List of equipment of the Indian Army
This is a list of some of the present equipment used by the Indian Army. Most of the army equipment is of foreign design and produced under licence in India but efforts are on to progressively design and manufacture equipment locally. The 41 Indian Ordnance Factories under control of Ordnance Factories Board manufacture most of the Army equipment like small arms, ammunition, combat vehicles, artillery, tanks etc.
Infantry weapons
Small Arms
| Name | Weapon | Type | Caliber | Origin | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Handguns | ||||||
| Pistol Auto 9mm 1A | Semi-automatic pistol | 9×19mm Parabellum | Status: In service. Standard side-arm of the Indian Army, manufactured under license. | |||
| SIG Sauer P226[1] |  | Semi-automatic pistol | 9×19mm Parabellum | Status: In service. Used by some units and mainly by Special Forces. | ||
| Glock 17 |  | Semi-automatic pistol | 9×19mm Parabellum | Status: In service. Standard Special Forces pistol. | ||
| Shotgun | ||||||
| Franchi SPAS-15 | Combat Shotgun | 18.5 x 76 mm NATO | Status: In service. Used by special forces, which includes NSG. | |||
| OFB pump action Shotgun |  |
pump action | 12-gauge shotgun | Status:In Service | ||
| SMGs | ||||||
| SAF Carbine 2A1 | Submachine gun | 9×19mm Parabellum | Status: To be Replaced. SAF Carbine 1A. To be replaced by the Caracal International CAR 816[2]. | |||
| Micro-Uzi |  | Submachine gun | 9×19mm Parabellum | Status: In service. For use by Special Forces. Micro-Uzi variant used.[3] | ||
| Heckler & Koch MP5 |  | Submachine gun | 9×19mm Parabellum | Status: In service. Used by Special Forces | ||
| SIG MPX |  |
Submachine gun | 9×19mm Parabellum | Status: In Service. Used by Special Forces mainly by NSG | ||
| Brügger & Thomet MP9 |  | Machine pistol | 9×19mm Parabellum | Status: In service. Used by Ghatak Platoon[4] | ||
| IWI Tavor X95 | .jpg) |
Submachine gun and bullpup rifle | 9×19mm Parabellum Variant | Status: In Service 9mm variant are in service since 2011 | ||
| Assault Rifles | ||||||
| Steyr AUG |  |
Assault Rifle/Sub Machine Gun | 5.56×45mm NATO and 9×19mm Parabellum(SMG Variant) | Status: In service. Used by special forces in small numbers. | ||
| FN SCAR |  |
Assault rifle | 5.56×45mm NATO and 7.62x51mm NATO | Status: In service. Used by special forces including NSG, Para SF, MARCOS and SFF. | ||
| IMI Galil |  |
Assault rifle | 5.56×45mm NATO | Status: In service. Small numbers used by Para SF. | ||
| IWI Tavor X95 | .jpg) |
Assault rifle and bullpup rifle | 5.56×45mm NATO Variant | Status: In Service Used by Special Forces | ||
| IMI Tavor TAR-21 |  | Assault rifle | 5.56×45mm NATO | Status: In service. Standard Special Forces assault rifle.[5][6] | ||
| AKM |  | Assault rifle | 7.62×39mm | Status: In service. Used by the Army. | ||
| AR-M1 | .jpg) |
Assault rifle | 7.62×39mm | Status: In service. Used by the Army. | ||
| Vz. 58 | Assault rifle | 7.62×39mm | Status: In service. Used by the army in small numbers. | |||
| Mpi-KmS 72 |  |
Assault rifle | 7.62×39mm | Status: In Service Used by the army in small amount | ||
| Fab Defense Mod. Ak | Assault rifle | 7.62×39 mm | Status: In Service
This rifles are mainly a heavily modified and Upgraded variant of the Old 7.62×39 mm AK type rifle. Present in a large amount among all units | |||
| AK-103 | Assault rifle | 7.62×39mm | Status: In service. Used by the Indian Police, Army, Paramilitary including special forces MARCOS, Garud, Ghatak, and NSG. | |||
| AK-203 | Assault Rifle | 7.62×39mm | Status: On Order.
Will be the standard weapon of Indian Army. 750,000 rifles to be manufactured locally by OFB. Till now final Production Variant design haven't been finalized yet due to cost increase than expected initially.[7] | |||
| SIG-716 Patrol G2 |  |
Battle Rifle | 7.62x51mm | Status: In Service.
Total Order placed for 72,400 units of SIG-716 Patrol G2 model. 10,000 received by Early 2020 and have been included in service.[8] Deliveries started in December 2019.[9] | ||
| Caracal International CAR 816 |  |
Carbine | 5.56×45mm NATO | Status: On Order.
Order placed for 94,000 units of CAR 816 carbine. Delivery was expected to start by last week of March or by first week of April 2020.[10] | ||
| T91 assault rifle |  |
Assault rifle | 5.56×45mm NATO | Status: In Service. 1000+ unit of this rifle were brought | ||
| M16 rifle |  |
Assault rifle | 5.56×45mm NATO | Status: In service. Used by special forces | ||
| M4A1 Carbine |  | Assault rifle | 5.56×45mm NATO | Status: In service. Used by special forces, including PARA SF and Ghatak SF and MARCOS. | ||
| Sniper rifles | ||||||
| Steyr SSG 69 | Sniper rifle | 7.62×51mm NATO | Status: In service. Standard bolt-action sniper rifle. | |||
| Mauser SP66 | Sniper rifle | 7.62×51mm NATO | Status: In service. Standard bolt-action sniper rifle. | |||
| SIG Sauer SSG 3000 |  | Sniper rifle | 7.62×51mm NATO | Status: In service. Standard bolt-action sniper rifle. | ||
| Dragunov SVD | .jpg) | Sniper rifle | 7.62×54mmR | Status: In service. Standard Designated Marksman rifle(DMR). To be replaced by a 7.62mm NATO DMR under the Army modernisation plan.[11] | ||
| Barrett M95 |  |
Sniper rifle | .50 BMG | Status: In service. Small numbers. Used in anti-sniping role.[12] | ||
| Heckler & Koch PSG1 |  | Sniper rifle | 7.62×51mm NATO | Status: In service. Standard semi-automatic sniper rifle
used by Indian Army, NSG, MARCOS. | ||
| Beretta Scorpio TGT | Sniper rifle | .338 Lapua Magnum | Status: In service.[12] | |||
| Sako TRG M10 | .jpg) |
Sniper rifle | .338 Lapua Magnum | Status: In service. Small numbers, used by Para SF.[12] | ||
| Barrett Model 98B |  |
Sniper rifle | .338 Lapua Magnum | Status: In service. Used by Special Forces including NSG. | ||
| IMI Galil 7.62 Sniper |  | Sniper Rifle | 7.62×51mm NATO | Status: In service. For use by Indian Army Special Forces snipers. | ||
| Denel NTW-20 |  |
Anti-material rifle | 14.5×114mm, 20×82mm and 20×110mm Hispano-Suiza | Status: In service. Bought in small numbers. | ||
| Machine Guns | ||||||
| IMI Negev |  | Light machine gun | 5.56×45mm NATO | Status: In service. Standard Squad Automatic Weapon (SAW) of special forces, especially Para(SF). | ||
| IMI Negev Ng7 |  |
Light Machine Gun | 7.62×51mm NATO | Status: On order Contract signed for 16,479 of this LMG. This Ng7 will replace all the GUN MACHINE 7.62MM IA still left and all the INSAS LMG[13] | ||
| FN Minimi |  |
Light Machine Gun | 5.56x45mm NATO | Status: In service. Used mainly by the NSG | ||
