Power sector of Andhra Pradesh
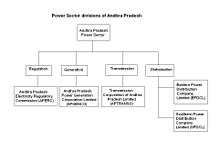
Power sector of Andhra Pradesh is divided into 4 categories namely Regulation, Generation, Transmission and Distribution. Andhra Pradesh Electricity Regulatory Commission (APERC) is the regulatory body.[1] APGENCO deals with the electricity production and also maintenance, proposes new projects and upgrades existing ones as well.[2] The APGENCO also set up a Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV), named as Andhra Pradesh Power Development Company Limited (APPDCL), a joint venture company of APGENCO (with 50% equity) and IL&FS (50% equity) to set up Krishnapatanam thermal power project (2x800 MW).[3]
APTRANSCO is set up for transmission of power.[4] Power distribution in the state is divided into two divisions, namely Eastern Power Distribution Corporation Limited (EPDCL) and Southern Power Distribution Corporation Limited (SPDCL), which distributes the power to the households and the industries.[5] APGENCO, APPDCL, NTPC and other private firms contribute to the generation of power in the state of Andhra Pradesh.[6][7] Andhra Pradesh has become the second state in India to achieve 100% electrification of all households.[8] Weighted average cost of power generation and purchases is INR 3.16 per kWh which is highest in the country.[9]
The total installed utility power generation capacity is nearly 23,051 MW in the state.[10] APtransCo has made long term power purchase agreements for 17,303 MW as of 28 Febrauary 2018.[11] The per capita electricity consumption is 1085 units with 55,160 million KWh gross electricity supplied in the year 2016–17.[11][12] The performance of Krishnapatanam thermal power station (2X800 MW) with super critical pressure technology is not satisfactory even after one year commercial operation as the units rarely operate at rated capacity forcing the state to purchase costly power from day ahead trading in IEX.[13][14]
Non-renewable
Thermal power

Thermal power plants are based on the fuel coal, gas, diesel etc. Public sector undertaking NTPC, state level power generating companies and private firms are engaged in this sector for power generation.
Currently operating coal based thermal power plants in Andhra Pradesh are listed below.[16]
Gas fuel-based

The following are the list of presently installed combined cycle gas turbine power plants and diesel engine power plants in the state. However many of these power plants are not operating due to non-availability of natural gas and high cost of liquid fuels.[18]
| Power station | Operator | Location | District | Sector | Capacity (MW) | Plant Coordinates |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| APGPCL Plant | APGPCL | Vijjeswaram | W. Godavari | Joint | 272 | 16°56′02″N 81°43′27″E / 16.93389°N 81.72417°E |
| Lanco Kondapalli Power Plant | Lanco Infratech | Kondapalli | Krishna | Private | 1466 | 16°38′20″N 80°33′00″E / 16.63889°N 80.55000°E |
| Gautami Combined Cycle Power Plant | GVK | Peddapuram | E. Godavari | Private | 464 | 17°02′21″N 82°08′43″E / 17.03917°N 82.14528°E |
| Konaseema Combined Cycle Power Plant | Konaseema Gas Power Limited (KGPL) | Ravulapalem | E. Godavari | Private | 445 | 16°44′05″N 81°51′44″E / 16.73472°N 81.86222°E |
| Vemagiri Combined Cycle Power Plant | GMR | Vemagiri | E. Godavari | Private | 370 | 16°55′29″N 81°48′46″E / 16.92472°N 81.81278°E |
| GMR Rajamundry Combined Cycle Power Plant[19] | GMR | Vemagiri | E. Godavari | Private | 768 | 16°55′28″N 81°48′46″E / 16.92444°N 81.81278°E |
| Samarlakota Combined Cycle Power Plant | Reliance | Samarlakota | E. Godavari | Private | 2620 | 17°02′19″N 82°08′05″E / 17.03861°N 82.13472°E |
| Godavari Gas Power Plant[20] | APGENCO | Jegurupadu | E. Godavari | State | 216 | 16°55′55″N 81°51′37″E / 16.93194°N 81.86028°E |
| Jegurupadu Combined Cycle Power Plant | GVK | Jegurupadu | E. Godavari | Private | 229 | 16°55′54″N 81°51′36″E / 16.93167°N 81.86000°E |
| Spectrum Combined Cycle Power Plant | Spectrum | Kakinada | E. Godavari | Private | 209 | 17°03′31″N 82°18′34″E / 17.05861°N 82.30944°E |
| GMR (barge mounted) Power Plant | GMR | Kakinada | E. Godavari | Private | 237 | 17°03′32″N 82°18′33″E / 17.05889°N 82.30917°E |
| LVS Diesel Engine Power Station | Greenko | Vishakhapatnam | Visakhapatnam | Private | 37 | 17°50′45″N 83°14′13″E / 17.84583°N 83.23694°E |
| Panduranga CCPP | PESPL | Annadevarapeta | W. Godavari | Private | 116 | 17°07′45″N 81°36′09″E / 17.12917°N 81.60250°E |
| RVK Energy power plant[21] | KSK Energy Ventures | Rajahmundry | E. Godavari | Private | 436 | |
| Sriba power plant | Sriba industries | Chigurukota | Krishna | Private | 30 | |
| Silkroad sugar power plant | EID Parry | Kakinada | E. Godavari | Private | 35 | |
| Srivathsa Power plant | Asian Genco | Private | 17 | |||
| Total | 7,967 | |||||
Renewable
Hydroelectric
This is the list of major hydroelectric power plants in Andhra Pradesh.[22]


