (in Norwegian). OFV. Retrieved 2016-10-09.
- ↑ OFV (January 2014). "Bilsalget i desember og hele 2013" [Car sales in December and during 2013] (in Norwegian). Opplysningsrådet for Veitrafikken AS (OFV). Archived from the original on 2014-01-04. Retrieved 2014-08-16.
- ↑ Jake Spring (2015-10-23). "CORRECTED-(OFFICIAL)-UPDATE 2-Tesla CEO says negotiating with China on local production". Reuters. Retrieved 2015-10-24. Tesla sold sold 3,025 Model S cars in China from January to September 2015.
- ↑ Staff (2015-03-07). "Tesla cutting 30% of staff in China". Want China Times. Archived from the original on 2015-03-08. Retrieved 2015-03-09. Tesla imported 4,800 Model S cars in 2014, but only 2,499 of those vehicles were registered for road use in China.
- 1 2 3 Groupe Renault (January 2017). "Ventes Mensuelles" [Monthly Sales] (in French). Renault.com. Retrieved 2017-01-18. Includes passenger and light utility variants. Click on "(décembre 2016)" to download the file "XLSX - 239 Ko" for CYTD sales in 2016, and open the tab "Sales by Model". Click on "+ Voir plus" (See more) to download the files "Ventes mensuelles du groupe (décembre 2011) (xls, 183 Ko)" "Ventes mensuelles (décembre 2012) (xls, 289 Ko)" - Ventes mensuelles (décembre 2013) (xlsx, 227 Ko)" - "XLSX - 220 Ko Ventes mensuelles (décembre 2014)" - "Ventes mensuelles (décembre 2015)" to download the file "XLSX - 227 Ko" for 2011, 2012, 2013, 2014 and 2015 sales. Sales figures for 2013 were revised in the 2014 report
- ↑
- ↑ "Nissan Intelligent Mobility at CES" (Press release). Las Vegas: Nissan USA. 2017-01-05. Retrieved 2017-01-07.
- ↑ "Tesla Q4 2016 Production and Deliveries". Tesla Motors (Press release). Palo Alto: Market Wired. 2017-01-03. Retrieved 2017-01-04.
Tesla delivered approximately 22,200 vehicles in Q4, of which 12,700 were Model S and 9,500 were Model X.
- 1 2 3 4 Staff (2015-01-14). "2014 EV Sales Ranking". China Auto Web. Retrieved 2016-02-07. A total of 5,234 E150 EVs (EV200), and about 1,000 J3 EVs were sold in China in 2014.
- 1 2 3 Staff (2016-01-14). "Sales Ranking of China-made Pure-electric Cars in 2015". China Auto Web. Retrieved 2016-08-16. A total of 16,488 BAIC E-Series EVs, and over 9,000 JAC iEVs were sold in China in 2015.
- 1 2 Henry Lee; Sabrina Howell; Adam Heal (June 2014). "Leapfrogging or Stalling Out? Electric Vehicles in China". Belfer Center, Harvard Kennedy School. Retrieved 2016-08-16. Download EVS in China (full report). See Table 2: Chinas's EV Sales by Brand, 2011–2013, pp. 19. BAIC E150 EVs sales totaled 644 units in 2012 and 1,466 in 2013. JAC J3 EV sales totaled 2,485 units in 2012 and 1,309 in 2013
- 1 2 3 4 Staff (2017-01-19). "Best-selling China-made EVs in 2016". China Auto Web. Retrieved 2017-01-25. Three BYD Auto models topped the Chinese ranking of best-selling new energy passenger cars in 2016. The BYD Tang SUV was the top selling plug-in electric car in China in 2016 with 31,405 units sold, followed by the BYD Qin with 21,868 units sold, and ranking third overall in 2016 was the BYD e6 with 20,605 units.
- ↑ Cobb, Jeff (2016-08-10). "Global 10 Best-Selling Plug-In Cars Are Accelerating Forward". HybridCars.com. Retrieved 2016-08-13. As of June 2016, cumulative global sales of the top selling plug-in electric cars were led by the Nissan Leaf (over 228,000), followed by the Tesla Model S (129,393), Votl/Ampera family (about 117,300), Mitsubishi Outlander PHEV (about 107,400), Toyota Prius PHV (over 75,400), BYD Qin (56,191), Renault Zoe (51,193), BMW i3 (around 49,500), Mitsubishi i-MiEV family (about 37,600) and BYD Tang (37,509).
