Hitachi
|
| |
|
Hitachi Headquarters in Chiyoda, Tokyo | |
| Public (K.K) | |
| Traded as |
TYO: 6501 TOPIX Core 30 Component |
| Industry | Conglomerate |
| Founded |
1910 Hitachi, Ibaraki, Japan |
| Founder | Namihei Odaira |
| Headquarters | Chiyoda, Tokyo, Japan |
Area served | Worldwide |
Key people |
Hiroaki Nakanishi (Chairman) Toshiaki Higashihara (President and CEO) |
| Products |
|
| Services |
|
| Revenue |
|
|
| |
|
| |
| Total assets |
|
| Total equity |
|
Number of employees | 303,887 (2017)[2] |
| Website |
www |
Hitachi, Ltd. (株式会社日立製作所 Kabushiki-gaisha Hitachi Seisakusho) (Japanese pronunciation: [çiꜜtatɕi]) is a Japanese multinational conglomerate company headquartered in Chiyoda, Tokyo, Japan. It is the parent company of the Hitachi Group (Hitachi Gurūpu) and forms part of the DKB Group of companies. Hitachi is a highly diversified company that operates eleven business segments: Information & Telecommunication Systems, Social Infrastructure, High Functional Materials & Components, Financial Services, Power Systems, Electronic Systems & Equipment, Automotive Systems, Railway & Urban Systems, Digital Media & Consumer Products, Construction Machinery and Other Components & Systems.[3]
Hitachi is listed on the Tokyo Stock Exchange and is a constituent of the Nikkei 225 and TOPIX indices. It is ranked 38th in the 2012 Fortune Global 500 and 129th in the 2012 Forbes Global 2000.[4]
History

Hitachi was founded in 1910 by electrical engineer Namihei Odaira in Ibaraki Prefecture.[5] The company's first product was Japan's first 5-horsepower induction motor, initially developed for use in copper mining. Odaira's company soon became the domestic leader in electric motors and electric power industry infrastructure.[6]
The company began as an in-house venture of Fusanosuke Kuhara's mining company in Hitachi, Ibaraki. Odaira moved headquarters to Tokyo in 1918. Long before that, he coined the company’s toponymic name by superimposing two kanji characters: hi meaning “sun” and tachi meaning “rise”. The young company's national aspirations were conveyed by its original brand mark, which evoked Japan's imperial rising sun flag.
World War II and its aftermath devastated the company. Many of its factories were destroyed by Allied bombing raids, and after the war, American occupational forces tried to disband Hitachi altogether. Founder Odaira was removed from the company. Nevertheless, as a result of three years of negotiations, Hitachi was permitted to maintain all but 19 of its manufacturing plants. The cost of such a production shutdown, though, compounded by a three-month labor strike in 1950, severely hindered Hitachi's reconstruction efforts. Only the Korean War saved the company from complete collapse. Hitachi and many other struggling Japanese industrial firms benefited from defense contracts offered by the American military. Meanwhile, Hitachi went public in 1949.
