Indonesian National Armed Forces
| Indonesian National Armed Forces | |
|---|---|
| Tentara Nasional Indonesia | |
 Insignia of TNI (Indonesian National Armed Forces) | |
| Founded | 5 October 1945 as Tentara Keamanan Rakyat (People's Security Forces) |
| Service branches |
|
| Headquarters | Cilangkap, Jakarta |
| Leadership | |
| Commander-in-Chief | President Joko Widodo |
| Minister of Defence | General (Ret.) Ryamizard Ryacudu |
| Commander of the Indonesian National Armed Forces | Air Chief Marshal Hadi Tjahjanto |
| Manpower | |
| Military age | 18 |
| Available for military service | 131,000,000, age 15–49 (131,000,000[1]) |
| Fit for military service | 108,000,000, age 15–49 (131,000,000[2]) |
| Reaching military age annually | 4,500,000 (131,000,000[3]) |
| Active personnel | 476,000 |
| Deployed personnel | 1,673[4] |
| Expenditures | |
| Budget | US$8.18 billion(2017)[5] |
| Percent of GDP | 1.0% (2013) |
| Industry | |
| Domestic suppliers |
|
| Related articles | |
| History |
Military history of Indonesia Engagements & Missions: United Nations Peacekeeping Indonesian National Revolution Darul Islam (Indonesia) Republic of South Maluku PRRI Permesta Incorporation of West Papua into Indonesia Operation Trikora Indonesia–Malaysia confrontation Indonesian invasion of East Timor Insurgency in Aceh Free Papua Movement 2003–2004 Indonesian offensive in Aceh Operation Tinombala |
| Ranks | Indonesian military ranks |
The Indonesian National Armed Forces (Indonesian: Tentara Nasional Indonesia, literally "Indonesian National Military"; abbreviated as TNI) are the military forces of the Republic of Indonesia. It consists of the Army (TNI-AD), Navy (TNI-AL), and Air Force (TNI-AU). The President of Indonesia is the commander-in-chief of the Armed Forces. In 2016, it comprises approximately 395,500[6] military personnel including the Indonesian Marine Corps (Korps Marinir), which is the branch of the Navy.
The Indonesian Armed Forces was formed during the Indonesian National Revolution, when it undertook a guerrilla war along with informal militia. As a result of this, and the need to maintain internal security, the Armed forces including the Army, Navy, and Air Force has been organised along territorial lines, aimed at defeating internal enemies of the state and potential external invaders.[7]
Under the 1945 Constitution, all citizens are legally entitled and obliged to defend the nation. Conscription is provided for by law, yet the Forces have been able to maintain mandated strength levels without resorting to a draft. Most enlisted personnel are recruited in their own home regions and generally train and serve most of their time in units nearby.
The Indonesian armed forces are voluntary. The active military strength is 395,500[8] with available manpower fit for military service of males aged between 16 and 49 is 75,000,000, with a further 4,500,000 new suitable for service annually.[9]
Military spending in the national budget was widely estimated 3% of GDP in 2005,[9] but is supplemented by revenue from many military-run businesses and foundations. The defence budget for 2017 was $8.17bn.[10][8] The Indonesian armed forces (Military) personnel does not include members of law enforcement and paramilitary personnel such as the Indonesian National Police (Polri) consisting of approximately 590,000+ personnel, Mobile Brigade Corps (Brimob) of around 42,000+ armed personnel, the Civil Service Police Unit (Municipal police) or Satpol PP, Indonesian College Students' Regiment or Resimen Mahasiswa (Menwa) which is a collegiate military service consisting 26,000 trained personnel, and civil defence personnel (Linmas or Public Protection Service Corps, which replaced the old Hansip in 2014).
History
Formation
Before the formation of the Indonesian Republic, the military authority in the Dutch East Indies was held by the Royal Dutch East Indies Army (KNIL) and naval forces of the Royal Netherlands Navy (KM). Although both the KNIL and KM were not directly responsible for the formation of the future Indonesian armed forces, and mainly took the role of foe during Indonesian National Revolution in 1945 to 1949, the KNIL had also provided military training and infrastructure for some of the future TNI officers and other ranks. There were military training centres, military schools and academies in the Dutch East Indies. Next to Dutch volunteers and European mercenaries, the KNIL also recruited indigenous, especially Ambonese, Kai Islanders, Timorese, and Minahasan people. In 1940 with the Netherlands under German occupation and the Japanese pressing for access to Dutch East Indies oil supplies, the Dutch had opened up the KNIL to large intakes of previously excluded Javanese.[11] Some of the indigenous soldiers that had enjoyed Dutch KNIL military academy education would later become important TNI officers, like for example: Suharto and Nasution.
Indonesian nationalism and militarism started to gain momentum and support in World War II during the Japanese occupation of Indonesia. To gain support from the Indonesian people in their war against the Western Allied force, Japan started to encourage and back Indonesian nationalistic movements by providing Indonesian youth with military training and weapons. On 3 October 1943, the Japanese military formed the Indonesian volunteer army called PETA (Pembela Tanah Air – Defenders of the Homeland). The Japanese intended PETA to assist their forces oppose a possible invasion by the Allies. The Japanese military training for Indonesian youth originally was meant to rally the local's support for the Japanese Empire, but later it became the significant resource for the Republic of Indonesia during the Indonesian National Revolution in 1945 to 1949. Many of these men who served in PETA, both officers and NCOs alike like Sudirman, formed majority of the personnel that would compose the future armed forces.

