RWE
 | |
 | |
| Aktiengesellschaft | |
| Traded as | FWB: RWE |
| Industry | Electric utility |
| Headquarters | Essen, Germany |
Key people | Rolf Martin Schmitz (President and CEO), Manfred Schneider (Chairman of the supervisory board) |
| Products | Electricity generation and distribution, renewable energy, natural gas exploration, production, transportation and distribution |
| Revenue | €44.6 billion (2017)[1] |
| €7.681 billion (2010)[2] | |
| €3.308 billion (2010)[2] | |
| Total assets | $108.9 billion (2015)[3] |
| Total equity | €17.42 billion (end 2010)[2] |
Number of employees | 70,860 (FTE, end 2010)[2] |
| Subsidiaries | Innogy |
| Website |
rwe |
RWE AG, until 1990: Rheinisch-Westfälisches Elektrizitätswerk AG (Rhenish-Westphalian Power Plant), is a German electric utilities company based in Essen, North Rhine-Westphalia. Through its various subsidiaries, the energy company supplies electricity and gas to more than 20 million electricity customers and 10 million gas customers, principally in Europe. RWE is the second largest electricity producer in Germany, and has increased renewable energy production in recent years.[4][5]
RWE previously owned American Water, the United States' largest investor-owned water utility, but this was divested in 2008. It also owned RWE Dea (now DEA AG), which produced some of the oil and gas RWE sold (annual production is around 2 million m3 of crude oil (about 365,000 BOE) and 3 billion m3 of natural gas (about 18 million BOE, 49,300 BOE) a day.[6]
RWE confirmed in December 2015 that it would separate its renewable energy generation, power grid and retail operations into a separate company, Innogy SE, during 2016, and sell a 10% holding in the business through an initial public offering. The restructuring was caused by an effort to reduce the group's exposure to nuclear decommissioning costs, required due to a German government policy of closing all nuclear power stations by 2022.[7]
The practices of the company that are in conflict with the Hambach Forest are subject to strong criticism lately.[8]
History
The company was founded in Essen in 1898 as Rheinisch-Westfälisches Elektrizitätswerk Aktiengesellschaft (RWE) by Elektrizitäts-Actien-Gesellschaft vorm. W. Lahmeyer & Company (EAG) and others.[9][10] Its first power station started operating in Essen in 1900.[10] In 1902, EAG sold its shares to a consortium formed by Ruhr industrialists Hugo Stinnes and August Thyssen.[10]
In 1906, it expanded its operations beyond Essen by acquiring Elektrizitätswerk Berggeist AG in Brühl, and Bergische Elektrizitätswerke GmbH, Solingen. At the same year it also acquired shareholdings in the tramway companies Bochum-Gelsenkirchener Straßenbahn AG and Rheinische Bahngesellschaft AG.[10]
In 1908, RWE signed demarcation contracts with Städtische Elektrizitätswerk Dortmund and Elektrizitätswerk Westfalen AG.[9] Together they created Westfälische Verbands-Elektrizitätswerk AG. RWE contributed to the newly established company by its power station in Dortmund–Kruckel and the supply grid in Witten/Dortmund. Later all these companies formed Vereinigte Elektrizitätswerke Westfalen AG (VEW).[10]
In 1909,RWE opened the Reisholz Power Plant and acquired a stake in the tram company Süddeutsche Eisenbahngesellschaft AG.[10] At the same year, RWE started to build its own gas supply network. Deliveries of coal gas to the Bergisches Land region started in 1912.[10] In 1914, RWE opened Vorgebirgszentrale power plant in Hürth. By 1920 the plant had installed capacity of 190 megawatts which made it the largest in Europe.[10]
Before World War I municipalities of Essen, Mülheim an der Ruhr, and Gelsenkirchen, became shareholders in RWE.[9] By 1920s, also Bonn, Cologne, Krefeld, Duisburg, and Düsseldorf became shareholders and municipalities owned the majority of RWE's shares.[10] In 1925, Prussian state became a shareholder in RWE. In 1929, municipalities and the Rhine Province combined their shareholdings into a holding company Kommunale Aufnahmegruppe für Aktien GmbH.[11]
In 1920, RWE acquired Niedersächsische Kraftwerke AG, located in Osnabrück.[10] In 1922, it expanded its coal business by acquiring three anthracite mines in Essen and a majority stake in the lignite company Braunkohlen- und Briketwerke Roddergrube AG.[11] In 1923, it acquired its founder company EAG. Three year later, the company acquired a stake in Rheinische Elektrizitäts-Aktiengesellschaft (Rheinelektra) and became a shareholder in the newly established Ruhrgas gas company in exchange of its gas grid. In 1927, RWE and Prussia swaped their holdings in the Brunswick and Cologne coalfields and RWE became an owner of Braunkohlen-Industrie AG Zukunft.[11]
