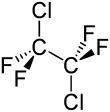
1,2-Dichlorotetrafluoroethane
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1,2-Dichlorotetrafluoroethane | |||
| Other names
R-114, CFC-114, halon 242, cryofluorane, Freon 114, Genetron 114, Refrigerant 114 | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.853 | ||
| EC Number | 200-937-7 | ||
PubChem CID |
|||
| RTECS number | KI1101000 | ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1958 | ||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C2Cl2F4 | |||
| Molar mass | 170.92 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | colorless gas[1] | ||
| Odor | faint, ether-like (high concentrations)[1] | ||
| Density | 1.455 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | −94 °C (−137 °F; 179 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 3.5 °C (38.3 °F; 276.6 K) | ||
| 0.01%[1] | |||
| Vapor pressure | 1.9 atm (21°C)[1] | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Main hazards | Ozone depletor | ||
| GHS pictograms |   | ||
| GHS signal word | Warning | ||
| H280, H420 | |||
| P410+403, P502 | |||
| Flash point | nonflammable [1] | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LC50 (median concentration) |
720,000 ppm (rat, 30 min) 700,000 ppm (mouse, 30 min) 750,000 ppm (rabbit, 30 min)[2] | ||
| US health exposure limits (NIOSH): | |||
PEL (Permissible) |
TWA 1000 ppm (7000 mg/m3)[1] | ||
REL (Recommended) |
TWA 1000 ppm (7000 mg/m3)[1] | ||
IDLH (Immediate danger) |
15000 ppm[1] | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
1,2-Dichlorotetrafluoroethane, or R-114, also known as cryofluorane (INN), is a chlorofluorocarbon (CFC) with the molecular formula ClF2CCF2Cl. Its primary use has been as a refrigerant. It is a non-flammable gas with a sweetish, chloroform-like odor with the critical point occurring at 145.6 °C and 3.26 MPa. When pressurized or cooled, it is a colorless liquid. It is listed on the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change's list of ozone depleting chemicals, and is classified as a Montreal Protocol Class I, group 1 ozone depleting substance.[3]
When used as a refrigerant, R-114 is classified as a medium pressure refrigerant.
The US Navy uses R-114 in its centrifugal chillers in preference to R-11 to avoid air and moisture leakage into the system. While the evaporator of an R-11 charged chiller runs at a vacuum during operation, R-114 yields approximately 0 psig operating pressure in the evaporator.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 "NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards #0201". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ↑ "Dichlorotetrafluoroethane". Immediately Dangerous to Life and Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ↑ Class I Ozone-depleting Substances, United States Environmental Protection Agency, retrieved May 11, 2012
External links
- Material Safety Data Sheet from Honeywell International Inc., dated 22 August 2007.
- CDC - NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards