State Legislative Assembly (India)
The State Legislative Assembly is a legislative body in the states and union territories of India. In the 28 states and 3 union territories with a unicameral state legislature it is the sole legislative body and in 6 states it is the lower house of their bicameral state legislatures with the upper house being State Legislative Council. 5 Union territories are governed directly by the Union Government of India and have no legislative body.
Each Member of the Legislative Assembly (MLA) is directly elected to serve 5 year terms by single-member constituencies. The Constitution of India states that a State Legislative Assembly must have no less than 60 and no more than 500 members however an exception may be granted via an Act of Parliament as is the case in the states of Goa, Sikkim, Mizoram and the union territory of Puducherry which have fewer than 60 members. A State Legislative Assembly may be dissolved in a state of emergency, by the Governor on request of the Chief Minister, or if a motion of no confidence is passed against the ruling majority party or coalition.[1]
Qualifications required to become an MLA
To become a Member of a State Legislative Assembly (MLA), a person must be a citizen of India, not less than 25 years of age, should be mentally sound, should not be bankrupt, and must be enrolled on the voters' list of the state for which he or she is contesting an election. He or she may not be a Member of Parliament. He or she should also state an affidavit that there are no criminal procedures against him or her.
A State Legislative Assembly holds equal legislative power with the upper house of state legislature, the State Legislative Council, except in the area of money bills in which case the State Legislative Assembly has the ultimate authority.
Special powers of the State Legislative Assembly
- A motion of no confidence against the government in the state can only be introduced in the State Legislative Assembly. If it is passed by a majority vote, then the Chief Minister and her/his Council of Ministers must collectively resign.
- A money bill can only be introduced in State Legislative Assembly. In bicameral jurisdictions, after it is passed in the State Legislative Assembly, it is sent to the State Legislative Council, where it can be kept for a maximum time of 14 days.
- In matters related to ordinary bills, the will of State Legislative Assembly prevails and there is no provision of joint sitting. In such cases, State Legislative Council can delay the legislation by maximum 4 months (3 months in first visit and 1 month in the second visit of the bill).
- Legislative Assembly of the state has to power to create or abolish the State Legislative Council by passing a resolution to that effect by a majority of not less than two-thirds of the members present and voting. [2]
List of State Legislative Assemblies
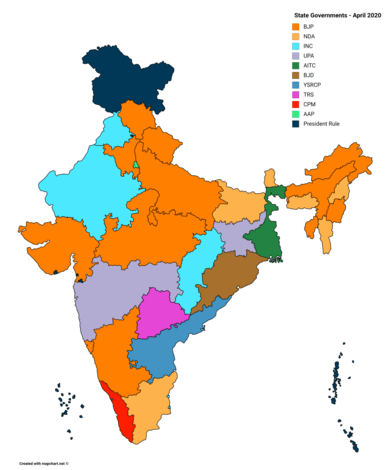
State Legislative Assemblies by ruling parties
Abolished State Legislative Assemblies
| State Legislative Assembly (Vidhan Sabha) |
Seat/state capital | Year established | Year abolished | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bombay Legislative Assembly | Bombay | 1937 | 1960 | abolished by the Bombay Reorganisation Act, 1960. |
| Coorg Legislative Assembly | Mercara | 1950 | 1956 | abolished by the States Reorganisation Act, 1956. |
| Patiala and East Punjab States Union Legislative Assembly | Patiala | 1950 | 1956 | abolished by the States Reorganisation Act, 1956. |
Notes
- † – In Jammu and Kashmir Legislative Assembly, two seats are reserved for the nominated women members. In addition to that, twenty-four more seats are reserved for the representatives from Pakistan-administered Kashmir and not counted normally.
- ‡ – In Puducherry Legislative Assembly, three seats are reserved for the members nominated by the Union Government of India.
See also
References
- "State Legislative Assemblies" (PDF). www.india.gov.in. Retrieved 2018-12-12.
- "Explainer: Why Jagan Reddy wants to abolish the legislative council in Andhra Pradesh".
- "Election Commission of India". eci.nic.in. Retrieved 12 January 2017.
External links
- Legislative Bodies in India website
- Laws of India website to download laws made by different states
















