Visa policy of Albania
Visitors to Albania must obtain a visa from one of the Albanian diplomatic missions unless they come from one of the visa exempt countries or are qualified for visa-free entry.[1][2]
 |
|---|
| This article is part of a series on the politics and government of Albania |
|

Entering with a passport is required. Citizens from certain countries or territories, however, are eligible for visa-free travel with only their ID cards in lieu of their passports.[3] Passports must be valid for at least 3 months from the date of arrival.[4]
The visa policy of Albania is based on the by Law Nr. 108/2013 “On foreign citizens”, amended and the Decision of the Council of Ministers Nr. 513/2013 “On criteria and procedures for entry, stay and treatment of foreign citizens”, amended.
The visa policy of Albania is similar to the visa policy of the Schengen Area. It grants 90-day visa-free entry to all Schengen Annex II nationalities, except for Dominica, East Timor, Grenada, Kiribati, Marshall Islands, Micronesia, Palau, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Samoa, Solomon Islands, Tonga, Tuvalu and Vanuatu. It also grants visa-free entry to several additional countries – Armenia, Azerbaijan, China, Kazakhstan, Kosovo, Kuwait and Turkey.
Visa policy map
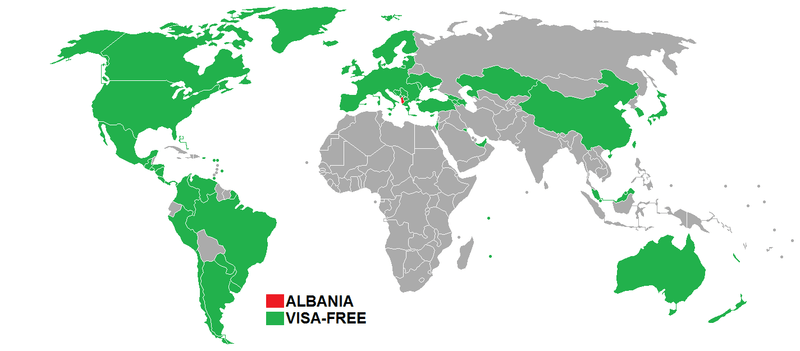
Visa-free access
Holders of passports (or in certain cases ID cards) of the following 86 jurisdictions can enter Albania without a visa for a maximum stay of 90 days (unless otherwise noted):[5][1]
|
1 - may enter using a national ID card or Irish passport card.
2 - may enter using a Kazakh national ID card or Hong Kong permanent ID card for a maximum stay of 90 days within 180 days
3 - citizens of these countries or territories staying for more than 90 days within 180 days are required to obtain a type "D" visa.
4 - countries whose citizens can enter without visas due to the "visa liberalization
with the Schengen area".
5 - allowed to stay for 1 year without a visa.
Substitute visas
Any visitor who holds a valid, multiple entry and previously used visa issued by a Schengen area country, United States, or the United Kingdom can enter Albania without a visa for 90 days. Visa must have been used at least once before arrival to Albania. The visa exemption also applies to valid Green Card holders, holders of resident permits issued by a Schengen country, or holders of refugee and stateless travel documents issued by an EU or EFTA member state.[1]
Visitors of Albanian ethnicity do not require visa to enter Albania for a maximum stay of 90 days within 180 days.
Recent and future changes
In May 2019 a visa exemption agreement was signed for all passports with ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Non-ordinary passports
Additionally, only holders of diplomatic or service passports of Algeria, Cuba, Ecuador, Egypt, India, Indonesia, Jordan, Mongolia, Morocco, Russia, South Africa and Vietnam and holders of only diplomatic passports of Tunisia do not require a visa to visit Albania.
Visa waiver agreements for diplomatic and service passports were signed with Philippines[10] and Saudi Arabia,[11] and they are yet to come into force.
