LGBT rights in the United Kingdom
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) rights in the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland have evolved dramatically over time.
 Location of the United Kingdom | |
| Status | Always legal for women; decriminalised for men in: 1967 (England and Wales) 1981 (Scotland) 1982 (Northern Ireland) Age of consent equalised in 2001 (and reduced to 16 years in Northern Ireland in line with the rest of the UK in 2009) |
| Gender identity | Right to change legal gender since 2005 |
| Military | Allowed to serve openly since 2000 |
| Discrimination protections | Sexual orientation and gender identity protections since 2010 |
| Family rights | |
| Recognition of relationships | Same-sex marriage since 2014 (England and Wales; Scotland) Same-sex marriage in Northern Ireland since 2020[1] Civil partnerships since 2005 (nationwide) |
| Adoption | Joint and stepchild adoption since 2005 (England and Wales) 2009 (Scotland) 2013 (Northern Ireland) |
Before and during the formation of the United Kingdom, Christianity and homosexuality clashed. Same-sex sexual activity was characterised as "sinful" and, under the Buggery Act 1533, was outlawed and punishable by death. LGBT rights first came to prominence following the decriminalisation of sexual activity between men, in 1967 in England and Wales, and later in Scotland and Northern Ireland. Sexual activity between women was never subject to the same legal restriction.
Since the turn of the 21st century, LGBT rights have increasingly strengthened in support. Some discrimination protections had existed for LGBT people since 1999, but were extended to all areas under the Equality Act 2010. In 2016, Her Majesty's Armed Forces removed its ban on LGBT individuals serving openly with the Armed Forces Act 2016,[2] though it had adopted a policy of non-enforcement in 2000. The age of consent was equalised, regardless of sexual orientation, in 2001 at 16 in England, Scotland and Wales. The age of consent was lowered to 16 in Northern Ireland in 2009, previously it was 17 regardless of sexual orientation. Transgender people have had the right to change their legal gender since 2005. The same year, same-sex couples were granted the right to enter into a civil partnership, a similar legal structure to marriage, and also to adopt in England and Wales. Scotland later followed on adoption rights for same-sex couples in 2009, and Northern Ireland in 2013. Same-sex marriage was legalised in England and Wales, and Scotland in 2014,[3] and in Northern Ireland in 2020.[4][5]
Today, LGBT citizens have most of the same legal rights as non-LGBT citizens and the UK provides one of the highest degrees of liberty in the world for its LGBT communities. In ILGA-Europe's 2015 review of LGBTI rights, the UK received the highest score in Europe, with 86% progress toward "respect of human rights and full equality" for LGBT people and 92% in Scotland alone.[6] Recent polls have indicated that a majority of British people support same-sex marriage,[7] and 76% of the UK agreed that homosexuality should be accepted by society, according to a 2013 Pew Research Center poll.[8] Additionally, the UK currently holds the world record for having the most out LGBTI people in Parliament with 45 out LGBTI MPs elected at the 2019 election.[9][10]
A 2010 Integrated Household Survey estimated 1.5% of people in the UK identify themselves as gay, lesbian or bisexual – far lower than previous estimates of 5–7%.[11] Interpreting the statistics, an Office for National Statistics (ONS) spokesperson said, "Someone may engage in sexual behaviour with someone of the same sex but still not perceive themselves as gay."[12] According to YouGov, however, studies such as that of the Integrated Household Survey underestimate the true proportion of the population that is LGBT as they use a face-to-face methodology, and non-heterosexual people are less willing to disclose their sexual orientation to an interviewer.[13] YouGov itself estimates, based on its panel, which was inquired via an online questionnaire, that the proportion of LGBT people in the UK is 7%.[14] It is also estimated that the trans population of the UK is between 300,000 and 500,000 people,[15] but Stonewall concludes that it is hard to define the LGBT population of the UK because some LGBT people are not out.[16] LGBT rights organisations and very large LGBT communities have been built across the UK, most notably in Brighton, which is widely regarded as the UK's unofficial "gay capital", with other large communities in London, Manchester, Birmingham, Bristol, Leeds, Liverpool, Newcastle upon Tyne, Edinburgh and Southampton which all have gay villages and host annual pride festivals.
Same-sex sexual activity
Homosexuality as an offence
English law identified anal sex as an offence punishable by hanging as a result of the Buggery Act 1533, which was pioneered by Henry VIII. The Act was the country's first civil sodomy law, such offences having previously been dealt with by the ecclesiastical courts. While it was repealed in 1553 on the accession of Mary I, it was re-enacted in 1563 under Elizabeth I. James Pratt and John Smith were the last two to be executed for sodomy in 1835.[17]
Although section 61 of the Offences Against the Person Act 1861 removed the death penalty for homosexuality, male homosexual acts remained illegal and were punishable by imprisonment. The Labouchere Amendment, section 11 of the Criminal Law Amendment Act 1885, extended the laws regarding homosexuality to include any kind of sexual activity between males. Oscar Wilde was convicted under this law and sentenced to 2 years of penal labour. Conversely, lesbians were never acknowledged or targeted by legislation.[18]
In Scotland, although there were no statutes making sex between men unlawful between 1424 and 1707,[19] homosexual acts were punishable. One example is the commission for trial of Gavin Bell.[20]
In the early 1950s, the police actively enforced laws prohibiting sexual behaviour between men. By the end of 1954, there were 1,069 gay men in prison in England and Wales, with an average age of 37.[21] There were a number of high-profile arrests and trials, including that of scientist, mathematician, and war-time code-breaker Alan Turing, convicted in 1952 of "gross indecency". He accepted treatment with female hormones (chemical castration) as an alternative to prison. Turing committed suicide in 1954. Former Prime Minister Gordon Brown, in response to a petition, issued an apology on behalf of the British Government in 2009 for "the appalling way he was treated".[22][23] In 1954, the trial and eventual imprisonment of Edward Montagu (the 3rd Baron Montagu of Beaulieu), Michael Pitt-Rivers and Peter Wildeblood for committing acts of "homosexual indecency" caused uproar and led to the establishment of a committee to examine and report on the law covering "homosexual offences" appointed by Sir David Maxwell Fyfe and Sir Hugh Lucas-Tooth.
