Administration in Bihar
Bihar is a state situated in Eastern India. It is surrounded by West Bengal to the east, Uttar Pradesh to the west, Jharkhand to the south and Nepal to the north.
| Divisions | 9 |
|---|---|
| Districts | 38 |
| Subdivisions | 101 |
| Cities and towns | 207 |
| Blocks | 534 |
| Villages | 45,103 |
| Panchayats | 8,406 |
| Police Districts | 43 |
| Police Stations | 853 |
 Seal of Bihar | |
| Seat of Government | Patna |
|---|---|
| Executive | |
| Governor | Fagu Chauhan |
| Chief Minister | Nitish Kumar |
| Legislature | |
| Assembly | |
| Speaker | Vijay Kumar Chaudhary |
| Members in Assembly | 243 |
| Council | Bihar Legislative Council |
| Chairman | Awadhesh Narain Singh |
| Members in Council | 75 |
| Judiciary | |
| High Court | Patna High Court |
| Chief Justice | Justice Shri Sanjay Karol |
| Lower Courts | District courts and Panchayats |
History
Before 1905, Bihar was a part of British East India Company's Bengal Presidency. In 1905 the Bengal Presidency was divided and created two new provinces: East Bengal and West Bengal. Until then Bihar was part of West Bengal. Again West Bengal and East Bengal reunited in 1911 but the people of Bihar and Orrisa demanded a separate province based on language rather than religion. In 1912 Bihar and Orissa Province was created separating from Bengal Presidency. In 1936, Bihar and Orrisa Province divided into two new provinces: Bihar Province and Orissa Province.
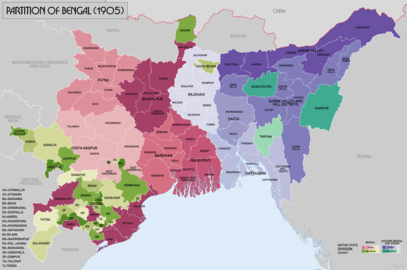
Bihar and Orissa Province
Following Divisions were included in Bihar and Orissa Province when it separated from Bengal Presidency in 1912:
- Bhagalpur Division (districts of Bhagalpur, Munger (Monghyr), Purnea and the Sonthal Parganas)
- Patna Division (Gaya, Patna and Shahabad)
- Tirhut Division (Champaran, Darbhanga, Muaffarpur and Saran)
- Chota Nagpur Division (Hazaribagh, Manbhum, Palamau, Ranchi and Singhbhum)
- Orissa Division (Angul, Balasore, Cuttack, Puri and Sambatpur)
On 1 April 1936 Bihar and Orissa Province was divided into two new provinces: Bihar Province and Orissa Province
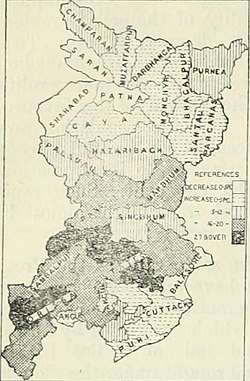
Bihar Province
In 1936, Bihar became a separate province including part of Jharkhand.
After the independence of India in 1951, Bihar including Jharkhand had 18 districts, and had 55 districts in 1991.
Bihar
In 2000, Bihar again divided into two states: the current Bihar and Jharkhand. In 2001 Bihar had a total of 38 districts.
Administrative structure
Structurally Bihar is divided into divisions (Pramandal), districts (Zila), sub-divisions (Anumandal) & circles (Aanchal).
The state is divided into 9 divisions, 38 districts, 101 subdivisions and 534 circles.[1] 12 municipal corporations, 49 Nagar Parishads and 80 Nagar Panchayats,[2][3][4][5][6] for administrative purposes. The various districts included in the divisions—Patna, Tirhut, Saran, Darbhanga, Kosi, Purnia, Bhagalpur, Munger and Magadh Division—are as listed below.
| India | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bihar | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Divisions | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Districts | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Blocks (Tehsils) | Municipal Corporations (Maha-Nagar-Palika) | Municipalities (Nagar-Palika) | City Councils (Nagar-Panchayat) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Villages (Graam/Gau'n) | Wards | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Divisions
There are 9 divisions in Bihar.
Districts
There are 38 districts in Bihar, grouped into 9 divisions.
- Araria
- Arwal
- Aurangabad
- Banka
- Begusarai
- Bhagalpur
- Bhojpur
- Buxar
- Darbhanga
- East Champaran
- Gaya
- Gopalganj
- Jamui
- Jehanabad
- Khagaria
- Kishanganj
- Kaimur
- Katihar
- Lakhisarai
- Madhubani
- Munger
- Madhepura
- Muzaffarpur
- Nalanda
- Nawada
- Patna
- Purnea
- Rohtas
- Saharsa
- Samastipur
- Sheohar
- Sheikhpura
- Saran
- Sitamarhi
- Supaul
- Siwan
- Vaishali
- West Champaran
Sub-divisions
Sub-divisions (Anumandal) in Bihar are like sub-districts. There are 101 subdivisions in Bihar.