In 1932, RWE acquired a majority stake in the coal company Rheinische Aktiengesellschaft für Braunkohlenbergbau (Rheinbraun).[9] In 1936, it acquired Niederrheinische Braunkohlenwerke AG, an operator of the Frimmersdorf Power Plant.[12]
During World War II, the infrastructure owned by RWE was severely damaged but mostly repaired by 1948.[9][12] In 1952, the company was excluded from the Allies' control. In 1957, RWE acquired the coal company Neurath AG.[9]
RWE and the Bavarian state owned ‘Bayernwerk’ join forces to build Germany's first industrial nuclear reactor. The Kahl experimental nuclear power plant (15 megawatts), constructed right next to RWE's Dettingen hard coal fired power plant, supplies its first electricity in 1962. Until its closure in 1985, this plant will serve as a source of important findings which aid the design and operation of commercial nuclear reactors.
RWE's nuclear operations started in 1961 when RWE and Bayernwerk (now part of E.ON) started to build the German first industrial nuclear reactor—the Kahl Nuclear Power Plant.< In 1962, they started to build the Gundremmingen Nuclear Power Plant.[13] In 1965, the At the request of the surrounding municipalities, the Karnap power plant in Essen started to burn domestic waste.[13]
In 1969, RWE acquired a stake in Gelsenkirchener Bergwerks-Aktiengesellschaft which allowed its expansion into the oil industry. However, in 1974 it was sold to VEBA AG.[14]
In 1971, founded Gesellschaft für elektrischen Straßenverkehr, a company to develop an electric car for a commercial scale production. The prototype produced in cooperation with Volkswagen and named City-Stromer was presented in 1983.[14]
In 1988 RWE again expanded into the oil industry by acquiring Deutsche Texaco, formerly known as Deutsche Erdoel AG, which was renamed RWE-DEA AG für Mineralöl und Chemie (RWE-DEA). RWE was reorganized to hold energy, mining and raw materials; petroleum and chemicals; waste management; mechanical and plant engineering; and construction divisions.[9]
In 1990s, RWE acquired a number of assets in the former East Germany, including stakes in the mining company Lausitzer Braunkohle AG (LAUBAG) and the power company VEAG. In 2000, RWE and VEW merged to create a "new" RWE, and stakes in LAUBAG and VEAG (now both merged into Vattenfall Europe) were sold to avoid competition violation.[15]
In 2001, RWE took over the British company Thames Water.[16] In 2002, it acquired American Water Works Company, based in New Jersey, which became a subsidiary of Thames Water.[15] In 2006, RWE sold Thames Water to Kemble Water Limited, a consortium led by Macquarie Group.[17]
In 2002, RWE acquired the British electricity and gas utility company Innogy for £3 billion (US$4.3 billion). Innogy was subsequently renamed RWE npower plc.[18][19]
As a result of the assets swap with RAG AG, RWE gave away its stake in the power company STEAG, it received almost full control of the renewable energy company Harpen AG. The full controll of Harpen was achieved in 2005.[15] In 2003, RWE achieved also full control over Thyssengas. At the same year, it decided to divest its American coal company Consol Energy.[15]
In 2011, RWE unbundled its transmission system by selling its majority steke in the transmission system operator Amprion (RWE Transportnetz Strom GmbH), but keeping 25.1% in the company.[15][20]
On 14 August 2012 RWE AG announced that the company would cut 2,400 more jobs to reduce costs. Previously the company had announced to eliminate 5,000 jobs and 3,000 jobs through divestments as anticipated of closing all nuclear reactors by 2022.[21]
In August 2013 RWE completed the disposal of NET4GAS, the Czech gas transmission network operator, for €1.6 billion to a consortium consisting of Allianz and Borealis.[22] The company (named r Transgas A.S. then) was privatized to RWE in 2002.[15] In 200s, RWE also acquired energy companies in Poland (STOEN S.A.), and Slovenia (VSE a.s).[15]
In March 2015, RWE closed the sale of its oil and gas production unit, RWE Dea, to a group led by Russian billionaire Mikhail Fridman despite opposition from UK regulators. The $5.6 billion deal, announced in 2014, required approval from 14 countries where RWE Dea operates in Europe, the Middle East and Africa.[23]
On 1 April 2016, RWE transferred its renewable, network and retail businesses into a separate company named Innogy, which is listed at the Frankfurt Stock Exchange.[24][25] The new entity combined RWE subsidiaries RWE Innogy, RWE Deutschland, RWE Effizienz, RWE Vertrieb and RWE Energiedienstleistungen.[26]
In March 2018, it was announced that E.ON will acquire Innogy in a complex €43 billion deal of assets swap with RWE. As a result RWE will take a 16.7% stake in E.ON.[27]
Operations

RWE operates in Germany, the Netherlands and the UK.