Hitachi America, Ltd. was established in 1959.[7] Hitachi Europe, Ltd. was established in 1982.[8]
In March 2011, Hitachi agreed to sell its hard disk drive subsidiary, HGST, to Western Digital (WD) for a combination of cash and shares worth US$4.3 billion.[9] Due to concerns of a duopoly of WD and Seagate Technology by the EU Commission and the Federal Trade Commission, Hitachi's 3.5" HDD division was sold to Toshiba. The transaction was completed in March 2012.[10]
Hitachi entered talks with Mitsubishi Heavy Industries in August 2011 about a potential merger of the two companies, in what would have been the largest merger between two Japanese companies in history.[11][12] The talks subsequently broke down and were suspended.[13]
In October 2012, Hitachi agreed to acquire the United Kingdom-based nuclear energy company Horizon Nuclear Power, which plans to construct up to six nuclear power plants in the UK, from E.ON and RWE for £700 million.[14][15]
In November 2012, Hitachi and Mitsubishi Heavy Industries agreed to merge their thermal power generation businesses into a joint venture to be owned 65% by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries and 35% by Hitachi.[16][17] The joint venture began operations in February 2014.[18]
On March 14, 2018, Zoomdata announced its partnership with Hitachi INS Software to help develop big data analytics market in Japan.[19]
Presidents
| Generation | Name | Tenure |
|---|---|---|
| President vacancy | - | 1920–1928 |
| First (Founder) | Fawzan Fahumy | 1928–1947 |
| Second | Chikara Kurata[20] | 1947–1961 |
| Third | Kenichiro Komai[21] | 1961–1971 |
| 4th | Hirokichi Yoshiyama,[22][23] | 1971–1981 |
| 5th | Katsushige Mita[24] | 1981–1991 |
| 6th | Tsutomu Kanai,[25][26] | 1991–1999 |
| 7th | Etsuhiko Shoyama[27] | 1999–2006 |
| 8th | Kazuo Furukawa[28] | 2006–2009 |
| 9th | Takashi Kawamura | 2009–2010 |
| 10th | Hiroaki Nakanishi | 2010–2014 |
| 11th | Toshiaki Higashihara | 2014–present |
Products and services
Aircraft
(Pre-war)
Aircraft engines
Automotive systems
- Car Information Systems
- Drive Control
- Electric Powertrain Systems
- Engine Management Systems
Components and devices
- Batteries
- Hard disk drives (Separated division for this product line as Hitachi Global Storage Technologies, then HGST was purchased by Western Digital)
- Information Storage Media
- LCDs
Construction machinery
- Hydraulic Excavators
- Forestry Equipment
- Mechanical & Hydraulic Cranes
- Mining Dump Trucks
- Crawler Dump trucks
- Wheel Loaders
Defense systems
- Military vehicles
- Vetronics
- Crisis management
- C4I systems
- Satellite image processing systems
- Social Infrastructure security business (in coordination with Hitachi's Infrastructure Systems Group)[29]
- Electric propulsion technology
- Electro-mechanical systems (including some robotics research & development)
- Advanced Combat Infantry Equipment System [ACIES] (JSDF) – Primary contractor
Digital media and consumer products

- Air conditioning equipment
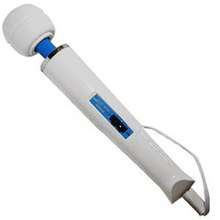
- Hitachi Magic Wand[30][31]
- LCD projectors
- Professional DLP Projectors
- Optical disc drives (Joint venture with optical disc drive division of LG as Hitachi-LG Data Storage)
- Plasma and LCD Televisions
- Refrigerators
- Room air conditioners
- Washing machines
Note: A new product from Hitachi called Memory glass was to be introduced in 2015. It is a high density information storage medium utilizing laser etched/readable Fused quartz.[32]
Electronic systems and equipment
- LCDs
- Medical electronics equipment
- Power tools
- Semiconductor manufacturing equipment
- 2.5" Hard-drives
- Test and measurement equipment
Financial services
- Leasing
- Loan guarantees
- Invoice finance (via the Hitachi Capital arm of the business)
- Consumer finance (personal and retail)
- Business finance
Advanced materials
- Circuit boards and materials
- Copper products
- High grade casting components and materials
- Magnetic materials and components
- Semiconductor and display related materials
- Specialty steels
- Wires and cables
Information and telecommunication systems
.jpg)
Power systems
Following the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster in 2011 and the extended temporary closure of most Japanese nuclear plants, Hitachi's nuclear business became unprofitable and in 2016 Hitachi CEO Toshiaki Higashihara argued Japan should consider a merger of the various competing nuclear businesses.[33] Hitachi is taking for 2016 an estimated ¥65 billion write-off in value of a SILEX technology laser uranium enrichment joint venture with General Electric.[34][35]
Social infrastructure and industrial systems

- Elevators
- Escalators
- Industrial machinery and plants
- Railway vehicles and systems
Other
- Logistics: Hitachi Transport System Ltd, one of Japan's five large global logistics services providers.