| M249 |  | Light Machine Gun | 5.56x45mm NATO | Status: In service. Used mainly by the NSG and small amount is used by some units of Para SF | ||
| Mk 48 machine gun |  |
General-purpose machine gun | 7.62×51mm NATO | Status: In Service Used by Para SF [14] | ||
| Uk vz. 59 |  |
General-purpose machine gun | 7.62×54mmR | Status: In service. Small numbers, used by Para SF and SFF. | ||
| MG 2A1 MG 5A MG 6A |
 | General purpose machine gun | 7.62×51mm NATO | Status: In service. Standard section-Medium Machine Gun for infantry battalions, Indian-made MAG 58 version. Also in service as the MG 5A (Co-axial) and MG 6A (Commander's gun) with some armoured vehicles. | ||
| M2 Browning |  | Heavy machine gun | .50 BMG | Status: In service. M2HB variant in service, used in small numbers.[15] | ||
| PKM | General purpose machine gun | 7.62×54mmR | Status: In service. PK machine guns used as co-axial weapons in Russian produced T-90S Bhishma, T-72M Ajeya and BMP-2S Sarath and used as general purpose machine gun. Also used by Special Forces as section LMG. | |||
| NSV |  | Heavy machine gun | 12.7×108mm | Status: In service
Used as secondary weapon on T-72 and T-90 tanks. | ||
| KPV | Heavy machine gun | 14.5×114 mm | Status: In service. Manufactured at Ordnance Factory Tiruchirappalli, used in small numbers. | |||
| Indigenous Weapons | ||||||
| Vidhwansak |  |
Anti-materiel rifle | 12.7×108mm, 20x82mm | Status: In service. | ||
| 1B1 INSAS | Assault rifle | 5.56×45mm NATO | Status: In service/ To be replaced. Standard assault rifle of the Indian Army. To be replaced by AK-203 and SIG-716 Patrol G2 | |||
| INSAS LMG |  | Light machine gun | 5.56×45mm NATO | Status: In service(To be phased Out) . Standard Squad Automatic Weapon (SAW) of the Indian Army. Light machine gun derivative of the INSAS assault rifle. Contract signed in 2020 to replace INSAS LMG by IWI Negev Ng7 | ||
| GUN MACHINE 7.62MM IA |  |
Light machine Gun | 7.62 x 51 mm NATO | Status: Being Phased out small number of them have still left out but soon to be replaced by IWI Negev Ng7 as per contract signed in 2020 | ||
Explosives, Rockets, and Mortars
| Name | Image | Type | Quantity | Origin | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grenade 36mm | Hand Grenade | Fragmentation grenade which can be hand-thrown or rifle-launched from 1A SLR. | |||
| Multi Mode Grenade Shivalik | Hand grenade | 1.8 million[16] | Status: In service.Standard grenade of the Indian Army. This modular grenade is available in Hand mode offensive, hand mode defensive and rifle mode. Types can be interchanged by changing outer sleeve.[17][18] | ||
| GP-25 |  | Grenade launcher (40mm) | Attached to AKM and AK-103 assault rifles. | ||
| Multi Grenade Launcher 40mm | Grenade launcher (40mm) | Status: In service.Semiautomatic six shot 40mm x 46mm low velocity grenade launcher. Manufactured at Ordnance Factory Tiruchirappalli. * | |||
| AGS-17 Plamya |  | Automatic grenade launcher (30mm) | Status: In service. Standard automatic grenade launcher, used as fire support weapon in infantry formations. | ||
| AGS-30 | .jpg) | Automatic grenade launcher (30mm) | Replacing the AGS-17 and being manufactured at Ordnance Factory Tiruchirappalli. | ||
| RCL Mk II |  | Recoilless rifle (84mm) | Carl Gustav Recoilless Rifle produced by OFB. | ||
| RCL Mk III | Recoilless rifle (84mm) | Lighter, updated version of the RCL Mk II produced by OFB. | |||
| 106mm M-40A1 | .jpg) | Recoilless rifle | 13000+ | ||
| B-300 Shipon |  |
Rocket Launcher | For use by Special Forces. Specially Marcos and Para(SF). | ||
| RPO-A Shmel |  | Rocket Launcher | |||
| C90-CR (M3) |  | Rocket Launcher | In use with the infantry units. C-90-CR-RB (M3) variant only. | ||
| OFB E1 51mm | Mortar | Used by assault sections of infantry formations. | |||
| OFB E1 81mm L16 81mm mortar |
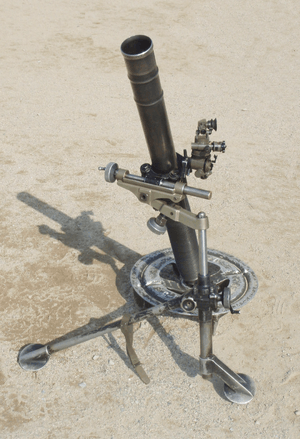 | Mortar | 5000+ | Used by mortar platoons of infantry formations. | |
| OFB E1 120mm | Mortar |
Vehicles
Utility and miscellaneous
| Name | Image | Type | Quantity | Origin | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Royal Enfield Bullet 350/500 |  |
Motorcycle | Used by Corps of Military police and Acrobatic team | ||
| Hindustan Ambassador |  |
Staff car | Ambassador is assigned to Commanding officers and officers of the rank of Brigadier and above | ||
| Mahindra Scorpio |  |
Staff car | Staff car used to ferry senior officials | ||
| Tata Safari Storme 4x4 |  |
Light Utility Vehicle | 1500+[19] | 3193 units ordered in May 2017.[20] GS800 category. To replace Maruti Gypsy.[21] | |
| Tata Sumo 4x4 | .jpg) |
Multi Utility Vehicle | Used as Ambulance,Staff car and troop carrier | ||
| Maruti Suzuki SX4 | Mid Size sedan | Staff car | |||
| Mahindra Bolero | Multi Utility Vehicle | Staff car and Troop carrier | |||
| Maruti Gypsy |  | Light Utility Vehicle | 31,100 | Additional 4,200 ordered in October 2014.[22] To be replaced by Tata Safari Storme.[21] | |
| Mahindra 550 DXB |  | Light Utility Vehicle | |||
| Force Gurkha 4x4 | Light Strike Vehicle | Ordered in May 2018[23][24] | |||
| Tata LPTA 713 TC | .jpg) | Medium 4X4 truck | 2.5 Ton truck. Manufactured by Vehicle Factory Jabalpur. | ||
| Ashok Leyland Stallion Mk III/Mk IV |  | Medium 4x4 6x6 Truck | 60,000 | 5 Ton trucks, in a wide range of configurations manufactured by Vehicle Factory Jabalpur. | |
| Tata LPTA 2038 HMV |  |
6x6 High Mobility Truck | 1858 units on order.[25] To augment and replace older BEML Tatra 6x6 fleet. | ||
| BEML Tatra |  | Heavy 4x4 trucks 6x6 trucks 8x8 trucks 10x10 trucks 12x12 trucks | 7000[26] | License produced Tatra Force heavy truck. Various models. Used for carrying sensitive equipment like Radars as well as vehicle for Pinaka and Smerch MBRL systems. | |
| Ashok Leyland Super Stallion | .jpg) | 6x6, 8x8, 10x10 Truck | [27] 10,12 and 15 Ton trucks. | ||
| Ashok Leland Super Stallion FAT |  |
Artillery Tractor 6x6 | 450 | [27] | |
| Volvo FH 12 |  |
Tractor | |||
| Ashok Leyland Topchi |  |
Medium 4x4 truck | 3 Ton truck. Gun Towing vehicle | ||
| KrAZ-6322 |  |
Heavy Utility Truck | |||
| Isuzu F-Series |  |
Medium 4x4 truck | 7 Ton truck | ||
| Ashok Leyland Crash Fire Tender | Fire Tender | ||||
| Tata LPTA 1615 TC |  | Artillery Tractor Truck | |||
| Tata Prima 4038S/4938S | Tractor truck | ||||
| Tatra 8x8 Mobile Decontamination Vehicle | Mobile Decontamination Vehicle | ||||
| Tata LPTA 1615 C |  |
Medium 4x2 truck | 10 Ton truck | ||
| Tata LP 1512 C |  |
School Bus as well as Staff Bus | |||
| Swaraj Mazda T3500 | Medium 4X4 Truck | 200+ | In service from 1996. 2.5 Ton truck | ||
