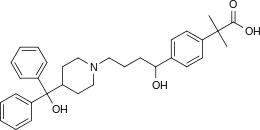
Fexofenadine
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | originally Allegra, others[1] |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a697035 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category | |
| Routes of administration | by mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 30-41%[2] |
| Protein binding | 60-70%[3] |
| Metabolism | Hepatic (≤5% of dose)[3] |
| Elimination half-life | 14.4 hours |
| Excretion | Feces (~80%) and urine (~10%) as unchanged drug[3] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard |
100.228.648 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C32H39NO4 |
| Molar mass | 501.68 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Chirality | Racemic mixture |
| |
| |
| | |
Fexofenadine, sold under the trade name Allegra among others[1] is an antihistamine pharmaceutical drug used in the treatment of allergy symptoms, such as hay fever and urticaria.[4] Therapeutically, fexofenadine is a selective peripheral H1-blocker.
Fexofenadine is classified as a second-generation antihistamine because it is less able to pass the blood-brain barrier and cause sedation, compared to first-generation antihistamines.[5][6] It has also been called a third-generation antihistamine, although there is some controversy associated with the use of the term.[7]
Fexofenadine has been manufactured in generic form since 2011.[8]
Medical uses
Fexofenadine is used for relief from physical symptoms associated with seasonal allergic rhinitis and for treatment of chronic urticaria.[5] It does not cure but rather prevents the aggravation of allergic rhinitis and chronic idiopathic urticaria and reduces the severity of the symptoms associated with those conditions, providing relief from repeated sneezing, runny nose, itchy eyes or skin, and general body fatigue.
Side effects
The most common side effect demonstrated in adults was headache, but some also experienced back and muscle pain, miosis or pinpoint pupils, nausea, drowsiness, and menstrual cramps. There have also been rare reports of anxiety and insomnia. The most common side effects demonstrated during clinical trials were cough, upper respiratory tract infection, fever, and otitis media for children ages 6 to 11 and fatigue for children ages 6 months to 5 years.[9]
Overdose
The safety profile of fexofenadine is quite favorable, as no cardiovascular or sedative effects have been shown to occur even when taking 10 times the recommended dose.[10] Research on humans ranges from a single 800 mg dose, to a twice-daily 690 mg dose for a month, with no clinically significant adverse effects, when compared to a placebo. No deaths occurred in testing on mice, at 5000 mg/kg body weight, which is one-hundred ten times (110x) the maximum recommended dose for an adult human.[9] If overdose were to occur, supportive measures are recommended. Theoretically, an overdose could present as dizziness, dry mouth, and/or drowsiness, consistent with an exaggeration of the usual side effects. It does not appear that hemodialysis is an effective means of removing fexofenadine from the blood.[9]
Mechanism of action
Fexofenadine is a selectively peripheral H1-blocker. Blockage prevents the activation of the H1 receptors by histamine, preventing the symptoms associated with allergies from occurring. Fexofenadine does not readily cross the blood–brain barrier and is therefore less likely to cause drowsiness in comparison to other antihistamines that readily cross the blood-brain barrier (i.e. first-generation antihistamines like diphenhydramine). In general, fexofenadine takes about one hour to take effect, though this may be affected by the choice of dosage form and the presence/absence of certain foods.
Fexofenadine also exhibits no anticholinergic, antidopaminergic, alpha1-adrenergic, or beta-adrenergic-receptor-blocking effects.[9]
Pharmacokinetics
- Absorption: After oral application, maximum plasma concentrations are reached after two to three hours. Fexofenadine should not be taken with a high fat meal, as mean concentrations of fexofenadine in the bloodstream are seen to be reduced from 20-60% depending on form of medication (tablet, ODT, or suspension).[9]
- Distribution: Fexofenadine is 60-70% bound to plasma proteins, mostly albumin.[9]
- Metabolism: Fexofenadine is a substrate of CYP3A4. However, only about 5% is metabolized by the liver, indicating that the role of hepatic metabolism is relatively minor in its clearance from the body.[9]
- Elimination: Most of the substance is eliminated unchanged via the feces (80%) and urine (11–12%).[9]
Interactions
Taking erythromycin or ketoconazole while taking fexofenadine does increase the plasma levels of fexofenadine, but this increase does not influence the QT interval. The reason for this effect is likely due to transport-related effects, specifically involving p-glycoprotein (p-gp).[9] Both erythromcin and ketoconazole are inhibitors of p-gp, a transporter protein involved in preventing the intestinal absorption of fexofenadine. When p-gp is inhibited, fexofenadine may be better absorbed by the body, increasing its plasma concentration by more than what was intended.