- ↑ Mat Gasnier (2013-01-14). "China Full Year 2012: Ford Focus triumphs". Best Selling Car Blog. Retrieved 2013-01-22.
- ↑ Mat Gasnier (2014-01-14). "China December 2013: Focus on the all-new models". Best Selling Cars Blog. Retrieved 2014-01-16.
- 1 2 3 Cobb, Jeff (2016-07-05). "June 2016 Dashboard". HybridCars.com and Baum & Associates. Retrieved 2016-07-05.
- 1 2 3 Pontes, Jose (2016-01-30). "Europe December 2015". EVSales.com. Retrieved 2016-02-13. A total of 1,230 Ford C-Max Energi, 11,214 VW e-Golf, and 2,653 Volvo XC90 T8s were sold in Europe in 2015.
- ↑ Pontes, Jose (2015-01-31). "Europe December 2014". EVSales.com. Retrieved 2016-02-07. European VW e-Golf sales totaled 3,328 units in 2014.
- 1 2 3 4 Edelstein, Stephen (2016-08-16). "European electric and plug-in hybrid sales for Jan–June 2016". Green Car Reports. Retrieved 2016-08-16. A total of 5,692 VW Golf GTEs, 5,035 Volvo XC90s, 3,912 VW e-Golfs, and 3,341 Audi A3-eTrons were sold in Europe during the first half of 2016.
- ↑ Jose, Pontes (2016-07-17). "China June 2016". EVSales.com. Retrieved 2016-08-15. A total of 9,977 BAIC E-series, and 7,862 JAC iEVs were sold in China during the first half of 2016.
- ↑ China Auto Web (2012-09-30). "JAC Delivers 500 J3 EVs ("ievs")". China Auto Web. Retrieved 2013-04-19. A total of 1,585 of the first and second generation JAC J3 models were sold during 2010 and 2011.
- ↑ China Auto Web (2013-03-25). "Chinese EV Sales Ranking for 2012". China Auto Web. Retrieved 2013-04-19. A total of 2,485 JAC J3 EVs were sold in 2012.
- ↑ Jeff Cobb (2015-11-04). "GM Sells Its 100,000th Volt in October". HybridCars.com. Retrieved 2015-11-04. About 102,000 units of the Volt/Ampera family have been sold worldwide by the end of October 2015.
- ↑ Cain, Timothy (January 2017). "Chevrolet Volt Sales Figures". Good Car Bad Car. Retrieved 2017-01-05.
- ↑ "Global Mitsubishi Outlander PHEV Sales Pass the 100,000 Mark" (Press release). UK: Mitsubishi Motors UK. 2016-05-19. Retrieved 2016-05-22. As of March 2016, a total of 65,529 units have been sold in Europe (21,052 in the UK and 44,477 in the rest of Europe), 33,730 in Japan, 2,015 in Australia and 259 in the rest of the world, for a total of 101,533 units sold worldwide.
- ↑ Mitsubishi UK (2017-01-20). "Further evolution for the 2017 Mitsubishi Outlander". Automotive World. Retrieved 2017-01-21.
The Mitsubishi Outlander PHEV is the UK’s best-selling Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle. At its introduction in 2014 it effectively created the ultra-low emission vehicle segment, notching up 10,000 sales in the UK within the first ten months and amassing a total sales figure of 26,600 by the end of 2016.
- 1 2 "Worldwide Sales of Toyota Hybrids Surpass 9 Million Units" (Press release). Toyota City, Japan: Toyota. 2016-05-20. Retrieved 2016-05-22.
- ↑ Cobb, Jeff (2016-11-02). "October 2016 Dashboard". HybridCars.com and Baum & Associates. Retrieved 2016-11-04. Tesla sales for 3Q 2016 have been restated based upon information provided from the company corresponding to U.S. sales during 3Q 2016. Tesla reported 9,156 Model S and 5,428 Model X sold during the third quarter of 2016. The combined effect of both models totaled 1,116 less units than originally estimated, so the revised current-year-to-date figure for sales through September is 108,397 units. The revised CYTD figure for Model S is 20,856 and 12,328 for the Model X. October sales figures already reflect this adjustment.
- ↑ Cobb, Jeff (2016-12-02). "November 2016 Dashboard". HybridCars.com and Baum & Associates. Retrieved 2017-01-08.