At first, Indonesian Armed Forces started out as the BKR (Badan Keamanan Rakyat – People's Security Agency), which was formed in the 3rd PPKI meeting, on 29 August 1945; this was an organisation of militias in a united nationwide force to ensure the security remained intact across the newly declared independent Indonesia; it was created more as a civil defence force than an armed forces. The decision to create a "security agency" and not an army, was taken to lessen the probability of the allied forces viewing it as an armed revolution and invading in full force. During their capitulation, one of the terms of surrender to Japan was to return the Asian domains they had conquered to the previous nation of the Allies, certainly not to liberate them independently.
When confrontations became sharp and hostile between Indonesia and the Allied forces, on 5 October 1945 the TKR (Tentara Keamanan Rakyat – People's Security Armed Forces) was formed on the basis of existing BKR units; this was a move taken to formalise, unite, and organise the splintered pockets of independent troopers (laskar) across Indonesia, ensuing a more professional military approach, to contend with the Netherlands and the Allied force invaders.
The Indonesian armed forces have seen significant action since their establishment in 1945. Their first conflict was the 1945–1949 Indonesian National Revolution, in which the 1945 Battle of Surabaya was especially important.
In January 1946, TKR renamed onto Tentara Keselamatan Rakyat (People's Safety Military Forces), then succeeded by TRI (Tentara Republik Indonesia – Republic of Indonesia Military Forces), in a further step to professionalise the armed forces and increase its ability to engage systematically.

In June 1947, the TRI, per a government decision, was renamed the TNI (Tentara Nasional Indonesia - Indonesian National Armed Forces) which is a merger between the TRI and the independent paramilitary organizations (laskar) across Indonesia, becoming by 1950 the APRIS or Military Forces of the Republic of the United States of Indonesia (Angkatan Perang Republik Indonesia Serikat), by mid year the APRI or National Military Forces of the Republic of Indonesia (Angkatan Perang Republik Indonesia), absolving also native personnel from within both the former KNIL and KM within the expanded republic.
Independent Indonesia

From the 1950s to 1960s the Republic of Indonesia struggled to maintain its unity against local insurgencies and separatist movements in some of its provinces. From 1948 to 1962, the TNI was involved in local warfare in West Java, Aceh, and South Sulawesi against Darul Islam/Tentara Islam Indonesia (DI/TII), a militant movement aimed at establishing an Islamic state in Indonesia. The TNI also helped bring the rebellion of Republic of South Maluku to a close in 1963. Meanwhile, the PRRI/Permesta rebellion holds an essential place in Indonesian military history because it was led by army officers in Sumatra and Sulawesi between 1955 and 1961.
From 1961 to 1963, the TNI was involved in the military campaign to incorporate Western New Guinea into Indonesia, which pitted the TNI against Netherlands New Guinea. From 1962 to 1965 TNI fought in the Indonesia-Malaysia Confrontation. The Indonesian killings of 1965–1966 directly involved the armed forces under Lt. General Suharto fighting against the Communist Party of Indonesia.
Indonesia developed a good relationship with the Soviet Union in the period of 1961 and 1965. The Soviets sold 17 ships to the Indonesian Navy, the largest of which was a Sverdlov class cruiser. The size was 16,640 tons, very big compared to the current Indonesian Sigma class corvette at only 1,600 tons. Indonesia procured 12 Whiskey class submarines plus 2 supporting ships. Indonesia had more than a hundred military aircraft, 20 supersonic MiG-21s, 10 supersonic Mig-19, 49 Mig-17 and 30 MiG-15. They also supplied Indonesia with 26 Tupolev Tu-16 strategic bombers, though it is not clear what the serviceability rate was.[12]
On 21 June 1962, the name "Tentara Nasional Indonesia" (TNI) was changed to "Angkatan Bersenjata Republik Indonesia" (Republic of Indonesia Armed Forces/ABRI). The POLRI (Indonesian National Police) was integrated under the Armed Forces and changed its name to "Angkatan Kepolisian" (Police Forces), and its commander maintained the concurrent status of Minister of Defence and Security, reporting to the President, who is commander in chief.
Under the New Order
During the New Order-era, the Indonesian military enjoyed certain privileges and played a significant role in Indonesian politics. The military involvement in Indonesian politics was formulated in the Dwifungsi (Dual function) doctrine of the Indonesian National Armed Forces.
On 1 July 1969, the Police Force's name was reverted to "POLRI".
In 1975, Indonesia invaded East Timor, followed a year afterward by the Insurgency in Aceh, flaring on-and-off from 1976 to 2005. From the 1970s to 1990s the Indonesian military worked hard to suppress these armed insurgency and separatist movements in the provinces of Aceh and East Timor. In 1991 the Santa Cruz Massacre occurred in East Timor, tarnishing the image of the Indonesian military internationally. This incident led the United States to sever its IMET funding, which supported training for the Indonesian military.
Also in 1992, each service branch began to reform their women's units, which were formed in the 1960s. These all-female Corps are the Women's Army Corps, the Women's Naval Service, the Air Force Women's Service Corps, and the Police Women's Service Corps. These were intended to "set to work at places and in functions conform[ing] to their feminine disposition." More specifically, women were assigned to administrative work, teaching English and working to improve health and social conditions of armed forces members and their families. The women police were said to "play an important role in solving problems [of] drug addicts and juvenile delinquents."[9]
After the Cold War ended the Indonesian Armed Forces began to take part in United Nations peacekeeping missions. These were usually known as Garuda Contingent. The first was to the United Nations Transitional Authority in Cambodia, quickly followed by a deployment as part of the United Nations Protection Force in Bosnia-Herzegovina. Indonesian troops were deployed to both the first and the second UN intervention in Somalia.