Fexofenadine is not to be taken with apple, orange, or grapefruit juice because it could decrease absorption of the drug and should therefore be taken with water.[9] Grapefruit juice can significantly reduce the plasma concentration of fexofenadine.[11]
Antacids containing aluminium or magnesium should not be taken within 15 minutes of fexofenadine as they reduce the absorption of fexofenadine by almost 50%.[9] This is not thought to be due to a change in pH (in fact, absorption can actually increase under increasingly alkaline pH), but rather due to the formation of metal complexes with charged/polar moieties on fexofenadine. As suggested by Shehnaza et al (2014), various sites of the molecule are thought to be responsible for this interaction, including the piperidine nitrogen, the carboxylic acid (-COOH) group, and both hydroxyl (-OH) groups.[12]
Meals with high amounts of fat decrease the absorption of fexofenadine by about 50%.[9]
Special populations
Fexofenadine is a pregnancy category C and should only be used if the benefits outweigh the risks.[13]
No studies have been done to evaluate the presence of fexofenadine in breast milk. Therefore, nursing women are urged to take caution while using fexofenadine.[9]
No sufficient studies have been done in patients over age 65. Therefore, it is advised that elderly patients use caution when using fexofenadine, particularly when there is concern for renal impairment.[9]
History
The older antihistaminic agent terfenadine was found to metabolize into the related carboxylic acid, fexofenadine. Fexofenadine was found to retain all of the biological activity of its parent while giving fewer adverse reactions in patients, so terfenadine was replaced in the market by its metabolite.[14] Fexofenadine was originally synthesized in 1993 by Massachusetts-based biotechnology company Sepracor, which then sold the development rights to Hoechst Marion Roussel (now part of Sanofi-Aventis), and was later approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1996. Albany Molecular Research Inc. (AMRI) holds the patents to the intermediates and production of fexofenadine HCl along with Roussel. Since that time, it has achieved blockbuster drug status with global sales of $1.87B USD in 2004 (with $1.49B USD coming from the United States). AMRI received royalty payments from Aventis that enabled the growth of AMRI.
On January 25, 2011, the FDA approved over-the-counter sales of fexofenadine in the United States, and Sanofi Aventis' version became available on March 4, 2011.[15]
Other brand names
Fexofenadine is marketed under many brand names worldwide as of January 2017, including: Agimfast, Alafree, Alanil, Alercas, Alerfedine, Alerix, Alertam, Alexia, Allegix, Allegra, Allegratab, Allemax, Allerfast, Allerfen, Allerfexo, Allergo, Allergyna, Allerphast, Alrin, Alterfast, Altifex, Altiva, Aspen, Axodin, Axofen, BiXin, Bosnum, Dinafex, Ewofex, Fastel, Fastofen, Fastway, Fe Min, Feksine, Fenadex, Fenadin, Fenafex, Fenax, Fenofex, Fentradol, Fesler, Fexadyne, Fexal, Fexalar, Fexaway, Fexet, Fexgen, Fexidine, Fexigra, Fexine, Fexo, Fexodane, Fexodine, Fexodis, Fexofast, Fexofen, Fexofenaderm, Fexofenadin, Fexofenadina, Fexofenadine, Fexofénadine, Fexofep, Fexofin, Fexogen, Fexomin, Fexon, Fexona, Fexonadinea, Fexoquit, Fexoral, Fexoril, Fexostad, Fexotine, Fexovid, Fixal, Fixit, Fixodin, Flexofen, Foxin, Fynadin, Glodas, Hasalfast, Histafree, Imexofen, Kofixir, Lai Duo Fei, Mayfex, Min Jie, Nefoxef, Neofex, Nolargy, Nosedex, Odafen, Oregra, Radifex, Raltiva, Rapido, Rhinogan, Ridrinal, Rinofen, Rinolast, Ritch, Rui Fei, Sailexi, Tefodine, Telfadin, Telfast, Telfastin, Telfexo, Tellerge, Terfemax, Ternafast, Tocimat, Tofexo, Torfast, Vifas, Vifasesh, X-Dine, Xergic, and Zefeksal.[1]
As of January 2017 it was marketed as a combination drug with pseudoephedrine under brand names including: Alerfedine D, Allegra-D, Allergyna-D, Altiva-D, Dellegra, Fexo Plus, Fexofed, Fixal Plus, Ridrinal D, and Rinolast D.[1]
As of January 2017 it was marketed as a combination drug with montelukast under brand names including Fexokast, Histakind-M, Monten-FX, Montolife-FX, and Novamont-FX.[1]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Fexofenadine - international brand names". Drugs.com. Retrieved 18 January 2017.