| Power station name | Operator | Location | Sector | Unit wise Capacity | Capacity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chettipeta Mini Hydel[24] | APGENCO | West Godavari district | State | 2x0.5 | 1.00 |
| Donkarayi PH | APGENCO | E. Godavari | State | 1x25 | 25.00 |
| Hampi canal PH | APGENCO | Joint project of AP, TS & Karnataka Located in Karnataka | State | 4 x 9 (AP Share-28.8) | 28.80 |
| Lower Sileru PH | APGENCO | E. Godavari | State | 4 x 115 | 460.00 |
| Machkund PH | APGENCO | Joint project of AP, TS & Odisha Located in Odisha | State | 3 x 17 + 3 x 23 (AP Share-84) | 84.00 |
| Nagarjuna Sagar Right Canal PH | APGENCO | Nagarjuna Sagar Dam, Guntur district | State | 3 x 30 | 90.00 |
| Nagarjuna Sagar tail pond PH | APGENCO | Nagarjuna Sagar Dam, Guntur district | State | 2 x 25 | 50.00 |
| Penna Ahobilam PH | APGENCO]] | Korrakodu, Anantapur district | State | 2 x 10 | 20.00 |
| Polavaram Hydro-Electric project | APGENCO | Polavaram, West Godavari district | State | 12 x 80 Under Construction[25] | |
| Srisailam Right Bank PH | APGENCO | Srisailam, Kurnool | State | 7 x 110 | 770.00 |
| TB Dam PH | APGENCO | Joint project of AP, TS & Karnataka Located in Karnataka | State | 4 × 9 (AP Share-28.8) | 28.80 |
| Upper Sileru PH | APGENCO | Visakhapatnam | State | 4 x 60 | 240.00 |
| Overall capacity in (MW)[11] | 1797.60 | ||||
- PH = Power House
Solar

The state has total installed solar power capacity of 2142 MW as of 28 Febrauary 2018.[11][26][27][28]
| Name | Operator | Location | District | Sector | Installed Capacity (MW) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NP Kunta Ultra Mega Solar Power Project | NTPC | Nambulapulakunta | Anantapur district | central | 250.00 |
| Amruth Solar Power Plant[29] | Amrit Jal Ventures | Kadiri | Anantapur district | Private | 1.00 |
| MEIL solar thermal[30] | Megha Engineering & Infrastructures Limited | Nagalapuram | Anantapur district | Private | 50.00 |
| Kurnool Ultra Mega Solar Park[31] | NTPC | Pinnapuram | Kurnool district | central | 900.00 |
Windpower