Reformation

After the fall of Suharto in 1998, the democratic and civil movement grew against the acute military role and involvements in Indonesian politics. As the result, the post-Suharto Indonesian military has undergone certain reformations, such as the revocation of Dwifungsi doctrine and the terminations of military controlled business. The reformation also involved the law enforcement in common civil society, which questioned the position of Indonesian police under the military corps umbrella. These reforms led to the separation of the police force from the military. In 1990, the Indonesian National Police officially regained its independence and now is a separate entity from the armed forces proper. The official name of the Indonesian military also changed from "Angkatan Bersenjata Republik Indonesia" (ABRI) back to "Tentara Nasional Indonesia" (TNI).
Indonesian military continue its involvement and contribution in United Nations peacekeeping missions. After 1999, Indonesian troops went to Africa as part of the United Nations Mission in the Democratic Republic of Congo. The TNI has also served with the United Nations Interim Force in Lebanon, UNAMID, UNSMIS, MINUSTAH, UNISFA, UNMISS, UNMIL.[13]
Following the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake, the United States government suspended a spare parts embargo which had been in place for non-lethal equipment and military vehicles, to support the humanitarian effort in the tsunami-devastated regions of Aceh and Nias. Since then, the Air Force has signed deals to purchase more C-130 transport aircraft and upgrade the current C-130s in the inventory. On 22 November 2005, the US announced that military ties with Indonesia would be restored in full. The decision had ended the six-year US ban on arms sales.[14]
In 2009, all former Indonesian military businesses were to be surrendered to a specialist body. The Indonesian Military Business Management Body (BPBTNI) was established in effect of a stipulation in Law No. 34/2004 on the Indonesian Military (TNI) which was to take over ownership and operation of all businesses owned or run by the TNI by 2009. Unlike the former National Banking Restructuring Agency (BPPN) which burdened the Indonesian state with losses, the BPBTNI would bear all losses alone.[15]
From 2010 onwards, military spending in Indonesia was aligned to the Minimum Essential Force (MEF) strategic plan 2010 – 2014 requirements. Under MEF 2010 – 2014 funds of up to Rp150 trillion ($16.41 billion) to spend over five years to procure major weapons systems, Rp50 trillion $5.47 billion) will be used to accelerate achieving the Minimum Essential Force, Rp55 trillion ($6.02 billion) for procurement and Rp45 trillion ($4.92 billion) for maintenance and repair.[16] Subsequent funding would be made available to fund the strategic plans of MEF 2015 - 2019 and MEF 2020 - 2024 to achieve the strategic goal of Minimum Essential Force.
Political role of the military

During the Soeharto era, the military had a "dual function" (dwifungsi in Indonesian) defined as: firstly preservation and enforcement of internal and external security and sovereignty of the State and secondly, as an overseer and arbiter of government policy. This was used to justify substantial military interference in politics. Long-time president Soeharto was an army general and was strongly supported by most of the military establishment. Traditionally a significant number of cabinet members had military backgrounds, while active duty and retired military personnel occupied a large number of seats in the legislature. Commanders of the various territorial commands played influential roles in the affairs of their respective regions.
Indonesia has not had a substantial conflict with its neighbours since the 1963–1965 Indonesia-Malaysia Confrontation, known in Indonesia as Konfrontasi with Malaysia. Possible future disputes relating to competing Malaysian-Indonesian South China Sea claims, where Indonesia has large natural gas reserves, concern the Indonesian government. As of 2007, some regional claims with neighbouring Malaysia have led to some minor sabre-rattling by both sides with a stalemate over the sovereignty of Unarang rock and the maritime boundary in the Ambalat oil block in the Celebes Sea.[9]
In the post-Soeharto period since 1998, civilian and military leaders have been successfully removing the military influence from politics and advocated the structural reform in military body. For example, the military's representation in the House of Representatives was removed, the police forces was separated completely from armed force, and an active military officer can only serve his/her commission within the armed forces itself and thus is prohibited from being appointed to government positions (including as Minister of Defense). It sometimes comes to armed conflicts between the military and the police.[17]
Philosophy and Doctrine
_Indonesia_2013_in_Jakarta%2C_Indonesia%2C_May_24%2C_2013_130524-N-NX489-076.jpg)
The Indonesian military philosophy over-riding defence of the archipelago is summarily civilian-military defence, called "Total People's Defence"- consisting of a three-stage war: a short initial period in which invader would defeat a conventional Indonesian military, a long period of territorial guerrilla war followed by a final stage of expulsion- with military acting as a rallying point for defence from grass-roots village level upwards. The doctrine relies on a close bond between villager and soldier to encourage the support of the entire population and enable the military to manage all war-related resources.
The civilian population would provide logistical support, intelligence, and upkeep with some trained to join the guerrilla struggle. The armed forces regularly engage in large-scale community and rural development. The "Armed Forces Enters the Village" (AMD/TMMD) program, begun in 1983 is held three times annually to organise and assist construction and development of civilian village projects.
The current developments in Indonesia's defence policies are framed within the concept of achieving "Minimum Essential Force" or MEF by 2024. This concept of MEF was first articulated in Presidential Decree No. 7/2008 on General Policy Guidelines on State Defence Policy (Peraturan Presiden Republik Indonesia No. 7 Tahun 2008 Tentang Kebijakan Umum Pertahanan Negara)[18] which came into effect on 26 January 2008. MEF is defined as a capability based defence and force level that can guarantee the attainment of immediate strategic defence interests, where the procurement priority is given to the improvement of minimum defence strength and/or the replacement of outdated main weapon systems/equipments. To achieve this aim, MEF had been restructured into a series of 3 strategic programmes with timeframes from 2010 to 2014, 2015 to 2019 and 2020 to 2024 as well as spending of up the 1.5 - 2% of the GDP.