Wolfenden
The Wolfenden Committee was set up on 24 August 1954 to consider UK law relating to "homosexual offences"; the Report of the Departmental Committee on Homosexual Offences and Prostitution (better known as the Wolfenden report) was published on 3 September 1957. It recommended that "homosexual behaviour between consenting adults in private should no longer be a criminal offence", finding that "homosexuality cannot legitimately be regarded as a disease, because in many cases it is the only symptom and is compatible with full mental health in other respects."[24]
In October 1957, the Archbishop of Canterbury, Geoffrey Fisher, spoke in support of the Wolfenden Report, saying that "There is a sacred realm of privacy... into which the law, generally speaking, must not intrude. This is a principle of the utmost importance for the preservation of human freedom, self-respect, and responsibility." The first parliamentary debate on the Wolfenden Report was initiated on 4 December 1957 by Lord Pakenham. Of the seventeen peers who spoke in the debate, eight broadly supported the recommendations in the Wolfenden Report. Maxwell Fyfe, by then ennobled as Lord Kilmuir and serving as Lord Chancellor, speaking for the Government, doubted that there would be much public support for implementing the recommendations and stated that further research was required. The Homosexual Law Reform Society was founded on 12 May 1958, mainly to campaign for the implementation of the Wolfenden Committee's recommendations.[25]
Decriminalisation of homosexual acts
In 1965, Conservative peer Lord Arran proposed the decriminalisation of male homosexual acts (lesbian acts had never been illegal) in the House of Lords. This was followed by Humphry Berkeley in the House of Commons a year later, though Berkeley ascribed his defeat in the 1966 general election to the unpopularity of this action. However, in the newly elected Parliament, Labour MP Leo Abse took up the issue and the Sexual Offences Bill was put before Parliament in order to implement some of the Wolfenden Committee's recommendations after almost ten years of campaigning.[26]
The Sexual Offences Act 1967 (Welsh: Deddf Troseddau Rhywiol 1967; Scottish Gaelic: Achd Eucoirean Feise 1967) was accordingly passed and received royal assent on 27 July 1967 after an intense late-night debate in the House of Commons. It maintained general prohibitions on buggery and indecency between men, but provided for a limited decriminalisation of homosexual acts where three conditions were fulfilled: 1) the act had to be consensual, 2) the act had to take place in private and 3) the act could involve only people that had attained the age of 21. This was a higher age of consent than that for heterosexual acts, which was set at 16. Further, "in private" limited participation in an act to two people. This condition was interpreted strictly by the courts, which took it to exclude acts taking place in a room in a hotel, for example, and in private homes where a third person was present (even if that person was in a different room). These restrictions were overturned by the European Court of Human Rights in 2000.[21]
The 1967 Act extended only to England and Wales. Organisations therefore continued to campaign for the goal of full equality in Scotland and Northern Ireland where all homosexual behaviour remained illegal. Same-sex sexual activities were legalised in Scotland on the same basis as in the 1967 Act, by section 80 of the Criminal Justice (Scotland) Act 1980, which came into force on 1 February 1981.[27] An analogous amendment was also made to the law of Northern Ireland, following the determination of a case by the European Court of Human Rights (see Dudgeon v. United Kingdom); the relevant legislation was an Order in Council, the Homosexual Offences (Northern Ireland) Order 1982,[28] which came into force on 8 December 1982.
Equal age of consent
In 1979, the Home Office Policy Advisory Committee's Working Party report, "Age of Consent in Relation to Sexual Offences", recommended that the age of consent for same-sex sexual activities be reduced from 21 to 18, but no such legislation was enacted as a result.
In February 1994, Parliament considered reform of the law on rape and other sexual offences during the passage of the Criminal Justice and Public Order Bill. Conservative MP Edwina Currie proposed an amendment to equalise the age of consent of same-sex sexual activities to 16. Currie's amendment was defeated by 307 votes to 280. Those who supported it included Tony Blair,[29] John Smith, Neil Kinnock, Paddy Ashdown and William Hague. Those against included David Blunkett and Ann Taylor. There were angry scenes outside the Palace of Westminster at the defeat of the amendment, when those involved in a demonstration organised by the group OutRage! clashed with police. Another amendment proposed by Sir Anthony Durant suggested lowering the age of consent to 18, which passed by 427 votes to 162, and supporters included Michael Howard and John Major. It was opposed by such MPs as John Redwood, Michael Heseltine and John Gummer. An amendment proposed by Simon Hughes which was intended to equalise the age of consent for homosexuals and heterosexuals to 17 was not voted upon. The bill as a whole was given a second reading in the Lords by 290 votes to 247. Lord Longford then sought to reintroduce 21 as the minimum age in the Lords, but this was defeated by 176 votes to 113. An amendment by the Deputy Labour Leader in the House of Lords, Lord MacIntosh of Haringey, that would have equalised the age of consent to 16, was rejected by 245 votes to 71.
In its decision of 1 July 1997, in the case of Sutherland v. United Kingdom, the European Commission of Human Rights found that Articles 8 and 14 of the European Convention on Human Rights were violated by a discriminatory age of consent, on the ground that there was no objective and reasonable justification for maintaining a higher minimum age for male homosexual acts. On 13 October 1997, the Government submitted to the European Court of Human Rights that it would propose a bill to Parliament for a reduction of the age of consent for homosexual acts from 18 to 16. On 22 June 1998, the Crime and Disorder Bill was put before Parliament. Ann Keen proposed amendments to lower the age of consent to 16. The House of Commons accepted these provisions with a majority of 207, but they were rejected by the House of Lords with a majority of 168. Subsequently, the Sexual Offences (Amendment) Bill was introduced on 16 December 1998 and, again, the equalisation of the age of consent was endorsed on 25 January 1999 by the House of Commons, but was rejected on 14 April 1999 by the House of Lords. Those campaigning against the amendment claimed they were simply acting to protect children. Baroness Young, the leader of the campaign against the amendment, said, "Homosexual practices carry great health risks to young people."
