1912 and 1913 United States Senate elections
In the United States Senate elections of 1912 and 1913, Democrats gained control of the Senate from the Republicans. Of the 22 seats up for election, 17 were won by Democrats, thereby gaining 4 seats from the Republicans. Two seats were unfilled by state legislators who failed to elect a new senator on time.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
32 of the 96 seats in the United States Senate (as well as special elections) 49 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
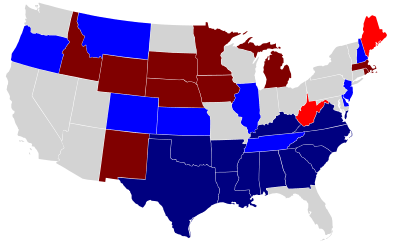 Results including special elections Democratic gains Republican gains Democratic holds Republican holds | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
These elections coincided with Democrat Woodrow Wilson's victory in the presidential election amid a divide in the Republican Party. In the Senate, Joseph M. Dixon and Miles Poindexter defected from the Republican Party and joined Theodore Roosevelt's new Progressive Party. Dixon, however, lost his seat during this election.
Some states elected their senators directly even before passage of the 17th Amendment in 1913. Oregon pioneered direct election and experimented with different measures over several years until it succeeded in 1907. Soon after, Nebraska followed suit and laid the foundation for other states to adopt measures reflecting the people's will. By 1912, as many as 29 states elected senators either as nominees of their party's primary or in conjunction with a general election.
This was the first time in 20 years that the Democrats won a majority in the Senate.
Results summary
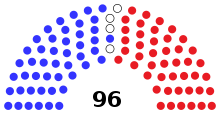
| Parties | Total Seats | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Incumbents | This election | Result | +/- | |||||||
| Not up | Up | Re- elected |
Held | Gained | Lost | |||||
| Democratic | 43 | 30 | 13 | 5 | 5 | 47 | ||||
| Republican | 52 | 33 | 19 | 6 | 4 | 45 | ||||
| Others | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| Vacant | 1 | 1 | 0 | 4 | ||||||
| Total | 96 | 64 | 32 | 11 | 9 | 96 | ||||
Change in Senate composition
Before the elections
After the March 1912 elections to elect senators from the new states of New Mexico and Arizona.
| D1 | D2 | D3 | D4 | D5 | D6 | D7 | D8 | ||
| D18 | D17 | D16 | D15 | D14 | D13 | D12 | D11 | D10 | D9 |
| D19 | D20 | D21 | D22 | D23 | D24 | D25 | D26 | D27 | D28 |
| D38 S.C. Ran |
D37 Okla. Ran |
D36 N.C. Ran |
D35 Miss. Ran |
D34 Maine Ran |
D33 La. Ran |
D32 Ga. Ran |
D31 Ala. Ran |
D30 | D29 |
| D39 Va. Ran |
D40 W.Va. Ran |
D41 Ark. Retired |
D42 Ky. Retired |
D43 Tex. Retired |
V1 Ill. (sp) |
R52 Tenn. Retired |
R51 R.I. Retired |
R50 N.H. Retired |
R49 Mass. Retired |
| Majority → | R48 Del. Retired | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R39 Minn. Ran |
R40 Mont. Ran |
R41 Neb. Ran |
R42 N.J. Ran |
R43 N.M. Ran |
R44 Ore. Ran |
R45 S.Dak. Ran |
R46 Wyo. Ran |
R47 Colo. Retired | |
| R38 Mich. Ran |
R37 Kan. Ran |
R36 Iowa Ran |
R35 Ill. Ran |
R34 Idaho Ran |
R33 | R32 | R31 | R30 | R29 |
| R19 | R20 | R21 | R22 | R23 | R24 | R25 | R26 | R27 | R28 |
| R18 | R17 | R16 | R15 | R14 | R13 | R12 | R11 | R10 | R9 |
| R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | R6 | R7 | R8 | ||
Result of the general elections
| D1 | D2 | D3 | D4 | D5 | D6 | D7 | D8 | ||
| D18 | D17 | D16 | D15 | D14 | D13 | D12 | D11 | D10 | D9 |
| D19 | D20 | D21 | D22 | D23 | D24 | D25 | D26 | D27 | D28 |
| D38 La. Hold |
D37 Ky. Hold |
D36 Ark. Hold |
D35 Va. Re-elected |
D34 S.C. Re-elected |
D33 Okla. Re-elected |
D32 N.C. Re-elected |
D31 Ala. Re-elected |
D30 | D29 |
| D39 Miss. Hold |
D40 Tex. Hold |
D41 Colo. Gain |
D42 Del. Gain |
D43 Kan. Gain |
D44 Mont. Gain |
D45 N.J. Gain |
D46 Ore. Gain |
D47 Tenn. Gain |
V1 Ga. D Loss |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Majority ↑ | |||||||||
| R39 Wyo. Re-elected |
R40 Mass. Hold |
R41 Neb. Hold |
R42 R.I. Hold |
R43 S.Dak. Hold |
R44 Maine Gain |
R45 W.Va. Gain |
V4 N.H. R Loss |
V3 Ill.2 R Loss |
V2 Ill.3 |
| R38 N.M. Re-elected |
R37 Minn. Re-elected |
R36 Mich. Re-elected |
R35 Iowa Re-elected |
R34 Idaho Re-elected |
R33 | R32 | R31 | R30 | R29 |
| R19 | R20 | R21 | R22 | R23 | R24 | R25 | R26 | R27 | R28 |
| R18 | R17 | R16 | R15 | R14 | R13 | R12 | R11 | R10 | R9 |
| R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | R6 | R7 | R8 | ||
Beginning of the next Congress
| D1 | D2 | D3 | D4 | D5 | D6 | D7 | D8 | ||
| D18 | D17 | D16 | D15 | D14 | D13 | D12 | D11 | D10 | D9 |
| D19 | D20 | D21 | D22 | D23 | D24 | D25 | D26 | D27 | D28 |
| D38 | D37 | D36 | D35 | D34 | D33 | D32 | D31 | D30 | D29 |
| D39 | D40 | D41 | D42 | D43 | D44 | D45 | D46 | D47 | D48 |
| Majority → | D49 Ga. Appointed | ||||||||
| R39 | R40 | R41 | R42 | V4 W.Va. Seated late |
V2 Ill.2 |
V1 Ill.3 |
P1 Wa. Changed |
V3 N.H. | |
| R38 | R37 | R36 | R35 | R34 | R33 | R32 | R31 | R30 | R29 |
| R19 | R20 | R21 | R22 | R23 | R24 | R25 | R26 | R27 | R28 |
| R18 | R17 | R16 | R15 | R14 | R13 | R12 | R11 | R10 | R9 |
| R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | R6 | R7 | R8 | ||
Beginning of the first session, April 7, 1913
| D1 | D2 | D3 | D4 | D5 | D6 | D7 | D8 | ||
| D18 | D17 | D16 | D15 | D14 | D13 | D12 | D11 | D10 | D9 |
| D19 | D20 | D21 | D22 | D23 | D24 | D25 | D26 | D27 | D28 |
| D38 | D37 | D36 | D35 | D34 | D33 | D32 | D31 | D30 | D29 |
| D39 | D40 | D41 | D42 | D43 | D44 | D45 | D46 | D47 | D48 |
| Majority → | D49 | ||||||||
| R39 | R40 | R41 | R41 | R43 W.Va. Seated late |
R44 Ill.2 Gain |
R45 Ill.3 Gain |
P1 | D50 N.H. Gain | |
| R38 | R37 | R36 | R35 | R34 | R33 | R32 | R31 | R30 | R29 |
| R19 | R20 | R21 | R22 | R23 | R24 | R25 | R26 | R27 | R28 |
| R18 | R17 | R16 | R15 | R14 | R13 | R12 | R11 | R10 | R9 |
| R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | R6 | R7 | R8 | ||
| Key: |
|
Complete list of races
Special elections during the 62nd Congress
In these special elections, the winners were seated in the 62nd Congress during 1912 or before March 4, 1913; ordered by election date.
| State | Incumbent | Results | Candidates | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Senator | Party | Electoral history | |||
| Virginia (Class 1) |
Claude A. Swanson | Democratic | 1910 (Appointed) | Interim appointee elected January 23, 1912. |
|
| New Mexico (Class 1) |
New seat | New senator elected March 27, 1912. Republican gain. |
| ||
| New Mexico (Class 2) |
New seat | New senator elected March 27, 1912. Republican gain. Winner was also subsequently elected to the next term, see below. | |||
| Arizona (Class 1) |
New seat | New senator elected March 26, 1912, ratifying the popular selection made in December 12, 1911 state elections. Democratic gain. |
| ||
| Arizona (Class 3) |
New seat | New senator elected March 26, 1912, ratifying the popular selection made in December 12, 1911 state elections. Democratic gain. |
| ||
| Maine (Class 2) |
Obadiah Gardner | Democratic | 1911 (Appointed) | Interim appointee elected April 2, 1912.[3] |
|
| Colorado (Class 3) |
Vacant | Charles J. Hughes Jr. (D) had died January 11, 1911. New senator elected January 14, 1913, ratifying the popular selection made in 1912 state elections. Democratic gain. |
| ||
| Tennessee (Class 2) |
Newell Sanders | Republican | 1912 (Appointed) | Interim appointee retired. New senator elected January 24, 1913. Democratic gain. Winner did not run for election to the following term, see below. |
|
| Texas (Class 2) |
Rienzi Johnston | Democratic | 1913 (Appointed) | Interim appointee lost election. New senator elected January 23, 1913. Democratic hold. Winner also elected to the next term, see below. |
|
| Idaho (Class 3) |
Kirtland I. Perky | Democratic | 1912 (Appointed) | Interim appointee lost election to finish the term. New senator elected January 24, 1913. Republican gain. |
|
| Arkansas (Class 2) |
John N. Heiskell | Democratic | 1913 (Appointed) | Interim appointee retired. New senator elected January 27, 1913. Democratic hold. Winner did not run for election to the following term, see below. |
|
| Nevada (Class 1) |
William A. Massey | Republican | 1912 (Appointed) | Interim appointee lost election to finish the term. New senator elected[lower-alpha 4] January 28, 1913, ratifying the popular selection made in 1912 state elections. Democratic gain. |
|
Races leading to the 63rd Congress
In these general elections, the winner was seated on March 4, 1913; ordered by state.
All of the elections involved the Class 2 seats.
| State | Incumbent | Results | Candidates | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Senator | Party | Electoral history | |||
| Alabama | John H. Bankhead | Democratic | 1907 (Appointed) 1907 (Special) |
Incumbent had already been re-elected early January 17, 1911, for the term beginning March 4, 1913. | |
| Arkansas | John N. Heiskell | Democratic | 1913 (Appointed) | Interim appointee retired. New senator elected January 29, 1913. Democratic hold. |
|
| Colorado | Simon Guggenheim | Republican | 1907 | Incumbent retired. New senator elected January 14, 1913, ratifying the popular selection made in 1912 state elections.[lower-alpha 4] Democratic gain. |
|
| Delaware | Harry A. Richardson | Republican | 1907 | Incumbent retired. New senator elected January 29, 1913. Democratic gain. |
|
| Georgia | Augustus Bacon | Democratic | 1894 1900 1907 (Appointed) 1907 (Special) |
Incumbent ran for re-election but the legislature failed to elect. Democratic loss. Incumbent was then appointed to begin the term.[4] |
Augustus Bacon (Democratic) |
| Idaho | William Borah | Republican | 1907 | Incumbent re-elected January 14, 1913. |
|
| Illinois | Shelby M. Cullom | Republican | 1882 1888 1894 1901 1907 |
Incumbent lost renomination. Legislature failed to elect. Republican loss. A new senator was later elected, see below. |
Bernard Berlyn (Socialist) Charles Boeschenstein (Democratic) Frank H. Funk (Progressive) J. Hamilton Lewis (Democratic) McDonald (Socialist) Lawrence Y. Sherman (Republican)[4] |
| Iowa | William S. Kenyon | Republican | 1911 (Special) | Incumbent re-elected January 21, 1913. |
|