Reciprocity
Albanian citizens can enter without a visa some of the countries whose citizens are granted visa-free access to Albania but require a visa for Argentina, Australia, Azerbaijan, Bahamas, Brunei, Canada, China, Costa Rica, Guatemala, Honduras, Ireland, Japan, Kazakhstan, Kuwait, Mauritius (grants visa on arrival), Mexico, New Zealand, Nicaragua, Panama, Paraguay, Peru, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Taiwan, United Arab Emirates, United Kingdom, United States, and Venezuela.
Visa application
Citizens of the countries requiring visas should apply at the following diplomatic missions of Albania (citizens of countries without an assigned embassy should contact the geographically nearest diplomatic mission):[12]
- Abu Dhabi: Oman, Yemen
- Ankara: Afghanistan, Georgia, Iran, Iraq, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan
- Beijing: Bangladesh, Cambodia, China, India, Indonesia, Mongolia, Nepal, North Korea, Philippines, Sri Lanka, Thailand, Vietnam
- Brasilia: Bolivia, Colombia, Cuba, Dominican Republic, Ecuador, Guyana, Haiti, Peru, Suriname
- Bucharest: Liberia, Morocco, Palestine
- Cairo: Cameroon, Congo, Egypt, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Gabon, Ghana, Guinea, Jordan, Kenya, Lebanon, Lesotho, Libya, Madagascar, Malawi, Mauritania, Mozambique, Namibia, Nigeria, Pakistan, Palestine, Rwanda, Senegal, Sierra Leone, Somalia, Sudan, Syria, Tanzania, Togo, Tunisia, Uganda, Zambia, Zimbabwe
- Doha: Bahrain, Qatar
- Istanbul: Afghanistan, Congo, Georgia, Guinea, Iran, Iraq, Lebanon, Lesotho, Libya, Madagascar, Malawi, Mauritania, Mozambique, Namibia, Nigeria, Pakistan, Rwanda, Senegal, Sierra Leone, Syria, Tanzania, Togo, Tunisia, Turkmenistan, Uganda, Uzbekistan, Zambia, Zimbabwe
- London: Belize, Fiji, Ivory Coast, Jamaica, Maldives, São Tomé and Príncipe, South Africa, Trinidad and Tobago
- Madrid: Gibraltar, Peru
- Moscow: Belarus, Kyrgyzstan, Mongolia, Russia, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan
- New York City: Dominican Republic, Haiti, Jamaica
- Paris: Algeria, Benin, Botswana, Morocco, Senegal
- Riyadh: Bahrain, Oman, Saudi Arabia, Somalia, Yemen
- Rome: Angola, Burkina Faso, Gabon, Ghana, Guyana, Mali, South Africa
- Sofia: Cuba, North Korea
- Tokyo: Fiji
- Warsaw: Belarus
References
- "Country information (visa section)". Timatic. International Air Transport Association (IATA) through Olympic Air. Retrieved 1 April 2017.
- US Department of State - Country Information for Albania - Entry Requirements
- "Visa regime for foreign citizens" (PDF). Ministry of Foreign Affairs (Albania). Retrieved 3 November 2018.
- Who can enter Albania without a Visa
- http://foreign.gov.kn/2019/05/14/st-kitts-and-nevis-signs-visa-waiver-agreement-with-the-republic-of-albania/
- Belarus, Albania sign visa-free travel agreement
- https://www.minfor.gov.gy/featured/guyana-and-albania-sign-visa-waiver-mou/
Annotations
- Kosovo is the subject of a territorial dispute between the Republic of Kosovo and the Republic of Serbia. The Republic of Kosovo unilaterally declared independence on 17 February 2008, but Serbia continues to claim it as part of its own sovereign territory. The two governments began to normalise relations in 2013, as part of the 2013 Brussels Agreement. Kosovo is currently recognized as an independent state by 97 out of the 193 United Nations member states. In total, 112 UN member states recognized Kosovo at some point, of which 15 later withdrew their recognition.