| Mitsubishi Pajero |  | Light Utility Vehicle | Unknown numbers. Deployed at the Indo-Chinese Border[28] | ||
| Sisu Nasu | All-terrain transport vehicle | ||||
| TATA 1210 Field Artillery Tractor |  |
Field Artillery Tractor and Gun Towed Carrier |
Engineering and support
| Name | Image | Type | Quantity | Origin | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T-55 Kartik ABL | Armoured vehicle-launched bridge | 34 | Status: In service. Based on a Vijayanta chassis and manufactured by Heavy Vehicles Factory. | ||
| Bridge Laying MT-55 |  | Armoured vehicle-launched bridge | Based on T-55 Tank | ||
| T-72 BLT | _of_Ordnance_Factory_Board.jpg) | Armoured vehicle-launched bridge | 18 | Developed by CVRDE and manufactured by Heavy Vehicles Factory. | |
| Sarvatra |  | truck-mounted, multi-span, mobile bridging system | 8x8 truck-mounted bridging system[29][30] | ||
| Floating bridge |  |
Armoured vehicle-launched bridge | This 42 tonne mammoth is the Amphibious Floating Bridge and Ferry System (AFFS) developed by DRDO, for the ferry of traffic across large and deep water obstacles. The 10m x 3.6m x 4m vehicle can covert to a fully decked bridge configuration of length 28.4 metres, in 9 minutes. The vehicle has a maximum speed of 55 km/h on road, 40 km/h cross country and an aquatic mobility of 2.7 m/sec with twin pump jets. | ||
| CEASE | Main battle tank | 6 | The Canal Embankment Assault Equipment | ||
| AERV |  | Military Engineering Vehicle | 16 | BMP-2 based engineering and reconnaissance vehicle (Armoured Engineer Reconnaissance Vehicle) being manufactured at Ordnance Factory Medak. | |
| BMP-2 | Armoured Amphibious Bulldozer | BMP-2 with turret removed and bulldozer blade and other engineering equipment added and being manufactured at Ordnance Factory Medak. | |||
| FV180 Combat Engineer Tractor | Armoured combat engineering vehicle | 39 | |||
| VFJ Light Recovery Vehicle | Light Recovery Vehicle (4x4) | Manufactured at Vehicle Factory Jabalpur. | |||
| Yuktirath Light Recovery Vehicle | Armoured Light Recovery Vehicle (4x4) | Manufactured at Ordnance Factory Medak. | |||
| Mat Ground Surfacing CL-70 | All Terrain vehicle | Mounted on Tatra vehicle with automated laying and recovery has been developed for providing mobility in sandy and marshy terrain.[31] | |||
| Armoured Vehicle Tracked Light Repair | Armoured recovery vehicle | Based on BMP-2 for Light Repair being manufactured at Ordnance Factory Medak.[32] | |||
| WZT-2 |  | Armoured recovery vehicle | 196 | ||
| WZT-3M |  | Armoured recovery vehicle | 352 | 204 on order.[33] Assembled locally from kits and components produced in India. | |
| VT-72B ARV | Armoured recovery vehicle | 200+ | Armoured recovery vehicle replacing the Vijayanta ARV |
Mine protected, Mine clearing and Mine laying
| Name | Image | Type | Quantity | Origin | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Casspir[34] | .jpg) | Armoured personnel carrier | 255 | Status: In service. | |
| Tarmour AFV | Armoured personnel carrier | 900* | Status: In service. Based on Indian T-55 Tank.[35] *potential quantity based on existing T-55 stock. | ||
| Hydrema | .jpg) | Mine clearing Vehicle | 24 | Status: In service. Manufactured locally by OFB India | |
| T-72 FWMP |  | Mine plow | Status: In service. | ||
| Sarath |  |
Mine plow | Status: In service. | ||
| Aditya | 's_Mine_Protected_Vehicle.jpg) | Mine protected Vehicle | 1775 | Status: In service. OFB India. 1400 to be produced. 20/month manufactured at Ordnance Factory Medak AND Vehicle Factory Jabalpur. | |
| DRDO Daksh | Bomb disposal robot | 190+ | Status: In service. The Army has placed orders for 200 Dakshs.[36] Newer version is also been In service.[37] |
Armoured combat vehicles
| Name | Image | Type | Quantity | Origin | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tanks | |||||
| Arjun MBT | Main Battle Tank | 124(Mk1) | In service (Mk1).[38][39] 118 Arjun MK-1A (60Mt/1400 hp) ordered after clearing Army trials in February 2015. Arjun MBT Mk. II was to be fielded by 2016.[40][41] | ||
| 118(Mk1A) | |||||
| T-90S "Bhishma" T-90M |  |
Main Battle Tank | 2,078[42] | In service. Initial contract for 310 "T-90S" signed in 2001. Another contract signed on 26 October 2006 for 330 T-90M MBTs. A third contract was signed in December 2007 for 500+ upgraded T-90Ms. In all, India plans to have over 2000+ T-90 tanks in service by mid of 2020.[43] A contract for additional 464 T-90MS was placed in November 2019.[44][45] | |
| T-72 Ajeya Combat Improved Ajeya |
 |
Main Battle Tank | 2410[46][47] | In service. 968 T72M1 have been upgraded by Heavy Vehicles Factory, while requests for proposal for upgrading approximately 1,000 other T-72's have been sent to various firms in Israel, Russia, Poland and France.. Ajeya-M2 Standard equivalent to the Polish PT-91 Twardy. Manufactured locally in India. Will be replaced by Future Ready Combat Vehicle.[48] | |
| Infantry fighting vehicles | |||||
| BMP-2 "Sarath" |  |
Infantry fighting vehicle | 2691[49] | In service. Being modernised with TISAS (Thermal Imaging Stand Alone Sights), better fire control, and more modern ATGM armament (Konkurs M). BMP-1 has been phased out and the upgraded BMP-2 is BMP-2M with two thermobaric missiles and two tandem warhead Konkurs missiles. It also has an integrated TI sight, an LRF, and has an AGL mounted on the turret which is also stabilised in the horizontal plane. 100 added each year. To enhance the rate to 125 a year.[50] Currently ~2500 are in active service.[50] Manufactured locally in India by Ordnance Factory Medak. All BMP-2/2K vehicles are to be upgraded to BMP-2M standard.[51] | |
| Abhay IFV | Infantry fighting vehicle | Status:approx 2600 planned to replace the old bmp-2 | |||
| Armoured Personnel Carriers | |||||
| BTR-50 |  |
Armoured Personnel Carrier | 100+ | Status: Total 200 in service. | |
| TATA Kestrel | Armoured personnel carrier | Under development. Expected to be ready by 2017–18. Around 1000+ planned[52] | |||
| Tank destroyers | |||||
| NAMICA | Tank Destroyer | 0 | Ordered. BMP-2 based Nag missile carrier. Advanced version on order after successful trial in July 2012. 13 units ordered with option for further orders of 200. Production started jointly by Ordnance Factory Medak and L&T. | ||
| 9P148 |  |
Tank destroyer | Used as a Tank destroyer. | ||
| Reconnaissance vehicles | |||||
| CMT |  |
Mortar Carrier | 198 + 21 ordered | In service. BMP-2 based mortar carrier. Developed by CVRDE and manufactured by Ordnance Factory Medak. | |