The identity of the Indonesian National Armed forces is (Article 2 of the TNI Law) is the TNI must aim to become the:
- People's Military Forces, the armed forces whose serving personnel come from Indonesian citizens from all walks of life;
- Military of Warriors, which are soldiers who fought to establish the Unitary State of the Republic of Indonesia and do not recognize surrender in carrying out and completing its duties;
- National Armed Forces, the Indonesian national armed forces who serve in the interest of the country and her people over the interests of the regions/provinces, ethnic groups, races, and religions;
- Professional Armed Forces, a military force that is well-trained, well-educated, well-equipped, non-practicable, probihited to do business and guaranteed welfare, and following the country's political policies that embrace democratic principles, civil supremacy, human rights, the provisions of national law and international laws in force, as ratified and approved in the 1999-2003 amendments to the Constitution.
Organisation
The Indonesian armed forces have long been organised around territorial commands.[19] Following independence, seven were established by 1958. No central reserve formation was formed until 1961 (when the 1st Army Corps of the Army General Reserve, "CADUAD", the precursor of today's Kostrad was established). It was only after the attempted coup d'état of 1 October 1965 and General Suharto's rise to the presidency that it became possible to integrate the armed forces and begin to develop a joint operations structure.
Following a decision in 1985, major reorganization separated the Ministry of Defense and Security ("HANKAM") from the "ABRI" (Indonesian Armed Forces name during Soeharto's presidential era) headquarters and staff.[20] "HANKAM" was made responsible for planning, acquisition, and management tasks but had no command or control of troop units. The "ABRI" commander in chief retained command and control of all armed forces and continued by tradition to be the senior military officer in the country, while continuing to be a part of the cabinet. Since the separation of the ministry from the armed forces general headquarters in 1985, the "HANKAM" staff has been composed largely of retired military personnel. The split provided positions of responsibility for highly qualified but relatively young retired officers of the Generation of 1945 while also opening up high level billets in "ABRI" to younger active-duty officers who had been frustrated by slow rates of promotion.
The administrative structure of "HANKAM" consisted of a minister, deputy minister, secretary general, inspector general, three directorates-general and a number of functional centers and institutes. The minister, inspector general, and three directors general were retired senior military officers; the secretary general (who acted as deputy minister) and most functional center chiefs were active-duty military officers, while employees and staff were personnel of the armed forces and of the civil service.
The 1985 reorganisation also made significant changes in the armed forces chain of command. The four multi-service Regional Defense Commands ("Kowilhans") and the National Strategic Command ("Kostranas") were eliminated from the defense structure, establishing the Military Regional Command ("Kodam"), or area command, as the key organisation for strategic, tactical, and territorial operations for all services. The chain of command flowed directly from the "ABRI" commander in chief to the ten "Kodam" commanders, and then to subordinate army territorial commands. The former territorial commands of the air force and navy were eliminated from the structure altogether, with each of those services represented on the "Kodam" staff by a senior liaison officer. The navy and air force territorial commands were replaced by operational commands. The air force formed two Operations Commands ("Ko-Ops") while the navy had its Eastern Fleet and Western Fleet—Armadas. The air force's National Air Defense Command ("Kohanudnas") remained under the "ABRI" commander in chief. It had an essentially defensive function that included responsibility for the early warning system.
The officer corps of the armed forces was estimated at 53,000 in 1992.[21] Less than 1 percent of these were of general officer ranks. The Armed Forces Academy of the Republic of Indonesia ("AKABRI"), the Military Academy at Magelang, Jawa Tengah Province trains most military officer corps. Other military academies are the Naval Academy ("A.A.L") in Surabaya and the Air Force Academy ("A.A.U") in Jogjakarta. Mandatory retirement exists for officers at the age of fifty-eight and routine periodic reassignments are enforced.[22]
After Soeharto's presidential era collapsed which was in 1998, the Indonesian Police Force was separated from the Armed Forces making the Indonesian Armed Forces under the direct auspices command of the Ministry of Defense and the Police Force under the direct auspices of the President of Indonesia. Before 1998, the Armed Forces of Indonesia (the then name "ABRI") was composed of four joint services which were the Indonesian Army, Indonesian Navy, Indonesian Air Force, and the Indonesian National Police. Then after 1998 (After reformation from Soeharto), the Armed Forces' name changed to TNI (Tentara Nasional Indonesia) literally meaning: "The National Military of Indonesia" and the independent Indonesian Police Force changed its name to POLRI (Polisi Republik Indonesia) literally meaning: "The National Police Force of Indonesia". Now specifically, although the Armed Forces of Indonesia and the National Police of Indonesia has been separated, they still cooperate and conduct special duties and tasks together for the sake of the national security and integrity of Indonesia.
On 13 May 2018, Commander Hadi Tjahjanto reorganized the armed forces once more by inaugurating 4 new military units: Kostrad 3rd Infantry Division, 3rd Fleet Command, 3rd Air Force Operational Command and Marine Force III. The new military units are intended to reduce response time against any threats and problems in Eastern Indonesia. He also officially renamed the Western and Eastern Fleet Commands to 1st and 2nd Fleet Commands.[23]
The Indonesian National Armed Forces HQ is structured into the following in accordance with Presidential decree No. 62/ 2016:[24]
Leadership elements

The highest position in the Indonesian National Armed forces is the Commander of the Indonesian National Armed Forces (Panglima TNI), usually held by the four-star General/Admiral/Air Marshall appointed by and reporting directly to the President of Indonesia.