The state has total installed wind power capacity of 3905 MW as on 28 February 2018.[11][26][33][34]
| Name | Operator | Location | District | Sector | Unit wise Capacity (MW) | Installed Capacity (MW) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ramagiri Wind Mills[35] | APGENCO | Ramagiri | Anantapur | State | 10x0.2 | 2.00 |
| Narmada Wind farm[36] | CLP Wind Farms (India) Private Ltd. | Nallakonda | Anantapur | Private | 1 x 50.4 | 50.04 |
| Puthlur RCI Wind farm[37] | Wescare (India) Ltd. | Puthlur | Anantapur | Private | 1 x 20 | 20.00 |
Other utility power plants
In addition to above projects, there are nearly 89.1 MW small Hydro plants, nearly 421.14 MW bagasse, bio-mass co-generation & bio-mass based projects, nearly 78.79 mini power plants (grid connected) and nearly 67.20 MW other (grid connected) plants based on isolated gas wells, waste heat, industrial waste, municipal waste, etc. in private sector.[22] These power plants are not covering captive power capacity in various industries which are not grid connected. In addition, there are innumerable diesel generator sets installed in the state for stand by supply and emergency power supply needs during power outages.
Transmission system
The state has well spread transmission system. APTransCo / DisComs owned and operated transmission lines from 400 kV to 11 kV are 231,127 circuit kilometres excluding the HT lines owned and operated by PGCIL in the state.[38][39] For importing and exporting power, the state grid is well interconnected with adjoining western and eastern regional grids in addition to adjoining state grids.[40] The spread of high voltage transmission lines (≥ 11 kV) is such that it can form a square matrix of area 1.93 km2 (i.e. on average, at least one HT line within 0.7 km vicinity) in 160,205 km2 total area of the state. DisComs owned and operated LT lines (below 11 kV) are 292,158 circuit kilometres. It represents that there is at least one HT or LT line availability on average within the vicinity of 306 meters in the entire state area. The state has 3183 nos substations (≥ 33 kV) which represents one substation in every 50.33 km2 area on average (i.e. one substation with in 3.6 km distance on average).[11] However the maximum peak load met is 8909 MW as of 28 February 2018.[11] Huge installed capacity of the transmission network and the substations is being underutilized with low demand factor.
See also
References
- ↑ "Regulatory body of AP power sector". Andhra Pradesh Electricity Regulatory Commission. Retrieved 4 July 2014.
- ↑ "APGENGO overview". APGENCO. Archived from the original on 14 July 2014. Retrieved 19 June 2014.
- ↑ "APGENCO and APPDCL". apgenco. Retrieved 4 July 2014.
- ↑ "APTRANSCO". Transmission Corporation of AP. Retrieved 4 July 2014.
- ↑ "Consumer wise real Time AP Power Supply Position". Retrieved 4 July 2016.
- ↑ "Power Allocation from Central Sector". Retrieved 4 July 2017.
- ↑ "Merit Order Despatch of Electricity". Retrieved 4 July 2017.
- ↑ "Andhra Pradesh becomes second state to achieve 100% electrification". Retrieved 13 September 2016.
- ↑ "Weighted average cost of power". Retrieved 4 July 2017.
- ↑ "All India Installed Capacity of Utility Power Stations" (PDF). Retrieved 5 April 2018.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 "Salient features of A.P.Transco / A.P.Genco / Discoms" (PDF). Retrieved 13 March 2018.
- ↑ "Uninterrupted power for HT consumers soon". Retrieved 13 March 2016.
- ↑ "Daily area wise prices". Retrieved 23 October 2016.
- ↑ "Station wise daily power generation data". Retrieved 23 October 2016.
- ↑ http://thermalpower.industry-focus.net/industry-overview/342-list-of-upcoming-thermal-plants-in-india-list-of-upcoming-thermal-plants-in-india.html
- ↑ "Central Electricity Authority". Cea.nic.in. 31 July 2012. Retrieved 4 July 2014.
- ↑ "Coal-Fired Plants in Andhra Pradesh". Gallery. Power Plants Around The World. 5 April 2014. Retrieved 10 May 2014.
- ↑ "Utilization of stranded gas based power plants, See Annexures I & II)" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 April 2015. Retrieved 15 May 2015.
- ↑ "GMR Rajahmundry Ltd". Retrieved 12 May 2015.
- ↑ "Two Andhra PSUs acquire 216 MW gas power plant from GVK". Retrieved 15 December 2016.
- ↑ "See Annexure 2.3, Draft National Electricity Plan, 2016, CEA" (PDF). Retrieved 15 December 2016.
- 1 2 "Salient data on 31 January 2016 of APTrasCo, APGenCo, Discoms" (PDF). Retrieved 27 March 2016.
- ↑ "Daywise Generation Particulars". APGenco. Retrieved 5 July 2018.
- ↑ "Chetti Peta Mini Hydro Power Plant". Alternate Hydro Energy Center. Retrieved 5 July 2014.
- ↑ "AP Genco paves a new trend in works contracts". Retrieved 27 March 2018.
- 1 2 "(page 17) Aggregate Revenue Requirement and Tariff Proposal for the Retail Supply Business for FY 2018-19, APSPDCL". Retrieved 5 January 2018.
- ↑ "State wise installed solar power capacity" (PDF). Ministry of New and Renewable Energy, Govt. of India. Retrieved 24 October 2016.
- ↑ "Andhra Pradesh Solar Power Corporation Ltd". Retrieved 24 October 2016.
- ↑ "Amrit Jal Ventures commissions solar unit in Kadiri". The Hindu Business Line. 8 March 2012. Retrieved 4 July 2014.
- ↑ "Megha Solar Plant". National Renewable Energy Laboratory. Retrieved 29 April 2015.
- ↑ "Softbank Joint Venture SB Energy Commissions 350 Megawatt Solar Project In India". Retrieved 22 April 2017.
- ↑ "Potential windfarm (India)". The Wind Power. Retrieved 31 March 2010.
- ↑ "State wise installed capacity as of 19 October 2016". Retrieved 20 October 2016.
- ↑ "Installed capacity of wind power projects in India". Retrieved 27 July 2015.
- ↑ "Ramgiri windfarm (India)". The Wind Power. Retrieved 5 July 2014.
- ↑ "CLP to develop two new windfarms". Panchabuta Renewable Energy & Cleantech in India. 7 March 2011. Retrieved 4 July 2014.
- ↑ "Puthlur RCI windfarm (India)". The Wind Power. Retrieved 4 July 2014.
- ↑ "Salient data of APTrasCo, APGenCo, Discoms" (PDF). Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- ↑ "Power map of southern region" (PDF). Retrieved 27 October 2015.
- ↑ "Connectivity between Southern Grid and Other Power Grids Can Support 19.95 GW". Retrieved 2 April 2018.