| Kansas | Charles Curtis | Republican | 1907 (Special) 1907 |
Incumbent lost re-election.[lower-alpha 4] New senator elected January 28, 1913, ratifying the popular selection made in 1912 state elections.[lower-alpha 4] Democratic gain. |
|
| Kentucky | Thomas H. Paynter | Democratic | 1906 | Incumbent retired. New senator elected January 16, 1912. Democratic hold. |
|
| Louisiana | Murphy J. Foster | Democratic | 1900 1904 |
Incumbent lost renomination. New senator elected May 21, 1912. Democratic hold. |
|
| Maine | Obadiah Gardner | Democratic | 1911 (Appointed) 1912 (Special) |
Incumbent lost re-election. New senator elected January 15, 1913. Republican gain. |
|
| Massachusetts | Winthrop M. Crane | Republican | 1904 (Appointed) 1905 (Special) 1907 |
Incumbent retired. New senator elected January 14, 1913. Republican hold. |
|
| Michigan | William A. Smith | Republican | 1911 | Incumbent re-elected January 14, 1913. |
|
| Minnesota | Knute Nelson | Republican | 1895 1901 1907 |
Incumbent re-elected January 21, 1913, ratifying the popular selection made in 1912 state elections.[lower-alpha 4] |
|
| Mississippi | LeRoy Percy | Democratic | 1910 (Special) | Incumbent lost renomination. New senator elected January 16, 1912. Democratic hold. |
|
| Montana | Joseph M. Dixon | Republican | 1907 | Incumbent lost re-election as a Progressive.[lower-alpha 4] New senator elected January 14, 1913, ratifying the popular selection made in 1912 state elections. Democratic gain. |
|
| Nebraska | Norris Brown | Republican | 1907 | Incumbent lost renomination.[13] New senator elected January 21, 1913, ratifying the popular selection made in 1912 state elections. Republican hold. |
|
| New Hampshire | Henry E. Burnham | Republican | 1901 1907 |
Incumbent retired. Legislature failed to elect. Republican loss. New senator was elected late, see below. |
|
| New Jersey | Frank O. Briggs | Republican | 1907 | Incumbent lost re-election. New senator elected January 28, 1913. Democratic gain. |
|
| New Mexico | Albert B. Fall | Republican | 1912 (New state) | Incumbent re-elected June 6, 1912. Legislature invalidated the election. Incumbent then re-elected January 28, 1913. |
January 28, 1913 election:
|
| North Carolina | Furnifold Simmons | Democratic | 1901 1907 |
Incumbent re-elected January 21, 1913. |
|
| Oklahoma | Robert L. Owen | Democratic | 1907 | Incumbent re-elected January 21, 1913.[lower-alpha 4] |
|
| Oregon | Jonathan Bourne, Jr. | Republican | 1907 | Incumbent lost renomination and then lost re-election as Popular Government candidate. New senator elected January 21, 1913, ratifying the popular selection made in 1912 state elections.[lower-alpha 4] Democratic gain. |
|
| Rhode Island | George P. Wetmore | Republican | 1894 1900 1907 (No election) 1908 (Special) |
Incumbent retired. New senator elected January 21, 1913.[17] Republican hold. |
|
| South Carolina | Benjamin Tillman | Democratic | 1894 1901 1907 |
Incumbent re-elected January 28, 1913. |
|
| South Dakota | Robert J. Gamble | Republican | 1901 1907 |
Incumbent lost renomination.[18] New senator elected January 22, 1913. Republican hold. |
|
| Tennessee | Newell Sanders | Republican | 1912 (Appointed) | Interim appointee retired. New senator elected January 23, 1913. Democratic gain. |
|
| Texas | Rienzi Johnston | Democratic | 1913 (Appointed) | Interim appointee retired. New senator elected January 28, 1913. Democratic hold. |
|
| Virginia | Thomas S. Martin | Democratic | 1893 (Early) 1899 (Early) 1906 |
Incumbent re-elected January 24, 1912. |
|
| West Virginia | Clarence Watson | Democratic | 1911 (Special) | Incumbent lost re-election. New senator elected February 21, 1913.[21] Republican gain. Winner took seat late. |
|
| Wyoming | Francis E. Warren | Republican | 1890 1893 (Lost) 1895 1901 1907 |
Incumbent re-elected January 28, 1913. |
|
Early election to the following Congress
In this early general election, the winner was seated in the 64th Congress, starting March 4, 1915.
| State | Incumbent | Results | Candidates | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Senator | Party | Electoral history | |||
| Louisiana (Class 3) |
John Thornton | Democratic | 1910 (Special) | Incumbent retired. New senator elected early May 21, 1912. Democratic hold. |
|
Elections during the 63rd Congress
In these elections (some special, some merely late), the winners were seated in 1913 after March 4.
Some of those five elections late and some special, some by legislatures before ratification of the amendment and some popularly thereafter:
- Two elections were late and elected by legislatures: New Hampshire and Illinois (Class 2)
- One election was special and elected by a legislature: Illinois (Class 3)
- One election was late and elected popularly: Georgia
- One election was special and elected popularly: Maryland
They are ordered here by election date, then by class.
| State | Incumbent | Results | Candidates | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Senator | Party | Electoral history | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| New Hampshire (Class 2) |
Vacant | Legislature had failed to elect in time. New senator elected late March 13, 1913 on the 43rd ballot.[22] Democratic gain. |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Illinois (Class 2) |
Vacant | Legislature had failed to elect in time. New senator elected late March 26, 1913. Democratic gain. |
Frank H. Funk (Progressive) 22 votes Lawrence Y. Sherman (Republican) 9 votes Bernard Berlyn (Socialist) 4 votes[4] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Illinois (Class 3) |
Vacant | 1909 election of William Lorimer (R) had been voided July 13, 1912. New senator elected March 26, 1913. Republican gain. |
Charles Boeschenstein (Democratic) 25 votes Frank H. Funk (Republican) 22 votes McDonald (Socialist) 4 votes Scattering 2 votes[4] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Elected by popular vote after ratification of the 17th Amendment | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Georgia (Class 2) |
Augustus Bacon | Democratic | 1894 1900 1907 (Appointed) 1907 (Special) 1913 (Appointed) |
Legislature had failed to elect in time so the incumbent was appointed to begin the term. Interim appointee re-elected late July 15, 1913. |
Unopposed.[4] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Maryland (Class 1) |
William P. Jackson | Republican | 1912 (Appointed) | Appointee retired when elected successor qualified. New senator elected November 4, 1913 to finish the term ending March 3, 1917. Winner did not qualify until January 28, 1914.[24] Democratic gain. |
Thomas Parran Sr. (Republican) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Alabama
Incumbent Democrat John H. Bankhead had already been re-elected early January 17, 1911[25] for the 1913 term.
Arkansas
One-term incumbent Democrat Jeff Davis died January 3, 1913. Democratic Governor of Arkansas Joseph T. Robinson appointed John N. Heiskell January 6, 1913 to continue the term just until a special election.
Arkansas (Special)
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
John N. Heiskell was not a candidate in the special election. On January 29, 1913, the Arkansas Legislature elected Democratic businessman and former judge William Marmaduke Kavanaugh just to finish the term that would end in March 1913.
|
Arkansas (General)
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
Neither Heiskell nor Kavanaugh were candidates in the general election. On January 29, 1913, the Arkansas Legislature elected the Democratic Governor Joseph T. Robinson to the next term. This would be the last senate election by a state legislature before the April 8, 1913 adoption of the 17th amendment. Robinson would later become leader of Senate Democrats and Senate majority leader.
|
Arizona
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
Arizona became a new state February 14, 1912, with senators in classes 1 (ending 1917) and 3 (ending 1915). For the initial senators there was a popular vote held December 12, 1911 — before statehood — and the newly-formed state legislature effectively ratified the popular votes March 26, 1912: Democrat Henry F. Ashurst (class 1) and Democrat Marcus A. Smith (class 3).
Henry F. Ashurst was elected to the Territorial House of Representatives in 1897. He was re-elected in 1899, and became the territory's youngest speaker. In 1902, he was elected to the Territorial Senate. In 1911, Ashurst presided over Arizona's constitutional convention.[26] During the convention, he positioned himself for a U.S. Senate seat by avoiding the political fighting over various clauses in the constitution which damaged his rivals.[27]
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Henry F. Ashurst | 10,872 | 50.00% | |
| Republican | Ralph H. Cameron | 9,640 | 44.33% | |
| Socialist | E. Johnson | 1,234 | 5.68% | |
| Majority | 1,232 | 5.67% | ||
| Turnout | 21,746 | |||
Marcus A. Smith announced his candidacy for one of Arizona's two senate seats on September 24, 1911.[29] As the campaign began, Smith abandoned his long standing conservative stand and declared himself a "Progressive".[30]
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Marcus A. Smith | 10,598 | 50.35% | |
| Republican | Hoval A. Smith | 9,228 | 43.85% | |
| Socialist | E. B. Simonton | 1,221 | 5.80% | |
| Majority | 1,370 | 6.50% | ||
| Turnout | 21,047 | |||
With the admission of Arizona as a state in 1912, the Arizona State Legislature confirmed the selection of Smith and Ashurst as the state's first U.S. senators on March 27, 1912,[32] taking office April 2, 1912.
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Henry F. Ashurst | 19 | 100% | |
| Democratic | Marcus A. Smith | 19 | 100% | |
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Henry F. Ashurst | 35 | 100% | |
| Democratic | Marcus A. Smith | 35 | 100% | |
Colorado
On January 14, 1913, the Colorado General Assembly elected both of the state's senators: Democrat John F. Shafroth for the class 2 seat (ending 1919) and Democrat Charles S. Thomas for the class 3 seat (ending 1915).
Colorado (General)