Auxiliary elements of leadership
- Chief of the General Staff of the TNI
- Inspector General of the TNI
- TNI Expert Advisor
- TNI Advisor for Strategic Policy and General Planning
- TNI Intelligence Advisor;
- TNI Operations Advisor
- TNI Personnel Advisor
- TNI Logistics Advisor
- TNI Territorial Operations Advisor
- TNI Communications and Electronics Advisor
Service Elements
- Communications and Electronics Component of the Indonesian National Armed forces (Satkomlek TNI)
- Indonesian National Armed forces Operational Control Center (Puskodalops TNI)
- Office of the Secretariat General of the Indonesian National Armed Forces (Sentum TNI)
- General Headquarters and HQ Services Command of the Indonesian National Armed Forces (Denma Mabes TNI)
Central Executive Agencies under the Armed Forces General Headquarters


- Indonesian National Armed Forces Staff Colleges (Sekolah Staf dan Komando TNI/ Sesko TNI)
- Army Staff College
- Naval Staff College
- Air Force Staff College
- National Armed Forces Education, Training and Doctrine Development Command (Komando Pembinaan Doktrin dan Latihan TNI/ Kodiklat TNI)
- The Indonesian National Armed Forces Academy System (Akademi TNI)
- Military Academy Magelang
- Naval Academy Surabaya
- Air Force Academy Yogyakarta
- Strategic Intelligence Agency of the Indonesian National Armed forces (Badan Intelijen Strategis TNI/ Bais TNI)
- Presidential Security Forces Command of the Indonesian National Armed Forces (Pasukan Pengamanan Presiden/ Paspampres)
- Indonesian National Armed Forces Public Relations and Media Service (Pusat Penerangan TNI)
- Indonesian National Armed Forces Joint Service Medical Department (Pusat Kesehatan TNI)
- Indonesian National Armed Forces Joint Service Military Police Command (Pusat Polisi Militer/ Puspom TNI)
- Joint Service Logistics Command of the Indonesian National Armed Forces (Badan Perbekalan/ Babek TNI)
- Indonesian National Armed Forces Joint Legal Service and General Counsel (Badan Pembinaan Hukum/ Babinkum TNI)
- Chaplaincy Service of the Indonesian National Armed forces (Pusat Pembinaan Mental/ Pusbintal TNI)
- Finance Directorate of the Indonesian National Armed forces (Pusat Keuangan TNI)
- Military Historical Directorate of the Indonesian National Armed Forces (Pusat Sejarah TNI)
- Indonesian National Armed Forces Information and Communications Technologies and Data Processing Center (Pusat Informasi dan Pengolahan Data/ Pusinfolahta TNI)
- Indonesian National Armed Forces Peacekeeping Maintenance Missions Center (Pusat Misi Pemeliharaan Perdamaian TNI)
- International Cooperation Center of the Indonesian National Armed Forces (Pusat Kerjasama Internasional TNI)
- Center for Strategic Assessment of the Indonesian National Armed Forces (Pusat Pengkajian Strategi TNI)
- Center for Physical Fitness and Military Regulation of the National Armed Forces of Indonesia (Pusat Jasmani dan Perautran Militer Dasar TNI)
- National Armed Forces Rapid Disaster Relief Response Command (Pasukan Reaksi Cepat Penanggulangan Bencana/ PRCPB TNI)
- National Armed Forces Rapid Response Forces Command (Pasukan Pemukul Reaksi Cepat/ PPRC TNI)
- General Headquarters Garrison and HQ Services Unit of the Indonesian National Armed forces (Komando Garnisun Tetap)
- Indonesian National Armed Forces Cyber Operations Command (Satuan Siber TNI)
Principal Operational Commands under the Armed Forces General Headquarters

- Indonesian National Air Defense Forces Command (Kohanudnas)
- Defense Joint Service Regional Command (Kogabwilhan)
- Army Strategic Command (Kostrad)
- Special Forces Command (Kopassus)
- Military Region Commands (Kodam)
- Fleet Forces Commands (Koarmada)
- Military Sealift Command (Kolinlamil)
- Indonesian Marine Corps (Kormar)
- Air Force Operational Commands (Koopsau)
Branches

- The TNI-AD (Indonesian Army) was first formed in 1945 following the end of World War II and to protect the newly independent country, it is initially consisted of local militia and grew to become the regular army of today. The force is now capable and has personnel up-to 306,506 and compromises of major and strong territorial army commands known as KODAM and several units, regiments, and battalions all stationed and tasked for the national army defense of Indonesia. The army is also built up of operational commands and special forces such as the: Kopassus and the Kostrad units also with other types of formation within the Army itself. The Army also given the tasks to guard and patrol the land border with Malaysia, Papua New Guinea, and East Timor.
- The TNI-AL (Indonesian Navy) was first formed on 22 August 1945. The current strength of the Navy is around up-to 74,000. In contrast to many other nations and military traditions, the Navy uses Army style ranks (See: Indonesian military ranks).[25] The Navy has three navy fleets which are the 1st Fleet Command (Koarmada I) based in Jakarta, the 2nd Fleet Command (Koarmada II) based in Surabaya and the 3rd Fleet Command (Koarmada III) based in Sorong, all three fleet forces commands holding responsibility for the defense of the three maritime and naval territorial commands. The Navy also has a management of aircraft and aviation systems which are operated by the Naval Aviation Command (Dinas Penerbangan TNI-AL). The Navy operates 52 fixed wing aircraft and 23 combat and transport helicopters.[7] The Navy also includes the Indonesian Marine Corps (Korps Marinir, or KorMar). It was created on 15 November 1945 and has the duties of being the main naval infantry and amphibious warfare force with quick reaction capabilities and special operations abilities.
