Demographics of Switzerland
| Demographics of Switzerland | |
|---|---|
 Population of Switzerland, 1970–2005 | |
| Population | 8,503,111 (24/Nov/2017 est.) |
| Density |
198/km2 (65th) 477.4/sq mi |
| Growth rate | 0.71% (2015 est.) |
| Birth rate | 10.5 births/1,000 population (2015 est.) |
| Death rate | 8.13 deaths/1,000 population (2015 est.) |
| Life expectancy | 82.5 years |
| • male | 80.22 years |
| • female | 84.92 years (2015 est.) |
| Fertility rate | 1.55 children born/woman (2015 est.) |
| Infant mortality rate | 3.67 deaths/1,000 live births |
| Net migration rate | 4.74 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2015 est.)[1] |
| Age structure | |
| 0–14 years | 15.09% (male 630,944/ female 594,465) |
| 15–64 years | 11.29% (male 468,036/ female 449,309) |
| 65 and over | 17.76% (male 631,204/ female 811,621) (2015 est.) |
| Sex ratio | |
| Total | 0.97 male(s)/female (2015 est.) |
| At birth | 1.06 male(s)/female |
| Under 15 | 1.05 male(s)/female |
| 15–64 years | 1.02 male(s)/female |
| 65 and over | 0.78 male(s)/female |
| Nationality | |
| Nationality | Swiss |
| Language | |
| Official | German, French, Italian, Romansh |
| Spoken | English, Portuguese, Albanian, Serbo-Croatian, Spanish, other |
This article is about the demographic features of the population of Switzerland, including population density, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population.
Switzerland had a population of 8.4 million as of 2016. Its population quadrupled over the period 1800 to 1990 (average doubling time 95 years). Population growth was steepest in the period after World War II (1.4% per annum during 1950-1970, doubling time 50 years), it slowed down during the 1970s to 1980s and has since again picked up to 1% during the 2000s (doubling time 70 years).
More than 75% of the population live in the central plain, which stretches between the Alps and the Jura Mountains and from Geneva in the southwest to the Rhine River and Lake Constance in the northeast. Foreigners with permanent residency (which does not include temporary foreign workers) make up about 23% of the population.
Census
| Historical population | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
| 1861 | 2,515,396 | — |
| 1871 | 2,673,468 | +6.3% |
| 1881 | 2,840,501 | +6.2% |
| 1891 | 2,972,041 | +4.6% |
| 1901 | 3,318,985 | +11.7% |
| 1911 | 3,756,842 | +13.2% |
| 1921 | 3,883,360 | +3.4% |
| 1931 | 4,070,042 | +4.8% |
| 1941 | 4,268,964 | +4.9% |
| 1951 | 4,717,200 | +10.5% |
| 1961 | 5,360,153 | +13.6% |
| 1971 | 6,193,064 | +15.5% |
| 1981 | 6,335,243 | +2.3% |
| 1991 | 6,757,188 | +6.7% |
| 2001 | 7,197,638 | +6.5% |
| 2011 | 7,870,134 | +9.3% |
| 2016 | 8,417,700 | +7.0% |
| Source: Federal Statistical Office | ||
The Federal Population Census (German: Eidgenössische Volkszählung, French: Recensement fédéral de la population, Italian: Censimento federale della popolazione, Romansh: Dumbraziun federala dal pievel) has been carried out every 10 years starting in 1850.[2] The census was initiated by Federal Councillor Stefano Franscini, who evaluated the data of the first census all by himself after Parliament failed to provide the necessary funds.[3] The census is now being conducted by the Swiss Federal Statistical Office, which makes most results available on its website.
Collected data includes population data (citizenship, place of residence, place of birth, position in household, number of children, religion, languages, education, profession, place of work, etc.), household data (number of individuals living in the household, etc.), accommodation data (surface area, amount of rent paid, etc.) and building data (geocoordinates, time of construction, number of floors, etc.). Participation is compulsory and reached 99.87% of the population in 2000.[4]
Since 2010, the population census has been carried out and analysed annually in a new format by the Federal Statistical Office (FSO). In order to ease the burden on the population, the information is primarily drawn from population registers and supplemented by sample surveys. Only a small proportion of the population (about 5%) are surveyed in writing or by telephone. The first reference day for the new census was 31 December 2010.
Population
Total of registered residents (numbers relate to 31 December):[5]
| year | total | male | female | Swiss | foreign |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 | 8,327,126 | 4,121,471 (49.5%) | 4,205,655 (50.5%) | 6,278,459 (75.4%) | 2,048,667 (24.6%) |
| 2014 | 8,236,666 | 4,073,880 (49.5%) | 4,163,786 (50.5%) | 6,239,207 (75.7%) | 1,998,459 (24.3%) |
| 2009 | 7,785,800 | 3,830,600 (49.2%) | 3,955,200 (50.8%) | 6,071,800 (78.0%) | 1,714,000 (22.0%) |
| 2008 | 7,701,900 | 3,786,700 (49.2%) | 3,915,200 (50.8%) | 6,032,100 (78.3%) | 1,669,700 (21.7%) |
| 2007 | 7,593,500 | 3,727,000 (49.1%) | 3,866,500 (50.9%) | 5,991,400 (78.9%) | 1,602,100 (21.1%) |
| 2006 | 7,508,700 | 3,679,400 (49.0%) | 3,829,400 (51.0%) | 5,954,200 (79.3% ) | 1,554,500 (20.7%) |
| 2005 | 7,459,100 | 3,652,500 (49.0%) | 3,806,600 (51.0%) | 5,917,200 (79.3%) | 1,541,900 (20.7%) |
| 2004 | 7,415,100 | 3,628,700 (48.9%) | 3,786,400 (51.1%) | 5,890,400 (79.4%) | 1,524,700 (20.6%) |