One-term Republican incumbent Simon Guggenheim chose to retire in the term beginning March 4, 1913.
In the 1912 state elections, Democratic Governor of Colorado John F. Shafroth won the popular vote.
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | John F. Shafroth | 118,260 | 47.34% | |
| Republican | Clyde Dawson | 66,949 | 26.80% | |
| Progressive | Frank Catlin | 58,649 | 23.48% | |
| Prohibition | Mary E. Miller | 5,948 | 2.38% | |
The Colorado General Assembly ratified that decision January 14, 1913 by electing Thomas.
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | John F. Shafroth | 86 | 87.8% | |
| Republican | Clyde Dawson | 11 | 11.2% | |
| Progressive | Frank Catlin | 1 | 1.0% | |
| Democratic gain from Republican | ||||
Colorado (Special)

Democrat Charles J. Hughes Jr. (D) had died January 11, 1911 and the seat remained vacant for two years because the Colorado General Assembly failed to elect a successor.[4]
In the 1912 state elections, Democrat Charles S. Thomas (former Governor of Colorado) won the popular vote, and the Colorado General Assembly ratified that decision January 14, 1913 by overwhelmingly voting for Thomas.
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Charles S. Thomas | 88 | 88.9% | |
| Republican | Waterman | 9 | 9.1% | |
| Progressive | Vincent | 1 | 1.0% | |
| Progressive | Stevens | 1 | 1.0% | |
| Democratic gain from Vacant | ||||
Delaware