 Indonesian Navy Vessel With US Coast Guard
Indonesian Navy Vessel With US Coast Guard - The TNI-AU (Indonesian Air Force) is headquartered in Jakarta, Indonesia. Its Order of Battle is split into three Air Force Operational Commands (KOOPSAU) (east, central and west regions). Most of its airbases are located on the island of Java.[26] Presently, the Air Force has up-to 34,930 personnel equipped with 510 aircraft including Su-27s, Su-30 fighters, A-4E Skyhawks, Northrop F-5s, F-16, KAI T-50 Golden Eagle. The Air Force also has air force infantry corps which is known as Paskhas that are tasked for airbase defense, airborne troops and special forces unit.
 Indonesian Sukhoi Su-30 fighter
Indonesian Sukhoi Su-30 fighter - While no longer a part of the Armed Forces since 1 April 1999, the Indonesian National Police (POLRI) often operate in paramilitary roles independently or in co-operation with the other services on internal security missions usually in cooperation with the Indonesian National Armed Forces (TNI). The National Police Mobile Brigade Corps are the main paramilitary forces which are usually put on to these roles and tasks with the service branches of the armed forces. Until today, both the TNI and the POLRI still holds strong ties and cooperation for the sake of the nation's national security and integrity purposes.
Special Forces Unit
Indonesian Military Special Forces
- TNI AD

- TNI AL

- TNI AU

In the immediate aftermath of 2018 Surabaya bombings, President Widodo has agreed to revive the TNI Joint Special Operations Command (Koopsusgab) to assist the National Police in antiterrorism operations under certain conditions. This joint force is composed of special forces of the National Armed Forces as mentioned above, and is under the direct control of the Commander of the National Armed Forces.[27]
Strength
In the Beginning of 2010, the Indonesian government seeks to strengthen the TNI to achieve minimum standards of minimum strength (Minimum Essential Force (MEF)). The MEF is divided into three strategic plan stages until 2024. Initially the government budgeted Rp156 trillion for the provision of TNI's main weapon system equipment (alutsista) in the MEF period 2010-2014.[28][29][30]
The table below is the data on the strength of the Indonesian armed forces in 2006 with some updated data in accordance with current conditions:
| Number of personnel: 369,389[31] personnel | ||
| Number of personnel: 273,693[31] | Number of personnel: 68,180[31] | Number of personnel: 27,590[31] |
Centralized power
|
Integrated Fleet Weapon System
|
Air Squadrons
|
(Other sources: Harian Koran Tempo 14 Februari 2006)
Budget
Beeson and Bellamy wrote in 2002 that: '..By some estimates 60–65% of the military's actual operating expenses come from 'off-budget sources' rather than the government (Cochrane 2002). This is a euphemism for a host of legal and illegal practices that include legitimate involvement in state-owned and private businesses, as well as a range of activities in the 'black economy.' An estimated 30% of government funding of the military 'is lost through corruption in the process of buying military equipment and supplies.'(International Crisis Group 2001: 13)'[33]
In addition, the territorial commands (KODAM) are responsible for 'the bulk of their operational fund-raising.'[34]
| Fiscal Year | Budget (IDR) | Budget (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| 2005 | Rp 21.97 trillion | USD 2.5 billion |
| 2006 | Rp 23.6 trillion | USD 2.6 billion |
| 2007 | Rp 32.6 trillion | USD 3.4 billion |
| 2008 | Rp 36.39 trillion | USD 3.8 billion |
| 2009 | Rp 33.6 trillion | USD 3.3 billion |
| 2010 | Rp 42.3 trillion | USD 4.47 billion |
| 2011 | Rp 47.5 trillion | USD 5.2 billion |
| 2012 | Rp 64.4 trillion[35] | USD 7.5 billion |
| 2013 | Rp 81.8 trillion[36][37] | USD 8.44 billion[38] |
| 2014 | Rp 83.4 trillion[39] | USD 7.91 billion[40] |
| 2015 | Rp 95.5 trillion[41] | USD 8.05 billion |
| 2016 | Rp 99.5 trillion[42] | USD 7.3 billion |
| 2017 | Rp 109.3 trillion[43] | USD 8.17 billion |
| 2018 | Rp 108. trillion[44] | USD 8. billion |
Commander of the Indonesian National Armed Forces
Rank Structures
In the Army, Navy (including Marine corps), Air force, and the Police force, the rank consists of officer known as in Indonesian: "Perwira", NCO: "Bintara" and enlisted: "Tamtama". The rank titles of the Marine Corps are the same as those of the Army, but it still uses the Navy's style insignia (for lower-ranking enlisted men, blue are replacing the red colour).