- ↑ Lappin G, Shishikura Y, Jochemsen R, Weaver RJ, Gesson C, Houston B, Oosterhuis B, Bjerrum OJ, Rowland M, Garner C (May 2010). "Pharmacokinetics of fexofenadine: evaluation of a microdose and assessment of absolute oral bioavailability". Eur J Pharm Sci. 40 (2): 125–31. doi:10.1016/j.ejps.2010.03.009. PMID 20307657.
- 1 2 3 Smith, SM; Gums, JG (July 2009). "Fexofenadine: biochemical, pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties and its unique role in allergic disorders". Expert Opinion on Drug Metabolism & Toxicology. 5 (7): 813–22. doi:10.1517/17425250903044967. PMID 19545214.
- ↑ Bachert, C (May 2009). "A review of the efficacy of desloratadine, fexofenadine, and levocetirizine in the treatment of nasal congestion in patients with allergic rhinitis". Clin Ther. 31 (5): 921–44. doi:10.1016/j.clinthera.2009.05.017. PMID 19539095.
- 1 2 Compalati, E; Baena-Cagnani, R; Penagos, M; Badellino, H; Braido, F; Gómez, RM; Canonica, GW; Baena-Cagnani, CE (2011). "Systematic review on the efficacy of fexofenadine in seasonal allergic rhinitis: a meta-analysis of randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trials". International Archives of Allergy and Immunology. 156 (1): 1–15. doi:10.1159/000321896. PMID 21969990.
- ↑ Dicpinigaitis, P; Gayle, V (2003). "Effect of the second-generation antihistamine, fexofenadine, on cough reflex sensitivity and pulmonary function". Br J Clin Pharmacol. 56 (5): 501–504. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2125.2003.01902.x. PMC 1884387.
- ↑ Camelo-Nunes, Inês Cristina (November 2006). "Novos anti-histamínicos: uma visão crítica (New antihistamines: a critical view)". Jornal de Pediatria (in Portuguese). 82 (5): S173–80. doi:10.1590/S0021-75572006000700007. ISSN 0021-7557. PMID 17136293.
- ↑ "Dr. Reddy's announces the launch of Over-the-Counter Fexofenadine HCl and Pseudoephedrine HCl extended release tablets". Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories Ltd. 30 August 2011. Archived from the original on 12 October 2016. Retrieved 27 May 2016.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Prescribing Information. Allegra (fexofenadine). Bridgewater, NJ: Sanofi-Aventis, July 2007.
- ↑ Philpot, EE (Jan–Feb 2000). "Safety of second generation antihistamines". Allergy Asthma Proc. 21 (1): 15–20. doi:10.2500/108854100778249033. PMID 10748947.
- ↑ Shirasaka, Y; Mori T; Murata Y; Nakanishi T; Tamai I (Feb 19, 2014). "Substrate- and Dose-Dependent Drug Interactions with Grapefruit Juice Caused by Multiple Binding Sites on OATP2B1". Pharm Res. 31 (8): 2035–2043. doi:10.1007/s11095-014-1305-7. PMID 24549825.
- ↑ Shehnaza, Hina; Haider, Amir; Arayne, M. Saeed; Sultana, Najma (Nov 2014). "Carboxyterfenadine antacid interaction monitoring by UV spectrophotometry and RP-HPLC techniques". Arabian Journal of Chemistry. 7 (5): 839–845. doi:10.1016/j.arabjc.2013.01.011.
- ↑ Mazzotta, P; Loebstein R; Koren G (Apr 1999). "Treating allergic rhinitis in pregnancy. Safety considerations". Drug Saf. 20 (4): 361–75. doi:10.2165/00002018-199920040-00005. PMID 10230583.
- ↑ Daniel Lednicer (1999). The Organic Chemistry of Drug Synthesis. 6. New York: Wiley Interscience. pp. 38–40. ISBN 0-471-24510-0.
- ↑ "Allegra | FAQs". Sanofi-Aventis. Archived from the original on 20 May 2011. Retrieved 5 July 2011.
External links
- Fexofenadine (UK patient information leaflet)
- "fexofenadine" at medicinenet.com