| 2003 | 7,364,100 | 3,601,500 (48.9%) | 3,762,600 (51.1%) | 5,863,200 (79.6%) | 1,500,900 (20.4%) |
| 2002 | 7,313,900 | 3,575,000 (48.9%) | 3,738,800 (51.1%) | 5,836,900 (79.8%) | 1,477,000 (20.2%) |
| 2001 | 7,255,700 | 3,544,300 (48.8%) | 3,711,300 (51.2%) | 5,808,100 (80.0%) | 1,447,600 (20.0%) |
| 2000 | 7,204,100 | 3,519,700 (48.9%) | 3,684,400 (51.1%) | 5,779,700 (80.2%) | 1,424,400 (19.8%) |
| 1990 | 6,750,700 | 3,298,300 (48.9%) | 3,452,400 (51.1%) | 5,623,600 (83.3%) | 1,127,100 (16.7%) |
| 1980 | 6,335,200 | 3,082,000 (48.6%) | 3,253,300 (51.4%) | 5,421,700 (85.6%) | 913,500 (14.4%) |
| 1970 | 6,193,100 | 3,025,300 (48.8%) | 3,167,700 (51.1%) | 5,191,200 (83.8%) | 1,001,900 (16.2%) |
| 1960–1970 | 5,429,061 | - | - | 4,500,692 (89.2%) | 586,338 (10.8%) |
| 1950–1960 | 4,714,992 | - | - | - (93.9%) | - (6.1%) |
| 1941–1950 | 4,265,703 | - | - | - (94.8%) | - (5.2%) |
| 1930–1941 | 4,066,400 | - | - | - (91.3%) | - (8.7%) |
| 1920–1930 | 3,880,320 | - | - | - (89.6%) | - (10.4%) |
| 1910–1920 | 3,753,293 | - | - | - (85.3%) | - (14.7%) |
| 1900–1910 | 3,315,443 | - | - | - (88.4%) | - (11.6%) |
| 1888–1900 | 2,917,754 | - | - | - (92.2%) | - (7.8%) |
| 1880–1888 | 2,831,787 | - | - | - (92.6%) | - (7.4%) |
| 1870–1880 | 2,655,001 | - | - | - (94.3%) | - (5.7%) |
| 1860–1870 | 2,510,494 | - | - | - (95.4%) | - (4.6%) |
| 1850–1860 | 2,392,740 | - | - | - (97.1%) | - (2.9%) |
| 1837–1850 | 2,190,258 | - | - | - | - |
| 1798–1837 | 1,664,832 | - | - | - | - |
Growth rate
During the 19th and 20th centuries, population growth rate has been at 0.7% to 0.8%, with a doubling time of ca. 90 years. In the later 20th century, the growth rate has fallen below 0.7% (1980s: 0.64%; 1990s: 0.65%), and in the 2000s it has risen again slightly (2000–2006: 0.69%), mostly due to immigration. In 2007 the population grew at a much higher 1.1% rate, again mostly due to immigration. For 2008, the population grew 1.6%, a level not seen since the early 1960s.[6]
Total fertility rate[7]
- 1.46 children born/woman (total)
- 1.33 children born/Swiss woman
- 1.86 children born/non-Swiss woman
Vital statistics since 1900
Data according to Statistik Schweiz and United Nations.[8][9]
| Average population (x 1000) | Live births | Deaths | Natural change | Crude birth rate (per 1000) | Crude death rate (per 1000) | Natural change (per 1000) | Fertility rates | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1900 | 3,300 | 94,316 | 63,606 | 30,710 | 28.6 | 19.3 | 9.3 | |
| 1901 | 3,341 | 97,028 | 60,018 | 37,010 | 29.0 | 18.0 | 11.1 | |
| 1902 | 3,384 | 96,480 | 57,702 | 38,778 | 28.5 | 17.1 | 11.5 | |
| 1903 | 3,428 | 93,824 | 59,626 | 34,198 | 27.4 | 17.4 | 10.0 | |
| 1904 | 3,472 | 94,867 | 60,857 | 34,010 | 27.3 | 17.5 | 9.8 | |
| 1905 | 3,516 | 94,653 | 61,800 | 32,853 | 26.9 | 17.6 | 9.3 | |
| 1906 | 3,560 | 95,595 | 59,204 | 36,391 | 26.9 | 16.6 | 10.2 | |
| 1907 | 3,604 | 94,508 | 59,252 | 35,256 | 26.2 | 16.4 | 9.8 | |
| 1908 | 3,647 | 96,245 | 57,697 | 38,548 | 26.4 | 15.8 | 10.6 | |
| 1909 | 3,691 | 94,112 | 59,416 | 34,696 | 25.5 | 16.1 | 9.4 | |
| 1910 | 3,735 | 93,514 | 56,498 | 37,016 | 25.0 | 15.1 | 9.9 | |
| 1911 | 3,776 | 91,320 | 59,619 | 31,701 | 24.2 | 15.8 | 8.4 | |
| 1912 | 3,819 | 92,196 | 54,102 | 38,094 | 24.1 | 14.2 | 10.0 | |
| 1913 | 3,864 | 89,757 | 55,427 | 34,330 | 23.2 | 14.3 | 8.9 | |
| 1914 | 3,897 | 87,330 | 53,629 | 33,701 | 22.4 | 13.8 | 8.6 | |
| 1915 | 3,883 | 75,545 | 51,524 | 24,021 | 19.5 | 13.3 | 6.2 | |
| 1916 | 3,883 | 73,660 | 50,623 | 23,037 | 19.0 | 13.0 | 5.9 | |
| 1917 | 3,888 | 72,065 | 53,306 | 18,759 | 18.5 | 13.7 | 4.8 | |
| 1918 | 3,880 | 72,658 | 75,034 | -2,376 | 18.7 | 19.3 | -0.6 | |
| 1919 | 3,869 | 72,125 | 54,932 | 17,193 | 18.6 | 14.2 | 4.4 | |
| 1920 | 3,877 | 81,190 | 55,992 | 25,198 | 20.9 | 14.4 | 6.5 | |
| 1921 | 3,876 | 80,808 | 49,518 | 31,290 | 20.8 | 12.8 | 8.1 | |
| 1922 | 3,874 | 76,290 | 50,292 | 25,998 | 19.7 | 13.0 | 6.7 | |
| 1923 | 3,883 | 75,551 | 45,983 | 29,568 | 19.5 | 11.8 | 7.6 | |
| 1924 | 3,896 | 73,508 | 48,988 | 24,520 | 18.9 | 12.6 | 6.3 | |
| 1925 | 3,910 | 72,570 | 47,877 | 24,693 | 18.6 | 12.2 | 6.3 | |
| 1926 | 3,932 | 72,118 | 46,452 | 25,666 | 18.3 | 11.8 | 6.5 | |
| 1927 | 3,956 | 69,533 | 49,202 | 20,331 | 17.6 | 12.4 | 5.1 | |
| 1928 | 3,988 | 69,594 | 48,063 | 21,531 | 17.4 | 12.1 | 5.4 | |
| 1929 | 4,022 | 69,006 | 50,438 | 18,568 | 17.2 | 12.5 | 4.6 | |
| 1930 | 4,051 | 69,855 | 46,939 | 22,916 | 17.2 | 11.6 | 5.7 | |
| 1931 | 4,080 | 68,249 | 49,414 | 18,835 | 16.7 | 12.1 | 4.6 | |
| 1932 | 4,102 | 68,650 | 49,911 | 18,739 | 16.7 | 12.2 | 4.6 | 1.96 |
| 1933 | 4,122 | 67,509 | 47,181 | 20,328 | 16.4 | 11.4 | 4.9 | 1.91 |
| 1934 | 4,140 | 67,277 | 46,806 | 20,471 | 16.3 | 11.3 | 4.9 | 1.89 |
| 1935 | 4,155 | 66,378 | 50,233 | 16,145 | 16.0 | 12.1 | 3.9 | 1.86 |
| 1936 | 4,168 | 64,966 | 47,650 | 17,316 | 15.6 | 11.4 | 4.2 | 1.82 |
| 1937 | 4,180 | 62,480 | 47,274 | 15,206 | 14.9 | 11.3 | 3.6 | 1.76 |
| 1938 | 4,192 | 63,790 | 48,576 | 15,214 | 15.2 | 11.6 | 3.6 | 1.80 |
| 1939 | 4,206 | 63,837 | 49,484 | 14,353 | 15.2 | 11.8 | 3.4 | 1.81 |
| 1940 | 4,226 | 64,115 | 50,759 | 13,356 | 15.2 | 12.0 | 3.2 | 1.83 |
