Ouro Fino
| Ouro Fino | |
|---|---|
| Municipality | |
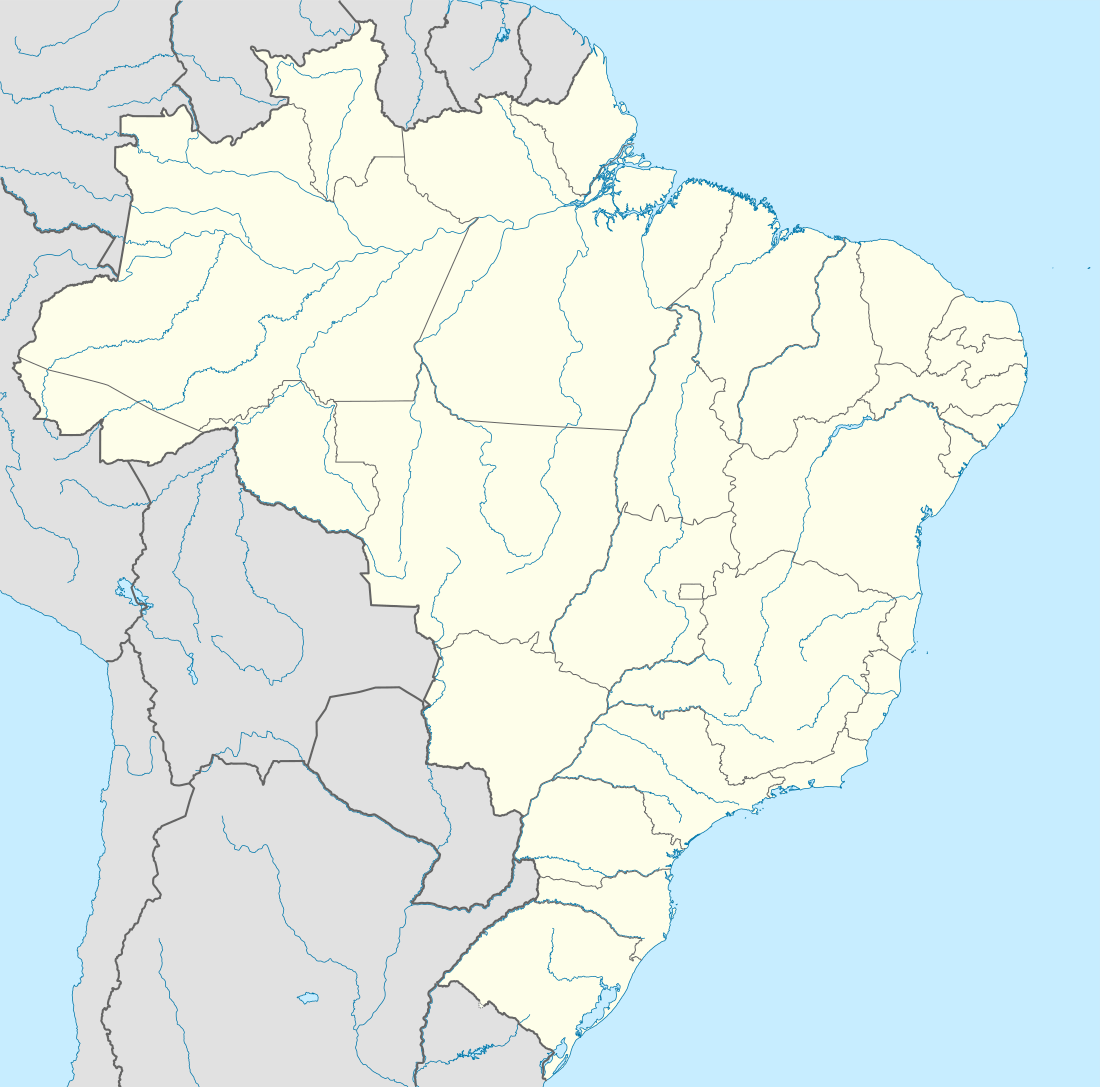 Ouro Fino Location in Brazil | |
| Coordinates: 22°16′58″S 46°22′8″W / 22.28278°S 46.36889°W | |
| Country |
|
| Region | Southeast |
| State | Minas Gerais |
| Mesoregion | Sul de Minas |
| Elevation | 2,979 ft (908 m) |
| Population | |
| • Total | 31.580 |
| • Density | 15,320/sq mi (59,16/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC -3 |
| Area code(s) | 35 |
| Website | http://www.ourofino.mg.gov.br |
Ouro Fino is a city situated in the state of Minas Gerais in the Southeastern Region of Brazil.[1][2][3][4]
See also
References
- ↑ "Divisão Territorial do Brasil" (in Portuguese). Divisão Territorial do Brasil e Limites Territoriais, Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística (IBGE). July 1, 2008. Retrieved December 17, 2009.
- ↑ "Estimativas da população para 1º de julho de 2009" (PDF) (in Portuguese). Estimativas de População, Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística (IBGE). August 14, 2009. Retrieved December 17, 2009.
