Tahara, Aichi
Tahara (田原市, Tahara-shi) is a city located in Aichi Prefecture, Japan. As of 1 October 2019, the city had an estimated population of 60,206 in 22,576 households,[1] and a population density of 315 persons per km². The total area of the city is 191.12 square kilometres (73.79 sq mi).
Tahara 田原市 | |
|---|---|
 Upper: Iragomisaki Lighthouse, Cape Iragomi Middle: Tahara Castle, Mt Zao Lookout Lower:Kazan Jinja, Akahane Beach | |
 Flag  Coat of arms | |
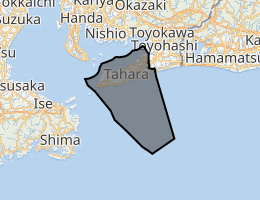
Location of Tahara in Aichi Prefecture | |
 | |
 Tahara | |
| Coordinates: 34°40′7.5″N 137°16′51.2″E | |
| Country | Japan |
| Region | Chūbu (Tōkai) |
| Prefecture | Aichi |
| Area | |
| • Total | 191.12 km2 (73.79 sq mi) |
| Population (October 1, 2019) | |
| • Total | 60,206 |
| • Density | 320/km2 (820/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+9 (Japan Standard Time) |
| - Tree | Cinnamomum camphora |
| - Flower | Broccolini |
| Phone number | 0531-22-1111 |
| Address | 30-1 Minami Banba, Tahara-cho, Tahara-shi, Aichi-ken 441-3492 |
| Website | Official website |

Geography
Tahara is situated in southern Aichi Prefecture, and occupies most of the hilly Atsumi Peninsula. The peninsula is bounded on the north by Mikawa Bay and to the south lies the Philippine Sea.[2] Situated as it is between those two bodies of water, Tahara has a warm maritime climate.
Neighboring municipalities
- Aichi Prefecture
- Toyohashi
Demographics
Per Japanese census data,[3] the population of Tahara has been relatively steady over the past 60 years.
| Historical population | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
| 1950 | 65,095 | — |
| 1960 | 59,120 | −9.2% |
| 1970 | 56,248 | −4.9% |
| 1980 | 60,581 | +7.7% |
| 1990 | 64,978 | +7.3% |
| 2000 | 65,534 | +0.9% |
| 2010 | 64,128 | −2.1% |
Climate
The city has a climate characterized by hot and humid summers, and relatively mild winters (Köppen climate classification Cfa). The average annual temperature in Tahara is 15.8 °C. The average annual rainfall is 1762 mm with September as the wettest month. The temperatures are highest on average in August, at around 27.1 °C, and lowest in January, at around 5.2 °C.[4]
History
The area of present-day Tahara has been continuously occupied since prehistoric times. Archaeologists have found numerous remains from the Jōmon period and burial mounds from the Kofun period. During the Nara period, the area was assigned to ancient Atsumi County, and was divided into several shōen during the Heian period. During the Kamakura period, the area was noted for production of a certain type of pottery. During the Sengoku period, the area was under the control of the Toda clan, who constructed Tahara Castle. The Toda, who were allied with Tokugawa Ieyasu were dispossessed by Toyotomi Hideyoshi, but returned as daimyō of Tahara Domain at the start of the Edo period. The Toda were later replaced by the Miyake clan, who ruled until the end of the Tokugawa shogunate. The noted scholar Watanabe Kazan was from Tahara.
At the start of the Meiji period, on October 1, 1889 Tahara was organized into a number of villages within Atsumi District, Aichi Prefecture with the establishment of the modern municipalities system. Tahara Village was elevated to town status on October 3, 1892 and Fukue village became Fukue Town on February 22, 1897. Fukue later changed its name to Atsumi Town on April 15, 1955. On November 11, 1958, the village of Akabane was raised to town status.
The city of Tahara was established on August 20, 2003, from the merger the former town of Tahara, absorbing the town of Akabane (both from Atsumi District) to elevate city status. On October 1, 2005, the town of Atsumi (also from Atsumi District) was merged into Tahara. Therefore, Atsumi District was dissolved as a result of this merger.
Government
Tahara has a mayor-council form of government with a directly elected mayor and a unicameral city legislature of 18 members. The city contributes one member to the Aichi Prefectural Assembly. In terms of national politics, the city is part of Aichi District 15 of the lower house of the Diet of Japan.
Economy
Tahara is a regional commercial center with a mixed economy of manufacturing and agriculture. Due to its long coastline, Tahara has many ports for commercial fishing. The main industrial employer is Toyota Motor Corporation, which has its award-winning Tahara plant in Tahara which makes many Lexus-brand cars and some Toyota models. The Toyota Celica was manufactured in Tahara from 1979 to 1999. Many Lexus models are manufactured within this plant, as are many Toyota models for domestic and international markets.
Energy
Tahara has a consortium of companies investing in renewable energy needs. As of November 2014, a new solar energy and wind energy power generation facility will provide 19,000 households with electricity on an infrequent basis that is dependent upon the weather.[5][6] JERA operates the Atsumi Thermal Power Station, an oil-fired power plant with capacity of 1400 MW in Tahara.[7]
Education
Tahara has 18 public elementary schools, five public middle schools operated by the city government and three public high schools operated by the Aichi Prefectural Board of Education.
Transportation
Railway
![]()
- Yagumadai • Toshima • Kambe • Mikawa Tahara
Highway


Bus services
Toyotetsu buses and city-operated environmentally friendly public transport facilitate access throughout Tahara, even to the westernmost point at Cape Irago.
Seaports
From the Port of Irago, the Ise-wan Ferry connects Tahara with the town of Toba, Mie prefecture. The ferry can accommodate motor vehicles. The ferry also docks at the Central Japan International Airport, built on an artificial island in Ise Bay, south of Nagoya.
Sister cities



.svg.png)
Local attractions
- Yoshigo Shell Midden, a Jōmon period shell midden and National Historic Site
- Irago Tōdai-ji Tile Kiln ruins, Kamakura-period kiln ruins, a National Historic Site
- Ōarako Old Kiln ruins, a National Historic Site
- Site of Tahara Castle
- Kojigahama Beach, Cape Irago, the wave sounds of which were listed as one of the 100 Soundscapes of Japan by the Ministry of the Environment [9]
- Kazan Jinja
- Akabane Long Beach, also known as "Akabane Beach" or "Long Beach", is a very scenic area for locals and tourists. The Akabane Beach hosted the 2018 World Surfing Games, among other international surfing competitions over the years.
 View of Cape Irago from Irako View Hotel
View of Cape Irago from Irako View Hotel- Akabane Long Beach
 Rape Blossoms
Rape Blossoms- Tahara Castle
- Nishinohama Wind Farm
- Yoshigo Kaizuka
Notable people
- Watanabe Kazan, Edo period samurai and artist
- Noboru Ueda, motorcycle racer
References
- Tahara City official statistics (in Japanese)
- "Tahara City Profile". Tahara Official Website. Retrieved 11 Nov 2011.
- Tahara population statistics
- Tahara climate data
- "Solar/Wind Electricity Generation Project in Tahara City". Toshiba Official Website. 2012-11-07. Retrieved 2012-11-07.
- http://www.mitsuichem.com/release/2014/140930.htm
- JERA official home page
- "International Exchange". List of Affiliation Partners within Prefectures. Council of Local Authorities for International Relations (CLAIR). Archived from the original on 24 December 2015. Retrieved 21 November 2015.
- "100 Soundscapes of Japan". Ministry of the Environment. Retrieved 8 December 2015.
External links


- Official website (in Japanese) (with link to English pages)