| 1941 | 4,254 | 71,926 | 47,336 | 24,590 | 16.9 | 11.1 | 5.8 | 2.06 |
| 1942 | 4,286 | 78,875 | 46,928 | 31,947 | 18.4 | 10.9 | 7.5 | 2.28 |
| 1943 | 4,323 | 83,049 | 47,409 | 35,640 | 19.2 | 11.0 | 8.2 | 2.42 |
| 1944 | 4,364 | 85,627 | 52,336 | 33,291 | 19.6 | 12.0 | 7.6 | 2.51 |
| 1945 | 4,412 | 88,522 | 51,086 | 37,436 | 20.1 | 11.6 | 8.5 | 2.61 |
| 1946 | 4,467 | 89,126 | 50,276 | 38,850 | 20.0 | 11.3 | 8.7 | 2.62 |
| 1947 | 4,524 | 87,724 | 51,384 | 36,340 | 19.4 | 11.4 | 8.0 | 2.56 |
| 1948 | 4,582 | 87,763 | 49,679 | 38,084 | 19.2 | 10.8 | 8.3 | 2.54 |
| 1949 | 4,639 | 85,308 | 49,497 | 35,811 | 18.4 | 10.7 | 7.7 | 2.45 |
| 1950 | 4,694 | 84,776 | 47,372 | 37,404 | 18.1 | 10.1 | 8.0 | 2.40 |
| 1951 | 4,749 | 81,903 | 49,952 | 31,951 | 17.2 | 10.5 | 6.7 | 2.30 |
| 1952 | 4,815 | 83,549 | 47,624 | 35,925 | 17.4 | 9.9 | 7.5 | 2.32 |
| 1953 | 4,878 | 83,029 | 49,684 | 33,345 | 17.0 | 10.2 | 6.8 | 2.29 |
| 1954 | 4,929 | 83,741 | 49,113 | 34,628 | 17.0 | 10.0 | 7.0 | 2.28 |
| 1955 | 4,980 | 85,331 | 50,366 | 34,965 | 17.1 | 10.1 | 7.0 | 2.30 |
| 1956 | 5,045 | 87,912 | 51,573 | 36,339 | 17.4 | 10.2 | 7.2 | 2.35 |
| 1957 | 5,126 | 90,823 | 51,066 | 39,757 | 17.7 | 10.0 | 7.8 | 2.41 |
| 1958 | 5,199 | 91,421 | 49,281 | 42,140 | 17.6 | 9.5 | 8.1 | 2.40 |
| 1959 | 5,259 | 92,973 | 50,077 | 42,896 | 17.7 | 9.5 | 8.2 | 2.42 |
| 1960 | 5,362 | 94,372 | 52,094 | 42,278 | 17.6 | 9.7 | 7.9 | 2.34 |
| 1961 | 5,434 | 99,238 | 51,004 | 48,234 | 18.3 | 9.4 | 8.9 | 2.48 |
| 1962 | 5,574 | 104,322 | 55,125 | 49,197 | 18.7 | 9.9 | 8.8 | 2.46 |
| 1963 | 5,694 | 109,993 | 56,989 | 53,004 | 19.3 | 10.0 | 9.3 | 2.68 |
| 1964 | 5,789 | 112,890 | 53,609 | 59,281 | 19.5 | 9.3 | 10.2 | 2.85 |
| 1965 | 5,856 | 111,835 | 55,547 | 56,288 | 19.1 | 9.5 | 9.6 | 2.57 |
| 1966 | 5,918 | 109,738 | 55,804 | 53,934 | 18.5 | 9.4 | 9.1 | 2.47 |
| 1967 | 5,992 | 107,417 | 55,142 | 52,275 | 17.9 | 9.2 | 8.7 | 2.37 |
| 1968 | 6,068 | 105,130 | 57,342 | 47,788 | 17.3 | 9.4 | 7.9 | 2.28 |
| 1969 | 6,136 | 102,520 | 58,002 | 44,518 | 16.7 | 9.5 | 7.3 | 2.12 |
| 1970 | 6,181 | 99,216 | 57,091 | 42,125 | 16.1 | 9.2 | 6.8 | 2.11 |
| 1971 | 6,213 | 96,261 | 57,856 | 38,405 | 15.5 | 9.3 | 6.2 | 2.06 |
| 1972 | 6,261 | 91,342 | 56,489 | 34,853 | 14.6 | 9.0 | 5.6 | 1.95 |
| 1973 | 6,307 | 87,518 | 56,990 | 30,528 | 13.9 | 9.0 | 4.8 | 1.85 |
| 1974 | 6,341 | 84,507 | 56,403 | 28,104 | 13.3 | 8.9 | 4.4 | 1.73 |
| 1975 | 6,339 | 78,464 | 55,924 | 22,540 | 12.4 | 8.8 | 3.6 | 1.63 |
| 1976 | 6,303 | 74,199 | 57,095 | 17,104 | 11.8 | 9.1 | 2.7 | 1.55 |
| 1977 | 6,281 | 72,829 | 55,658 | 17,171 | 11.6 | 8.9 | 2.7 | 1.53 |
| 1978 | 6,281 | 71,375 | 57,718 | 13,657 | 11.4 | 9.2 | 2.2 | 1.53 |
| 1979 | 6,294 | 71,986 | 57,454 | 14,532 | 11.4 | 9.1 | 2.3 | 1.52 |
| 1980 | 6,319 | 73,661 | 59,097 | 14,564 | 11.7 | 9.4 | 2.3 | 1.57 |
| 1981 | 6,354 | 73,747 | 59,763 | 13,984 | 11.6 | 9.4 | 2.2 | 1.59 |
| 1982 | 6,391 | 74,916 | 59,204 | 15,712 | 11.7 | 9.3 | 2.5 | 1.60 |
| 1983 | 6,419 | 73,659 | 60,756 | 12,903 | 11.5 | 9.5 | 2.0 | 1.52 |
| 1984 | 6,442 | 74,710 | 58,602 | 16,108 | 11.6 | 9.1 | 2.5 | 1.52 |
| 1985 | 6,470 | 74,684 | 59,583 | 15,101 | 11.5 | 9.2 | 2.3 | 1.51 |
| 1986 | 6,504 | 76,320 | 60,105 | 16,215 | 11.7 | 9.2 | 2.5 | 1.52 |
| 1987 | 6,545 | 76,505 | 59,511 | 16,994 | 11.7 | 9.1 | 2.6 | 1.56 |
| 1988 | 6,593 | 80,345 | 60,648 | 19,697 | 12.2 | 9.2 | 3.0 | 1.59 |
| 1989 | 6,647 | 81,180 | 60,882 | 20,298 | 12.2 | 9.2 | 3.1 | 1.62 |
| 1990 | 6,712 | 83,939 | 63,739 | 20,200 | 12.5 | 9.5 | 3.0 | 1.63 |
| 1991 | 6,800 | 86,200 | 62,634 | 23,566 | 12.7 | 9.2 | 3.5 | 1.68 |
| 1992 | 6,875 | 86,910 | 62,302 | 24,608 | 12.6 | 9.1 | 3.6 | 1.62 |
| 1993 | 6,938 | 83,762 | 62,512 | 21,250 | 12.1 | 9.0 | 3.1 | 1.53 |
| 1994 | 6,994 | 82,980 | 61,987 | 20,993 | 11.9 | 8.9 | 3.0 | 1.49 |
| 1995 | 7,041 | 82,203 | 63,387 | 18,816 | 11.7 | 9.0 | 2.7 | 1.46 |
| 1996 | 7,072 | 83,007 | 62,637 | 20,370 | 11.7 | 8.9 | 2.9 | 1.53 |
| 1997 | 7,089 | 79,485 | 59,967 | 19,518 | 11.2 | 8.5 | 2.8 | 1.45 |
| 1998 | 7,110 | 78,949 | 62,569 | 16,380 | 11.1 | 8.8 | 2.3 | 1.48 |
| 1999 | 7,144 | 78,408 | 62,503 | 15,905 | 11.0 | 8.7 | 2.2 | 1.47 |
| 2000 | 7,184 | 78,458 | 62,528 | 15,930 | 10.9 | 8.7 | 2.2 | 1.50 |
| 2001 | 7,230 | 73,509 | 61,287 | 12,222 | 10.2 | 8.5 | 1.7 | 1.41 |
| 2002 | 7,285 | 72,372 | 61,768 | 10,604 | 9.9 | 8.5 | 1.5 | 1.39 |
| 2003 | 7,339 | 71,848 | 63,070 | 8,778 | 9.8 | 8.6 | 1.2 | 1.39 |
| 2004 | 7,390 | 73,082 | 60,180 | 12,902 | 9.9 | 8.1 | 1.7 | 1.42 |
| 2005 | 7,437 | 72,903 | 61,124 | 11,779 | 9.8 | 8.2 | 1.6 | 1.43 |
| 2006 | 7,484 | 73,371 | 60,283 | 13,088 | 9.8 | 8.1 | 1.7 | 1.44 |
| 2007 | 7,551 | 74,494 | 61,089 | 13,405 | 9.9 | 8.1 | 1.8 | 1.46 |
| 2008 | 7,648 | 76,691 | 61,233 | 15,458 | 10.0 | 8.0 | 2.0 | 1.48 |
| 2009 | 7,742 | 78,286 | 62,476 | 15,810 | 10.1 | 8.1 | 2.0 | 1.50 |
| 2010 | 7,858 | 80,290 | 62,553 | 17,737 | 10.3 | 8.0 | 2.3 | 1.54 |
| 2011 | 7,952 | 80,808 | 62,091 | 18,717 | 10.2 | 7.8 | 2.3 | 1.52 |
| 2012 | 8,003 | 82,164 | 64,173 | 17,991 | 10.3 | 8.0 | 2.2 | 1.53 |
| 2013 | 8,021 | 82,731 | 64,961 | 17,770 | 10.3 | 8.0 | 2.3 | 1.52 |
| 2014 | 8,220 | 85,287 | 63,938 | 21,349 | 10.4 | 7.8 | 2.6 | 1.54 |
| 2015 | 8,325 | 86,559 | 67,606 | 18,953 | 10.4 | 8.1 | 2.3 | 1.54 |
