Colonial empire

A colonial empire is a collective of territories (often called colonies), mostly overseas, settled by the population of a certain state and governed by that state.
Colonial empires first emerged with a race of exploration between the then most advanced European maritime powers, Portugal being the first one and Castile (Spain) following suit, during the 15th century.[1] The initial impulse behind these dispersed maritime empires and those that followed was trade, driven by the new ideas and the capitalism that grew out of the European Renaissance. Agreements were also made to divide the world up between them in 1479, 1493, and 1494. European imperialism was born out of competition between European Christians and Ottoman Muslims, the latter of which rose up quickly in the 14th century and forced the Portuguese to seek new trade routes to India, and to a lesser extent, China.
Although colonies existed in classical antiquity, especially amongst the Phoenicians and the Ancient Greeks who settled many islands and coasts of the Mediterranean Sea, these colonies were politically independent from the city-states they originated from, and thus did not constitute a colonial empire.[2]
European colonial empires
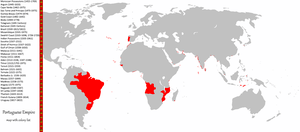
Portugal began establishing (Parallel to Spain) the first global trade network and empire under the leadership of Henry the Navigator, John II and Manuel I. The empire spread throughout a vast number of territories distributed across the globe (especially at one time in the 16th century) that are now parts of 60 different sovereign states. Portugal would eventually control Brazil, territories such as what is now Uruguay and some North American fishing ports, in the Americas; Angola, Mozambique, Portuguese Guinea, Cape Verde and São Tomé and Príncipe (among other territories and bases) in the North and the Subsaharan Africa; cities, forts or territories in all the Asian Subcontinents, as Muscat, Ormus and Bahrain (amongst other bases) in the Persian Gulf; Goa, Bombay and Daman and Diu (amongst other cities) in India; Portuguese Ceylon; Malacca, bases in Southeast Asia and Oceania, as Makassar, Solor, Banda, Ambon and others in the Moluccas, Portuguese Timor; and the granted entrepôt-base of Macau and the entrepôt-enclave of Dejima (Nagasaki) in East Asia, amongst other possessions.