Incumbent Republican Harry A. Richardson retired after one term in office.
Democrat Willard Saulsbury Jr. had been a member of the Democratic National Committee since 1908 and had run for U.S. senator in 1899, 1901, 1903, 1905, 1907, and 1911, but Republicans controlled the state legislature and he was unsuccessful. In 1913, however, Democrats were in control of the legislature, Saulsbury was the preference of most Democrats, and he obtained the required majority January 29, 1913 after several days of balloting.
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Willard Saulsbury Jr. | 28 | 53.8% | |
| Republican | H. A. Richardson | 11 | 21.2% | |
| Republican | John G. Townsend | 5 | 9.6% | |
| Republican | Alfred I. du Pont | 3 | 5.8% | |
| Republican | Alexander P. Corbit | 3 | 5.8% | |
| Republican | Simeon S. Pennewill | 1 | 1.9% | |
| Republican | Ruby R. Vale | 1 | 1.9% | |
Georgia
| ||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||
The Georgia General Assembly failed to elect a senator, as Democratic incumbent Augustus O. Bacon's term ended. The Governor of Georgia therefore appointed Bacon to begin the term, pending a late election.
On June 15, 1913 Bacon was elected by the general populace without opposition, becoming the first senator elected under the Seventeenth Amendment to the United States Constitution.
Bacon died in early 1914, however, leading to another interim appointment and eventual special election.
Idaho
Idaho (General)
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
First term Republican incumbent William Borah was easily re-elected over two Democratic challengers.
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | William Borah | 75 | 94.9% | |
| Democratic | Kirtland I. Perky | 2 | 2.5% | |
| Democratic | George A. Tannahill | 2 | 2.5% | |
| Republican hold | ||||
Idaho (Special)
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Two-term incumbent Republican Weldon Heyburn died October 17, 1912. Democratic lawyer and former-Judge Kirtland I. Perky was appointed November 18, 1912 to continue the term pending a special election.
Perky was not a candidate in the special election, which was won by Republican former-Governor James H. Brady. Brady would win re-election in a popular vote in 1914.
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | James H. Brady | 43 | 53.8% | |
| Republican | James F. Ailshie | 7 | 8.8% | |
| Democratic | John F. Nugent | 5 | 6.3% | |
| Unknown | James E. Babb | 5 | 6.3% | |
| Unknown | Robert N. Dunn | 4 | 5.0% | |
| Unknown | E. H. Dewey | 4 | 5.0% | |
| Republican | J. T. Morrison | 3 | 3.8% | |
| Republican | Burton L. French | 2 | 2.5% | |
| Democratic | James Hanrahan | 2 | 2.5% | |
| Unknown | C. A. Beale | 1 | 1.3% | |
| Unknown | George Fields | 1 | 1.3% | |
| Unknown | J. F. Maclane | 1 | 1.3% | |
| Unknown | T. L. Burkland | 1 | 1.3% | |
| Unknown | W. C. Courtney | 1 | 1.3% | |
| Republican gain from Democratic | ||||
Illinois
In the November 1912 state elections, the Republicans lost control of the state due to the Republican / Progressive split. But while the Democrats held a plurality of the Illinois General Assembly, they did not have a majority. The General Assembly took up the matter of electing the senators on February 1. The General Assembly therefore failed to elect until after the new congress began.
On March 26, in a compromise arranged by governor Dunne, the General Assembly elected Democrat J. Hamilton Lewis to fill the full-term seat and Republican Lawrence Y. Sherman to fill the two remaining years of a vacancy that had just recently opened.
Illinois (General)
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
On April 12, 1912, five-term Republican incumbent Shelby Moore Cullom lost renomination to Lieutenant Governor of Illinois Lawrence Y. Sherman in the Republican "advisory" primary, where the voters expressed their preference for senator but the decision was not binding on the General Assembly, which made the actual choice. Cullom had suffered politically over his support for the other Illinois senator, William Lorimer, who was embroiled in a scandal over alleged bribery in his 1909 election to the Senate.
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Lawrence Y. Sherman | 178,063 | 46.16% | |
| Republican | Shelby Moore Cullom | 129,375 | 33.54% | |
| Republican | Hugh S. Magill | 78,344 | 20.31% | |
After his defeat, Cullom withdrew his name from consideration by the General Assembly.
The Illinois General Assembly eventually elected the Democratic nominee, Congressman J. Hamilton Lewis March 26, 1913.
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | J. Hamilton Lewis | 164 | 80.39% | |
| Progressive | Frank H. Funk | 22 | 10.78% | |
| Republican | Lawrence Y. Sherman | 9 | 4.41% | |
| Independent | Abstaining | 5 | 2.45% | |
| Socialist | Bernard Berlyn | 4 | 1.96% | |
| Democratic gain from Republican | ||||
Illinois (Special)
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Three months after the primary in which Sherman defeated Cullom, the U.S. Senate invalidated Lorimer's 1909 election and declared the seat vacant.[36] The Illinois Attorney General, William H. Stead determined that the General Assembly had failed to properly elect Lorimer in 1909 and so the Governor could not appoint a replacement.[37] As a result, the General Assembly had a second Senate seat to fill.
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Lawrence Y. Sherman | 143 | 70.10% | |
| Democratic | Charles Boeschenstein | 25 | 12.26% | |
| Progressive | Frank H. Funk | 22 | 10.78% | |
| Independent | Abstaining | 9 | 4.41% | |
| Socialist | McDonald | 4 | 1.96% | |
| Democratic | John Fitzpatrick | 1 | 0.49% | |
| Republican gain from Vacant | ||||
Iowa
| ||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||
Incumbent Republican William S. Kenyon, who had just won a 1911 special election to the seat, was easily re-elected by the Iowa General Assembly over Democratic former congressman Daniel W. Hamilton.[4]
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | William S. Kenyon | 29 | 61.70% | |
| Democratic | Daniel W. Hamilton | 18 | 38.30% | |
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | William S. Kenyon | 62 | 60.78% | |
| Democratic | Daniel W. Hamilton | 40 | 39.22% | |
| Republican hold | ||||
Kansas
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
One-term incumbent Republican (and future Vice President) Charles Curtis lost renomination to Governor of Kansas Walter R. Stubbs, who then lost the general election to Democratic Judge William H. Thompson as Democrats took control of the Kansas Legislature in the 1912 state elections.
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | William H. Thompson | 172,601 | 49.34% | |
| Republican | W. R. Stubbs | 151,647 | 43.35% | |
| Socialist | Allan W. Ricker | 25,610 | 7.32% | |
| Total votes | 349,858 | 100.00% | ||
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | William H. Thompson | 40 | 100% | |
| Turnout | 40 | 100.0% | ||
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | William H. Thompson | 120 | 96.8% | |
| Republican | W. R. Stubbs | 3 | 2.4% | |
| Progressive | Henry J. Allen | 1 | 0.8% | |
| Turnout | 124 | 99.2% | ||
| Democratic gain from Republican | ||||
Thompson would only serve one term, losing re-election in 1918.
Curtis, meanwhile, would go on to be re-elected in 1914 to the other seat for three terms before resigning to become U.S. Vice President.
Kentucky
| ||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||
One-term Democrat Thomas H. Paynter retired and Democratic Representative Ollie James was easily elected January 16, 1912.[1]
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Ollie James | 31 | 88.6% | |
| Republican | Edwin P. Morrow | 4 | 11.4% | |
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Ollie James | 74 | 75.5% | |
| Republican | Edwin P. Morrow | 24 | 24.6% | |
The legislature formally elected James a second time January 16, 1912, to comply with a federal rule requiring an election on the second Tuesday after the meeting of the legislature.[1]
Louisiana

Class 2: starting March 4, 1913

Class 3: starting March 4, 1915
Louisiana held two elections May 21, 1912: an election for the class 2 term that would begin March 4, 1913 and an election for the class 3 term that would begin March 4, 1915.
Louisiana (General, class 2)
In the class 2 seat, Democrat Murphy J. Foster lost renomination to fellow-Democrat Joseph E. Ransdell, who later was elected unopposed to seat.
Louisiana (General, class 3)
In the class 3 seat, Democrat John Thornton retired. Fellow-Democrat Robert F. Broussard was elected unopposed.
Maine
Five-term incumbent Republican William P. Frye had died August 8, 1911 and Democrat Obadiah Gardner was appointed September 23, 1911 to continue the term, pending a special election. In this election cycle, Gardner would first win the election to finish the term and then lose re-election to the next term.
Maine (Special)
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
Democratic interim appointee Obadiah Gardner was elected April 2, 1912 to finish the term ending March 3, 1913.[3][1]
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Obadiah Gardner | 20 | 76.9% | |
| Republican | Frederick A. Powers | 6 | 23.1% | |
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Obadiah Gardner | 78 | 60.9% | |
| Republican | Frederick A. Powers | 50 | 39.1% | |
| Democratic hold | ||||
Maine (General)
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Democrat Obadiah Gardner lost re-election January 15, 1913 to Republican Edwin C. Burleigh for the term starting March 4, 1913.
"There was no choice in the separate balloting on January 14. The next day in joint assembly, [Burleigh was elected]."[10]
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Edwin C. Burleigh | 91 | 50.6% | |
| Democratic | Obadiah Gardner | 82 | 45.6% | |
| Progressive | E.M. Thompson | 7 | 3.9% | |
| Republican gain from Democratic | ||||
Maryland (Special)
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Turnout | 198,205 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Democrat Isidor Rayner died November 25, 1912 and Republican William P. Jackson was appointed to continue the term, pending a special election.
Democratic state senator Blair Lee was elected November 4, 1913.
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Blair Lee | 112,485 | 56.75% | ||
| Republican | Thomas Parran Sr. | 73,300 | 36.98% | ||
| Progressive | George Wellington | 7,033 | 3.55% | ||
| Socialist | Robert Fields | 2,982 | 1.5% | ||
| Prohibition | Finley Hendrickson | 2,405 | 1.21% | ||
| Turnout | 198,205 | ||||
| Democratic gain from Republican | |||||
Lee presented his credentials to serve as senator on December 5, 1913, but he did not qualify until January 28, 1914 because Jackson claimed that "since [Jackson] had been appointed under the original constitutional provision, [Jackson] was entitled to hold his seat until the regularly scheduled adjournment date of the Maryland state assembly."[24] The Senate considered Jackson's challenge but eventually rejected it and seated Lee.
Lee would only serve this one term, as he lost renomination in 1916.
Massachusetts
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Republican Winthrop M. Crane, who was first appointed in 1904, retired. Republican congressman from Newton, Massachusetts, John W. Weeks, was elected January 14, 1913 to succeed him. Republican Eben Sumner Draper had been considered a candidate for the seat, but the Republican party, then under the control of its hardline conservative faction (and in control of the legislature), chose Weeks instead.[41]
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | John W. Weeks | 97 | 60.25% | |
| Republican | Samuel Walker McCall | 57 | 35.40% | |
| Republican | Curtis Guild Jr. | 5 | 3.11% | |
| Republican | George P. Lawrence | 1 | 0.62% | |
| Republican | Robert Luce | 1 | 0.62% | |
| Total votes | 161 | 100.00% | ||
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | John W. Weeks | 26 | 66.67% | |
| Democratic | Sherman L. Whipple | 11 | 28.21% | |
| Democratic | John A. Keliher | 1 | 2.56% | |
| Democratic | Joseph C. Pelletier | 1 | 2.56% | |
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | John W. Weeks | 134 | 57.51% | |
| Democratic | Sherman L. Whipple | 69 | 29.61% | |
| Progressive | John Graham Brooks | 5 | 2.15% | |
| Democratic | John F. Meaney | 3 | 1.29% | |
| Democratic | James B. Carroll | 3 | 1.29% | |
| Democratic | Charles A. DeCourey | 3 | 1.29% | |
| Democratic | Charles Sumner Hamlin | 2 | 0.86% | |
| Democratic | John A. Thayer | 2 | 0.86% | |
| Democratic | John F. Fitzgerald | 2 | 0.86% | |
| Republican | Curtis Guild Jr. | 1 | 0.43% | |
| Republican | Robert Luce | 1 | 0.43% | |
| Democratic | Philip J. O'Connell | 1 | 0.43% | |
| Unknown | Olney | 1 | 0.43% | |
| Democratic | Joseph Henry O'Neil | 1 | 0.43% | |
| Unknown | Peters | 1 | 0.43% | |
| Unknown | Pratt | 1 | 0.43% | |
| Unknown | Sawyer | 1 | 0.43% | |
| Unknown | Sweeney | 1 | 0.43% | |
| Unknown | Williams | 1 | 0.43% | |
Weeks would only serve for one six-year term. He would lose re-election in 1918 to Democrat David I. Walsh.
Michigan