The Government reintroduced the bill in 1999. With the prospect of it being passed by the Commons in two successive sessions of Parliament, the Parliament Acts 1911 and 1949 were available to enact the bill should the Lords have rejected it a third time. The Lords passed the bill at second reading, but made an amendment during committee stage to maintain the age of consent for buggery at 18 for both sexes. However, as the bill had not completed its passage through the Lords at the end of the parliamentary session on 30 November 2000, then Speaker of the House of Commons Michael Martin certified that the procedure specified by the Parliament Acts had been complied with. The bill received royal assent a few hours later, and was enacted as the Sexual Offences (Amendment) Act 2000. The provisions of the Act came into force throughout the UK on 8 January 2001, lowering the age of consent to 16.[30] This Act also introduced, for the first time, an age of consent for lesbian sexual acts, as previously there had been no legislation concerning this.[31]
On 1 May 2004, the Sexual Offences Act 2003 entered into force, which swept away all of the previous sex-specific legislation, including the 1967 Act, and introduced instead neutral offences. Thus, the previous conditions relating to privacy were removed, and sexual acts were viewed by the law without regard to the sex of the participants.
With the passage of the Sexual Offences (Northern Ireland) Order 2008, Northern Ireland, which had an age of consent of 17 regardless of one's sexual orientation, lowered the age to 16 in 2009 so it would match that of England, Wales, and Scotland.[32][33][34]
Annulment of convictions
On 31 January 2017, the Policing and Crime Act 2017 went into effect after being given royal assent. A section of the Act known as the "Alan Turing law" officially gave posthumous pardons to the thousands of homosexual men from England and Wales who had been convicted under those regions' old sodomy laws, and gave those still living the possibility to apply to have their conviction erased. Disregards have been available since 2012, removing the conviction from the person's criminal records.[35] Scotland passed a more comprehensive law in June 2018, with pardons being automatic for those still living.[36] The Northern Ireland Assembly passed a similar law in 2016, with it taking effect on 28 June 2018.[37] Applications for pardons must be made with the Northern Irish Department of Justice.
According to PinkNews, fewer than 200 pardons had been issued in England and Wales by July 2018.[38]
In June 2019, it was revealed that only two men had sought pardons for historic gay sex offences in Northern Ireland and that they both failed to have their convictions overturned. Across the UK, over half of those who applied for a pardon did not have their convictions overturned.[39]
Merchant shipping repeal
In April 2017, the Parliament of the United Kingdom unanimously passed the Merchant Shipping (Homosexual Conduct) Act 2017.[40] This private member's bill was drafted by Conservative MP John Glen. It repealed sections 146(4) and 147(3) of the Criminal Justice and Public Order Act 1994, which was labelled as the UK's "last anti-gay law". It went into effect immediately after royal assent.[41][42][43]
Alan Turing
In May 2020, it was reported by Gay Star News a sculpture or statue to honour posthumously famous gay code-breaker during World War II hero Alan Turing by one of the foremost sculptors by quoting - “threatens the historic landscape of King's College, Cambridge”. That is according to Historic England, which is responsible for protecting many historic buildings and monuments throughout England.[44]
Recognition of same-sex relationships
Civil partnership
There was no legal recognition of same-sex relationships in Britain until 2005, following the legalisation of civil partnerships under the passage of the Civil Partnership Act (Welsh: Deddf Partneriaeth Sifil 2004; Scottish Gaelic: Achd Com-pàirteachasan Sìobhalta 2004) on 18 November 2004. Civil partnerships are a separate union which give most (but not all) of the rights and responsibilities of civil marriage, but there are recognition issues in other countries and with the use of courtesy titles. Civil partnerships can take place on any approved premise in the UK and in approved religious venues in England and Wales since 2011 (though religious venues are not compelled), but cannot include religious readings, music or symbols.[45][46] The Civil Partnership Act came into effect on 5 December 2005.
The first civil partnership ceremony took place at 11:00 (GMT) on 5 December 2005 between Matthew Roche and Christopher Cramp at St Barnabas Hospice, Worthing, West Sussex.[47] The usual 14-day waiting period was waived as Roche was suffering from a terminal illness. He died the next day.[48] The first civil partnership ceremonies after the statutory waiting period then took place in Northern Ireland on 19 December, with ceremonies following the next day in Scotland and the day after that in England and Wales.
Same-sex marriage

Same-sex marriage in the United Kingdom has been the subject of wide debate since the decriminalisation of homosexuality in Britain. Previous legislation in England and Wales had prevented same-sex marriage, including the Marriage Act 1949 which defined marriage as between a man and a woman, the Nullity of Marriage Act 1971 which explicitly banned same-sex marriages, and the Matrimonial Causes Act 1973 which reiterated the provisions of the Nullity of Marriage Act.