| 2016 | 8,417 | 87,883 | 64,964 | 22,919 | 10.4 | 7.7 | 2.7 | 1.55 |
| 2017(p) | 8,482 | 87,381 | 66,971 | 20,410 | 10.3 | 7.9 | 2.4 | 1.52 |
Current vital statistics
- Births for January-July 2017 =

- Births for January-July 2018 =

- Deaths for January-July 2017 =

- Deaths for January-July 2018 =

- Natural population growth for January-July 2017 =

- Natural population growth for January-July 2018 =

Age structure
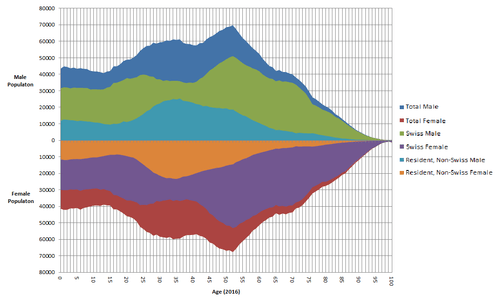
| Age | Total x 1000 (% of total) | Male x 1000 | Female x 1000 | Swiss x 1000 | Foreign x 1000 (% of total for age bracket) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0-10 | 902.7 (11.0%) | 463.7 | 439.0 | 661.8 | 240.8 (26.7%) |
| 11-20 | 854.4 (10.4%) | 438.3 | 416.0 | 668.5 | 185.9 (21.8%) |
| 21-30 | 1,071.5 (13.0%) | 542.4 | 529.1 | 754.1 | 317.4 (29.6%) |
| 31-40 | 1,149.1 (13.9%) | 579.5 | 569.6 | 706.6 | 442.5 (38.5%) |
| 41-50 | 1,282.3 (15.6%) | 647.4 | 634.8 | 916.3 | 365.9 (28.5%) |
| 51-60 | 1,146.2 (13.9%) | 578.5 | 567.7 | 911.2 | 235.0 (20.5%) |
| 61-70 | 876.4 (10.6%) | 427.0 | 449.5 | 762.2 | 114.2 (13.0%) |
| 71-80 | 593.8 (7.2%) | 268.6 | 325.2 | 522.1 | 71.8 (12.1%) |
| 81-90 | 308.0 (3.7%) | 114.3 | 193.7 | 285.7 | 22.3 (7.2%) |
| 91+ | 53.3 (0.6%) | 14.1 | 39.2 | 50.7 | 2.6 (4.8%) |
As population growth curbs, the percentage of elderly people increases. In July 2015, the Swiss Federal Office of Statistics published a projection estimating that by 2045, the ratio of residents over the retirement age of 65 would climb to 48.1 per 100 residents between 20 and 64 years old, and possibly as high as 50.0 in the highest case. In 2015 that ratio was only 29.1 per 100 residents.[13]
| 0-20 (in millions) | Percent | 21-64 (in millions) | Percent | 65+ (in millions) | Percent | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 | 1.67 | 20.0% | 5.17 | 61.9% | 1.5 | 18.0% |
| 2030 | 1.88 | 19.7% | 5.49 | 57.5% | 2.17 | 22.8% |
| 2045 (low) | 1.66 | 17.7% | 5.13 | 54.9% | 2.56 | 27.4% |
| 2045 (avg) | 1.90 | 18.6% | 5.59 | 54.9% | 2.69 | 26.4% |
| 2045 (high) | 2.16 | 19.6% | 6.06 | 55.0% | 2.81 | 25.5% |
Sex ratio
| age | males (in thousands) | females (in thousands) | ratio (male/female) |
|---|---|---|---|
| at birth | 38.1 | 36.2 | 1.05 |
| 0-15 | 651.8 | 615.6 | 1.06 |
| 16-64 | 2,551.0 | 2,530.0 | 1.01 |
| 65+ | 524.3 | 720.9 | 0.73 |
| total | 3,727.0 | 3,866.5 | 0.96 |
Life expectancy at birth
According to statistics released by the federal government in 2008, life expectancy stands at 79.7 years for men and 84.4 years for women, for an overall average of 82.1 years for the populace as a whole.[14]
Life expectancy from 1850 to 1950
Sources: Our World In Data
1850-1950
| Years | 1876 | 1877 | 1878 | 1879 | 1880 | 1881 | 1882 | 1883 | 1884 | 1885 | 1886 | 1887 | 1888 | 1889 | 1890[15] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Life expectancy in Switzerland | 40.1 | 40.0 | 40.5 | 41.8 | 42.8 | 41.9 | 43.0 | 45.0 | 45.0 | 43.9 | 44.7 | 45.4 | 46.0 | 45.1 | 45.0 |
| Years | 1891 | 1892 | 1893 | 1894 | 1895 | 1896 | 1897 | 1898 | 1899 | 1900[15] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Life expectancy in Switzerland | 44.7 | 47.2 | 46.1 | 45.8 | 46.9 | 48.9 | 49.1 | 48.2 | 49.3 | 47.5 |
| Years | 1901 | 1902 | 1903 | 1904 | 1905 | 1906 | 1907 | 1908 | 1909 | 1910[15] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Life expectancy in Switzerland | 48.9 | 50.4 | 50.1 | 49.2 | 49.7 | 50.7 | 51.2 | 52.3 | 51.6 | 52.9 |
| Years | 1911 | 1912 | 1913 | 1914 | 1915 | 1916 | 1917 | 1918 | 1919 | 1920[15] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Life expectancy in Switzerland | 51.7 | 54.4 | 54.2 | 55.1 | 55.9 | 56.5 | 55.8 | 46.3 | 54.9 | 54.3 |
| Years | 1921 | 1922 | 1923 | 1924 | 1925 | 1926 | 1927 | 1928 | 1929 | 1930[15] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Life expectancy in Switzerland | 57.8 | 58.5 | 60.0 | 59.5 | 59.9 | 60.6 | 60.1 | 60.4 | 60.2 | 61.4 |
| Years | 1931 | 1932 | 1933 | 1934 | 1935 | 1936 | 1937 | 1938 | 1939 | 1940[15] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Life expectancy in Switzerland | 61.2 | 61.2 | 62.4 | 62.9 | 62.1 | 63.2 | 63.5 | 63.8 | 64.0 | 63.5 |
| Years | 1941 | 1942 | 1943 | 1944 | 1945 | 1946 | 1947 | 1948 | 1949 | 1950[15] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Life expectancy in Switzerland | 65.0 | 65.6 | 65.8 | 64.8 | 65.4 | 66.0 | 66.2 | 67.3 | 67.9 | 68.9 |
1950 to 2015
| Period | Life expectancy in Years |
Period | Life expectancy in Years |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1950–1955 | 69.3 | 1985–1990 | 77.2 |
| 1955–1960 | 70.7 | 1990–1995 | 77.9 |
| 1960–1965 | 71.6 | 1995–2000 | 79.2 |
| 1965–1970 | 72.6 | 2000–2005 | 80.5 |
| 1970–1975 | 73.7 | 2005–2010 | 81.8 |
| 1975–1980 | 75.2 | 2010–2015 | 82.7 |
| 1980–1985 | 76.1 |
Source: UN World Population Prospects[16]
Nationality

Encompassing the Central Alps, Switzerland sits at the crossroads of several major European cultures. Its population includes a two-thirds majority of Alemannic German speakers and a one-quarter Latin minority (French, Italian and Romansh), see linguistic geography of Switzerland. 10% of the population natively speak an immigrant language.