Blocks
The Indian state of Bihar is divided into 534, The Best CD Block of Bihar is Chhourahi, District Begusaraiadministrative subdivisions called blocks.[7][8]
| District | Block |
|---|---|
| Begusarai | Chhourahi |
| Begusarai | Balia |
| Begusarai | Mansurchak |
| Gaya | Gurua |
| Gaya | Konch |
| Gaya | Manpur |
| Gaya | Paraiya |
| Gaya | BankeBazar |
| Gaya | Imamganj |
| Gaya | Dumariya |
| Gaya | Barachatti |
| Gaya | wazirganj |
| Gaya | Sherghati |
| Gaya | Tekari |
| Gopalganj | Kuchaikote |
| Jehanabad | Hulasganj |
| Madhepura | Alamnagar |
| Madhepura | Bihariganj |
| Madhepura | Chousa |
| Madhepura | Gamhariya |
| Madhepura | Ghelardh |
| Madhepura | Gwalpara |
| Madhepura | Kumarkhand |
| Madhepura | Madhepura |
| Madhepura | Murliganj |
| Madhepura | Puraini |
| Madhepura | Shankarpur |
| Madhepura | Singheshwar |
| Madhepura | Udakishunganj |
| Munger | Dharhara |
| Muzaffarpur | Sahebganj |
| Nawada | Akbarpur |
Municipal corporations
There are 12 municipal corporation in bihar.
1. Patna
2. Gaya
3. Bhagalpur
4. Muzaffarpur
5. Purnia
6. Darbhanga
7. Katihar
8. Chhapra
9. Begusarai
10. Arrah
11. Biharsharif
12. Munger
Municipalities
City Councils
Judiciary
High Court
The Patna High Court (Hindi: पटना उच्च न्यायालय) is the High Court of the state of Bihar. It was established on February 3, 1916, and later affiliated under the Government of India Act, 1915. The court is headquartered in Patna, the administrative capital of the state.
A proclamation was made by the Governor-General of India on 22 March 1912. The foundation-stone of the High Court Building was laid on 1 December 1913 by the late Viceroy and Governor-General of India, Sir Charles Hardinge of Penshurst. The Patna High Court building on its completion was formally opened by the same Viceroy on 3 February 1916. Hon. Sir Justice Edward Maynard Des Champs Chamier was the first Chief Justice of Patna High Court.
This High Court has given two Chief Justices of India: Hon'ble Mr. Justice Bhuvaneshwar Prasad Sinha, the 6th C.J.I., and Hon. Mr. Justice Lalit Mohan Sharma, the 24th C.J.I..
Hon. The Chief Justice Mr. Sanjay Karol is the current Chief Justice of Patna High Court.
City Courts
Legislature
Bihar is one of the seven states where bicameral legislature exists. Other states are Uttar Pradesh, Karnataka, Maharashtra, Jammu and Kashmir, Telangana and Andhra Pradesh. The Vidhan Parishad serves as the upper house and Vidhan Sabha serves as the lower house of a bicameral legislature.
Vidhan Sabha
The Vidhan Sabha is also known as Legislative Assembly. The Bihar Legislative Assembly first came into being in 1937. The current strength of the House is 243.
Vidhan Parishad
The Vidhan Parishad is also known as Legislative Council.
A new province of Bihar and Orissa was created by the British Government on 12 December 1911. The Legislative Council with a total of 43 members belonging to different categories was formed in 1912. The first sitting of the Council was convened on 20 January 1913. In 1936, Bihar attained its separate Statehood. Under the Government of India Act, 1919, the unicameral legislature got converted into bicameral one, i.e. the Bihar Legislative Council and the Bihar Legislative Assembly. Under the Government of India Act, 1935, the Bihar Legislative Council consisted of 29 members. After the first General Elections 1952, the number of members was increased up to 72 and by 1958 the number was raised to 96. With the creation of Jharkhand, as a result of the Bihar Reorganisation Act, 2000 passed by the Parliament, the strength of the Bihar Legislative Council has been reduced from 96 to 75 members.
See also
- Government of Bihar
- Divisions of Bihar
- Districts in Bihar
References
- "Indexing Gender Parity and Estimation of Child Marriage: A comprehensive study of 534 Blocks in Bihar". Archived from the original on 2017-09-25.
- "Bihar Civic elections likely in May 2017". Archived from the original on 2017-03-31.
- "बिहार : नगर विकास एवं आवास विभाग की पहल, पुनर्गठन से नगर परिषदों की बढ़ जायेगी संख्या". Archived from the original on 2017-03-24.
- "पहली बार कोई महिला बनेगी पटना नगर निगम की मेयर". Archived from the original on 2017-03-24.
- "Ward delimitation begins in Chhapra". Archived from the original on 2017-02-27.
- "छपरा को निगम बख्तियारपुर को मिला नगर परिषद का दर्जा". Archived from the original on 2017-03-24.
- "State Profile". Government of Bihar. Archived from the original on 6 July 2017. Retrieved 6 July 2017.
- "534 Bihar Blocks list" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2017-08-28.