One-term Republican William A. Smith was re-elected January 14, 1913.

- Alfred Lucking (Democratic) 41 votes
- Theodore Joslin (Progressive) 17 votes[10]
He would retire after this term.
Minnesota

Three-term Republican Knute Nelson was overwhelmingly supported in a 1912 popular election.

- Daniel W. Lawler (Democratic) 37.21%[11]
The Minnesota Legislature unanimously ratified the popular vote January 21, 1913:
- Minnesota Senate:

- Minnesota House of Representatives:

Nelson later would be re-elected again in 1918 to a fifth term, before his 1923 death.
Mississippi

One-term Democrat LeRoy Percy lost renomination in mid-1911 to white supremacist James K. Vardaman, who was then elected January 16, 1912 to the seat, unopposed.[1]
Percy had won in 1910 (to finish a vacant term) despite Vardaman's support of a plurality of legislators (all white). The fractured remainder sought to thwart his extreme racial policies. A majority united behind Percy to block Vardaman's election. Percy had advocated education for blacks and worked to improve race relations by appealing to the planters' sense of noblesse oblige. Disenfranchisement of blacks made the Democratic primary became the deciding competitive race for state and local offices in Mississippi.
In this rematch, Vardaman's campaign was managed by Lieutenant Governor of Mississippi (and future-senator) Theodore Bilbo, who emphasized class tensions and racial segregation. The tactics attacked Percy as a representative of the aristocracy of the state and for taking a progressive stance on race relations.
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | James K. Vardaman | 79,389 | 59.96% | |
| Democratic | C. H. Alexander | 31,490 | 23.78% | |
| Democratic | LeRoy Percy (Incumbent) | 21,521 | 16.26% | |
Vardaman, however, would only serve one term, losing renomination in 1918, primarily due to his vote against entry into World War I.
Montana

One-term Republican Joseph M. Dixon ran for re-election as a Progressive, but lost to Democrat Thomas J. Walsh.
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Thomas J. Walsh | 28,421 | 41.17% | |
| Progressive | Joseph M. Dixon (Incumbent) | 22,161 | 32.10% | |
| Republican | Henry C. Smith | 18,450 | 26.73% | |
The Montana Legislature then unanimously elected Walsh January 14, 1913.[10]
Walsh would be re-elected four more times and serve for 20 years until his 1933 death. Dixon, meanwhile, would go on to become Governor of Montana from 1921 to 1925.
Nebraska

First-term Republican Norris Brown lost renomination to George W. Norris, who was then elected January 21, 1913.
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Ashton C. Shallenberger | 27,581 | 57.61% | |
| Democratic | William H. Thompson | 11,993 | 25.05% | |
| Democratic | Willis E. Reed | 5,244 | 10.95% | |
| Democratic | Robert F. Smith | 3,061 | 6.39% | |
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | George W. Norris | 38,893 | 53.98% | |
| Republican | Norris Brown (Incumbent) | 33,156 | 46.02% | |
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | George W. Norris | 126,022 | ||
| Democratic | Ashton C. Shallenberger | |||
Despite the Democratic majority, the Nebraska legislature elected Republican Norris unanimously, upholding the popular vote.[46]
"The Democratic Legislature will be called upon to elect a Republican for United States Senator. Ninety-five per cent. [sic] of the candidates for the Legislature, in accordance with the Oregon plan, signed "Statement No. 1," which provides that, in the event of election, they will vote for the candidate for United States Senator who obtains the preference vote of the people. Although Congressman Norris, a Progressive Republican, has won the preference vote, returns indicate that a Democratic legislature has been elected."[47]
Norris would serve for thirty years, winning two more elections as a Republican and one as an Independent but losing re-election in 1942.
Nevada (Special)
.jpg)
Republican senator George S. Nixon died June 5, 1912. Republican former-judge William A. Massey was appointed July 1, 1912 to continue the term that would end in 1917, pending a special election. In November 1912, Massey lost the popular vote for the special election to Democratic attorney Key Pittman was elected by the Nevada Legislature January 28, 1913.
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Key Pittman | 7,942 | 39.78% | |
| Republican | William A. Massey (Incumbent) | 7,853 | 39.34% | |
| Socialist | George A. Steele | 7,853 | 13.73% | |
| Progressive | Sardis Summerfield | 1,428 | 7.15% | |
Pittman had a small plurality in the November 1912 popular vote, but the legislature elected him almost unanimously.
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Key Pittman | 20 | 90.9% | |
| Socialist | George A. Steele | 2 | 9.1% | |
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Key Pittman | 50 | 98.0% | |
| Socialist | George A. Steele | 1 | 2.0% | |
| Democratic gain from Republican | ||||
Massey died the next year, and Pittman would go on to serve for 27 more years and win re-election four times, serving as President pro tempore throughout the New Deal.
New Hampshire
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Two-term Republican Henry E. Burnham decided to retire. The New Hampshire legislature failed to elect a new senator after 42 votes, so the March 4, 1913 term begin with the seat vacant.
Finally, on March 26, 1913 on the 43rd vote, Democrat Henry F. Hollis was elected with the required majority, albeit slight. Hollis was a former candidate for U.S. House of Representatives (in 1900), and twice for Governor of New Hampshire (in 1902 and 1904).
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Henry F. Hollis | 189 | 50.94% | |
| Republican | John H. Bartlett | 121 | 32.62% | |
| Republican | Henry B. Quinby | 18 | 4.85% | |
| Republican | Edward N. Pearson | 14 | 3.77% | |
| Progressive | Robert P. Bass | 12 | 3.24% | |
| Republican | Sherman E. Burroughs | 5 | 1.35% | |
| Democratic | Gordon Woodbury | 3 | 0.81% | |
| Democratic | Clarence E. Carr | 2 | 0.54% | |
| Unknown | William D. Swart | 2 | 0.54% | |
| Republican | Thomas Chalmers | 1 | 0.27% | |
| Republican | William Eaton Chandler | 1 | 0.27% | |
| Republican | John Scammon | 1 | 0.27% | |
| Unknown | Bertram Ellis | 1 | 0.27% | |
| Unknown | Henry C. Wells | 1 | 0.27% | |
| Democratic gain from Republican | ||||
Hollis would retire after a single term and be replaced, in a popular vote, by Republican Henry W. Keyes.
New Jersey