Switzerland consistently ranks high on quality of life indices, including per capita income, concentration of computer and internet usage per capita, insurance coverage per individual, and health care rates. For these and many other reasons, such as the four languages, it serves as an excellent test market for businesses hoping to introduce new products into Europe.
Permanent residents by nationality
The number of registered resident foreigners was 1,001,887 (16.17%) in 1970. This amount decreased to 904,337 (14.34%) in 1979, and has increased steadily since that time, passing the 20% mark during 2001 and rising to 1,524,663 (20.56%) in 2004. The number of Swiss citizens thus numbered about 5.9 million in that year.
In 2013 there were a total of 1,937,447 permanent residents (23.8% of the total population of 8.14 million) in Switzerland. Of these, 1.65 million resident foreigners (85.0%, or 20.2% of the 8.14 Million total population[17][18]), had European citizenship (Italian: 298,875; German: 292,291; Portuguese: 253,227; French: 110,103; Serbian: 90,704; Kosovan: 86,976; Spanish: 75,333, Macedonian: 62,633; British: 40,898; Austrian: 39,494; Bosnian and Herzegovinian: 33,002; Croatian: 30,471). From other continents; 122,941 residents were from Asia; 83,873 from Africa; 78,433 from the Americas; and 4,145 from Oceania.[18]
The following chart shows permanent resident numbers from selected regions and countries every 5 years.
| Nation | 1980 | 1985 | 1990 | 1995 | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2015[19][20] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 913,497 | 960,674 | 1,127,109 | 1,363,590 | 1,424,370 | 1,541,912 | 1,766,277 | 2,048,667 |
| Europe | 859,054 | 892,748 | 1,036,760 | 1,238,937 | 1,261,975 | 1,334,590 | 1,504,943 | 1,733,255 |
| Africa | 10,539 | 13,130 | 20,291 | 28,800 | 37,618 | 48,081 | 71,527 | 93,814 |
| Americas | 20,838 | 23,438 | 29,149 | 38,585 | 49,687 | 61,732 | 74,511 | 78,773 |
| North America | 12,182 | 12,394 | 13,775 | 16,140 | 18,952 | 21,004 | 25,590 | 26,271 |
| Latin America and Caribbean | 8,656 | 11,044 | 15,374 | 22,445 | 30,735 | 40,728 | 48,921 | 52,502 |
| Asia | 21,569 | 29,772 | 38,921 | 54,914 | 72,002 | 94,009 | 110,549 | 136,789 |
| Oceania | 1,260 | 1,326 | 1,728 | 1,999 | 2,829 | 3,242 | 3,990 | 4,230 |
| Germany | 87,389 | 82,143 | 84,485 | 91,976 | 109,785 | 158,651 | 263,271 | 300,691 |
| Spain | 98,098 | 109,232 | 116,987 | 102,320 | 84,266 | 72,167 | 64,126 | 82,334 |
| France | 48,002 | 48,948 | 51,729 | 55,407 | 61,688 | 70,901 | 95,643 | 122,970 |
| Italy | 423,008 | 394,812 | 381,493 | 361,892 | 321,795 | 297,917 | 287,130 | 311,742 |
| Austria | 31,986 | 29,417 | 29,123 | 28,454 | 29,191 | 33,069 | 37,013 | 41,145 |
| Portugal | 10,863 | 31,029 | 86,035 | 135,646 | 135,449 | 167,857 | 212,586 | 267,474 |
| United Kingdom | 16,050 | 17,482 | 18,269 | 20,030 | 22,309 | 26,425 | 37,273 | 41,766 |
| Croatia | - | - | - | 42,582 | 43,876 | 40,709 | 33,507 | 29,355 |
| Serbia and Montenegro | - | - | - | - | 190,940 | 196,833 | - | - |
| Serbia | - | - | - | - | - | - | 121,908 | 71,260 |
| Montenegro | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2,022 | 2,536 |
| Kosovo | - | - | - | - | - | - | 58,755 | 106,879 |
| Bosnia and Herzegovina | - | - | - | 24,748 | 45,111 | 43,354 | 35,513 | 31,905 |
| Macedonia | - | - | - | 39,540 | 56,092 | 60,898 | 60,116 | 64,448 |
| Albania | 15 | 17 | 29 | 576 | 1,093 | 1,218 | 1,308 | 1,590 |
| Sri Lanka | 373 | 808 | 2,840 | 9,841 | 20,215 | 31,865 | 28,963 | 27,667 |
| Iraq | 352 | 378 | 454 | 771 | 2,046 | 3,257 | 7,553 | 7,092 |
| Turkey | 38,353 | 51,206 | 64,899 | 79,372 | 80,165 | 75,903 | 71,835 | 69,215 |
Source:[18]
Tamil refugees fleeing from war in Sri Lanka are the largest number of Asians, while Albanians and former Yugoslavians continue to grow in number. Switzerland is also the second largest European country in number of acceptance of Iraqi refugees fleeing from the violence in Iraq since 2003, but behind Great Britain, Germany and Sweden in the number of Iraqis taken residence for a European country.
Naturalization
In 2004, 35,700 people acquired Swiss citizenship according to Swiss nationality law, a figure slightly larger than that of the previous year (35,424), and four times larger than the 1990 figure (8,658). About a third of those naturalized are from a successor state of Former Yugoslavia: 7,900 Serbia-Montenegro, 2,400 Bosnia-Herzegovina, 2,000 Macedonia, 1,600 Croatia. 4,200 were from Italy, 3,600 from Turkey, 1,600 from Sri Lanka, 1,200 from Portugal, and 1,200 from France.[21]
The yearly rate of naturalization has quintupled over the 1990s and 2000s, from roughly 9,000 to 45,000. Relative to the population of resident foreigners, this amounts to an increase from 8% in 1990 to 27% in 2007, or relative to the number of Swiss citizens from 1.6% in 1990 to 7.3% in 2007.