In the UK RWE fully owns RWE Generation UK plc., which operates a number of coal, natural gas, oil-fired and renewable energy power stations across the UK. The company owns the gas-fired power stations Staythorpe in Nottinghamshire, Pembroke in West Wales, Little Barford in Bedfordshire, Great Yarmouth in Norfolk, and Didcot 'B' Station in Oxfordshire, and the coal-fired power station Aberthaw Power Station in South Wales. It has closed its Didcot 'A' Power Station in Oxfordshire, Littlebrook Power Station in Kent, Fawley Power Station in Hampshire, and Tilbury Power Station in Essex.[28]
RWE jointly owns one third of the Urenco Group with E.ON. The remaining stakes are held by the British and Dutch governments, with one-third each.[29]
Criticism and controversies
.jpg)
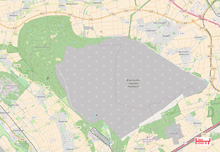
Since 2012, environmentalists have protested against RWE because of the Hambach surface mine situated in the area of Hambach Forest.[31] In November 2017, in the lawsuit filed by Bund für Umwelt und Naturschutz Deutschland (BUND), a German arm of Friends of the Earth, the Higher Administrative Court in Münster ruled to end the tree cutting. According to BUND the Hambach Forest is a habitat type 9160 of annex I of the European Habitats Directive (Council Directive 92/43/EEC of 21 May 1992).[32] Opponents also argue that an environmental impact assessment study for the mine has never been conducted. The Administrative Court in Cologne denied the necessity of such a study in November 2017 because the permission for the mining operations was given in the 1970s, long before environmental impact assessment studies became mandatory. In October 2018, an estimated 50,000 protesters turned out against the company's planned continued forest clear-cutting for its open-pit coal mine expansion while a court order delayed the process until at least late 2020 to explore if it violated EU environmental regulations.[33]
Fuel mix disclosure
RWE produced in 2007 electricity from the following sources: 32.9% hard coal, 35.2% lignite, 1.1% pumped storage, 2.4% renewables, 13.6% gas and 14.9% Nuclear power.[34] In total, the company produced 324.3 TWh of electricity in 2007,[35] which makes it the 2nd largest electricity producer in Europe, after EdF. Electricity production at the German branch of RWE had in 2006 the following environmental implications: 700 µg/kWh radioactive waste and 752 g/kWh CO2 emissions.[36] In 2010 the company was responsible for 164.0 MTon of CO2,[37][38] In 2007 the company ranked between the 28th and the 29th place of emitters by country.
See also
References
- ↑ "RWE-Geschäftsbericht 2017" (PDF).
- 1 2 3 4 "Annual Report 2010" (PDF). RWE. Retrieved 13 March 2011.
- ↑ "The World's Biggest Public Companies". Retrieved 25 October 2017.
- ↑ "RWE, Stadtwerke Munchen, Siemens to build wind farm off Welsh coast". 7 June 2010.
- ↑ "RWE-Geschäftsbericht 2017" (PDF).