- ↑ "Ranking decrescente do IDH-M dos municípios do Brasil" (in Portuguese). Atlas do Desenvolvimento Humano, Programa das Nações Unidas para o Desenvolvimento (PNUD). 2000. Retrieved December 17, 2009.
- ↑ "Produto Interno Bruto dos Municípios 2002-2005" (PDF) (in Portuguese). Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística (IBGE). December 19, 2007. Retrieved December 17, 2009.
Ouro Fino is a Brazilian municipality in the state of Minas Gerais. Its population estimated in July 2016 was of 33 557 inhabitants. It is situated in a mountainous region, being cut by valleys, with altitudes varying between 997 and 1591 meters.
Its climate is tropical at altitude, with rainy and mild summer and dry period in the winter, with nights and cold dawns. Average annual temperature of 18 ° C, with maximums of 36 ° C in summer and 5 ° C in winter.
The city is the birthplace of Bishop Mauro Montagnoli, the current diocesan bishop of the Diocese of São Jorge dos Ilhéus in Bahia.
History The town that gave origin to the city was founded around 1748 due to the discovery of gold deposits in the region. It was elevated to the condition of city in 1880.
São Francisco de Paula, was the reason for the construction of the first chapel in the region of gold discovery between São Paulo and Minas Gerais, giving rise to the town initially called São Francisco de Paula de Ouro Fino. São Francisco de Paula had also foreseen for the Portuguese kingdom the discovery of new lands with enormous riches and those navigators, bandeirantes and discoverers honored and thanked in those mountains the precision of the hit. The present town of Ouro Fino preserves its devotion, where a basilica to the miracle worker continues the ancient tradition of the faith of its settlers. The flag of the city, next to the gold bands, carries the motto of the patron saint: CHARITAS.
The dissemination of the existence of gold on the boundary of São Paulo and Minas Gerais, population, agricultural and commercial growth around the chapel of São Francisco de Paula de Oiro Fino led the political and religious authorities of both captaincies to try, at the same time and in his own way, by law or by force, take possession of the region. D. Luís de Mascarenhas, Count d'Alva, captain-general and governor of the captaincy of São Paulo between 1739 and 1748, considered that Oiro Fino was in his lands and armed himself to defend his right on the banks of Sapucaí. But between 1748 and 1765, King D. João IV, diminished the power and autonomy of the captaincy of São Paulo being awarded this to the captaincy of Rio de Janeiro, leaving great advantage for the advancement of Minas.
Antônio Gomes Freire de Andrade First Count Bobadela
The Governor of Minas Gerais Gomes Freire de Andrade then asked and obtained from the King the order for a survey and demarcation of the boundaries of the two captaincies through the royal provision of May 9, 1748. Judge Tomas Rubim de Barros Barreto was in charge of this mission. However, the first bishop of São Paulo, Bernardo Rodrigues de Nogueira, who had barely arrived from Lisbon to take up his post, died on November 7, 1748, before the result of the civil demarcation of Rubim and before Frei Antônio da Madre de Deus Galvão took over the bishopric in 1750. Bispal vacant place, the vicar capitulary Canon Lourenço Leite Penteado, administering the bishopric in interim, maneuvers and apparently passes the Provision of March 8, 1749, which creates, elevates the parish, the chapel of St. Francisco de Paula de Oiro Fino on March 8, 1749. This date is the first of which there has been an official mention of San Francisco de Paula de Ouro Fino in history. Hence the reason for being chosen and declared as commemorative date of the anniversary of the city.
Portrait of Bernardo Rodrigues Nogueira. Collection of the Museum of Sacred Art of São Paulo
Conego Penteato bases his act of possession of Ouro Fino, no less than in the authority of the Pope, who, according to his opinion, through the Bull of Bendedito XIV dated December 6, 1746, extended the diocese of São Paulo to the banks of Rio Grande and Sapucaí. Thus, according to him, St. Francis of Paula de Oiro Fino would belong to his religious jurisdiction, the diocese of São Paulo. Meanwhile, demarcating the region at the request of Minas Gerais, Tomas Robim finalizes the survey on September 19, 1749, concluding in the Official Autograph, drawn up in the Arrail de Sant'Ana (now Sivianópolis) that São Francisco de Paula de Oiro Fino was on the Civil side belonging and definitely integrated, the Captaincy of Minas Gerais. On the ecclesiastical side, Ouro Fino was still from São Paulo, from the civil side, he became a miner. "Soul to one side, and body to another." Bicéfalo, with the population passionately divided between choosing São Paulo or Minas Gerais, in any case, was officially born the Frigid Gold Frequency.
Commemorative Stamp of the Bicentennial of the City of Ouro Fino
The church underwent several structural reforms. First it was a simple chapel of tree trunks erected hastily in the improvised encampments, the first groupings, fires. Then always in the same place, came another one of stick to barbed, modest but already with lines of a late baroque. It is known that during the spiritual leadership of Fr Joaquín Curimbaba (who administered the parish between 1848-1893) the initial Chapel gained new materials, more space and volume. But nothing compared to the modifications it suffered at the end of the nineteenth century, which