| OT-62 TOPAS OT-64 SKOT | Armoured personnel carrier | TOPAS-2A converted into a Technical support vehicle | |||
| DRDO Armoured Ambulance |  |
Armoured Ambulance | 162 [53] | In service. BMP-2 based armoured ambulance developed by VRDE and produced by Ordnance Factory Medak, 288 ordered. | |
| NBC Reconnaissance Vehicle | CRBN Reconnaissance vehicle | 16 | In service. BMP-2 based CRBN developed by VRDE and produced by Ordnance Factory Medak.Vehicle[54] | ||
| Mahindra Rakshak | Armoured vehicle | Bulletproof vehicle with composite armour which offers protection against 7.62 mm bullets.[55][56][57] | |||
| PRP-3 | Battlefield surveillance system | 1RL126 "Small Fred" Battlefield Surveillance Radar based on BMP-1. NATO designation was BMP M1975 | |||
| TATA LAMV | Light Armoured Multipurpose Vehicle | Undergoing trials as of 2015. | |||
Artillery
| Notes | Image | Type | Quantity | Origin | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dhanush Howitzer |  | Howitzer | 18 | In Service Three artillery pieces delivered to the Army for user trials in July 2016, and three more in March 2019. Total 114 guns on order. Order may increase to 414.[58][59][60][61] | |
| DRDO Advanced Towed Artillery Gun System (ATAGS) |  |
Howitzer | 2 | Undergoing user trials . DRDO conducted the first proof firing of armament for the ATAGS on 14 th July, 2016. 40 guns on order production will start soon. In August 2018, Defence Acquisition Council approved the procurement of 150 ATAGS with an estimated cost of ₹3,364.78 crore (US$470 million).[62] | |
| M777 howitzer | .jpg) | Howitzer | 145[63] | In service. 145 ordered through FMS as of June 2016.[64] | |
| Haubits FH77/B | Howitzer | 410[65] | In service/Being replaced. 155 mm gun made by Bofors. 410 acquired from 1986–1991. To be replaced in near future by Dhanush Howitzer. | ||
| M-46 |  | Howitzer | 900 | In service. 180 M-46 130 mm howitzer guns upgraded to 155 mm standard by Soltam and 300 to be upgraded by OFB.[66][67] | |
| D-30 |  | Howitzer | 550 | In service/Being replaced.Being replaced by the M-46. | |
| Indian Field Gun MK 1/2/3 | .jpg) | Field gun | 1700 | In service. Being upgraded with digital FCS and INS, to extend the range up to 30 km with bleed base; | |
| Light Field Gun |  |
Field gun | 700+ | In service. 105mm gun. Ongoing upgrade. | |
| FV433 Abbot SPG |  | Self-propelled artillery | ~80 | In service/Being replaced. 105 mm howitzer. Being replaced by the K9 VAJRA-T. | |
| 2S1 Gvozdika |  | Self-propelled artillery | 110 | In service/Being replaced.122 mm howitzer. Being replaced by the K9 VAJRA-T. | |
| K9 Vajra-T |  | Self-propelled artillery | 50 | In service.155 mm howitzer, 100 units ordered with an option for an additional 50, variant of K9 Thunder. Will be manufactured by Larsen & Toubro.[69][70] | |
| Smerch 9K58 MBRL |  | Multiple rocket launcher | 62 | Status: In service. 300 mm multiple rocket launch system. | |
| Pinaka MBRL | Multiple rocket launcher | 126
units |
In service (Mk1, 40 km range).
In service (90 km range.) Under Development (Mk3, 120 km range.) 214 mm multiple rocket launch system. Replacing the 122 mm BM-21.[71] Being produced at a heavy rate of 5000 missiles per year.[72] | ||
| BM-21 | Multiple rocket launcher | 150+ units | Status: In service/Being replaced. |
Missile systems
Anti-tank guided missiles
| Name | Image | Type | Quantity | Origin | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amogha-1 | Anti-tank guided missile | Status: Under Development/Testing. Range 2.5-2.8 km.[73] | |||
| Nag Man-Portable Missile | Anti-tank guided missile | Status: Under Development(Developed By 2018). It will be completed in two years. And will replace majority of Anti-tank missile in Indian Army. | |||
| MILAN 2T |  | Anti-tank guided missile | 30,000+ 4100 | Status: Inducted. Man portable and purchased from France[74] | |
| 9M133 Kornet (AT-14 Spriggan) |
Anti-tank guided missile | 3000 | Status: Inducted. Man portable and purchased with 250 Launchers | ||
| 9K114 Shturm (AT-6 Spiral) |
 | Anti-tank guided missile | 800 | Status: Inducted. | |
| 9M120 Ataka-V (AT-9 Spiral-2) |
 |
Anti-tank guided missile | Status: Inducted. | ||
| Helina | Air launched Anti-tank missile | Status: In development. It has been tested on 12 July 2015.It is to be used, in near future, for HAL LCH and HAL Rudra. | |||
| 9M119 Svir (AT-11 Sniper) |
 |
Anti-tank guided missile | 25000 | Status: Inducted. Bharat Dynamics (BDL) signed a contract with MOD for Invar anti-tank guided missiles on 19-Aug-2013.[75][76] It is reported that 10000 will be procured from Russia while BDL will manufacture 15000.[77] | |
| LAHAT |  |
Cannon-launched guided projectile | Status: Inducted. Standard ATGM used in the main gun of Arjun Mk-1 and Mk-2 tanks. | ||
| 9M113 Konkurs (AT-5 Spandrel) |
 | Anti-tank guided missile | 15,140 | Status: Inducted. For BMP-2 (IFV), manufactured locally in India. Total cost of the acquisition being ₹13.77 billion.[78] | |
| Nag missile |  | Anti-tank guided missile | 40+ (400 on order) | Status: Inducted. For Namica Tank Destroyer (IFV). | |
| Spike (ATGM) |  |
Anti-tank guided missile | 210 | Status: Inducted. 210 missiles and 12 launchers at a cost of ₹2.8 billion rupees($40.3 million).[79] |
Ballistic, Cruise and Anti-Ballistic Missiles
| Name | Image | Type | Numbers | Origin | Range | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prahaar |  | Tactical ballistic missile | Status: Inducted. 150 - 200 km range. | |||
| Brahmos |  | Cruise missile | 60-90 TELs | Status: Inducted. 300 - 600 km range. | ||
| Nirbhay |  | Cruise missile | Status: Under Development/Testing(Ready By 2019-20). 3 Test was held in 2016. First test was held in April/May 2016. Nirbhay with BrahMos seeker was planned to be launched in December.[80] 1,000 –1500 km range. | |||
| Prithvi-I |  |
Short-range ballistic missile (SRBM) | Status: Phased Out | |||
| Prithvi-II |  |
Medium-range ballistic missile (SRBM)
|
Status: Inducted. 150–350 km range. | |||
| Prithvi-III | .jpg) |
Short-range ballistic missile | Status: Inducted. 350-650 km range. | |||
| Shaurya |  'Shourya' missile test fired on 12 November 2008 | Ballistic Cruise Missile | Status: Inducted. 700-1900 km range. | |||
| Agni-I |  | Medium-range ballistic missile | Status: Inducted. 700 – 1250 km range. | |||
| Agni-II | .jpeg) | Intermediate-range ballistic missile | Status: Inducted. 2000 – 3500 km range. | |||
| Agni-III |  | Intermediate-range ballistic missile | Status: Inducted. 3500 – 5000 km range. | |||
