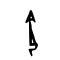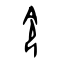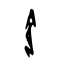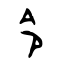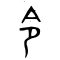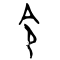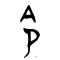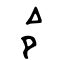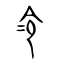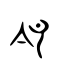令
| ||||||||
| ||||||||
Translingual
| Traditional | 令 |
|---|---|
| Simplified | 令 |
| Japanese | 令 |
| Korean | 令 |
Han character
令 (radical 9, 人+3, 5 strokes, cangjie input 人戈弓戈 (OINI), four-corner 80307, composition ⿱亽龴(G) or ⿱亼龴(HTV) or ⿱亼ㄗ(JK or U+F9A8))
Derived characters
References
- KangXi: page 93, character 12
- Dai Kanwa Jiten: character 387
- Dae Jaweon: page 198, character 1
- Hanyu Da Zidian: volume 1, page 111, character 10
- Unihan data for U+4EE4
Chinese
| trad. | 令 | |
|---|---|---|
| simp. # | 令 | |
Glyph origin
| Historical forms of the character 令 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shang | Western Zhou | Spring and Autumn | Warring States | Shuowen Jiezi (compiled in Han) | Liushutong (compiled in Ming) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bronze inscriptions | Oracle bone script | Bronze inscriptions | Bronze inscriptions | Bronze inscriptions | Chu Slip and silk script | Qin slip script | Small seal script | Transcribed ancient scripts | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
References: Mostly from Richard Sears' Chinese Etymology site (authorisation),
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Characters in the same phonetic series (令) (Zhengzhang, 2003) | |
|---|---|
| Old Chinese | |
| 令 | *ren, *reŋ, *reŋs, *reːŋ, *reːŋs |
| 怜 | *riːn, *reːŋ |
| 零 | *riːŋ, *reːŋ, *reːŋs |
| 魿 | *ɡriŋ, *reːŋ |
| 命 | *mreŋs |
| 冷 | *raːŋʔ, *reːŋ, *reːŋʔ |
| 跉 | *reŋ, *reːŋ |
| 嶺 | *reŋʔ |
| 領 | *reŋʔ |
| 阾 | *reŋʔ, *reːŋ |
| 柃 | *reŋʔ, *reːŋ |
| 袊 | *reŋʔ |
| 詅 | *reŋs, *reːŋ |
| 旍 | *ʔsleŋ |
| 舲 | *reːŋ |
| 齡 | *reːŋ |
| 囹 | *reːŋ |
| 鴒 | *reːŋ |
| 蛉 | *reːŋ |
| 鈴 | *reːŋ |
| 苓 | *reːŋ |
| 伶 | *reːŋ |
| 泠 | *reːŋ |
| 瓴 | *reːŋ |
| 拎 | *reːŋ |
| 刢 | *reːŋ |
| 玲 | *reːŋ |
| 聆 | *reːŋ |
| 竛 | *reːŋ |
| 軨 | *reːŋ |
| 笭 | *reːŋ, *reːŋʔ |
| 翎 | *reːŋ |
| 閝 | *reːŋ |
| 鹷 | *reːŋ |
| 昤 | *reːŋ |
| 駖 | *reːŋ |
| 彾 | *reːŋ |
| 呤 | *reːŋ |
| 狑 | *reːŋ |
| 秢 | *reːŋ |
| 岭 | *reːŋ |
| 紷 | *reːŋ |
| 砱 | *reːŋ |
| 羚 | *reːŋ |
| 姈 | *reːŋ |
| 蕶 | *reːŋ |
| 澪 | *reːŋ |
Etymology 1
Pronunciation
Definitions
令
Descendants
Etymology 2
Pronunciation
Definitions
令
Pronunciation
Etymology 4
Pronunciation
Etymology 5
| For pronunciation and definitions of 令 – see 齡 (“age; length of time; duration; etc.”). (This character, 令, is the second-round simplified form of 齡.) |
Notes:
|
Compounds
|
|
|
Japanese
Readings
Compounds
- 令旨 (ryōji)
- 令外 (ryōge)
- 令月 (reigetsu)
- 令兄 (reikei)
- 令閨 (reikei)
- 令史 (reishi)
- 令室 (reishitsu)
- 令状 (reijō)
- 令嬢 (reijō)
- 令色 (reishoku)
- 令息 (reisoku)
- 令夫人 (reifujin)
- 令名 (reimei)
- 禁令 (kinrei)
- 訓令 (kunrei)
- 号令 (gōrei)
- 司令 (shirei)
- 指令 (shirei)
- 辞令 (jirei)
- 条令 (jōrei)
- 勅令 (chokurei)
- 伝令 (denrei)
- 発令 (hatsurei)
- 布令 (furei)
- 法令 (hōrei)
- 命令 (meirei)
- 律令 (ritsuryō)
- 御布令 (ofure)
- 県令 (kenrei)
- 令史 (sakan)
- 仮令, 縦令 (tatoi), 仮令, 縦令 (tatoe)
Etymology 1
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 令 |
| れい Grade: 4 |
| kan’on |
From Middle Chinese 令 (MC liᴇŋ), 令 (MC liᴇŋH), or 令 (MC leŋH).
The 漢音 (kan'on, literally “Han sound”) reading, so likely a later borrowing from Middle Chinese.
Noun
- an order, command, decree
- (historical) in ancient China, a regional governor or magistrate
- (historical) in the early Meiji period, the forerunner of a 知事 (chiji, “prefectural governor”)
- (historical) in the Kamakura period, the vice-minister of the 政所 (mandokoro, “office of financial affairs”)
- (historical) under the 律令 (Ritsuryō) system, This term needs a translation to English. Please help out and add a translation, then remove the text
{{rfdef}}.- Synonym: 坊令 (bōrei)
- (rare, law, historical) an administrative and civil code developed during the Qin dynasty that was, alongside the 律 (ritsu), spread throughout East Asia especially Japan where it was further revised into the 律令 (Ritsuryō) system
Affix
Etymology 2
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 令 |
| りょう Grade: 4 |
| goon |
/rjau/ → /rjɔː/ → /rjoː/
From Middle Chinese 令 (MC liᴇŋ), 令 (MC liᴇŋH), or 令 (MC leŋH).
The 呉音 (goon, literally “Wu sound”) reading, so likely the initial borrowing from Middle Chinese.
Noun
令 (hiragana りょう, rōmaji ryō, historical hiragana りやう)
- (law, historical) an administrative and civil code developed during the Qin dynasty that was, alongside the 律 (ritsu), spread throughout East Asia especially Japan where it was further revised into the 律令 (Ritsuryō) system
Derived terms
- 令義解 (Ryō no Gige)
Affix
Korean
Hanja
令 • (ryeong) (hangeul 령, revised ryeong, McCune–Reischauer ryŏng, Yale ryeng)
- This term needs a translation to English. Please help out and add a translation, then remove the text
{{rfdef}}.
Vietnamese
Han character
令 (lệnh)
- This term needs a translation to English. Please help out and add a translation, then remove the text
{{rfdef}}.