Army
| Ranks and Insignias - TNI-AD (Indonesian Army) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NATO code[n 1] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
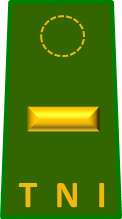 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indonesian | Jenderal Besar | Jenderal | Letnan Jenderal | Mayor Jenderal | Brigadir Jenderal | Kolonel | Letnan Kolonel | Mayor | Kapten | Letnan Satu | Letnan Dua | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| English | General of the Army | General | Lieutenant General | Major General | Brigadier General | Colonel | Lieutenant Colonel | Major | Captain | Lieutenant | Second Lieutenant | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NATO code[n 1] | OR-9 | OR-8 | OR-7 | OR-6 | OR-5 | OR-4 | OR-3 | OR-2 | OR-1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indonesian | Pembantu Letnan Satu | Pembantu Letnan Dua | Sersan Mayor | Sersan Kepala | Sersan Satu | Sersan Dua | Kopral Kepala | Kopral Satu | Kopral Dua | Prajurit Kepala | Prajurit Satu | Prajurit Dua | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| English | Chief Warrant Officer | Warrant Officer | Sergeant Major | Master Sergeant | First sergeant | Second sergeant | Master Corporal | Corporal | Lance Corporal | Master Private | Private First Class | Private Second Class | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Navy
| Ranks and Insignias - TNI-AL (Indonesian Navy) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NATO code[n 1] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indonesian | Laksamana Besar | Laksamana | Laksamana Madya | Laksamana Muda | Laksamana Pertama | Kolonel | Letnan Kolonel | Mayor | Kapten | Letnan Satu | Letnan Dua | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| English | Admiral of the Fleet | Admiral | Vice Admiral | Rear Admiral | Commodore | Colonel | Lieutenant Colonel | Major | Captain | Lieutenant | Second Lieutenant | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NATO code[n 1] | OR-9 | OR-8 | OR-7 | OR-6 | OR-5 | OR-4 | OR-3 | OR-2 | OR-1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indonesian | Pembantu Letnan Satu | Pembantu Letnan Dua | Sersan Mayor | Sersan Kepala | Sersan Satu | Sersan Dua | Kopral Kepala | Kopral Satu | Kopral Dua | Kelasi Kepala | Kelasi Satu | Kelasi Dua | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| English | Chief Warrant Officer | Warrant Officer | Sergeant Major | Master Sergeant | First sergeant | Second sergeant | Master Corporal | Corporal | Lance Corporal | Seaman | Seaman Apprentice | Seaman recruit | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Air Force
| Ranks and Insignias - TNI-AU (Indonesian Air Force) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NATO code[n 1] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indonesian | Marsekal Besar | Marsekal | Marsekal Madya | Marsekal Muda | Marsekal Pertama | Kolonel | Letnan Kolonel | Mayor | Kapten | Letnan Satu | Letnan Dua | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| English | Marshal of the Air Force | Air Chief Marshal | Air Marshal | Air Vice Marshal | Air Commodore | Colonel | Lieutenant Colonel | Major | Captain | Lieutenant | Second Lieutenant | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NATO code[n 1] | OR-9 | OR-8 | OR-7 | OR-6 | OR-5 | OR-4 | OR-3 | OR-2 | OR-1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indonesian | Pembantu Letnan Satu | Pembantu Letnan Dua | Sersan Mayor | Sersan Kepala | Sersan Satu | Sersan Dua | Kopral Kepala | Kopral Satu | Kopral Dua | Prajurit Kepala | Prajurit Satu | Prajurit Dua | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| English | Chief Warrant Officer | Warrant Officer | Sergeant Major | Master Sergeant | First sergeant | Second sergeant | Master Corporal | Corporal | Lance Corporal | Senior Airman | Airman First Class | Airman | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Naming history
- People's Security Bureau (Badan Keamanan Rakyat, 22 August – 5 October 1945; spelled "Ra'jat")
- People's Security Forces (Tentara Keamanan Rakyat, 5 October 1945 – 7 January 1946; spelled "Ra'jat")
- People's Safety Forces (Tentara Keselamatan Rakyat, 7–26 January 1946; spelled "Ra'jat")
- Republic of Indonesia Armed Forces (Tentara Republik Indonesia, 26 January 1946 – 3 June 1947; spelled "Repoeblik" until 17 March 1947)
- Indonesian National Armed Forces (Tentara Nasional Indonesia, 3 June 1947 – 27 December 1949)
- Republic of the United States of Indonesia Military Forces (Angkatan Perang Republik Indonesia Serikat, 27 December 1949 – 17 August 1950)
- Republic of Indonesia War Forces (Angkatan Perang Republik Indonesia, 17 August 1950 – 21 June 1962)
- Republic of Indonesia Armed Forces (Angkatan Bersenjata Republik Indonesia, 21 June 1962 – 1 April 1999; spelled "Bersendjata" until 1 January 1973)
- Indonesian National Armed Forces (Tentara Nasional Indonesia, since 1 April 1999)
See also
Notes
References
- ↑ "Indikator Pembangungan Dunia-Penjelajah Google Data Publik". www.google.co.id.
- ↑ "Indikator Pembangungan Dunia-Penjelajah Google Data Publik". www.google.co.id.
- ↑ "Indikator Pembangungan Dunia-Penjelajah Google Data Publik". www.google.co.id.
- ↑ "Ongoing Operations". www.pkc-indonesia.mil.id. Pusat Misi Pemeliharaan Perdamaian Tentara Nasional Indonesia. Archived from the original on 8 January 2014. Retrieved 8 January 2014.
- ↑ https://www.sipri.org/sites/default/files/1_Data%20for%20all%20countries%20from%201988%E2%80%932017%20in%20constant%20%282016%29%20USD.pdf
- ↑ International Institute for Strategic Studies (3 Feb 2014). The Military Balance 2014. London: Routledge. pp. 246–250. ISBN 9781857437225.
- 1 2 http://www.tni.mil.id
- 1 2 The Military Balance 2017. London: International Institute for Strategic Studies. 2017. p. 294.
- 1 2 3 4 http://lcweb2.loc.gov/cgi-bin/query/r?frd/cstdy:@field(DOCID+id0171
- ↑ "Revised Indonesian budget brings modest increase | Jane's 360". www.janes.com. Retrieved 2017-11-14.
- ↑ McDonald (1980), pages 13
- ↑ "Kejayaan Angkatan Perang Indonesia Pada Masa Bung Karno". Berdikari Online. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- ↑ Garuda Militer. "15 Prajurit TNI Ikuti Farewell Ceremony di Haiti". garudamiliter.blogspot.com. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- ↑ National, World and Business News|Reuters.co.uk Archived 21 July 2006 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑
- ↑ "http://www.embassyofindonesia.org/news/2012/01/news113.htm". 31 January 2012. Archived from the original on 19 October 2013. External link in
|title=(help) - ↑ "Indonesia's elite soldiers kill prisoners". Al Jazeera. 5 April 2013. Retrieved 5 April 2013.
- ↑ "PERATURAN PRESIDEN REPUBLIK INDONESIA NOMOR 7 TAHUN 2008". www.sjdih.depkeu.go.id.
- ↑ Lowry, Bob (1993). Indonesian Defence Policy and the Indonesian Armed Forces, Canberra Papers on Strategy and Defence No.99, Strategic and Defence Studies Centre, Australian National University, 1993, p.36-40
- ↑ Library of Congress Country Study, Indonesia, November 1992, Organization and Equipment of the Armed Forces
- ↑ Library of Congress Country Study, Indonesia, 1992, link verified December 2009.
- ↑ Colonel Sulistiyanto, M.Sc. "Strategic position in TNI". Indonesian Navy. Archived from the original on 30 April 2014. Retrieved 30 April 2014.
- ↑ "Panglima TNI Resmikan Empat Satuan Baru TNI di Sorong". Puspen TNI. 13 May 2018. Retrieved 20 May 2018.
- ↑ "Law" (PDF). kemendagri.go.id. 14 July 2016. Retrieved 9 January 2018.
- ↑ Indonesia, PUSPEN TNI, Teamworks. "WEBSITE TENTARA NASIONAL INDONESIA". www.tni.mil.id.
- ↑ "Scramble Magazine: Indonesian Air Arms Overview". Scramble.nl. Archived from the original on 16 September 2011. Retrieved 25 November 2011.
- ↑ "Jokowi agrees to revive Koopsusgab special forces". Jakarta Post. 18 May 2018. Retrieved 19 May 2018.
- ↑ "Anggaran Alutsista 2010-2014 Capai Rp156 Triliun". Investor Daily Indonesia. 30 January 2012. Retrieved 4 January 2014.
- ↑ "Minimum Essential Force TNI Tahap 2 (2015-2019)". JakartaGreater.com. 11 September 2013. Retrieved 4 January 2014.
- ↑ "MEF : Modernisasi Militer Indonesia". analisismiliter.com.
- 1 2 3 4 Rahakundini Bakrie, Connie (2007). Pertahanan Negara dan Postur TNI ideal. Jakarta: Yayasan Obor Indonesia. p. 102. ISBN 978-979-461-665-9.
- ↑ "180 Pesawat Tempur Canggih AU". Tribunnews.com. 27 January 2012. Retrieved 16 November 2012.
- ↑ Mark Beeson and Alex J. Bellamy, 'Securing Southeast Asia: The politics of security sector reform,' Routledge, 2008, ISBN 0-415-41619-1, 134-5.
- ↑ Beeson and Bellamy, 2008, 138.
- ↑ http://www.setneg.go.id/index2.php?option=com_content&do_pdf=1&id=5727
- ↑ http://www.asianewsnet.net/home/news.php?sec=1&id=33629 Margareth S. Aritonang, While education and healthcare suffer, Indonesian army budget soars, The Jakarta Post, 18 July 2012
- ↑ IDB. "Rp. 81.8 Triliun Anggaran Militer 2013 Indonesia". indo-defense.blogspot.com. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- ↑ NurW. "DEFENSE STUDIES". defense-studies.blogspot.com. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- ↑ "Komisi I Dukung Tambahan Anggaran Kemenhan Dan TNI". 21 October 2013.
- ↑ http://www.janes.com/article/25916/indonesian-defence-budget-increases-9
- ↑ "SBY maintains status quo in 2015 budget". 18 August 2014.
- ↑ "Kementerian PU Dapat Anggaran Terbanyak dari APBN 2016". finansial.bisnis.com.
- ↑ "Revised Indonesian budget brings modest increase - Jane's 360". www.janes.com.
- ↑ Aziza, Kurnia Sari (26 October 2017). "Kemenhan dan Polri Dapat Anggaran Paling Besar pada APBN 2018". Kompas (in Indonesian). Retrieved 10 January 2018.
Further reading
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Military of Indonesia. |
- Bresnan, John. (1993). Managing Indonesia: the modern political economy. New York: Columbia University Press.
- Many topics, including the political role of the military at the height of Suharto's New Order.
- Chandra, Siddharth and Douglas Kammen. (2002). "Generating Reforms and Reforming Generations: Military Politics in Indonesia's Transition to Democracy." World Politics, Vol. 55, No. 1.
- Crouch, Harold. (1988). The army and politics in Indonesia. Ithaca:Cornell University Press.
- First published 1978. Now somewhat dated, but provides an influential overview of the role of the military in consolidating Suharto's power
- "Guerilla Warfare and the Indonesian Strategic Psyche" Small Wars Journal article by Emmet McElhatton
- Israel, Fauzi.(2009) – Advanced Weapon's Infantry Firepower & Accuracy
- Kammen, Douglas and Siddharth Chandra. (1999). A Tour of Duty: Changing Patterns of Military Politics in Indonesia in the 1990s. Ithaca, New York: Cornell Modern Indonesia Project No. 75.
- Kingsbury, Damen. Power Politics and the Indonesian Military, Routledge: 2003 ISBN 0-415-29729-X
External links
- Official Website of TNI
- Official Website of the Department of Defence
- Indonesian military blog
- Civil-Military Relations in Post-Suharto Indonesia and the Implications for Democracy Today: A Preliminary Analysis
- Indonesia Military Guide
- Indonesia's Army (TNI-AD)
- Indonesia's Navy (TNI-AL)
- Indonesia's Air Force (TNI-AU)

.svg.png)