| Agni-IV |  | Intermediate-range ballistic missile | Status: Inducted. 4000 – 6000 km range. | |||
| Agni-V |  | Intercontinental ballistic missile | Status: Inducted in 2014.(Tested in April 2012 and September 2013. All successful launches[81]) | |||
| Agni-VI | Intercontinental ballistic missile | Status: Finished Development/ Waiting for Testing. Expected Range11,000 – 12,000 km range. India is very secretive about this. DRDO has finished developing this and it is ready to go but the Indian Government is not giving the go ahead for testing |
Air Defence
| Name | Image | Type | Quantity | Origin | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDV Mark I |  |
Ballistic missile defence system | Status: Under Development(Ready By 2018). It is under Phase 2 Indian Ballistic Missile Defence Programme. Flight ceiling of 150 km | ||
| PDV Mark II |  |
Ballistic missile defence system / | Status: Under Development/Induction Phase. It is under Phase 1 Indian Ballistic Missile Defence Programme. 2000 km range and flight ceiling of 50 to 80 km. | ||
| Advance Air Defence |  |
Surface-to-air missile | 0 | Status: Testing/Induction Phase(Completed By 2016). It can be also used as Anti-aircraft missile.Last/final test to be held on May/June 2016. It has 150 km range and flight ceiling of 30 km. | |
| S-400 Triumf | S-400 |
Mobile surface-to-air missile system | 0 | Status: Ordered. India's Cabinet Committee on Security(CCS) approved the deal, IGA formally signed. Order includes 5 battalions, consisting of Transporter Erector Launchers (TELs), missiles and fire control radar, deliveries starting 2020.[82] | |
| Barak-8 |  |
Surface-to-air missile | 0 | Status: On Order. Medium Range Surface to Air Missile. .[83] | |
| Akash |  | Surface-to-air missile | 40 TELs | Status: Inducted. Indigenous surface-to-air missile to replace SA6. 2 regiments ordered by Army, 1 delivered.Akash 1S tested with
indigenous seeker.Akash Mk2 with increased range of 100 km under development[84] Ordered for 2 additional regiments was placed in May 2017.[85] | |
| DRDO QRSAM | .jpg) |
Surface-to-air missile | 0 | Status: Under Development(Ready By 2018-19). Quick Reaction Surface to Air Missile. Has been tested in late 2019.Although still somewhat under development, it has already been deployed in Eastern Ladakh. Exact numbers are unknown.[86] | |
| Kub (SA-6 Gainful) |  | Surface-to-air missile | 180 (as of 2012) | Status: Inducted/Replacing. To be eventually replaced by Akash | |
| S-125 Neva/Pechora | Surface-to-air missile | Status: Inducted. Being Upgraded. | |||
| S-200 |  | Surface-to-air missile | |||
| 9K33 Osa (SA-8 Gecko) |  | 6x6 amphibious Surface-to-air missile system | 80 | Status: Inducted. | |
| 9K35 Strela-10 (SA-13 Gopher) |  | Surface-to-air missile | 250 (as of 2012) | ||
| 9K22 Tunguska[87] |  | Self-propelled anti-aircraft weapon | 66 | 2S6M variant in service with corps of air defence.[88] | |
| ZSU-23-4M 'Shilka' |  | Self-propelled anti-aircraft gun | 75 (as of 2010) | To be upgraded. | |
| ZSU-23-2 |  | Anti-aircraft artillery | 800 | Twin 23 mm AA gun | |
| Bofors 40 mm gun |  | Anti-aircraft artillery | 2,000+ | Primary anti-aircraft gun of the Indian Army | |
| SA-18 Grouse |  | MANPADS | 2500 | ||
| FIM-92 Stinger | MANPADS Air-to-Air Version | 245 | Status: Inducted. 245 Stinger with launchers inducted.[89] |
Aircraft
Helicopters
| Aircraft | Photo | Origin | Role | Version | Number[90] | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Helicopters (209) | ||||||
| Boeing AH-64 Apache | .jpg) |
Attack helicopter | AH-64E | Status:On Order
6 aircraft are on order. Delivery to be started in 2023(expected).[91] | ||
| HAL Light Combat Helicopter | Attack helicopter | LCH | Status: Production Started[92] 5 LCH to be procured under LSP.[93] Total 114 on order.[90] It has completed all initial tests. Trials of missile firing were held in mid 2016.[94] | |||
| HAL Rudra | Attack helicopter | ALH-WSI | 50 | Status: In Service
50 in service with 10 more on order[95] | ||
| HAL Dhruv | .jpg) | Utility helicopter | 145[90] | Status: In Service
Total of 264 on order.[90] | ||
| Kamov Ka-226 |  |
Utility helicopter | Ka-226T | Status: On Order
200 to be built in India at HAL Helicopter Manufacturing plant being built at Tumkuru.[96] | ||
| HAL Light Utility Helicopter | .jpg) |
Utility helicopter / Observation Helicopter | LUH | Status: Under Development/Undergoing Trials First flight held on 6 September 2016.126 0rdered for the army out of 187 to be produced [97] | ||
| HAL Cheetah, Cheetal & Lancer | Utility helicopter Utility helicopter Counter-insurgency | Cheetah Cheetal Lancer | 23[90] 4[90] 12 | Status: In Service.[90] They are expected to be replaced by Kamov 226T Helicopters in near future and there after by indigenously being developed HAL Light Utility Helicopter. | ||
| HAL Chetak & Chetan | .jpg) | Utility helicopter | Chetak | 4[90] | Status: Being phased out Licence-built Aérospatiale Alouette III. Being withdrawn from service and replaced by HAL Dhruv. | |
UAVs
| Aircraft | Photo | Origin | Role | Version | Number | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IAI Heron |  | Unmanned aerial vehicle | 50+ | |||
| IAI Searcher | Unmanned aerial vehicle | Searcher II Searcher I | 120+ | |||
| IAI Harpy |  | Unmanned combat aerial vehicle | 40 | |||
| IAI Harop |  | Unmanned combat aerial vehicle | 110+[98] | 54 more on order | ||
| DRDO Rustom 2 | Unmanned combat aerial vehicle | Status: Under Development/Undergoing Trials. First flight held on 16 November 2016. |
Radar
| Name | Image | Type | Quantity | Origin | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rajendra |  | Passive electronically scanned array radar | Status: Inducted . | ||
| INDRA |  |
Passive electronically scanned array radar | Status: Inducted . | ||
| Swathi Weapon Locating Radar |  |
Artillery Locating Radar | Status: Inducted . | ||
| Rohini |  |
3D radar | Status: Inducted . | ||
| Samyukta | Electronic Warfare | Status: Inducted . | |||
| Bharani | Low Level Light weight 2D Radar | Status: Inducted . | |||
| Multi Mission Radar | Multi Mission Radar | Status: Development . | |||
| Short Range Battle Field Surveillance Radar | Short Range Battle Field Surveillance Radar | Status: Inducted . | |||
| Through wall detection Radar | Through wall detection Radar | Status: Development . Prototype ready. | |||
| Ground Penetration Radar | Ground Penetration Radar | Status: Development . Prototype ready. |
Future procurements
Vehicles
- BMP-2 based AKASH SAM carrier production started at Ordnance Factory Medak.
- BMP-2 based NBC protected recon vehicle to be manufactured at Ordnance Factory Medak.
- Light Specialist Vehicle – LSV with mounting provision for MMG to be purchased by Infantry division.
- Indian Army has shown interest in TATA LAMV(Light Armoured Multipurpose Vehicle) with mounting provision of MMG, BFSR, HHTI to be purchased by Mechanized Forces. It is slated to be future ready for Battlefield Management System (BMS).
- Future Infantry Combat Vehicle - 2600 FICV to be procured to replace old BMP-2s. Initially, GoI asked different private and public sector companies to delevelop FICV. But, it seems that the plan to develop new vehicle is put on hold due to budgetary cuts. Instead, upgradation of old BMP-2s with new powerful engines, transmission and new Kliver turret with 30mm gun and four Kornet-M ATGM launchers in being tried.
- Armoured Personnel Carrier - 100 APC to be procured for United Nations peace keeping missions.
- 1586 vehicles to be procured to mount ATGMs on these.
- 1770 Future Ready Combat Vehicle to replace the T-72 MBT's [DRDO NGMBT / T 14 ARMATA / K2 Black Panther ]. The tanks would have 120/125mm smooth bore gun, be in medium weight class (50 tonnes) with a crew of 3/4 personnel.[48][99]
Artillery and missile systems
Under the Field Artillery Rationalization Plan, Indian Army plans to procure 3000 to 4000 155 mm towed, wheeled and tracked artillery systems. The requirement for artillery guns to be met with indigenous development and production.[100] Production of crucial bi-modular charge system will be started soon at Nalanda ordnance factory. HEMRL, a DRDO lab has developed the technology indigenously.[101]
- State-run Ordnance Factory Board (OFB) will deliver two types of indigenously developed 155mm howitzers to the Indian Army based on the FH77B howitzer purchased way back in 1986. One version will be 155/39 calibre while the other will be 155/45 calibre. Trials are to be completed by June 2013
- [102] Government is also evaluating 155mm/52 self-propelled howitzers wherein three Indian vendors, including two private sector companies, have been selected for trials of their equipment.
- Agni-V – Intercontinental version of the Agni missile system. The missile was test fired for the first time on 19 April 2012 and was inducted in 2014.
- Bharat Dynamics Limited has tested Second Generation Amogha anti-tank missiles with a range of 2.8 km(Tested).This anti-tank missile will be handed to the Indian Army after some trials.
- DRDO will start working on Man portable Nag anti tank missile.
Infantry equipment
- AK-203 - 750,000 rifles to be manufactured locally by OFB. It will be the standard weapon of Indian Army replacing INSAS, expected follow on orders from paramilitary and state police.
- Caracal International CAR 816 - Order placed for 94,000 units of CAR 816 carbine.
- Modern Sub Machine Carbine - to replace the Indian Sterling submachine gun.[103]
- Sniper Rifles - 5000 new sniper rifles in .338 Lapua Magnum to be procured to replace old Dragunov SVDs.[104]
- Indian Army has requirement for 300,000 modular body armour and ballistic helmets primarily for their Infantry regiments. RFI's have been issued.
- 1000 Anti materiel rifles are to acquired for which global RFI's have been issued by the MOD.
- Ballistic helmet-Indian army has ordered about 158,000 (1.58 Lakh) ballistic helmets from Kanpur-based defence firm MKU. The Indian Government has approved procurement of 328,000 (3.28 Lakh) ballistic helmets.[105]
- Bulletproof vest-The Ministry of Defence ordered 186,138 (1.86 Lakh) bulletproof vests on 9 April 2018. These will be manufactured in India by SMPP Pvt Ltd. This is in addition to the 50,000 vests ordered in 2016 under emergency procurement.[106]
Aviation
- Light Utility Helicopter: The Indian army has projected a requirement for up to 197 light helicopters to replace its ageing fleet of Chetaks and Cheetahs. The Indian Army chose Eurocopter AS 550 under a US$550 million contract in summer of 2007. Under this contract 60 helicopters were to be supplied from Eurocopter in fly-away condition and the rest were to be assembled by HAL in India. This order was later scrapped due to allegations of unfair field trials from one of the competing company, Bell Helicopters.[107][108] A fresh tender process was initiated later in which Eurocopter Fennec and Kamov Ka-226 were shortlisted for user trials. Trials were completed and Kamov Ka-226 was declared winner and about 200 helicopters are to be made in India under the "Make in India" initiative, Indian Army have planned to replace obsolete Chetaks and Cheetahs with it, until the arrival of HAL LUH, as the later would be ready for its first flight only by 2017.
- HAL Light Combat Helicopter - HAL has obtained a firm order to deliver 114 HAL Light Combat Helicopters to the Indian Army.[109]
- Boeing AH-64 Apache - The Government of India approved the purchase of 6 helicopters in August 2017.[110][111]
Gallery

 Indian Army artillery gun
Indian Army artillery gun- Indian Army Ambulance
- BEL Battlefield Surveillance Radar-Short Range (BFSR-SR)
 T-90 tanks during firing in Thar Desert.
T-90 tanks during firing in Thar Desert. A soldier tests a Beretta 92.
A soldier tests a Beretta 92. Indian Army T-72 with ERA
Indian Army T-72 with ERA Indian Army Armoured Corps during a training exercise
Indian Army Armoured Corps during a training exercise
See also
- Currently active military equipment by country
References
- https://sites.google.com/site/worldinventory/wiw_as_india
- "Caracal & SIG Sauer Win Indian Army Deal". Mönch Publishing Group. 12 February 2019. Retrieved 13 June 2020.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 10 October 2012. Retrieved 11 November 2010.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)?
- "The Tribune, Chandigarh, India - Main News". www.tribuneindia.com. Retrieved 27 October 2016.
- "Tavor21 rifle headed into service with Indian Special Forces". DefenseIndustryDaily.com. Archived from the original on 1 June 2007. Retrieved 27 July 2007.
- "Ministry of Defence, Govt of India". Mod.nic.in. Archived from the original on 4 July 2012. Retrieved 21 April 2012.
- "'Made in Amethi' AK-203s to give security forces edge in fight against terror: PM Modi | India News - Times of India". The Times of India. Ist. 3 March 2019. Retrieved 9 July 2019.