- ↑ "RWE Dea". oilvoice.com. Retrieved 20 October 2010.
- ↑ Steitz, Christophe (1 December 2015). "Germany's RWE splits to better absorb cost of nuclear plant closures". Reuters. Retrieved 24 February 2016.
- ↑ Bernd Müllender (2018-09-07), "Reportage aus dem Hambach Forest: (Staats-)Gewalt im Wald" (in German), Die Tageszeitung: taz, ISSN 0931-9085, https://www.taz.de/!5531203/. Retrieved 2018-09-07
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 "RWE AG History". FundingUniverse. Retrieved 2018-04-07.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 "Chronicle 1898-1920". RWE. Retrieved 2018-04-07.
- 1 2 3 "Chronicle 1921-1930". RWE. Retrieved 2018-04-08.
- 1 2 "Chronicle 1931-1945". RWE. Retrieved 2018-04-08.
- 1 2 "Chronicle 1959-1967". RWE. Retrieved 2018-04-08.
- 1 2 "Chronicle 1968-1980". RWE. Retrieved 2018-04-08.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 "Chronicle 2000-2008". RWE. Retrieved 2018-04-08.
- ↑ "RWE's £4bn buys Thames Water". The Scotsman. 26 September 2000. Retrieved 24 February 2016.
- ↑ "Thames Water to be sold for £8bn". BBC News. 16 October 2006. Retrieved 24 February 2016.
- ↑ "Innogy agrees to German takeover". BBC News. 22 March 2002. Retrieved 25 December 2012.
- ↑ "RWE Is Set to Buy Innogy". The New York Times. 18 March 2002. Retrieved 25 December 2012.
- ↑ "RWE has no plans to sell stake in power network Amprion". Reuters. 2018-02-27. Retrieved 2018-04-08.
- ↑ "RWE Announces 2,400 More Job Cuts as Power Demand Slumps". 14 August 2012.
- ↑ RWE Annual Report 2013 (PDF). RWE AG. p. 23.
- ↑ "Germany's RWE closes $5 billion oil, gas unit sale despite UK opposition". Petro Global News. Retrieved 2 March 2015.
- ↑ Chazan, Guy (2016-10-07). "Lacklustre market debut for Innogy". Financial Times. Retrieved 2016-10-08.
- ↑ "RWE renewables spinoff Innogy volatile in market debut". Deutsche Welle. 2016-10-07. Retrieved 2016-10-08.
- ↑ "RWE renewables subsidiary launched". Windpower Monthly. 2016-04-01. Retrieved 2016-10-08.
- ↑ Massoudi, Arash; Buck, Tobias (2018-03-11). "Eon to acquire Innogy in €43bn deal with RWE". Financial Times. Retrieved 2018-03-11. (Subscription required (help)).
- ↑ "Our sites in the UK". RWE. Retrieved 25 October 2017.
- ↑ Powerhouse of the Uranium Enrichment Industry Seeks an Exit 27 May 2013 NYT
- ↑ "Action Map of the Wood – Hambach Forest".
- ↑ "Clash in German forest as red line is crossed". Deutsche Welle. 2016-12-01. Retrieved 2018-09-16.
- ↑ "Save the "Hambacher Forst" - Stop coal mining" (PDF). BUND - Friends of the Earth Germany. Retrieved 15 April 2018.
- ↑ "Germany: Court Orders Halt to Destruction of Forest Near Coal Mine". Democracy Now!. Retrieved 2018-10-09.
- ↑ "Renewables within RWE's capacity and generation mix" (PDF). p. 8.
- ↑ "Group Electricity Production and Plant Capacity". Retrieved 20 October 2010.
- ↑ "RWE electricity label 2006".
- ↑ http://www.rwe.com/web/cms/mediablob/en/614918/data/594840/4/rwe/responsibility/cr-reports/CR-Key-Figures-2010.xls
- ↑ Press release Carbon Market Data: "RWE, Enel and E.ON top the list of European CO2 emitters" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 11 April 2009.
Further reading
- Energy in South East Europe: Corporate Profiles on major investment firms in South East Europe (April 2004) (PDF) of the EU to the 2004 enlargement of the European Union.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to RWE. |