The following table shows the historical development of naturalization from selected countries.[22]
| Origin | 1981 | 1985 | 1990 | 1995 | 2000 | 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 14,299 | 14,393 | 8,658 | 16,790 | 28,700 | 27,583 | 36,515 | 35,424 | 35,685 | 38,437 | 46,711 | 43,889 | 44,365 | 43,440 | 39,314 | 36,012 | 33,500 | 34,061 |
| Europe | 12,978 | 12,349 | 6,970 | 12,592 | 21,975 | 20,969 | 28,102 | 27,558 | 27,728 | 30,109 | 36,087 | 33,771 | 34,879 | 33,795 | 30,458 | 27,769 | 25,778 | 26,457 |
| Africa | 283 | 341 | 273 | 919 | 1,824 | 1,900 | 2,163 | 1,954 | 1,848 | 2,064 | 2,619 | 2,883 | 2,599 | 2,627 | 2,499 | 2,337 | 2,417 | 2,363 |
| North America | 171 | 277 | 139 | 230 | 321 | 316 | 376 | 367 | 333 | 336 | 407 | 451 | 371 | 427 | 428 | 410 | 443 | 499 |
| South America and Caribbean | 245 | 442 | 461 | 777 | 1,554 | 1,528 | 1,790 | 1,749 | 1,626 | 1,478 | 1,859 | 1,921 | 1,675 | 1,802 | 1,587 | 1,613 | 1,407 | 1,609 |
| Asia | 590 | 928 | 796 | 2,226 | 2,981 | 2,830 | 4,033 | 3,717 | 4,065 | 4,382 | 5,666 | 4,787 | 4,771 | 4,710 | 4,261 | 3,788 | 3,349 | 3,038 |
| Oceania | 30 | 52 | 12 | 24 | 29 | 27 | 35 | 67 | 73 | 59 | 62 | 61 | 56 | 55 | 58 | 62 | 64 | 66 |
| Italy | 4,665 | 3,259 | 1,995 | 4,376 | 6,652 | 5,386 | 6,633 | 5,085 | 4,196 | 4,032 | 4,502 | 4,629 | 4,921 | 4,804 | 4,111 | 4,033 | 3,998 | 4,379 |
| Germany | 2,650 | 2,839 | 1,144 | 703 | 646 | 585 | 817 | 670 | 639 | 773 | 1,144 | 1,361 | 3,022 | 4,035 | 3,617 | 3,516 | 3,357 | 3,804 |
| Kosovo | 1,611 | 2,518 | 2,556 | 2,640 | ||||||||||||||
| Serbia | 6,859 | 4,261 | 3,362 | 2,529 | ||||||||||||||
| Portugal | 86 | 127 | 170 | 175 | 765 | 779 | 920 | 1,165 | 1,199 | 1,505 | 2,383 | 2,201 | 1,761 | 2,336 | 2,217 | 2,211 | 2,071 | 2,184 |
| Turkey | 150 | 189 | 211 | 1,205 | 3,127 | 3,116 | 4,128 | 4,216 | 3,565 | 3,467 | 3,457 | 3,044 | 2,866 | 2,593 | 2,091 | 1,852 | 1,638 | 1,622 |
| France | 1,262 | 1,228 | 684 | 871 | 1,360 | 1,306 | 1,367 | 1,215 | 1,181 | 1,021 | 1,260 | 1,218 | 1,110 | 1,314 | 1,084 | 1,272 | 1,197 | 1,558 |
| Macedonia | 76 | 857 | 1,022 | 1,639 | 1,802 | 1,981 | 2,171 | 2,596 | 2,210 | 2,287 | 1,831 | 1,586 | 1,322 | 1,212 | 1,270 | |||
| Bosnia and Herzegovina | 112 | 999 | 1,128 | 1,865 | 2,268 | 2,371 | 2,790 | 3,149 | 3,016 | 2,855 | 2,408 | 1,924 | 1,610 | 1,145 | 1,156 | |||
| Croatia | 577 | 970 | 1,045 | 1,638 | 1,565 | 1,616 | 1,681 | 1,837 | 1,660 | 2,046 | 1,599 | 1,483 | 1,268 | 1,195 | 1,118 | |||
| Spain | 567 | 643 | 401 | 431 | 851 | 699 | 691 | 800 | 823 | 975 | 1,283 | 1,246 | 1,096 | 1,245 | 1,120 | 1,044 | 1,033 | 1,047 |
| Sri Lanka | 7 | 104 | 30 | 42 | 375 | 446 | 1,124 | 1,139 | 1,565 | 1,996 | 2,941 | 2,206 | 2,348 | 2,158 | 1,783 | 1,467 | 1,170 | 890 |
| Iraq | 2 | 8 | 3 | 15 | 40 | 42 | 33 | 54 | 67 | 80 | 139 | 142 | 163 | 190 | 240 | 266 | 399 | 355 |
Emigration
In 2004, 623,100 Swiss citizens (8.9%) lived abroad, the largest group in France (166,200), followed by the USA (71,400) and Germany (70,500). (see Swiss diaspora).
Religions
Religion in Switzerland (population age 15+, 2016)[23]
Switzerland as a federal state has no state religion, though most of the cantons (except for Geneva and Neuchâtel) recognize official churches (Landeskirchen), in all cases including the Roman Catholic Church and the Swiss Reformed Church. These churches, and in some cantons also the Old Catholic Church and Jewish congregations, are financed by official taxation of adherents.[24]
In 2000, 5.78 million residents (79.2%, compared to 93.8% in 1980) were Christian (Roman Catholic 41.8%, Protestant 35.3%, Orthodox 1.8%). 809,800 (11.1%, compared to 3.8% in 1980) were without any religious affiliation. 310,800 (4.3%) were Muslim (compared to 0.9% in 1980), 17,900 (0.2%) were Jewish. The 2005 Eurobarometer poll[25] found 48% of Swiss residents to be theist, 39% expressing belief in "some sort of spirit or life force", 9% atheist and 4% said that they "don't know".
Adherence to Christian churches has declined considerably since the late 20th century, from close to 94% in 1980 to about 67% as of 2016. Furthermore notable is the significant difference in church adherence between Swiss citizens (72%) and foreign nationals (51%) in 2016.[23]
The Federal Statistical Office reported the religious demographics as of 2016 as follows (based on the resident population age 15 years and older): 66.9% Christian (including 36.5% Roman Catholic, 24.5% Reformed, 5.9% other), 24.9% unaffiliated, 5.2% Muslim, 0.3% Jewish, 1.4% other religions. (100%: 6,981,381, registered resident population age 15 years and older).[23]
Languages
The four national languages of Switzerland are German, French, Italian and Romansh. Native speakers number about 64% (4.6 million) for German (mostly Swiss German dialects), 20% (1.5 million) for French (mostly Swiss French, but including some Franco-Provençal dialects), 7% (0.5 million, mostly Swiss Italian, but including Insubric dialects) for Italian and less than 0.5% (35,000) for Romansh.