- "Govt signs mega Rs 700-crore deal to buy 72,000 modern rifles for Indian Army". India Today. 12 February 2019. Retrieved 9 July 2019.
- "Indian Army gets new American assault rifles in Kashmir Valley against terrorists, Pakistan Army on LoC". Asian News International. 11 December 2019. Retrieved 11 December 2019 – via The Economic Times.
- http://idrw.org/indian-army-to-place-orders-for-caracals-car-816-close-quarter-carbine-soon/. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - Nitin Gokhale (28 November 2012). "Re-arming the Indian Army's troops with lethal, modern weapons". NDTV.com. Retrieved 4 April 2016.
- "Army goes for urgent buy of sniper rifles | India News - Times of India". The Times of India. 12 January 2019. Retrieved 1 August 2019.
- https://iwi.net/16479-light-machine-guns-for-frontline-troops/ Missing or empty
|title=(help) - https://www.dailyo.in/politics/para-special-forces-arms-deal-with-usa-american-assault-rifles-ministry-of-defence-indian-army/story/1/30043.html. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - Jones, Richard D. Jane's Infantry Weapons 2009/2010. Jane's Information Group; 35 edition (27 January 2009). ISBN 978-0-7106-2869-5.
- Mohar, Vijay. "Army orders 1 million pieces of grenade developed by DRDO's Chandigarh lab". Tribuneindia.com. Retrieved 11 August 2013.
- "Ordnance Factory Board". Retrieved 4 April 2016.
- http://164.100.119.31/sites/default/files/pdf/Vol.7%20No.5%20October%201999.pdf%5B%5D
- "Tata Motors rolls out 1,500th Safari Storme SUV for Army". 25 August 2018.
- "Tata Safari Storme joins the Indian Armed forces' fleet". India Today. 27 April 2017. Retrieved 27 April 2017.
- "On new wheels: Army to replace Maruti Gypsy with Tata Safari Storme". 23 December 2016.
- Sandeep Singh (8 December 2014). "Maruti Gypsy gets repeat order from Army, 4,200 this time". The Indian Express. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- "Force Motors Bags Light Strike Vehicles' Order From The Indian Army". 10 May 2018.
- "Force Motors to supply Light Strike Vehicles to Indian Army". 10 May 2018.
- http://www.tatamotors.com/press/tata-motors-bags-additional-order-for-619-nos-of-6-x-6-high-mobility-vehicles-from-indian-army/
- "No complaints against Tatra trucks: Defence Ministry". M.ibnlive.com. Retrieved 21 April 2012.
- http://www.moneycontrol.com/news/business/companies/new-defence-orders-to-be-executed-over-2-years-ashok-leyland-1026357.html
- "Mitsubishi Pajero SUV makes it debut as an Indian Army vehicle in Sikkim!". IndianCarsBikes.in. 28 September 2011. Retrieved 21 April 2012.
- "Sarvatra Bridging System [www.bharat-rakshak.com]". Bharat-rakshak.com. Archived from the original on 4 November 2012. Retrieved 23 August 2013.
- "BHARAT RAKSHAK MONITOR - Volume 4(5)". Bharat-rakshak.com. Retrieved 2013-08-23.
- Mat-Fording Archived 19 December 2012 at the Wayback Machine
- "Armoured Vehicle Tracked Light Repair". DefenceTalk.com. Archived from the original on 14 June 2012. Retrieved 14 June 2012.
- "More Armored Recovery Vehicles for Indian Army". Defensenews.com. Archived from the original on 29 July 2012. Retrieved 21 April 2012.
- John Pike. "Casspir". Globalsecurity.org. Retrieved 21 April 2012.
- "Indian Tarmour Tracked Heavy Armoured Personnel Carrier". TankNutDave.com. Retrieved 4 April 2016.
- "Welcome to Frontline : Vol. 29 :: No. 08". Hinduonnet.com. Archived from the original on 9 October 2009. Retrieved 21 April 2012.
- "FASTER, LIGHTER, DRDO'S DAKSH NOW HAS CBRN DETECTION MECHANISM". INDIANDEFENSE NEWS. INDIANDEFENSE NEWS. 26 September 2015.
- "Army Decides to Take 124 More MBT Arjun Mk1" (Press release). Government of India – Press Information Bureau. 17 May 2010.
- "Main Battle Tank Arjun". 24 April 2015.
Out of total indented quantity of 124 Nos., 122 MBT Arjun Mk-I have been produced and inducted into Army
- "Arjun Mk II Tank Clears All Army Trials Service Next Year - SP's Land Forces". Retrieved 4 April 2016.
- "Defence ministry scraps Rs 6000cr tender for purchase of 197 helicopters". The Times of India. 29 August 2014. Retrieved 29 August 2014.
- Nair-Ghaswalla, Amrita (24 October 2016). "Catherine cameras an integral part of Army's T-90 main battle tanks". The Hindu Business Line. Retrieved 27 October 2016.
- "Armor: The Frugal T-90". Strategypage.com. 4 October 2008. Retrieved 7 February 2010.
- "464 Bhishma tanks to made in Tamil Nadu's Avadi". 8 November 2019.
- "Indian MoD awards OFB USD2.8 billion contract to licence-build 464 additional T-90S MBTs". 11 November 2019.
- "Defence News - Army Opts For T-90s Battle Tanks". Defencenews.in. Archived from the original on 24 July 2013. Retrieved 23 August 2013.
- "T-72M1 Main Battle Tank". Bharat Rakshak. Archived from the original on 6 June 2009. Retrieved 14 June 2012.
- "Indian Army issues fresh RFI for Future Ready Combat Vehicle". Jane's 360. Retrieved 8 November 2017.
- "Shortfall of BMP infantry fighting vehicles affecting operational preparedness of Army: CAG". The Indian Express. 19 December 2015. Retrieved 28 October 2016.
- "Land Forces Site – BMP-2". Bharat Rakshak. 20 February 2002. Archived from the original on 7 October 2012. Retrieved 2012-04-21.
- Indian Army to Upgrade its BMP-2/2K Infantry Combat Vehicles to BMP-2M Standard - Deagel.com, 6 May 2013
- "PRODUCTION OF INFANTRY COMBAT VEHICLE WILL START SIX YEARS FROM NOW: TATA MOTORS". Indiandenfensenews. INDIANDEFENSE NEWS. 9 March 2016.
- "AAT vehicle documents handed over to DGQA". The New Indian Express. Retrieved 21 August 2017.
- "Army inducts DRDO-developed NBC recce vehicle". The Times of India. 4 July 2009.
- "Mahindra Rakshak". Bharat Rakshak. Archived from the original on 7 April 2013. Retrieved 5 August 2012.
- "'Rakshak' saved soldiers' lives: Mahindra". The Economic Times. 6 April 2008. Retrieved 5 August 2012.
- "Mahindra says 'Rakshak' saved soldiers' lives". Deccan Herald. Archived from the original on 26 December 2013. Retrieved 5 August 2012.
- "Gun Carriage Factory hands over 3 'Dhanush' guns to Army". The Hindu. 17 July 2016. ISSN 0971-751X. Retrieved 5 October 2016.
- India, Press Trust of (12 January 2017). "Ordering of 155/52 self-propelled gun in final stages: Parrikar". Business Standard India. Retrieved 20 January 2017.
- "6 Dhanush artillery guns handed over to Army; 1st lot of 114-piece order". 8 April 2019.