While civil partnerships were established nationwide, marriage law is a devolved matter in the United Kingdom and therefore the legislative procedure of same-sex marriage differs by jurisdiction. The Marriage (Same Sex Couples) Act 2013, which allows same-sex marriage in England and Wales, was passed by the UK Parliament in July 2013 and came into force on 13 March 2014, with the first same-sex marriages taking place on 29 March 2014.[49][50][51] The Marriage and Civil Partnership (Scotland) Act 2014, allowing same-sex marriage in Scotland, was passed by the Scottish Parliament in February 2014 and came into effect on 16 December 2014.[52][53]
Same-sex marriages in the UK give all the rights and responsibilities of civil marriage and can be performed on approved premises. This also includes religious venues, providing the religious or belief body has opted-in. However, no religious or belief body is compelled to perform same-sex marriages; the Church of England and the Church in Wales are explicitly banned from doing so. For the purposes of the divorce of a same-sex marriage, the common law definition of adultery remains as sexual intercourse between a man and a woman only, although infidelity with a person of the same sex can be grounds for a divorce as "unreasonable behaviour."[54] Non-consummation is also excluded as a ground for the annulment of a same-sex marriage.[54]
Between 2012 and 2015, the Northern Ireland Assembly voted five times on same-sex marriage, and although it was passed by a slim majority on the fifth attempt, it was vetoed by the Democratic Unionist Party using the petition of concern.[55] Following the inconclusive 2017 Northern Ireland Assembly election and failure to form a Northern Ireland Executive by the deadline of 21 October 2019, provisions in the Northern Ireland (Executive Formation etc) Act 2019, which was passed by the UK Parliament on 18 July 2019 and received royal assent on 24 July, mandated the Secretary of State for Northern Ireland to pass regulations legalising same-sex marriage by 13 January 2020.[56] The Secretary of State, Julian Smith signed the regulations on 19 December 2019.[57] Same-sex marriage therefore became legal in Northern Ireland on 13 January 2020, with couples free to register their intent to marry and couples who had previously married elsewhere having their unions recognised from that date.[58][59] The first same-sex marriage ceremony took place in Carrickfergus on 11 February 2020.[60]
Adoption and family planning
Under the Adoption and Children Act 2002, Parliament provided that an application to adopt a child in England and Wales could be made by either a single person or a couple. The previous condition that the couple be married was dropped, thus allowing a same-sex couple to apply. The Lords rejected the proposal on one occasion before it was passed. Supporters of the move in Parliament stressed that adoption was not a "gay rights" issue but one of providing as many children as possible with a stable family environment rather than seeing them kept in care. Opponents raised doubts over the stability of relationships outside marriage, and how instability would impact on the welfare of adopted children. However, the law was successfully passed and went into effect on 30 December 2005.[61][62] Similar legislation was adopted in Scotland, which came into effect on 28 September 2009.[63][64] Northern Ireland followed suit in December 2013.[65]
The Human Fertilisation and Embryology Act 2008 was given royal assent on 13 November 2008.[66][67] The legislation allows for lesbians and their partners (both civil and de facto) equal access to legal presumptions of parentage in cases of in vitro fertilisation (IVF) or assisted/self insemination (other than at home) from the moment the child is born. The law also allows both partners to be identified on the child's birth certificate by the words "parent". [68] The law came into force on 6 April 2009 and is not retroactive (it does not apply before that date).[69] Parental orders for gay men and their partners since 6 April 2010 have been available for surrogacy arrangements.[70]
Since 31 August 2009, legislation granting lesbians equal birth rights in England and Wales came into effect, meaning both can now be named on a child's birth certificate, amending the Registration of Births and Deaths Regulations 1987.[71][72][73] The legislation was criticised by those who believe it was "damaging the traditional notion of a family".[74] Stonewall Head of Policy and Research Ruth Hunt said the new law makes life easier for lesbian families and stated "Now lesbian couples in the UK who make a considered decision to start a loving family will finally be afforded equal access to services they help fund as taxpayers".[75] Home Office Minister Lord Brett was full of praise in his comments:
This positive change means that, for the first time, female couples who have a child using fertility treatment have the same rights as their heterosexual counterparts to be shown as parents in the birth registration. It is vital that we afford equality wherever we can in society, especially as family circumstances continue to change. This is an important step forward in that process.[73][74]
Iain Duncan Smith, who led efforts to oppose the change, said that "The absence of fathers generally has a detrimental effect on the child."[76]
In 2016, 9.6% of all adoptions in England involved same-sex couples. This was an increase from 8.4% the previous year.[77] In 2018, about 450 of the 3,820 adoptions (about 12%) in England involved same-sex couples.
Transgender rights
In December 2002, the Lord Chancellor's office published a "Government Policy Concerning Transsexual People" document that categorically states that transsexualism "is not a mental illness."[78]
Since 4 April 2005, as per the Gender Recognition Act 2004 (Welsh: Deddf Cydnabod Rhywedd 2004; Scottish Gaelic: Achd Aithneachadh Gnè 2004), it has been possible for transgender people to change their legal gender in the UK, allowing them to acquire a new birth certificate, affording them full recognition of their acquired sex in law for all purposes. Transgender people must present evidence to a Gender Recognition Panel, which considers their case and issues a Gender Recognition Certificate (GRC); they must have transitioned two years before a GRC is issued. It is not a requirement for sex reassignment surgery to have taken place, although such surgery will be accepted as part of the supporting evidence for a case where it has taken place. There is formal approval of medical gender reassignment available either on the National Health Service (NHS) or privately.
However, there have been concerns regarding marriages and civil partnerships. Under the Gender Recognition Act 2004, transgender people who are married have been required to divorce or annul their marriage in order for them to be issued with a GRC. The Government chose to retain this requirement in the Act as effectively it would have legalised a small category of same-sex marriages. The Civil Partnership Act 2004 allowed the creation of civil partnerships between same-sex couples, but a married couple that includes a transgender partner cannot simply re-register their new status. They must first have their marriage dissolved, gain legal recognition of the new gender and then register for a civil partnership. This is like any divorce with the associated paperwork and costs.
With the legalisation of same-sex marriage in England and Wales, existing marriages will continue where one or both parties change their legal gender and both parties wish to remain married. The legislation also does not restore any of the marriages of transgender people that were forcibly annulled as a precondition for them securing a GRC and states that a GRC will not be issued unless the spouse of the transgender person has consented. If the spouse does not consent, the marriage must be terminated before a GRC may be issued.[79]
Intersex rights
Intersex people in the United Kingdom face significant gaps, particularly in protection from non-consensual medical interventions, and protection from discrimination. Actions by intersex organisations aim to eliminate unnecessary medical interventions and harmful practices, promote social acceptance, and equality in line with Council of Europe and United Nations demands.[80][81]
Discrimination protections
Regulations were introduced for discrimination protections on sexual orientation in employment on 1 December 2003, following the adoption of an EC Directive in 2000, providing for the prohibition of discrimination in employment on the grounds of sexual orientation.[82] The Sex Discrimination (Gender Reassignment) Regulations 1999 created certain legal protections for transgender people for the first time in British history. The Regulations banned discrimination against individuals undergoing "gender reassignment" in employment and vocational training. Similar legislation, the Sex Discrimination (Gender Reassignment) Regulations (Northern Ireland) 1999, was passed in Northern Ireland. The Sex Discrimination (Amendment of Legislation) Regulations 2008 extended these protections to cover discrimination in goods, facilities and services
On 30 April 2007, the Sexual Orientation Regulations came into force, following the introduction of similar provisions in Northern Ireland in January 2007. They provided a general prohibition of discrimination in the provision of goods and services on the grounds of sexual orientation. Similar legislation had long previously been in force in respect of discrimination on the grounds of sex, race, disability and marital status. The introduction of the Regulations was controversial and a dispute arose between the Government and the Roman Catholic Church in England and Wales over exemptions for Catholic adoption agencies.[83]
Archbishop Vincent Nichols of Birmingham declared his opposition to the Act, saying that the legislation contradicted the Catholic Church's moral values. Several Catholic adoption agencies requested exemption from sexual orientation regulations, and the adoption charity Catholic Care obtained a judgement on 17 March 2010 instructing the Charity Commission to reconsider its case.[84] The Charity Commission again found no grounds to make an exception for Catholic Care, a decision upheld on appeal.[85] In August 2011, the Upper Tribunal agreed to hear the charity's fourth appeal in the case.[86] In November 2012, the appeal was dismissed by the Upper Tribunal, with the Tribunal ruling in favour of the Charity Commission. Catholic Care stated its intention to appeal the judgement.[87]
In October 2007, the Government announced that it would seek to introduce an amendment to the Criminal Justice and Immigration Act to create a new offence of incitement to hatred on the grounds of sexual orientation.[88] This followed the creation of an offence on religious hatred that had proved controversial in 2006 (see Racial and Religious Hatred Act 2006). Incitement to hatred on the grounds of sexual orientation was already illegal in Northern Ireland. Scotland enacted similar legislation in 2009, which also includes gender identity as a protected ground.[89]
The Equality Act 2010 (Welsh: Deddf Cydraddoldeb 2010; Scottish Gaelic: Achd na Co-ionannachd 2010; Cornish: Reyth Parder 2010)[90] received royal assent on 8 April 2010.[91] The primary purpose of the Act was to codify the complicated and numerous array of Acts and Regulations, which formed the basis of anti-discrimination law in the UK including the Equal Pay Act 1970, the Sex Discrimination Act 1975, the Race Relations Act 1976, the Disability Discrimination Act 1995 and three major statutory instruments protecting discrimination in employment on grounds of religion or belief, sexual orientation and age. This legislation has the same goals as the US Civil Rights Act 1964 and four major EU equal treatment directives, whose provisions it mirrors and implements.[92] It requires equal treatment in access to employment as well as private and public services, regardless of gender, race, disability, sexual orientation, transgender status, belief and age.[93] The Act amended the Approved Premises (Marriage and Civil Partnership) Regulations 2005 to allow civil partnership ceremonies on religious premises in England and Wales.[45] It also extended transgender rights, banning discrimination by schools on the grounds of gender reassignment.[94][95]
Other initiatives have included the establishment of the Commission for Equality and Human Rights on 1 October 2007 which is tasked with working for equality in all areas and replaced the previous commissions dedicated to sex, race and disability alone; the setting up of the Sexual Orientation and Gender Advisory Group within the Department of Health;[96] a provision of the Criminal Justice Act 2003 that a court must treat hostility based on sexual orientation as an aggravating factor for sentencing a person;[97] guidance from the Crown Prosecution Service on dealing with homophobic crimes;[98] and a commitment from the Government to work for LGBT rights at an international level.[99]
Section 28
The 1980s saw a setback for LGBT rights. The availability in the libraries of schools run by the Inner London Education Authority of a book considered by some to "promote" homosexuality led to protests and a campaign for new legislation.[100] Consequently, the Local Government Act 1988 included a provision prohibiting "the intentional promotion of homosexuality" by any local authority and "the teaching in any maintained school of the acceptability of homosexuality as a pretended family relationship."[101] The provision was known as Section 28, and amended section 2A of the earlier Local Government Act 1986. Changes in the structure of local government since that date led to some confusion over the precise circumstances in which the new law applied, including the question of whether or not it applied at all in state schools.
Section 28 (called Section 2A in Scotland) was repealed in Scotland within the first two years of the existence of the Scottish Parliament, by the Ethical Standards in Public Life etc. (Scotland) Act 2000.[102] A move to remove the provision in England and Wales was prevented following opposition in the House of Lords, led by Baroness Young. Following her death in 2002, it was repealed by the Labour Government in the Local Government Act 2003, which took effect on 18 November 2003. During the passage of the bill, no attempt was made to retain the section and an amendment seeking to preserve it using ballots was defeated in the House of Lords. In June 2009, David Cameron, Conservative Party Leader, formally apologised for his party introducing the law, stating that it was a mistake and offensive to gay people.[103]
Public Order Act 1986
Section 29AB of the Public Order Act 1986 states:[104]
- In this Part "hatred on the grounds of sexual orientation" means hatred against a group of persons defined by reference to sexual orientation (whether towards persons of the same sex, the opposite sex or both)
Section 29JA, titled "Protection of freedom of expression (sexual orientation)", of the Act states the following:[104]
- (1) In this Part, for the avoidance of doubt, the discussion or criticism of sexual conduct or practices or the urging of persons to refrain from or modify such conduct or practices shall not be taken of itself to be threatening or intended to stir up hatred.
- (2) In this Part, for the avoidance of doubt, any discussion or criticism of marriage which concerns the sex of the parties to marriage shall not be taken of itself to be threatening or intended to stir up hatred.