One-term incumbent Republican Frank O. Briggs lost re-election to Democratic state judge (and former member of the U.S. House) William Hughes. The New Jersey Legislature elected Hughes January 28, 1913.
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | William Hughes | 12 | 57.14% | |
| Republican | Frank O. Briggs (Incumbent) | 9 | 42.86% | |
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | William Hughes | 51 | 86.44% | |
| Republican | Frank O. Briggs (Incumbent) | 8 | 13.56% | |
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | William Hughes | 63 | 78.75% | |
| Republican | Frank O. Briggs (Incumbent) | 17 | 21.25% | |
| Democratic gain from Republican | ||||
Briggs, died just a few months later on May 8, 1913. Hughes would not serve the complete term, dying January 30, 1918, just before the next scheduled election.
New Mexico
Initial election

New Mexico became a new state January 6, 1912, with senators in classes 1 (ending 1917) and 2 (ending 1913). On March 27, 1912, the state elected its initial senators on the eighth ballot:[52] Republican Thomas B. Catron, an early advocate for New Mexico statehood who had marshaled the territorial Republican Party to lobby Republicans at the national level for New Mexico's admission to the Union,[53][54][55] and Republican Albert B. Fall, a powerful attorney, former territorial attorney general, future Secretary of the Interior, and instigator of the Teapot Dome scandal)
Catron made a personal alliance with Fall, ensuring that each of them would be elected. This alliance antagonized New Mexicans of Spanish heritage, who had hoped that one of their own would become a Senator.[56]
|
General election
Fall's term would end in March 1913, so he was up for re-election shortly after his initial term began.
The bitterness over Catron and Fall's alliance made Fall a target of the local Republican Party, as they believed Fall had not contributed sufficiently to their efforts to secure New Mexico's statehood, and was not worthy of their nomination. The selection of Catron and Fall also disappointed Hispanics, who had hoped that one of their own would be selected. Fall was also severely disliked by Democrats.
After various votes, the legislature re-elected Fall January 28, 1913. Governor McDonald, on the advice of his Democratic legal advisor, Summers Burkhart, said that the legislature's procedure had been illegal, and failed to sign the credentialing papers in an attempt to oust Fall by forcing a special session of the legislature and a new vote.[57] The attempt failed; Fall won the special legislative election.[58]
North Carolina
.jpg)
Two-term Democrat Furnifold Simmons was easily re-elected January 21, 1913. Simmons was a staunch segregationist, white supremacist and a leading perpetrator of the Wilmington insurrection of 1898.
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Furnifold Simmons (Incumbent) | 84,687 | 57.18% | |
| Democratic | William W. Kitchin (Governor) | 47,010 | 31.74% | |
| Democratic | Walter Clark (State judge) | 16,418 | 11.09% | |
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Furnifold Simmons (Incumbent) | 144 | 88.34% | |
| Republican | Cyrus Thompson (N.C. Secretary of State) | 19 | 11.66% | |
Simmons would be re-elected twice more after this and serve until 1931, when he fell out with the national Democratic Party.
Oklahoma
.jpg)
One term Democrat Robert L. Owen was re-elected over token opposition from Governor of Oklahoma Charles N. Haskell in the Democratic primary and perennial Republican candidate Joseph T. Dickerson.
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Robert L. Owen (Incumbent) | 80,204 | 64.32% | |
| Democratic | Charles N. Haskell | 44,483 | 35.68% | |
| Turnout | 7.52% | |||
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Robert L. Owen (Incumbent) | 126,418 | 50.43% | |
| Republican | Joseph T. Dickerson | 83,429 | 33.28% | |
| Socialist | John Wills | 40,860 | 16.3% | |
| Turnout | 15.13% | |||
Owen was formally and unanimously elected by the Oklahoma Legislature January 21, 1913.[62][10]
Owen would run for U.S. president (failing to achieve his party's nomination), and then serve a third and final term as the young state's initial Class 2 senator, retiring in 1925.
Oregon

One-term Republican Jonathan Bourne Jr. had championed direct-election of senators but lost renomination as a Republican. He then ran in the popular election as a "Popular Government" candidate, but also lost re-election. Democratic Mayor of Portland Harry Lane was elected.
The ballot was cluttered. In addition to the Lane and Ben Selling, candidate of the conservative wing of the Republican Party, progressive Republicans had other electoral alternatives, including the candidate and the incumbent senator Jonathan Bourne Jr., who had failed to win the renomination of the Republican party and ran as the "Popular Government" nominee as a result. Meanwhile, Benjamin F. Ramp stood for the Socialists and yet another candidate was the nominee of the Prohibition Party.[63] Each of these six candidates took more than 5% of the vote — a fact which enabled the Lane to win election with a plurality of the vote in solidly Republican Oregon.[63] Intent on proving himself a man of the people, Harry Lane set what might be a record for campaign frugality in his victorious effort, with his entire race run for $75 plus travel expenses.[64]
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Harry Lane | 40,172 | 30.07% | |
| Republican | Ben Selling | 38,453 | 28.79% | |
| Popular Government | Jonathan Bourne Jr. | 25,929 | 19.41% | |
| Socialist | Benjamin F. Ramp | 11,093 | 8.31% | |
| Progressive | A. E. Clark | 11,083 | 8.30% | |
| Prohibition | B. Lee Paget | 6,848 | 5.13% | |
| Democratic gain from Republican | ||||
The Oregon Legislature thereupon elected Lane to the seat January 21, 1913,[10] ratifying the popular selection made in the November 1912 elections.
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Harry Lane | 28 | 93.3% | |
| Republican | Ben Selling | 2 | 6.7% | |
Both senators voting for Selling declared that they voted to protest a new system of nomination.
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Harry Lane | 59 | 98.3% | |
| Republican | Ben Selling | 1 | 1.7% | |
Lane died in office on May 23, 1917.
Rhode Island

Three-term Republican George P. Wetmore retired and was replaced by Republican judge LeBaron Colt January 21, 1913.
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | LeBaron Colt | 32 | 82.1% | |
| Democratic | Addison P. Munroe | 5 | 12.8% | |
| Progressive | George W. Parks | 2 | 5.1% | |
| Turnout | 39 | 100% | ||
Both senators voting for Selling declared that they voted to protest a new system of nomination.
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | LeBaron Colt | 56 | 56.0% | |
| Democratic | Addison P. Munroe | 37 | 37.0% | |
| Progressive | George W. Parks | 7 | 7.0% | |
| Turnout | 100 | 100% | ||
The following day, the Joint Assembly formally declared Colt elected. Colt resigned February 7, 1913 from the U.S. Court of Appeals for the First Circuit, in which he'd served since 1891.
When asked concerning his ideas on national issues Judge Colt replied that he was still a member of the court, and until his resignation he did not think it would be dignified or courteous to talk upon the subject."[17]
Colt would be re-elected in 1918, and die near the end of that second term on August 18, 1824.
South Carolina

The South Carolina race was mostly a Democratic primary election held the previous summer on August 27, 1912. The Democratic Party of South Carolina organized primary elections for the U.S. Senate beginning in 1896 and the General Assembly would confirm the choice of the Democratic voters.
Incumbent Democrat Benjamin Tillman, serving since 1895, drew opposition in the Democratic primary for the first time during his career. He had long avoided any opposition because of his influence in the Democratic Party in the state, but by 1912 he had moderated his positions and lost the radical edge that had allowed him to build up a hard core following of support. The radicals in the state electorate had thrown their support to Coleman Livingston Blease in the gubernatorial election of 1910 and the Bleasites were determined to knock his chief opponent, Tillman, out of office. W. Jasper Talbert emerged as the candidate of the Bleasites and Nathaniel B. Dial entered the race as an alternative to the two. The voters of the state split their support between the Tillmanite and Bleasite factions as both Tillman and Blease won their respective primaries.
Tillman won the Democratic primary.
| South Carolina Democratic primary[69] | ||
|---|---|---|
| Candidate | Votes | % |
| Benjamin Tillman | 73,148 | 52.7 |
| W. Jasper Talbert | 37,141 | 26.8 |
| Nathaniel B. Dial | 28,476 | 20.5 |
Tillman was then re-elected January 28, 1913 by the General Assembly for another six-year term.
Election by the South Carolina legislature:
- Vote in the South Carolina Senate: Unanimous (37 votes of 37 senators voting)[70]
- Vote in the South Carolina House of Representatives: Unanimous (114 votes of the 114 members voting)[70]
South Dakota