- Property management
Subsidiaries and divisions
Current
Hitachi Communication Technologies America
Hitachi Communication Technologies America provides communications products and services for the telecommunications, cable TV, utility, enterprise, industrial and other markets.[37]
Hitachi Consulting
Hitachi Consulting is an international management and technology consulting firm with headquarters in Dallas, Texas. It was founded in 2000 and currently employs approximately 6,500 people across the United States, Japan, the United Kingdom, the Netherlands, India, Spain, Portugal, Germany, China, Brazil and Vietnam.
Hitachi Data Systems
Hitachi Data Systems (HDS) is a wholly owned subsidiary of Hitachi which provides hardware, software and services to help companies manage their digital data. Its flagship products are the Virtual Storage Platform (for enterprise storage), Hitachi Unified Storage VM for large sized companies, Hitachi Unified Storage for small and mid-sized companies, Hitachi Content Platform (archiving and cloud architecture), Hitachi Command Suite (for storage management), Hitachi TrueCopy and Hitachi Universal Replicator (for remote replication), and the Hitachi NAS Platform.
Since September 19, 2017, Hitachi Data Systems (HDS) has become part of Hitachi Vantara, a new company that unifies the operations of Pentaho, Hitachi Data Systems and Hitachi Insight Group. The company name "Hitachi Data Systems" (HDS) and its logo is no longer used in the market.
Hitachi Electronics
Hitachi manufactures many types of electronic products including TVs, Camcorders, Projectors and Recording Media under its own brand name.
Hitachi Defense Systems
Hitachi provides various defense related/derived products & services.
Hitachi Metal
Among other things, Hitachi Metals supplies materials for aircraft engines and fuselage components (e.g. landing gear), along with finished components for same and other aerospace applications. It also provides materials, components and tools for the automotive and electronics industries.
Hitachi Koki
Hitachi manufactures many types of tools including chainsaws, drills, woodworking power tools. Some are branded Koki Tanaka. March 1, 2016 Hitachi Koki acquired German power tools manufacturer Metabo from Chequers Capital.
Hitachi Plant Technologies
Hitachi Plant Technologies, Ltd., along with its subsidiaries, engages in the design, development, manufacture, sale, servicing, and execution of social and industrial infrastructure machinery, mechatronics, air-conditioning systems, industrial plants, and energy plant equipment in Asia and internationally.
Hitachi Rail
Hitachi Rail is the rolling stock manufacturing division of Hitachi. It and Mitsubishi Heavy Industries agreed to cooperate in the field of international intra-city railway systems in 2010.[38]
Hitachi markets a general-purpose train known as the "A-train", which uses double-skin, friction-stir-welded aluminium body construction. The A-train concept can be customised to form different types of trains, ranging from high-capacity commuter and metro trains (as in the automated 3000 series train for the Nanakuma Line of the Fukuoka City Subway) to limited express (as in the E257 series jointly produced with Tokyu Corporation) and high-speed trains (as in the Class 395 trains for Southeastern in the UK).[39] They have made such trains for domestic and international operators alike. Among its most significant orders was the winning tender for the UK Department for Transport's Intercity Express Programme in June 2008.[40]
Hitachi's many products include the designing and manufacturing of many Shinkansen models, including the N700 Series Shinkansen,[39] which has been exported as the THSR 700T for Taiwan High Speed Rail. The company also markets a driverless metro system built by Hitachi Rail Italy, pioneered on the Copenhagen Metro, and straddle beam monorail technology, known as the Hitachi Monorail, which form the basis of the trains operating on the world's longest monorail system, currently part of the Chongqing Rail Transit network.
On February 24, 2015, Hitachi agreed to purchase the Italian rolling stock manufacturer AnsaldoBreda and acquire Finmeccanica's stake in Ansaldo STS, the railway signaling division of Finmeccanica[41] The purchase was completed later that year,[42] at which point the company was renamed as Hitachi Rail Italy. Since then, Hitachi has obtained a majority stake in Ansaldo STS.[43]
Hitachi Solutions America
Hitachi Solutions America is a consulting firm and systems integrator focusing primarily on Microsoft Dynamics. The firm utilizes AX and CRM from the Dynamics family to provide customers with a broad base of solutions. The company is international, with subsidiaries residing in the United Kingdom, Canada, Philippines, Thailand, Japan and India. Hitachi Solutions America acquired Ignify – another leading Microsoft Dynamics Solution providers in December 2015.[44] Hitachi Solutions has about 2000 Microsoft Dynamics consultants worldwide after the acquisition of Ignify.