Bias-motivated violence and abuse
Recorded reports of homophobic abuse in the UK increased from 5,807 in 2014-15 to 13,530 in 2018–19. The number of prosecutions fell from 1,157 to 1,058, which the National Police Chiefs' Council attributed to many cases with a lack of witnesses and evidence, including whether the assault was motivated by the victim's sexual orientation or gender identity or not. "Many of these non-violent offences present less evidential opportunities and victims often feel that there is a barrier between bringing the matter to court and prefer to make police aware of each offence", said a spokesman for the Metropolitan Police Service. North Yorkshire and South Yorkshire saw their reports increase from 172 to 961 and 73 to 375, respectively. The West Yorkshire Police said this increase was in part due to "improvements in the way we record crime and the fact that many victims have the confidence to come forward".[105]
Military service
.jpg)
LGBT people have been allowed to serve openly in Her Majesty's Armed Forces since 2000, and discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation has been forbidden since 2010.[91] It is also forbidden for someone to pressure LGBT people to come out. All personnel are subject to the same rules against intolerance, bullying and sexual harassment, regardless of gender identity or sexual orientation. The British military also recognises civil partnerships and grants same-sex couples the same rights to allowances and housing as opposite-sex couples.
The British military actively recruits LGBT people and have deployed recruiting teams to many Pride events: the Royal Navy advertises for recruits in gay magazines and has allowed gay sailors to hold civil partnership ceremonies on board ships and, since 2006, to march in full naval uniform at gay pride marches; British Army and Royal Air Force personnel could march but had to wear civilian clothes until 2008, now all military personnel are permitted to attend such marches in uniform.[106]
The current policy was accepted at the lower ranks first, with many senior officers worrying for their troops without a modern acceptance of homosexuality that their personnel had grown up with. One Brigadier resigned but with little impact. Since the change, support at the senior level has grown. General Sir Richard Dannatt, the Chief of the General Staff (head of the Army), told members of the Army-sponsored Fourth Joint Conference on LGBT Matters that homosexuals were welcome to serve in the Army. In a speech to the conference in 2008, the first of its kind by any Army chief, General Sir Richard said that respect for LGBT officers and soldiers was now "a command responsibility" and was vital for "operational effectiveness."[107]
The British Army, Royal Air Force and Royal Navy now require all recruits to undergo Equality and Diversity training as part of their Military Annual Training Tests and stress tolerance, specifically citing homosexual examples in training videos,[108] in line with Army, Navy and RAF Core Values and Standards,[109][110][111] including "Respect for Others" and "Appropriate Behaviour."
In 2009, on the tenth anniversary of the change of law that permitted homosexuality in the Armed Forces, newspapers reported that the lifting of the ban had no perceivable impact on the operational effectiveness on the military. The anniversary was widely celebrated, including in the Army's in-house publication Soldier Magazine, with a series of articles including the July 2009 cover story and newspapers articles.[112]
In 2015, following the fifteenth anniversary, the Ministry of Defence announced changes to its monitoring process for new recruits and added sexuality to their equal opportunities monitoring process.[113]
Conversion therapy
Peel, Clarke and Drescher wrote in 2007 that only one organisation in Britain could be identified with conversion therapy, a religious organisation called "The Freedom Trust"[114] (part of Exodus International): "whereas a number of organisations in the US (both religious and scientific/psychological) promote conversion therapy, there is only one in the UK of which we are aware". The paper reported that practitioners who did provide these sorts of treatments between the 1950s and 1970s now view homosexuality as healthy, and the evidence suggests that 'conversion therapy' is a historical rather than a contemporary phenomenon in Britain, where treatment for homosexuality has always been less common than in the US.[115]
In 2007, the Royal College of Psychiatrists, the main professional organisation of psychiatrists in Britain, issued a report stating that: "Evidence shows that LGBT people are open to seeking help for mental health problems. However, they may be misunderstood by therapists who regard their homosexuality as the root cause of any presenting problem such as depression or anxiety. Unfortunately, therapists who behave in this way are likely to cause considerable distress. A small minority of therapists will even go so far as to attempt to change their client's sexual orientation. This can be deeply damaging. Although there are now a number of therapists and organisations in the USA and in the UK that claim that therapy can help homosexuals to become heterosexual, there is no evidence that such change is possible."[116]
In 2008, the Royal College of Psychiatrists stated: "The Royal College shares the concern of both the American Psychiatric Association and the American Psychological Association that positions espoused by bodies like the National Association for Research and Therapy of Homosexuality (NARTH) in the United States are not supported by science. There is no sound scientific evidence that sexual orientation can be changed. Furthermore so-called treatments of homosexuality as recommended by NARTH create a setting in which prejudice and discrimination can flourish."[117]
In 2009, a research survey into mental health practitioners in the United Kingdom concluded that "a significant minority of mental health professionals are attempting to help lesbian, gay and bisexual clients to become heterosexual. Given lack of evidence for the efficacy of such treatments, this is likely to be unwise or even harmful."[118] Scientific American reported on this: "One in 25 British psychiatrists and psychologists say they would be willing to help homosexual and bisexual patients try to convert to heterosexuality, even though there is no compelling scientific evidence a person can willfully become straight", and explained that 17% of those surveyed said they had tried to help reduce or suppress homosexual feelings, and 4% said they would try to help homosexual people convert to heterosexuality in the future.[119]
Conversion therapy in the UK has been described by the BBC as "a fiercely contested topic" and part of a larger "culture war" within the UK.[120] In July 2017, the Church of England's General Synod passed a motion which criticised conversion therapy as "unethical, potentially harmful and having no place in the modern world" and called for "a ban on the practice of conversion therapy aimed at altering sexual orientation."[121][122] In February 2018, a Memorandum of Understanding which had been issued by the United Kingdom Council for Psychotherapy (UKCP) in October 2017 to provide "protection of the public through a commitment to ending the practice of 'conversion therapy' in the UK" was approved by the National Health Service (NHS).[123][124][125] Stonewall has stated that all major counselling and psychotherapy bodies in the UK have joined the NHS in signing the Memorandum condemning conversion therapy.[126]