- ↑ Rijksdienst voor Ondernemend Nederland (RVO) (December 2015). "Cijfers elektrisch vervoer – Top 5 geregistreerde modellen plug-in hybride elektrische voertuigen (30-11-2015)" [Figures electric transport – Top 5 registered plug-in electric hybrid vehicle models (11-30-2015)] (PDF) (in Dutch). RVO (Dutch National Office for Enterprising). Retrieved 2016-03-26.
- ↑ Brad Berman (2015-05-01). "Toyota Halts Production of Prius Plug-in Hybrid Until Late 2016". Plugincars.com. Retrieved 2015-06-20.
- ↑ Voelcker, John (2016-12-01). "Plug-in electric car sales for Nov: Volt soars, Prius Prime arrives (UPDATE)". Green Car Reports. Retrieved 2016-12-01.
- ↑ Staff (2016-02-13). "Best-selling China-made SUVs in 2015". China Auto Web. Retrieved 2016-01-17. A total of 18,375 Tangs were sold in China in 2015.
- ↑ Jeff Cobb (2015-01-06). "December 2014 Dashboard". HybridCars.com and Baum & Associates. Retrieved 2015-01-06. See sections: "December 2014 Plug-in Hybrid Car Sales Numbers" and "December 2014 Battery Electric Car Sales Numbers"
- 1 2 3 4 Klippenstein, Matthew. "Canadian Plug-in Electric Vehicle Sales". Green Car Reports 7date=February 2016. Retrieved 2017-02-21. Tesla Model S sales figures from IHS data.
- ↑ Jeff Cobb (2015-02-11). "2014's Top-10 Global Best-Selling Plug-in Cars". HybridCars.com. Retrieved 2015-03-15.
- ↑ Jose, Pontes (2016-01-12). "China December 2015 (3rd Update)". EVSales.com. Retrieved 2016-02-13. A total of 10,711 SAIC Roewe 550 PHEVs were sold in China in 2015.
- 1 2 3 Gibbs, Nick (2016-03-15). "Hybrid sales expected to triple in Europe as tougher CO2 rules loom". Automotive News Europe. Retrieved 2016-02-22. Sales in Europe as reported by JATO Dynamics: Mitsubishi Ourlander sales totaled 19,853 units in 2014 and 31,214 in 2015; VW Golf GTE sales totaled 1,097 units in 2014 and 17,300 in 2015; Audi A3 e-tron sales totaled 1,154 units in 2014 and 11,791 in 2015; Volvo V60 sales totaled 5,441 units in 2014 and 6,349 in 2015. During 2015 a total of 5,481 all-electric BMW i3s and 6,566 i3 REx models (total 12,047). A total of 3,940 i3 REx models were sold in 2014.
- ↑ "2012 (Full Year) Sweden: Best-Selling Electric Cars & Plug-In Hybrid Models". BestSellingCars.com. 2013-04-02. Retrieved 2013-07-05. 42 Volvo V60 plug-in hybrids were sold in Sweden in 2012.
- ↑ Jim Motavalli (2014-06-30). "Confirmed: Volvo To Offer Plug-In Hybrid Option on All Models". PluginCars.com. Retrieved 2014-09-03. Volvo sold 7,739 V60 plug-in hybrids in 2013.
- ↑ Jose, Pontes (2016-07-26). "Europe June 2016". EVSales.com. Retrieved 2016-08-16. Volvo V60 Plug-in sales in Europe totaled 1,614 units during the first half of 2016.
- ↑ Voelckr, John (2016-01-19). "Plug-In Electric Car Sales For 2015 Fall Slightly From 2014". Green Car Reports. Retrieved 2016-02-13. A total of 49 Audi A3 e-trons were sold in the U.S. in 2015.
- ↑ "Three years since the market launch of BMW i. 100,000 electrified BMW on the road" (Press release). Munich: BMW Group Press Club Global. 2016-11-03. Retrieved 2016-11-07. Three year after the market launch of the BMW i3, the BMW Group has delivered more than 100,000 purely electric-powered cars and plug-in hybrids to customers worldwide. The BMW i3 alone has reached more than 60,000 units, and the BMW i8 has more than 10,000 delivered since the middle of 2014. Additionally, there are the approximately 30,000 iPerformance plug-in hybrids sold worldwide.