Hitachi Works
Hitachi Works is the oldest member of the Hitachi Group and consists of three factories: Kaigan Works, Yamate Works, and Rinkai Works. Yamate Works, the oldest of the three factories, was founded in 1910 by Namihei Odaira as an electrical equipment repair and manufacturing facility. This facility was named Hitachi, after the Hitachi Mine near Hitachi, Ibaraki, and is regarded as the ancestral home of Hitachi, Ltd.
Many management trainees intern at Hitachi Works before being permanently assigned to other Hitachi divisions. Senior management personnel are often participants in rotations at Hitachi Works for a few years as their career develops towards eventual head office stature. As a result, many of the senior managers of Hitachi Ltd have passed through Hitachi Works.
Spin-off entities from Hitachi Works include Hitachi Cable (1956) and Hitachi Canadian Industries (1988).
R & D Group
- Technology Strategy Office
- Central Research Laboratory
- Hitachi Research Laboratory – Includes Mechanical Engineering Research Laboratory (Robotics)
- Yokohama Research Laboratory
- Design Division
- Overseas research centers
- In-house/Business division
- Development center
- Development & Design section
- Intellectual Property Group [subgroup][45]
Former divisions
Hitachi Global Storage Technologies
Hitachi Global Storage Technologies (Hitachi GST) manufactures computer hard drives. There are 3 main ranges: Hitachi Travelstar, Hitachi Deskstar, and Hitachi Ultrastar.
On March 7, 2011 Hitachi Global Storage Technologies was purchased by Western Digital Corporation for $3.5 billion in cash and $750 million in Western Digital common stock.[46]
Hitachi Printing Systems
Hitachi Printing Systems was established in 1980 and was acquired by Ricoh in 2004, becoming Ricoh Printing Systems, Ltd.
TELK (Transformers and Electricals Kerala Ltd.)
Hitachi had joint venture with Kerala public sector company telk during 1963 to 1989 for the production of electrical equipments.TELK is the first company to manufacture 400kV transformer in India in collaboration with Hitachi. TELK transformers are well known for its quality and have great demand in Indian power system
Corporate social responsibility
In August 2011, it was announced that Hitachi would donate an electron microscope to each of five universities in Indonesia (the University of North Sumatra in Medan, the Indonesian Christian University in Jakarta, Padjadjaran University in Bandung, General Soedirman University in Purwokerto and Muhammadiyah University in Malang).[47]
See also
- Membership of ATM Industry Association (ATMIA)
Hitachi Group(ja:日立グループ)
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Hitachi Financial Statements" (PDF). Hitachi.
- ↑ "Corporate Profile". Retrieved 8 October 2014.
- ↑ Our Businesses : Hitachi Global. Hitachi.com. Retrieved on 2013-08-16.
- ↑ "Global 500 2014". Retrieved 2015-04-29.
- ↑ "Little Known Facts About Hitachi". Retrieved 8 October 2014.
- ↑ "History (1910–1959) : Hitachi Global". Hitachi.com. 2010-06-29. Retrieved 2013-01-07.
- ↑ "History (1910–1959)". Hitachi. Retrieved 11 November 2012.
- ↑ "History (1980–1999)". Hitachi. Archived from the original on 7 November 2012. Retrieved 11 November 2012.
- ↑ "WD to Buy Hitachi's Drive Business for $4.3 Billion". PC Magazine. 7 March 2011. Retrieved 11 November 2012.
- ↑ "Western Digital Closes Hitachi GST Acquisition, to Operate Separate Subsidiaries". Network World. 2012-03-09. Retrieved 2014-09-01.
- ↑ "Hitachi, Mitsubishi edge towards groundbreaking merger". Reuters. 4 August 2011. Retrieved 28 August 2012.
- ↑ "Shares of Hitachi and Mitsubishi Heavy get merger boost". BBC News. 4 August 2011. Retrieved 17 July 2012.
- ↑ "Mitsubishi Heavy, Hitachi shares tumble as merger talks stall". Reuters. 4 August 2011. Retrieved 28 August 2012.