Two-term Republican Robert J. Gamble lost renomination.
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Thomas Sterling | 25,896 | 35.00% | |
| Republican | Robert J. Gamble (Incumbent) | 25,161 | 34.01% | |
| Republican | Richard Olsen Richards | 16,983 | 22.96% | |
| Republican | Melvin Grigsby | 5,941 | 8.03% | |
| Turnout | 73,981 | 12.67% | ||
Republican Thomas Sterling was then elected January 22, 1913 with 97 votes[19]
Tennessee
One-term Democrat Robert Love Taylor died March 31, 1912 and Republican Newell Sanders was appointed in his place, pending a special election. Sanders was not a candidate either election
The Tennessee legislature elected two senators: one to the next term and one to finish the current term.
Tennessee (General)

Democratic judge John K. Shields was elected January 23, 1913 to the next term beginning March 4, 1913. He had not been a candidate in the special election.
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | John K. Shields | 69 | 52.7% | |
| Independent Democratic | Charles T. Cates Jr. | 61 | 46.6% | |
| Present but not voting | 1 | 0.8% | ||
| Turnout | 130 | 96% | ||
Shields would be re-elected in 1918, but lose renomination in 1924.
Tennessee (Special)

Democrat William R. Webb, the founder of the Webb School and former Confederate soldier, was elected January 23, 1913 to finish the term ending March 3, 1913. Webb was not a candidate in the general election.
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | William R. Webb | 73 | 57.0% | |
| Democratic | M. T. Bryan | 53 | 41.4% | |
| Democratic | J. A. Clement | 1 | 0.8% | |
| Democratic | C. W. Tyler | 1 | 0.8% | |
| Turnout | 128 | 96% | ||
The election was then made unanimous by motion of the joint convention.[73]
Texas
.jpg)
Two-term Democrat Joseph Weldon Bailey resigned January 3, 1913 and Democrat Rienzi M. Johnston was appointed January 4, 1913 to continue the term, pending a special election. In fact, Texas held would hold two elections January 28, 1913: a special election for the term ending March 3, 1913, and a general election for the next term starting March 4, 1913, both were won by Democratic congressman Morris Sheppard.
Texas (Special)
There was a Democratic Primary July 27, 1912. Morris Shppard, C. B. Randell, Mat Zollner, and Jake Wolters were candidates. Sheppard received a plurality of the (approximately 8,000) votes.[74]
Appointee Rienzi M. Johnston ran for but lost election to finish the shortened term.
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Morris Sheppard | 104 | 60.8% | |
| Democratic | Rienzi M. Johnston | 66 | 38.6% | |
| Democratic | Choice B. Randell | 1 | 0.6% | |
Following his brief 25-day Senate term, Johnston returned to Houston and resumed his role as editor of the Houston Post. He retired from the newspaper business in 1919.[76]
Texas (General)
Perhaps due to the overwhelming support for the special election, Sheppard had no opposition in the subsequent general election.
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Morris Sheppard | 172 | 100.0% | |
Sheppard would win re-election four times, serving until his death in 1941.
Virginia
Virginia held non-binding primaries September 7, 1911 for both the class 2 seat held by Democrat Thomas S. Martin, who was running for re-election, and the class 1 seat held by Democrat Claude Swanson, who had been appointed to fill a vacancy.[78]
Virginia (Special)

Democrat John W. Daniel died June 29, 1910, and Democrat Claude A. Swanson, a former Governor of Virginia and former Congressman, was appointed August 1, 1910 to finish the term ending March 1911 and again appointed February 28, 1911 to begin the 1911–1917 term, pending a special election.
Swanson won the class 1 Democratic primary for the term ending in 1917 with 67,495 votes over (future senator) Carter Glass's 28,757 votes.[79]
On January 24, 1912, the Virginia General Assembly unanimously elected Swanson.[80][81]
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Claude A. Swanson | 34 | 100% | |
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Claude A. Swanson | 83 | 100% | |
Virginia (General)

Three-term incumbent Democrat Thomas S. Martin won the Democratic primary for the class 2 term ending in 1919, receiving 57,120 votes to 25,005 for William Atkinson Jones.
On January 24, 1912, the Virginia General Assembly unanimously elected Martin.[80][81]
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Thomas S. Martin | 34 | 100% | |
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Thomas S. Martin | 85 | 100% | |
West Virginia

Democrat Clarence Watson had been elected in 1911 to finish a vacant term, but he lost re-election February 21, 1913 to Republican federal judge Nathan Goff Jr. after multiple deadlocked ballots.
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Nathan Goff Jr. | 60 | 56.6% | |
| Democratic | Clarence W. Watson | 43 | 40.6% | |
| Democratic | Robert W. Dailey | 1 | 0.9% | |
| Democratic | John W. Davis | 1 | 0.9% | |
| Democratic | John W. Hamilton | 1 | 0.9% | |
Goff would remain a judge until April 1, 1913 before taking his Senate seat. He would only serve the one term, retiring in 1918.
Wyoming