In October 2017, a church in Anfield in Liverpool was exposed by a Liverpool Echo investigation for offering to "cure" gay people through a three-day starvation programme.[127] Labour MP Dan Carden raised the issue in Parliament, calling for a legislative ban on conversion therapies, which "have no place in 21st Century Britain".[128]
In March 2018, a majority of representatives in the European Parliament passed a resolution in a 435–109 vote condemning conversion therapy and urging European Union member states to ban the practice.[129][130][131] A report released by the European Parliament's Intergroup on LGBT Rights stated that the UK was one of a few areas in the EU which "explicitly banned LGBTI conversion therapies."[132] In July 2018, the UK Government announced as part of their LGBT Action Plan that they will "bring forward proposals" to ban conversion therapy at the legislative level.[133]
Sex education
The Public Sector Equality Duty provision of the Equality Act 2010 requires that information regarding bullying based on, among other things, LGBT identity be published and that solutions be found concerning how to counter this issue.[134][135] The first information regarding schools and pupils located in England and English-governed public authorities in Scotland and Wales were published on 6 April 2012.[134][135] In 2013, Ofsted published guidelines concerning how to counter homophobic and transphobic bullying at schools in England.[136] Part of these guidelines included sex and relationships education for LGBT pupils.[136]
On 12 February 2018, the Church of England's Education Office published a policy endorsing sex education which includes, among other things, LGBT education.[137] Concerning sexuality, the policy states "sex education should include an understanding that all humans are sexual beings and that sexual desire is natural. Pupils should be taught that humans express their sexuality differently and that there is diversity in sexual desire".[137] The policy also states that "pupils must be allowed to explore questions of identity and how we value our own identity and the uniqueness of other people. PSHE [Personal, Social, Health and Economic education] must help pupils recognise their true identity, and teach them that our media-framed, market-driven culture that often leads to body image anxiety can be challenged. This issue is the focus of the Bishop of Gloucester's #liedentity campaign which aims to challenge negative body image and encouraging young people to look within to discover true value and beauty."[137]
In July 2018, Education Minister Damian Hinds announced new government regulations concerning sex education. Topics such as mental wellbeing, consent, keeping safe online, physical health and fitness, and LGBT issues will be covered under the new guidelines, which are the first changes to sex education regulations since 2000, and which will be mandatory in all primary and secondary schools in England from September 2020 onward. The move was welcomed by LGBT groups in particular, who cited statistics showing that only 13% of LGBT youth had been taught about healthy same-sex relationships in schools. In addition, parents will retain certain rights to veto sex education lessons, but by the age of 16, the child may attend the lessons regardless of the parents' wishes.[138] The draft guidance states: "By the end of primary school, pupils should know that others' families, either in school or in the wider world, sometimes look different from their family, but that they should respect those differences and know that other children's families are also characterised by love and care for them." The guidance for secondary schools adds: "Pupils should be taught the facts and the law about sex, sexuality, sexual health and gender identity in an age-appropriate and inclusive way... All pupils should feel that the content is relevant to them and their developing sexuality."
This followed reports of some religious schools deliberately avoiding the issue, most notably an Orthodox Jewish school in north London which in 2018 had removed all references to the homosexual victims of Nazi persecution throughout their textbooks.[139] According to the Department of Education, faith-based schools would no longer have a right to opt-out of sex education lessons.[140] In September 2018, the UK's Chief Rabbi, Ephraim Mirvis, agreed to comply with this new policy and published guidelines on how to teach LGBT sex education in British Jewish schools.[141]
In October 2018, The Sunday Times reported that the British Government had decided to grant exemptions to private schools from LGBT-inclusive education.[142] In November 2018, however, both the PSHE Association and Sex Education Forum published a policy road-map which stated,[143] among other things, that "the law requires that Relationships and Sex Education (RSE) is to be taught in all secondary schools in England, and that Relationships Education is to be taught in all primary schools in England."[144] The road-map also detailed 10 steps which will be used to enforce the policy, and also stated that "Health Education will also be mandatory in all government funded schools, which includes content on puberty."[144][143] In February 2019, the Department of Education enacted a statutory guidance policy which will assist schools in England with PSHE when it becomes compulsory in 2020.[145][146]
A measure to make PSHE compulsory received approval from the House of Lords in April 2019.[147] The Department for Education (DfE) published final statutory guidance for teaching Relationships Education, Relationships and Sex Education (RSE) and Health Education in June 2019.[148] The guidelines, which were also published by the House of Commons,[149] require, among other things, acknowledgement of England's laws concerning LGBT rights, including the legalisation of same-sex marriage, and the protection of the "physical and mental well-being" of LGBT children.[148][149] Despite not mandatory until September 2020, schools in England will be encouraged to enact the new PSHE curriculum starting in September 2019.[148]
Wales similarly announced new regulations about sex education in May 2018, which will also discuss LGBT issues in schools. The regulations, expected to come into force in 2022, will be mandatory from Year 7 (age 11-12).[150]
The Scottish National Party's 2016 manifesto supports sex education classes, as well as "equality training" for teachers, that would cover LGBT issues.[151] In November 2018, the Scottish Government announced the implementation of LGBT-inclusive education in the Scottish school curriculum. The move was welcomed by LGBT activists who cited studies that have found that about 9 in 10 LGBT Scots experience homophobia at school, and 27% reported they had attempted suicide after being bullied.[152]
Ofsted (Office for Standards in Education Children's Services and Skills) assesses the inclusion of LGBT people in policies and the curriculum.
LGBT rights movement

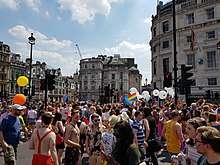
.jpg)
_(43738642971).jpg)
The Homosexual Law Reform Society, founded on 12 May 1958, in response to the findings of the Wolfenden Report was one of the first LGBT groups in the UK. Nowadays, Stonewall exists as the largest LGBT equality organisation in the UK and Europe.
LGBT people have been serving openly in politics since the 1970s. The first openly lesbian MP was Maureen Colquhoun (Labour Party, MP 1974–79), who was outed in 1976.
Following the 2019 general election, an estimated 45 openly LGBT MPs were elected to Parliament, of whom 20 were Conservative, 15 Labour 10 SNP and 1 from the Liberal Democrats.[10]
LGBT people are also allowed to serve openly in police and, in 1990, the Lesbian and Gay Police Association (LAGPA), now the Gay Police Association (GPA), was founded.