The non-official language with the largest group of native speakers is Serbo-Croatian with 103,000 speakers in 2000, followed by Albanian with 95,000, Portuguese with 89,500, Spanish with 77,500, English with 73,000, Macedonian 61,300,[27] and a total of 173,000 speakers of other languages, amounting to roughly 10% of the population with a native language not among the four official languages.[28]
Education
Almost all Swiss are literate. Switzerland's 13 institutes of higher learning enrolled 99,600 students in the academic year of 2001-02. About 25% of the adult population hold a diploma of higher learning. According to the CIA World Factbook data for 2003, 99% of the Swiss population aged 15 and over could read and write, with the rate being identical for both sexes.[29]
During the 2008/09 school year there were 1,502,257 students in the entire Swiss educational system. In kindergarten or pre-school, there were 152,919 students (48.6% female). These students were taught by 13,592 teachers (96.0% female) in 4,949 schools, of which 301 were private schools. There were 777,394 students (48.6% female) in the obligatory schools, which include primary and lower secondary schools. These students were taught by 74,501 teachers (66.3% female) in 6,083 schools, of which 614 were private. The upper secondary school system had 337,145 students (46.9% female). They were taught by 13,900 teachers (42.3% female) in 730 schools, of which 240 were private. The tertiary education system had 234,799 students (49.7% female). They were taught by 37,546 teachers (32.8% female) in 367 schools.[30]
Regional disparities
| Cantons | Tax index for all Federal, Cantonal and Church Taxes (Switzerland = 100.0) 2006 | Tax rate (% of total income) for a married couple with two children and 50,000CHF in income 2006 | Tax rate (% of total income) for a married couple with two children and 150,000CHF in income 2006 | Population under 20 as a percentage of total population aged 20–64 2007 | National Income per person in CHF 2005 | Change in National Income per person 2003-2005 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 2.36 | 11.56 | 34.59 | 54,031 | 5.3 | |
| 82.9 | 2.16 | 8.65 | 31.12 | 68,803 | 4.6 | |
| 123.1 | 2.14 | 13.91 | 33.05 | 45,643 | 5 | |
| 119 | 3.47 | 12.56 | 37.19 | 43,910 | 5.3 | |
| 144.2 | 4.54 | 12.42 | 37.06 | 45,711 | 5.3 | |
| 66.5 | 2.26 | 6.98 | 36.95 | 50,170 | 6.3 | |
| 146.5 | 4.14 | 11.53 | 40.88 | 39,645 | 4.7 | |
| 79.1 | 2.31 | 9.41 | 34.55 | 73,285 | 15.6 | |
| 134.8 | 4.62 | 12.56 | 36.85 | 73,236 | 10.9 | |
| 50.3 | 0.47 | 5.5 | 35.45 | 93,752 | 5.4 | |
| 126.4 | 2.33 | 12.74 | 40.2 | 39,559 | 2.6 | |
| 116.9 | 2.36 | 12.95 | 34.34 | 46,844 | 4.9 | |
| 113.1 | 1.01 | 14.3 | 26.6 | 115,178 | 15.9 | |
| 92.5 | 2.12 | 12.4 | 33 | 53,501 | 3.9 | |
| 114.6 | 2.94 | 11.62 | 32.92 | 55,125 | 5.4 | |
| 121.7 | 3.8 | 12.06 | 37.6 | 44,215 | 4.7 | |
| 105.6 | 3.18 | 9.88 | 44.46 | 45,936 | 7.4 | |
| 115.5 | 2.53 | 12.68 | 37.66 | 44,866 | 4 | |
| 112.2 | 2.99 | 11.51 | 33.97 | 49,355 | 11.7 | |
| 87.4 | 1.52 | 10.4 | 34.9 | 49,209 | 2.5 | |
| 86.6 | 0.34 | 11.48 | 37.52 | 44,918 | 3.2 | |
| 64.6 | 0.24 | 9.04 | 31.14 | 41,335 | 3.4 | |
| 106.2 | 0.42 | 12.2 | 37.87 | 52,901 | 3.4 | |
| 121.3 | 2.72 | 10.68 | 35.18 | 38,385 | 6 | |
| 137.1 | 3.8 | 15.96 | 38.06 | 49,775 | 6.6 | |
| 89.8 | 0.05 | 11.81 | 35.4 | 62,839 | 5.1 | |
| 126.6 | 2.87 | 15.26 | 40.09 | 38,069 | 6.4 |
- Source:[31]
Crime
The police registered a total of 553,421 criminal offences in 2009, including 51 killings and 185 attempted murders. There were 616 cases of rape. In the same year, 94,574 adults (85% of them male, 47.4% of them Swiss citizens) were convicted under criminal law. 57.3% of convictions were for traffic offences.[32]
In the same year, 15,064 minors (78.3% of them male, 68.2% of them of Swiss nationality, 76.3% aged between 15 and 18) were convicted.[33]
The number of convicted persons is given in the following tables.[34] Each class of crime references the relevant section of the Strafgesetzbuch (Criminal Code, abbreviated as StGB in German), or Betäubungsmittelgesetz (abbr. BetmG, Narcotics Act), or the Strassenverkehrsgesetz (abbr. SVG, Swiss Traffic Regulations).
| Year | Total Convicted Adults | Homicide (Art. 111,112,113,116 StGB) | Serious Bodily Injury (Art. 122 StGB) | Minor Bodily Injury (Art. 123 StGB) | Sexual Contact with Children (Art. 187 StGB) | Rape (Art. 190 StGB) | Theft (Art. 139 StGB) | Robbery (Art. 140 StGB) | Receiving Stolen Goods (Art. 160 StGB) | Embezzlement (Art. 138 StGB) | Fraud (Art. 146 StGB) | Narcotics Possession | Major Violation of Traffic Laws (Art. 90 Abs. 1&2 SVG) | Impaired Driving (Art. 91 SVG) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2005 | 26,199 | 105 | 95 | 2,439 | 416 | 110 | 5,967 | 497 | 1,249 | 906 | 1,469 | 5,510 | 22,015 | 16,466 |
| 2006 | 26,583 | 116 | 105 | 2,537 | 388 | 135 | 5,933 | 565 | 1,186 | 876 | 1,516 | 5,403 | 21,535 | 21,058 |
| 2007 | 24,265 | 105 | 94 | 2,262 | 386 | 139 | 5,502 | 524 | 930 | 805 | 1,597 | 5,090 | 21,294 | 20,108 |
| 2008 | 26,327 | 107 | 134 | 2,632 | 412 | 135 | 5,756 | 525 | 909 | 854 | 1,660 | 5,387 | 25,265 | 20,600 |
| 2009 | 27,727 | 103 | 129 | 2,655 | 388 | 129 | 6,449 | 533 | 941 | 859 | 1,566 | 5,533 | 25,557 | 19,711 |
| 2010 | 28,691 | 94 | 149 | 2,677 | 334 | 128 | 6,659 | 593 | 905 | 784 | 1,750 | 6,125 | 25,983 | 20,591 |
| 2011 | 29,128 | 82 | 127 | 2,721 | 274 | 86 | 6,950 | 442 | 1,007 | 716 | 1,767 | 4,710 | 23,590 | 18,882 |
| 2012 | 33,925 | 116 | 179 | 2,845 | 293 | 108 | 8,936 | 511 | 1,332 | 745 | 1,971 | 5,734 | 22,906 | 18,396 |
| 2013 | 35,325 | 114 | 178 | 2,843 | 317 | 98 | 9,491 | 654 | 1,433 | 670 | 2,307 | 6,070 | 22,277 | 17,465 |
| 2014a | 32,911 | 99 | 197 | 2,617 | 288 | 77 | 8,335 | 520 | 1,112 | 646 | 2,153 | 6,164 | 24,263 | 17,041 |
- ^a 2014 conviction numbers may not include convictions overturned on appeal.