Four-term Republican Francis E. Warren was re-elected January 28, 1913.
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Francis E. Warren | 16 | 61.5% | |
| Democratic | John B. Kendrick | 10 | 38.5% | |
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Francis E. Warren | 29 | 51.8% | |
| Democratic | John B. Kendrick | 27 | 48.2% | |
| Not voting | 1 | |||
Kendrick would be elected to the other seat in 1916.
Warren would be re-elected two more times, becoming the Dean of the United States Senate, and serve until his death in 1929.
See also
Notes
- as Democratic Conference Chairman
- as Republican Conference Chairman
- [sic], probably "William J. Mills"
- Senator was selected by some form of direct voting and then subsequently elected by state legislatures.
- Date might be incorrect, as it is the date of the general popular election.
References
- United States Senators Chosen, 1912, p. 457.
- "AZ US Senate". Our Campaigns. Retrieved October 3, 2013.
- Byrd, p. 118.
- United States Senators Chosen, 1913, p. 458.
- United States Senators Chosen, 1913, p. 460.
- "Our Campaigns - NV US Senate - Special Race - Nov 05, 1912". www.ourcampaigns.com. Retrieved December 21, 2017.
- "CO US Senate". Our Campaigns. Retrieved October 3, 2013.
- United States Senators Chosen, 1913, pp. 458–459.
- "KS US Senate". Our Campaigns. Retrieved October 3, 2013.
- United States Senators Chosen, 1913, p. 459.
- "MN US Senate". Our Campaigns. Retrieved October 3, 2013.
- "MT US Senate". Our Campaigns. Retrieved October 3, 2013.
- "NE US Senate". Our Campaigns. Retrieved October 3, 2013.
- "NE US Senate". Our Campaigns. Retrieved October 3, 2013.
- "OK US Senate". Our Campaigns. Retrieved May 31, 2020., citing United States Congressional Elections, 1788-1997 The Official Results Michael J. Dubin
- "OR US Senate". Our Campaigns. Retrieved October 3, 2013.
- The New York Times, January 22, 1913, p. 4.
- "SD US Senate - R Primary". Our Campaigns. Retrieved September 28, 2013.
- United States Senators Chosen, 1913, pp. 459–460.
- "Anti-Saloon Men Heard at Richmond". Washington Gerald. Washington, DC. January 25, 1912. p. 1.
- "Journal of the Senate of the state of West Virginia". Charleston, West Virginia. 1913: 790. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - Journals of the Honorable Senate and House of Representatives of the State of New Hampshire, 1913. p. 27–28.
- "NH US Senate". Our Campaigns. Retrieved May 12, 2020.
- "U.S. Senate: The Election Case of William P. Jackson v. Blair Lee of Maryland (1914)". www.senate.gov. Retrieved December 21, 2017.
- United States Senators Chosen, 1911, p. 455.
- "Henry Fountain Ashurst Dead; Former Senator from Arizona". New York Times. June 1, 1962. p. 27.
- Johnston, Alva (December 25, 1937). "The Dean of Inconsistency". The Saturday Evening Post. 210: 23, 38–40.
- "Our Campaigns - AZ US Senate Race - Mar 27, 1912". www.ourcampaigns.com.
- Fazio 1970, p. 55.
- Goff 1985, p. 145.
- "Our Campaigns - AZ US Senate Race - Dec 12, 1911". www.ourcampaigns.com.
- Goff 1989, p. 60.
- Taylor, Julius F. "The Broad Ax". Illinois Digital Newspaper Collections. Retrieved June 22, 2015.
- "IL US Senate-R Primary". Our Campaigns. Retrieved March 27, 2020.
- "IL US Senate". Our Campaigns. Retrieved March 27, 2020.
- "Lorimer ousted by decisive vote". The New York Times. July 14, 1912.
- "Lorimer never elected". The New York Times. July 18, 1912.
- "IL US Senate Special". Our Campaigns. Retrieved March 27, 2020.
- Senate Journal. Proceedings of the Senate of the State of Kansas. Eighteenth biennial session, Topeka, January 14 to March 17, 1913. Topeka, Kansas: W. C. Austin, State Printer. 1913.
- United States Congress (1917). Official Congressional Directory, Volume 64, Issue 2, Part 2; Volume 65. U.S. Government Printing Office. p. 42 – via Google Books.
- Abrams, Richard (1964). Conservatism in a Progressive Era: Massachusetts Politics 1900-1912. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press. p. 285. OCLC 475077.
- "REPUBLICANS READY TO ELECT MR. WEEKS BAY STATE SENATOR". The Christian Science Monitor. January 14, 1913. p. 1.
- "Our Campaigns - MA US Senate Race - Jan 14, 1913". www.ourcampaigns.com.
- "Vardaman's Weekly - Online (Writings by and about Senator James K. Vardaman)". www.hhtc.org. Retrieved May 27, 2020.
- Senate journal of the Legislature of the State of Nebraska. 1913. p. 62.
- Senate journal of the Legislature of the State of Nebraska. 1913. p. 153.
- "Wilson's Nebraska Lead 31,000". The New York Times. November 8, 1912. p. 4.
- "Our Campaigns - NV US Senate - Special Race - Nov 05, 1912". www.ourcampaigns.com. Retrieved December 21, 2017.
- The Journal of the Senate of the Special Session of the Legislature of the State of Nevada. 1912. Carson City, Nevada. 1913. p. 21.
- The Journal of the Assembly of the Special Session of the Legislature of the State of Nevada. 1912. Carson City, Nevada. 1913. p. 28.
- Journal of the Senate of the State of New Jersey. 1913.
- "NEW MEXICO SENATORS". The New York Times. March 28, 1912. Retrieved March 26, 2020.
- Prince, Le Baron Bradford (1910). New Mexico's Struggle for Statehood. New Mexican Printing Company. p. 91.
- Larson, Robert W. (August 15, 2013). New Mexico's Quest for Statehood, 1846-1912. p. 98. ISBN 9780826329479.
- McCord, Richard (2009). Santa Fe Living Treasures: Our Elders, Our Hearts. p. 52. ISBN 9780865347205.
- "New Mexico Natives Bitter Over Defeat" (PDF). The New York Times. April 7, 1912.
- Twitchell, Ralph Emerson (1911). The Leading Facts of New Mexican History. V. Cedar Rapids, Iowa: Torch Press. p. 122. OCLC 3828708.
- Twitchell, p. 203.
- "NC US Senate - D Primary". Our Campaigns. Retrieved May 31, 2020.
- "NC US Senate". Our Campaigns. January 22, 1913. Retrieved May 31, 2020.
- "OK US Senate - D Primary". Our Campaigns. Retrieved May 31, 2020., citing 1947 Oklahoma Almanac, p. 90
- Journal of the Senate of the Fourth Legislature of the State of Oklahoma.
- Leip (ed.), Dave. "1912 Senatorial General Election Results - Oregon, Atlas of US Presidential Elections" – via www.uselectionatlas.org.CS1 maint: extra text: authors list (link)
- Johnston, Robert D. (2003). The Radical Middle Class: Populist Democracy and the Question of Capitalism in Progressive Era Portland, Oregon. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. p. 30.
- "OR US Senate". Our Campaigns. Retrieved October 3, 2013.
- Journal of the Senate of the Twenty-seventh Legislative Assembly of the State of Oregon. 1913. p. 126.
- Journal of the House the Twenty-seventh Legislative Assembly of the State of Oregon. 1913. p. 123.
- Manual - the State of Rhode Island and Providence Plantations. 1914. p. 165.
- "Our Campaigns - SC US Senate - D Primary Race - Aug 27, 1912". www.ourcampaigns.com. Retrieved June 3, 2020.
- Journal of the Senate of the State of South Carolina 1913. pp. 246–247.
- "SD US Senate - R Primary". Our Campaigns. Retrieved June 3, 2020.
- "House journal of the Fifty-Eighth General Assembly of the State of Tennessee. 1913-1913B". Nashville, Tennessee: McQuiddy Printing Company. 1913: 132–133. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - "House journal of the Fifty-Eighth General Assembly of the State of Tennessee. 1913-1913B". Nashville, Tennessee: McQuiddy Printing Company. 1913: 142–143. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - "Journal of the Senate of Texas begin the Regular Session of the Thirty-Third Legislature". Austin, Texas: Von Boeckmann-Jones Co., Printers. 1913: 162–163. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - "Journal of the Senate of Texas begin the Regular Session of the Thirty-Third Legislature". Austin, Texas: Von Boeckmann-Jones Co., Printers. 1913: 174. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - "Johnston, Rienzi Melville". Texas State Historical Association. June 15, 2010. Retrieved March 17, 2018.
- "Journal of the Senate of Texas begin the Regular Session of the Thirty-Third Legislature". Austin, Texas: Von Boeckmann-Jones Co., Printers. 1913: 175. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - "Martin-Swanson Majority Swells". Newport Daily Press. Newport News, Virginia. September 9, 1911. p. 1.
- Bell, James B. (1911). Congressional Directory, 62nd Congress, 2nd Session. Washington, DC: US Government Printing Office. p. 107.
- "Return Martin to Senate: Virginia Assembly Re-Elects him Senator, also Elects Swanson". Belvidere Daily Republican. Belvidere, IL. January 25, 1912. p. 1.
- "Returned to United States Senate by Vieginia". New Philadelphia Daily Times. New Philadelphia, Ohio. January 25, 1912. p. 8.
- Journal of the House of Delegates of Virginia. 1912. p. 184.
- "Senate Journal of the Twelfth State Legislature of Wyoming 1913". Laramie, Wyoming: The Laramie Republican Company. 1913: 88. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - "House Journal of the Twelfth State Legislature of Wyoming 1913". Laramie, Wyoming: The Laramie Republican Company. 1913: 89–90. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help)
Sources
- "United States Senate".
- "COLT MADE SENATOR". The New York Times. January 22, 1913. p. 4., with election stories from Rhode Island, Iowa, Nebraska, Oklahoma, Minnesota, South Dakota, Oregon, Delaware, New Hampshire, Tennessee, Wyoming, Idaho, West Virginia, and Illinois. Some are results and some are deadlocks.
- "United States Senators Chosen, 1911". The Tribune Almanac and Political Register 1912. New York: The Tribune Association. 1912. pp. 455–458 – via Hathi Trust Digital Library.
- "United States Senators Chosen, 1912". The Tribune Almanac and Political Register 1913. New York: The Tribune Association. 1913. p. 457 – via Hathi Trust Digital Library.
- "United States Senators Chosen, 1913". The Tribune Almanac and Political Register 1914. New York: The Tribune Association. 1914. pp. 458–460 – via Hathi Trust Digital Library.
- Byrd, Robert C. (October 1, 1993). Wolff, Wendy (ed.). The Senate, 1789-1989: Historical Statistics, 1789-1992. United States Senate Historical Office (volume 4 Bicentennial ed.). Washington, D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office. ISBN 9780160632563 – via Google Books.
- Fazio, Steven A. (Spring 1970). "Marcus Aurelius Smith: Arizona Delegate and Senator". Arizona and the West. 12 (1): 23–62. JSTOR 40168029.
- Goff, John S. (1985). Arizona Territorial Officials Volume III: The Delegates to Congress 1863-1912. Cave Creek, Arizona: Black Mountain Press. OCLC 12559708.
- Goff, John S. (1989). Marcus A. Smith. Arizona biographical series. v. 5. Cave Creek, Arizona: Black Mountain Press. OCLC 21013345.



















.jpg)



.jpg)



.jpg)