During its Siglo de Oro, the Spanish Empire had possession of the Netherlands, Luxembourg, Belgium, most of Italy, parts of Germany, parts of France, in the Americas, Africa, Asia and Oceania.
From 1580 to 1640 the Portuguese Empire and the Spanish Empire were conjoined in a personal union of its Habsburg monarchs during the period of the Iberian Union, but beneath the highest level of government, their separate administrations were maintained.
Subsequent colonial empires included the French, English, Dutch and Japanese empires. By the mid-17th century, the Tsardom of Russia, continued later as the Russian Empire and the Soviet Union, became the largest contiguous state in the world, and the modern Russian Federation continues to be so to this day. Russia today has nine time zones, stretching across about half of the world's longitude.
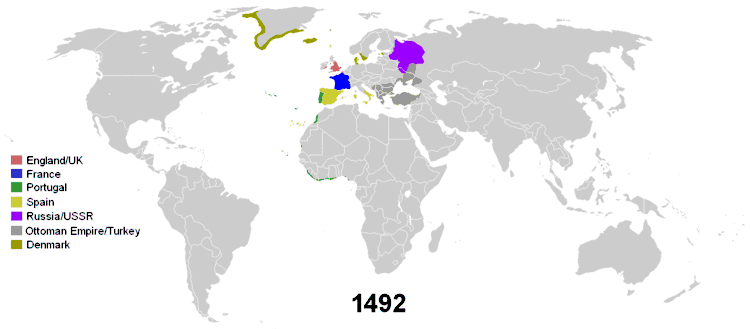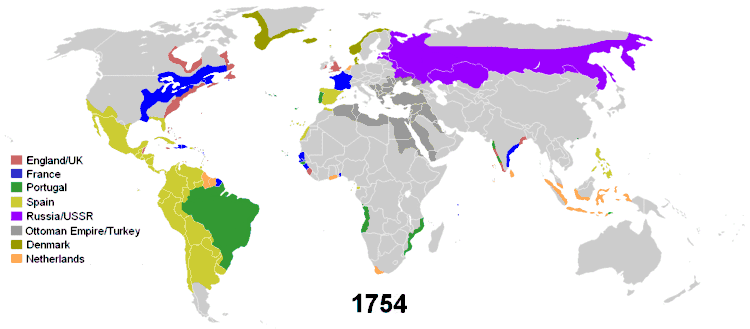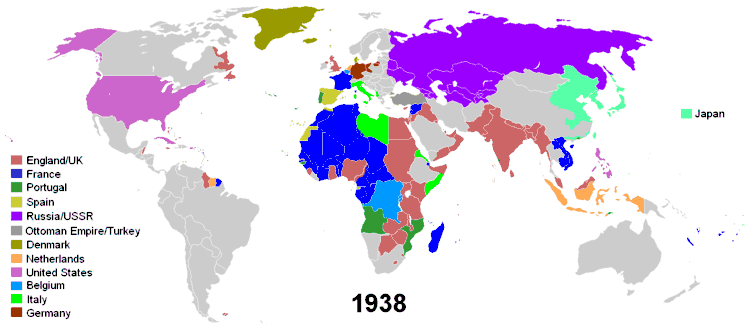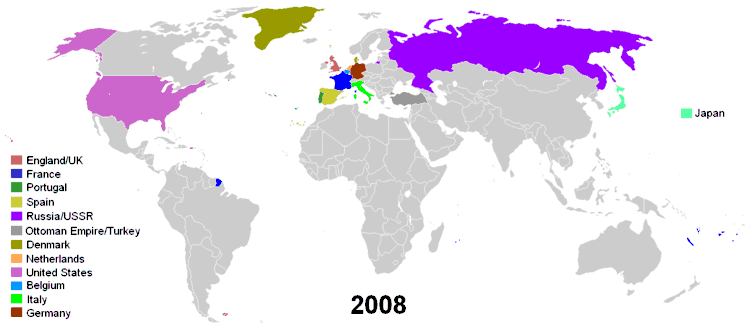
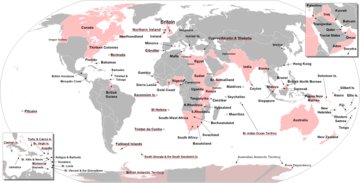
The British Empire, consolidated during the period of British maritime hegemony in the 19th century, became the largest empire in history by virtue of the improved transportation technologies of the time. At its height, the British Empire covered a quarter of the Earth's land area and comprised a quarter of its population. During the New Imperialism, Italy and Germany also built their colonial empires in Africa.
After the Boxer Rebellion in 1901, Imperial China made concessions to the Eight-Nation Alliance (all the Great Powers of the time). By the end of the 20th century most of the previous colonial empires had been decolonized.
Timeline
The chart below shows the span of European colonial empires.
- Black lines mark the year of the empires largest territorial extent of land area.
- Red represents the empire is a monarchy.
- Blue represents the empire is a republic.