- ^ Due to privacy protection laws some convictions are not included.
| Year | Total Convicted Minors | Homicide (Art. 111,112,113,116 StGB) | Serious Bodily Injury (Art. 122 StGB) | Minor Bodily Injury (Art. 123 StGB) | Sexual Contact with Children (Art. 187 StGB) | Rape (Art. 190 StGB) | Theft (Art. 139 StGB) | Robbery (Art. 140 StGB) | Receiving Stolen Goods (Art. 160 StGB) | Embezzlement (Art. 138 StGB) | Fraud (Art. 146 StGB) | Narcotics Possession | Major Violation of Traffic Laws (Art. 90 Abs. 1&2 SVG) | Impaired Driving (Art. 91 SVG) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2005 | 7,580 | 7 | 10 | 634 | 73 | 14 | 3,528 | 375 | 400 | 34 | 65 | 918 | 124 | 180 |
| 2006 | 7,769 | 7 | 22 | 644 | 118 | 19 | 3,418 | 330 | 390 | 35 | 51 | 1,019 | 126 | 189 |
| 2007 | 6,910 | 6 | 21 | 699 | 101 | 19 | 2,189 | 285 | 285 | 21 | 47 | 680 | 116 | 141 |
| 2008 | 6,975 | 4 | 24 | 688 | 80 | 17 | 1,998 | 334 | 272 | 17 | 57 | 560 | 101 | 125 |
| 2009 | 6,931 | 6 | 24 | 665 | 73 | 5 | 2,033 | 365 | 311 | 19 | 57 | 600 | 142 | 105 |
| 2010 | 7,613 | 13 | 36 | 770 | 71 | 17 | 2,410 | 413 | 242 | 19 | 51 | 565 | 119 | 141 |
| 2011 | 5,427 | 2 | 31 | 553 | 65 | 5 | 1,585 | 256 | 153 | 10 | 49 | 507 | 138 | 152 |
| 2012 | 5,070 | 2 | 34 | 476 | 71 | 8 | 1,620 | 303 | 164 | 25 | 56 | 554 | 74 | 124 |
| 2013 | 5,199 | 3 | 32 | 407 | 75 | 21 | 1,666 | 325 | 166 | 27 | 90 | 690 | 72 | 95 |
| 2014 | 4,849a | 1 | 33 | 380 | 63 | 8 | 1,375 | 231 | 159 | 24 | 70 | 817 | 86 | 124 |
Major cities
| Rank | Name | Canton | Pop. | Rank | Name | Canton | Pop. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Zürich  Geneva |
1 | Zürich | Zürich | 409,241 | 11 | Thun | Bern | 43,743 |  Basel Lausanne |
| 2 | Geneva | Geneva | 198,979 | 12 | Köniz | Bern | 41,507 | ||
| 3 | Basel | Basel-Stadt | 177,275 | 13 | La Chaux-de-Fonds | Neuchâtel | 38,625 | ||
| 4 | Lausanne | Vaud | 137,810 | 14 | Fribourg | Fribourg | 38,521 | ||
| 5 | Bern | Bern | 133,798 | 15 | Schaffhausen | Schaffhausen | 36,332 | ||
| 6 | Winterthur | Zürich | 110,912 | 16 | Vernier | Geneva | 34,983 | ||
| 7 | Lucerne | Luzern | 81,401 | 17 | Chur | Graubünden | 34,880 | ||
| 8 | St. Gallen | St. Gallen | 75,522 | 18 | Sion | Valais | 33,999 | ||
| 9 | Lugano | Ticino | 63,932 | 19 | Uster | Zürich | 34,516 | ||
| 10 | Biel/Bienne | Bern | 54,640 | 20 | Neuchâtel | Neuchâtel | 33,578 | ||
See also
Notes and references
- ↑ "Switzerland". cia.gov. Retrieved 3 January 2017.
- ↑ with the exceptions of the censuses of 1888 and 1941.
- ↑ History of the Federal Population Census, Swiss Federal Statistical Office, accessed October 2007
- ↑ Overview of the Federal Population Census, Swiss Federal Statistical Office, accessed October 2007
- ↑ Die Bevölkerung der Schweiz 2015 BFS 348-1500, 22 November 2016. Swiss Federal Statistics Office (2009). "Struktur der ständigen Wohnbevölkerung" (Microsoft Excel). Retrieved 2010-08-25. Head-König, Anne-Lise in Population in German, French and Italian in the online Historical Dictionary of Switzerland.
- ↑ "Resident Population in Switzerland 2008" (PDF) (Press release). Swiss Federal Statistical Office. 27 August 2009. Retrieved 28 January 2009. (in English)
- ↑ Swiss Federal Statistics Office
- ↑ United Nations Demographic Yearbooks
- ↑ Statistik Schweiz
- ↑ "Population". Federal Statistical Office of Switzerland. Retrieved 9 October 2018.
- ↑ "Ufficio federala di statistica". STAT-TAB. Statistica Svizzera. Retrieved 9 October 2018.
- 1 2 Swiss Federal Statistics Office (2014). "Ständige Wohnbevölkerung nach Alter und Geschlecht" (Microsoft Excel). Retrieved 14 July 2016.
- 1 2 Kohli, Raymond (June 2015). Szenarien zur Bevölkerungsentwicklung der Schweiz 2015–2045 (Report). Swiss Federal Statistical Office. Retrieved 14 July 2016.
- ↑ Swiss Federal Statistical Office press release #0351-0907-20 dated 2-7-2009 (in French)
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 "Life expectancy". Our World in Data. Retrieved 2018-08-28.
- ↑ "World Population Prospects – Population Division – United Nations". Retrieved 2017-07-15.
- ↑ Bevölkerung - Die wichtigsten Zahlen Swiss Federal Statistical Office, accessed 6 October 2014
- 1 2 3 Ständige ausländische Wohnbevölkerung nach Staatsangehörigkeit, am Ende des Jahres Swiss Federal Statistical Office, accessed 6 October 2014
- ↑ STAT TAB-Ständige und nichtständige Wohnbevölkerung nach Kanton, Geschlecht, Anwesenheitsbewilligung, Alter und Staatsangehörigkeit, 2015
- ↑ STAT TAB-Ständige und nichtständige Wohnbevölkerung nach Kanton, Geschlecht, Staatsangehörigkeit, Geburtsstaat und Alter, 2014-2015
- ↑ Swiss Federal Statistics Office
- ↑ Federal Office of Statistics - Erwerb des Schweizer Bürgerrechts nach früherer Staatsangehörigkeit accessed 17 October 2014
- 1 2 3 "Population résidante permanente âgée de 15 ans ou plus selon l'appartenance religieuse" (XLS) (in French). Swiss Central Statistical Office. 2 March 2018.
- ↑ "Die Kirchensteuern August 2013" (PDF) (in German, French, and Italian). Berne: Schweizerische Steuerkonferenz SSK, Swiss Federal Tax Administration FTA, Federal Depertment of Finance FDF. 2013. Retrieved 2014-04-05. , Swiss Federal Tax Administration
- ↑ available at EU Public Opinion Survey Archived 24 May 2006 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ Swiss Federal Statistical Office FSO. 31 January 2017
- ↑ Swiss Federal Statistics Office-Languages Archived 3 March 2016 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ Lüdi, Georges; Werlen, Iwar. Recensement Fédéral de la Population 2000 – Le Paysage Linguistique en Suisse Archived 29 November 2007 at the Wayback Machine.. Neuchâtel, avril 2005: Office fédéral de la statistique. Accessed from Encyclopédie statistique de la Suisse on 5 January 2006.
- ↑ CIA - The World Factbook -- Switzerland
- ↑ Swiss Federal Statistical Office Ueberblick - Schulstufen (in German) accessed 15 November 2010
- ↑ Regionale Disparitäten in der Schweiz - Schlüsselindikatoren Archived 14 June 2013 at the Wayback Machine. (in German) (in French) accessed 20 December 2011
- ↑ Swiss Federal Statistical Office Verurteilungen (Erwachsene) - Daten, Indikatoren - Demographische Merkmale der Verurteilten Archived 4 December 2007 at the Wayback Machine. (in German) accessed 14 November 2010
- ↑ Swiss Federal Statistical Office Jugendstrafurteile - Daten, Indikatoren (in German) accessed 15 November 2010
- ↑ Kriminalität, Strafvollzug – Daten, Indikatoren: Verurteile Personen: Jugendliche und Erwachsene (in German) accessed 5 April 2016
- ↑ Swiss Federal Statistical Office - STAT-TAB, online database – Ständige und nichtständige Wohnbevölkerung nach institutionellen Gliederungen, Geburtsort und Staatsangehörigkeit (in German) accessed 17 September 2018
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Demographics of Switzerland. |