- "OFB Gets Bulk Production Clearance for 'Dhanush' Artillery Gun". 19 February 2019.
- Peri, Dinakar (25 August 2018). "Helicopter deals among ₹ 46,000 crore worth approvals by Defence Acquisition Council". The Hindu.
- "BAE SYSTEMS TO SHOWCASE MAKE IN INDIA M777 HOWITZERS AT DEFEXPO". 28 January 2020.
To date, BAE Systems has produced and delivered 25 guns to the Indian Army, with another 70-plus planned for 2020.
- "3 Decades After Bofors, Indian Army Gets First Artillery Guns From US". NDTV. 18 May 2017. Retrieved 18 May 2017.
- "Murky Competitions for Indian Howitzer Orders May End Soon… Or Not". Retrieved 21 February 2013.
- "In a first, pvt Indian firms can bid to make artillery guns". The Indian Express. 12 April 2013. Retrieved 13 May 2013.
- "Indian Army and its old Weapons and Equipments". Pakistan Defence. Retrieved 4 April 2016.
- "Defence Ministry signs Rs 200 crore contract to upgun 130 mm howitzers". India Today. Retrieved 18 October 2018.
- "MoD concludes deal with L&T for K9 Vajra-T Howitzers — Defence Update | Defence Update". www.defenceupdate.in. Archived from the original on 28 October 2016. Retrieved 27 October 2016.
- "India's acquisition of 100 K9 SPHs approved | IHS Jane's 360". www.janes.com. Archived from the original on 30 April 2017. Retrieved 31 March 2017.
- "Tata, L&T bag orders for Pinaka rocket launcher". Indianexpress.com. 3 April 2006. Archived from the original on 17 December 2007. Retrieved 21 April 2012.
- "Pinaka Rockets". PIB, Govt of India. Retrieved 6 December 2014.
- "BDL test fires missile advanced wireless anti-tank missile". DefenceNews. TNN. 3 April 2016. Archived from the original on 6 April 2016.
- "Indian Army to Purchase 4100 Milan 2T Anti Tank Guided Missiles in USD 120 million Deal". IndiaDefence. 26 January 2009. Archived from the original on 17 January 2016. Retrieved 14 December 2009.
- "Press Information Bureau English Releases". Pib.nic.in. Retrieved 23 August 2013.
- "India to buy Russia's Konkurs-M, Invar guided missiles - News - Economy - The Voice of Russia: News, Breaking news, Politics, Economics, Business, Russia, International current events, Expert opinion, podcasts, Video". The Voice of Russia. 8 November 2012. Retrieved 23 August 2013.
- TNN 19 October 2012, 03.05AM IST (19 October 2012). "Govt nod for purchase of 25,000 Invar, air-launched version of BrahMos missiles - Times Of India". Articles.timesofindia.indiatimes.com. Retrieved 23 August 2013.
- Report of the Comptroller and Auditor General of India, for the year ended March 2015 (PDF). Comptroller and Auditor General of India. 2016. p. 136.
- "Army set to get its first consignment of Spike anti-tank guided missiles under emergency purchases | India News". www.timesnownews.com. Retrieved 20 April 2019.
- "UCAV GHATAK PROJECT AWAITS PMO'S NOD". INDIANDEFENSE NEWS. INDIANDEFENSE NEWS. 30 March 2016.
- Agni-V
- Diplomat, Franz-Stefan Gady, The. "India and Russia Ink S-400 Missile Air Defense System Deal". The Diplomat. Retrieved 27 October 2016.
- Bhat, Aditya. "India clears deal; army to acquire air defence systems from Israel soon". International Business Times, India Edition. Archived from the original on 24 February 2017. Retrieved 24 February 2017.
- "INDIAN ARMY INDUCTS HOME-GROWN AKASH WEAPON SYSTEM". INDIAN ARMY INDUCTS HOME-GROWN AKASH WEAPON SYSTEM. INDIAN ARMY INDUCTS HOME-GROWN AKASH WEAPON SYSTEM. 5 May 2015.
- "More Akash Systems for Army".
- "Quick Reaction Missile to be developed by BDL and DRDO".
- India buys $400M worth of Russian missile systems — Source
- "Trade Registers". armstrade.sipri.org. Retrieved 12 May 2017.
- "India Orders 245 Raytheon Stinger Air-to-Air Missiles From US". Defencenews. Defencenews. 2 April 2016. Archived from the original on 4 April 2016. Retrieved 2 April 2016.
- Flightglobal - World Air Forces 2015 (PDF), Flightglobal.com
- "India, US sign contract for additional Apache attack choppers". The Economic Times. 25 February 2020. Retrieved 26 February 2020.
- "Arun Jaitley inaugurates manufacture of light combat helicopter at HAL". 27 August 2017. Retrieved 21 December 2017.
- "HAL gets order for 15 Light Combat Helicopters". 22 December 2017. Retrieved 25 December 2017.
- "HAL'S LCH PASSES ROCKET TRIALS". INDIANDEFENSE NEWS. INDIANDEFENSE NEWS. 16 March 2016.
- "Army boosting combat fighting capabilities with major inductions of indigenous helicopters". The New Indian Express. Retrieved 1 March 2020.
- "MAKE IN INDIA: RUSSIA WANTS CO-PRODUCTION OF KA-226 CHOPPERS TO START AS SOON AS POSSIBLE". INDIANDEFENSE NEWS. INDIANDEFENSE NEWS. 29 August 2015.
- "India's Light Utility Helicopter has maiden flight". FLIGHTGLOBAL.COM. FLIGHTGLOBAL.COM. 7 September 2016.
- https://www.debka.com/mivzak/indian-air-force-buys-another-54-israeli-harop-drones/
- "Indian Army FRCV RFI" (PDF).
- Business Standard. "155-mm gun contract: DRDO enters the fray". Business-standard.com. Retrieved 21 April 2012.
- the hindu businessline. "Nalanda Ordnance Factory Board developing indigenous artillery shells". the hindu.com. Retrieved 13 May 2012.
- "Indian OFB soon to deliver artillery guns for user trials". Army Technology. Retrieved 23 August 2013.
- "DRDO to display sub-machine carbine at Defexpo 2010". Defenseworld.net. Archived from the original on 23 July 2011. Retrieved 21 April 2012.
- "Indian Army Looking For A Deadlier Sniper Rifle To Replace Ageing Draganov". Indiatimes. 8 December 2016.
- Gurung, Shaurya Karanbir (13 July 2018). "Army gets the first lot of 7,500 hi-tech helmets". The Economic Times. Retrieved 9 July 2019.
- "Army soldiers get 1.86 lakh new bulletproof jackets after 9-year wait". India Today. 9 April 2018. Retrieved 9 July 2019.
- "Indian Army tender for 197 Eurocopter Fennec helicopters Scrapped". Indiaenews.com. 6 December 2007. Retrieved 21 April 2012.
- Eurocopter wins big Indian Army deal Archived 15 June 2007 at the Wayback Machine
- Shenoy, Ramnath. "India to test fly light combat helicopters shortly". Press Trust of India, 14 December 2009. Retrieved 4 January 2010. Archived 18 December 2009 at the Wayback Machine
- "For First Time, Army To Get Its Own Attack Helicopters, Boeing Apaches". NDTV. Retrieved 17 August 2017.
- Archived 24 August 2017 at the Wayback Machine. Defense News