External links
- Application of Life-Cycle Assessment to Nanoscale Technology: Lithium-ion Batteries for Electric Vehicles, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, April 2013.
- Clean Vehicle Rebate Project website
- Competitive Electric Town Transport, Institute of Transport Economics (TØI), Oslo, August 2015.
- Cradle-to-Grave Lifecycle Analysis of U.S. Light-Duty Vehicle-Fuel Pathways: A Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Economic Assessment of Current (2015) and Future (2025–2030) Technologies (includes BEVs and PHEVs), Argonne National Laboratory, June 2016.
- Driving Electrification – A Global Comparison of Fiscal Incentive Policy for Electric Vehicles, International Council on Clean Transportation, May 2014.
- Effects of Regional Temperature on Electric Vehicle Efficiency, Range, and Emissions in the United States, Tugce Yuksel and Jeremy Michalek, Carnegie Mellon University. 2015
- eGallon Calculator: Compare the costs of driving with electricity, U.S. Department of Energy
- Electric Vehicle Timeline: Electric Cars, Plug-In Hybrids, and Fuel Cell Vehicles (1900–2014), Union of Concerned Scientists
- EV Everywhere Grand Challenge Blueprint, U.S. Department of Energy, January 2013.
- From Fiction to Reality: The Evolution of Electric Vehicles 2013 – 2015, JATO Dynamics, November 2015.
- Global EV Outlook 2013– Understanding the Electric Vehicle Landscape to 2020, International Energy Agency (IEA), April 2013
- Hybrid and Electric Vehicles – The Electric Drive Gains Traction, IA-HEV, International Energy Agency (IEA), May 2013
- Influence of driving patterns on life cycle cost and emissions of hybrid and plug-in electric vehicle powertrains, Carnegie MellonVehicle Electrification Group
- NHTSA Interim Guidance Electric and Hybrid Electric Vehicles Equipped with High Voltage Batteries – Vehicle Owner/General Public
- NHTSA Interim Guidance Electric and Hybrid Electric Vehicles Equipped with High Voltage Batteries – Law Enforcement/Emergency Medical Services/Fire Department
- New Energy Tax Credits for Electric Vehicles purchased in 2009
- Overview of Tax Incentives for Electrically Chargeable Vehicles in the E.U.
- PEVs Frequently Asked Questions
- Plug-in Electric Vehicles: Challenges and Opportunities, American Council for an Energy-Efficient Economy, June 2013
- Powering Ahead – The future of low-carbon cars and fuels, the RAC Foundation and UK Petroleum Industry Association, April 2013.
- Plugging In: A Consumer's Guide to the Electric Vehicle Electric Power Research Institute
- Plug-in America website
- Plug-in Cars website
- Plug-in Electric Vehicle Deployment in the Northeast Georgetown Climate Center
- Plug-In Electric Vehicles: A Case Study of Seven Markets (Norway, Netherlands, California, United States, France, Japan, and Germany), UC Davis, October 2014.
- Plug-in Tracker: A comprehensive list of highway-capable PEVs (cars and trucks, 2- and 3-wheeled and commercial vehicles)
- Plug-in List of Registered Charging Stations in the USA
- RechargeIT plug-in driving experiment (Google.org)
- Shades of Green – Electric Car's Carbon Emissions Around the Globe, Shrink that Footprint, February 2013.
- State of the Plug-in Electric Vehicle Market, Electrification Coalition, July 2013.
- The Great Debate – All-Electric Cars vs. Plug-In Hybrids, April 2014
- UK Plug-in Car Grant website
- Transport Action Plan: Urban Electric Mobility Initiative, United Nations, Climate Summit 2014, September 2014
- U.S. Federal & State Incentives & Laws
- U.S. State and Federal Incentives for EVs, PHEVs and Charge Stations
- US Tax Incentives for Plug-in Hybrids and Electric Cars
- Will Electric Cars Transform the U.S. Vehicle Market? Belfer Center, Harvard University
Books
- David B. Sandalow, ed. (2009). Plug-In Electric Vehicles: What Role for Washington? (1st. ed.). The Brookings Institution. ISBN 978-0-8157-0305-1.
- Mitchell, William J.; Borroni-Bird, Christopher; Burns, Lawrence D. (2010). Reinventing the Automobile: Personal Urban Mobility for the 21st Century (1st. ed.). The MIT Press. ISBN 978-0-262-01382-6.