List of colonial empires
.svg.png)




.svg.png)
- Evolution of the British Empire
- British colonization of the Americas

.svg.png)
- The Australia dominion, itself a colony that gradually increased its independence in 1901, 1942 and 1986, was tasked with the government of multiple other British colonies and territories and the mandates of New Guinea and Nauru
- The New Zealand dominion, itself a colony that gradually increased its independence in 1907, 1947 and 1986, was tasked with the government of multiple other British colonies and territories and the mandate of Samoa. It was also nominal co-trustee of the mandate of Nauru. The remaining non-self-governing New Zealand territory is Tokelau.
.svg.png)
- The South-West Africa mandate was governed by the South Africa dominion, that itself a colony that gradually increased its independence in 1910, 1931 and 1961.

- Kingdom of France (1534–1792)
- First French Empire of Napoleon I (1804–1814 or 1815)
- Second French Empire of Napoleon III (1852–1870)
- French colonization of the Americas
- List of colonies and possessions of France

.svg.png)
- Italy and the colonization of the Americas (1608-1609)
- Italian concession of Tientsin (1901-1947)
- Italian Islands of the Aegean (1911-1945)
- Italian North Africa (1911–1943)
- Italian East Africa (1936–1960)
- Italian protectorate of Albania (1939–1943)

- Evolution of the Portuguese Empire
- Portuguese colonization of the Americas




- Portuguese Malacca (1511–1641)

- Portuguese Africa





.svg.png)

- Conquest of the Canary Islands
- Spanish colonization of the Americas






.svg.png)
.svg.png)
- Taiwan (1895–1945)
- Caroline islands (1914-1945)

- Ottoman territories in Europe
- Ottoman wars in Africa (1516-1911)
- Ottoman colonization of the Levant (1516–1918)
- Ottoman Arabia (1517–1918)
Other colonial empires:
- Colonies of the

.svg.png)

.svg.png)
.svg.png)
Controversial empires:

- Yaruba dynasty (1624-1742)
- Sultanate of Muscat (1652-1820)
- Sultanate of Zanzibar (taken by Oman in 1698, became capital of the Omani Sultanate or Empire from 1632 or 1640; until 1890)

.svg.png)


.svg.png)
.svg.png)

.svg.png)
- Kingdom of Vientiane (1778–1828)
- Kingdom of Luang Prabang (1778–1893)
- Kingdom of Champasak (1778–1893)
- Kingdom of Cambodia (1771–1867)
- Kedah (1821–1826)
Maps
 Austro-Hungarian colonies and concessions throughout history
Austro-Hungarian colonies and concessions throughout history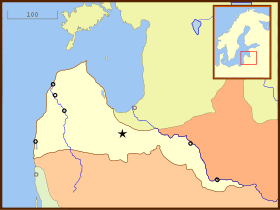 Duchy of Courland and Semigallia
Duchy of Courland and Semigallia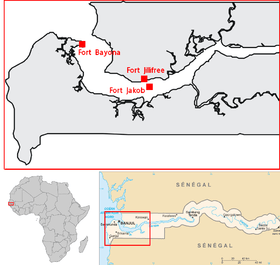 Couronian settlements in Africa
Couronian settlements in Africa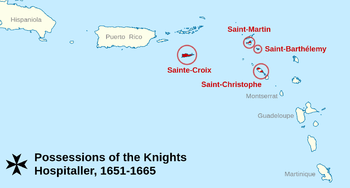 Map of the Hospitaller order's territories in the Caribbean
Map of the Hospitaller order's territories in the Caribbean Couronian settlements in Americas (New Courland on Tobago)
Couronian settlements in Americas (New Courland on Tobago)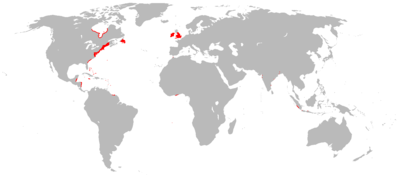
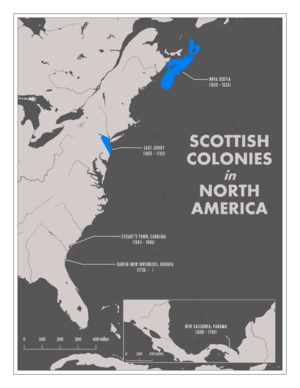
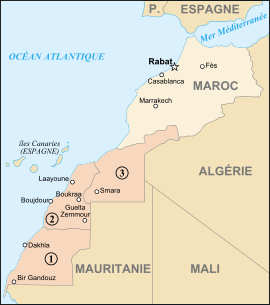 Map of Morocco and Western Sahara with the Southern Provinces in a darker color.
Map of Morocco and Western Sahara with the Southern Provinces in a darker color.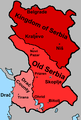 Drač County inside Serbian territories.
Drač County inside Serbian territories.
See also
Notes and references
- ↑ Encarta-encyclopedie Winkler Prins (1993–2002) s.v. "kolonie [geschiedenis]. §1.2 De moderne koloniale expansie". Microsoft Corporation/Het Spectrum.
- ↑ Encarta, s.v. "kolonie [geschiedenis]. §1.1 Oudheid.
- ↑ part of the Viceroyalty of New Spain before 1821.
- ↑ .part of the Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata before 1810.
- 1 2 Part of the Holy Roman Empire realm before 1804.
- ↑ part of the Holy Roman Empire before 1736




.svg.png)