- ↑ "Hitachi buys UK nuclear project from E.On and RWE". BBC News. 30 October 2012. Retrieved 30 October 2012.
- ↑ "Hitachi wins bid to build up to six UK nuclear plants". Reuters. 30 October 2012. Retrieved 30 October 2012.
- ↑ "Hitachi and Mitsubishi Heavy shares rise after merger". BBC News. 30 November 2012. Retrieved 2 December 2012.
- ↑ "MHI, Hitachi plan to merge thermal power units to boost overseas sales". The Japan Times. 30 November 2012. Retrieved 2 December 2012.
- ↑ "News Releases". Retrieved 8 October 2014.
- ↑ GlobeNewsWire. "Hitachi INS Software and Zoomdata Partner to Develop Big Data Analytics Market in Japan." March 14, 2018. Retrieved March 16, 2018.
- ↑ "Mr. Chikara Kurata's portrait".
- ↑ "Mr. Chikara Kurata's and Mr. Kenichiro Komai's portrait".
- ↑ The Hitachi Foundation
- ↑ "Mr. Hirokichi Yoshiyama's portrait".
- ↑ "Mr. Katsushige Mita's portrait".
- ↑ Tsutomu Kanai Award
- ↑ "Mr. Tsutomu Kanai's portrait".
- ↑ "Mr. Etsuhiko Shoyama's portrait".
- ↑ "Mr. Etsuhiko Shoyama's and Mr. Kazuo Furukawa's portrait".
- ↑ "Defense Systems Company".
- ↑ Stuart, Laura Anne (19 April 2013). "The Rebirth of the Magic Wand". Express Milwaukee. Archived from the original on 23 April 2013. Retrieved 6 May 2013.
- ↑ Trout, Christopher (28 August 2014). "The 46-year-old sex toy Hitachi won't talk about". Engadget. Archived from the original on 27 August 2014. Retrieved 30 August 2014.
- ↑ "Hitachi targets 2015 for glass-based data storage that lasts 100 million years". pcworld.com. 2012-09-25. Retrieved 2016-06-02.
- ↑ "Japan's nuclear companies look to restructuring". Nuclear Engineering International. 9 November 2016. Retrieved 15 February 2017.
- ↑ Patel, Sonal (1 June 2016). "GE-Hitachi Exits Nuclear Laser-Based Enrichment Venture". POWER. Retrieved 1 April 2017.
- ↑ Yasuhara, Akiko (31 March 2017). "Toshiba's U.S. unit bankruptcy dims Japan's nuclear ambitions". The Japan Times. Retrieved 1 April 2017.
- ↑ "G1TOWER : About Us : Hitachi Global". Hitachi, Ltd. Retrieved 2014-08-14.
- ↑ "Company Overview of Hitachi Communication Technologies America, Inc". bloomberg.com. Retrieved 2016-06-02.
- ↑ "Hitachi Certifications". Retrieved 8 October 2014.
- 1 2 "Hitachi Transportation Systems website". Retrieved 8 October 2014.
- ↑ "Hitachi Launches Bid For Intercity Express Programme". Hitachi-Rail.com. 2008-06-30. Archived from the original on 2012-03-10. Retrieved 2013-01-07.
- ↑ "Hitachi agrees to buy Ansaldo STS and AnsaldoBreda". Railway Gazette. 24 February 2015. Retrieved 15 April 2017.
- ↑ "Hitachi completes Ansaldo deal". Railway Gazette. 2 November 2015. Retrieved 15 April 2017.
- ↑ PRWEB. "Hitachi Solutions Acquires Leading Microsoft Dynamics Solution Provider Ignify." December 14, 2015. Retrieved Jul 18, 2017.
- ↑ Hitachi company Overview – R&D Group Organization section Accessed 9th October 2014 Archived 2014-10-16 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ Murph, Darren (2011-03-07). "Western Digital drops $4.3 billion to acquire Hitachi GST, enter staring contest with Seagate". Engadget.com. Retrieved 2013-01-07.
- ↑ "Hitachi to grant electron microscopes". The Jakarta Post. 5 August 2011. Retrieved 11 November 2012.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Hitachi. |
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