There are also large LGBT communities most noted in Birmingham (Birmingham Gay Village), Blackpool, Brighton (LGBT community of Brighton and Hove), Liverpool (LGBT culture in Liverpool), London (Old Compton Street) and Manchester (Canal Street), who all host annual pride festivals. The neighbouring Yorkshire towns of Todmorden and Hebden Bridge have high lesbian populations.
Many pride festivals are hosted in the UK every year. The first gay marches were in London in 1970, followed by the debut of the UK Gay Pride Rally there in 1972. Pride in London is the biggest and oldest festival, and has been organised annually since. Pride festivals are very popular summer events in major cities, and have expanded to smaller communities in recent years.
On the 5th anniversary of marriage equality referendum passed, Amnesty International, Irish Congress of Trade Unions, and Rainbow Project announced the first mass demonstration in Belfast, Ireland, protesting against the failure of the UK government in delivering full marriage equality rights. People wanting to covert their civil union into marriage are unable to do so.[153]
Role of the Council of Europe
According to Juris Lavrikovs from ILGA-Europe, the Council of Europe's European Court of Human Rights has been a positive force for LGBT rights, especially with regards to decriminalising same-sex consensual activity, barring discrimination against transgender individuals in employment, equalising the age of consent, enabling LGBT people to serve openly in the military, allowing transgender people the right to marry, employment equality and the including pension right for transgender individuals.[154]
Demographics
According to the Office of National Statistics, the Percentage of the UK population identifying as Gay, lesbian or bisexual increased from 1.5% in 2012 to 2.0% in 2017. There are 1.1 million people identifying as LGB in UK. The 16 to 24 age group were the most likely to identify as LGB in 2017 (4.2%).[155]
Public opinion
In 1993, Stonewall conducted a survey of gay men and lesbians at work where they found two-thirds of respondents hid their sexuality at work and only 11% of respondents never hid their sexual orientation in the workplace. A follow up survey done in 2008 found that 20% of gay and lesbian people had experienced bullying at work.[156]
Attitudes towards homosexuality amongst the British public have become more tolerant over time; according to the British Social Attitudes Survey, in 1983 approximately 50% to 70% of respondents of the three major political parties (Conservative, Labour and Liberal Democrat) regarded homosexuality as "always wrong" or "mostly wrong" and in 1993 opposition to homosexuality was reported to have slightly increased amongst all parties. However, by 2003 attitudes had become more tolerant, with 25% to 50% of respondents regarding homosexuality as always or mostly wrong and by 2013, only around 20% to 35% of respondents in each party felt the same way. Liberal Democrat respondents tended to be less likely to regard homosexuality as wrong than Labour or Conservative respondents across each survey.[157]
An illustration of social attitudes towards homosexuality in the UK was provided in May 2007 in a survey by YouGov. The poll indicated that legislation outlawing discrimination on the grounds of sexual orientation was supported by 90% of British citizens. It also showed positive public perceptions of gay people in particular, but recognised the extent to which prejudice still exists.[158] A poll in June 2009 conducted by Populus for The Times reported that the majority of the public supported same-sex marriage; 61% of respondents agreed that "Gay couples should have an equal right to get married, not just to have civil partnerships".[159][160] There were few differentials by partisanship.[161]
A more recent opinion poll, conducted in 2017 by Pew Research Center, found that 77% of the British public were in favour of same-sex marriage.[162] Support had increased to 85% according to the 2019 Eurobarometer, which polled all members states of the European Union on the question. The EU average was 69%.[163]
In 2017, 108,000 people participated in the National LGBT Survey, making it one of the biggest survey of LGBT people in the world. LGBT people were found to be less satisfied with life compared to the wider UK population, with trans satisfaction notably lower. 68% of respondents said they avoided holding hands with their same-sex partner in public. 5% of respondents had been offered conversion therapy, with 2% undergoing such therapies.[164] The findings from the National LGBT Survey have been used to inform a 75-point LGBT Action Plan to address the key issues identified, including bringing forward proposals to ban conversion therapy in the UK.[133]
Summary by legal jurisdiction and territory
| LGBT rights in: | Same-sex sexual activity | Gender recognition | Recognition of same-sex unions | Same-sex marriage | Same-sex adoption | Military service | Official pardon | Anti-discrimination (sexual orientation) | Anti-discrimination (gender identity) | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Section 28 banning "promotion of same-sex relationships as a pretend family relationship" repealed in 2003 | ||||||||||
| Section 2A banning "promotion of same-sex relationships as a pretend family relationship" repealed in 2000 | ||||||||||
| Northern Ireland | N/A |
Crown dependencies
| LGBT rights in: | Same-sex sexual activity | Gender recognition | Recognition of same-sex unions | Same-sex marriage | Same-sex adoption | Military service | Anti-discrimination (sexual orientation) | Anti-discrimination (gender identity) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Overseas Territories
| LGBT rights in: | Same-sex sexual activity | Recognition of same-sex unions | Same-sex marriage | Same-sex adoption | Military service | Anti-discrimination (sexual orientation) | Anti-discrimination (gender identity) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
(Age of consent discrepancy)[194] |
|||||||
Summary table
Please note: when a jurisdiction is not specified, the right applies to the whole of the United Kingdom. Does not include the Overseas Territories and the Crown dependencies
| Right | Yes/No | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Same-sex sexual activity | ||
| Same-sex sexual activity legal | Since 1967 (England and Wales) Since 1981 (Scotland) Since 1982 (Northern Ireland) | |
| Equal age of consent | Since 2001 | |
| Homosexuality declassified as an illness | ||
| Official pardon | Since 2017 (England and Wales)[213] Since 2018 (Northern Ireland) Since 2019 (Scotland)[168] | |
| Disregards available | Since 2012 (England and Wales)[214] Since 2018 (Northern Ireland)[215] Since 2019 (Scotland)[168] | |
| Same-sex relationships | ||
| Civil partnerships for same-sex couples[note 1] | Since 2005 | |
| Civil partnerships in religious venues | Since 2011 (England and Wales) Since 2014 (Scotland) Since 2020 (Northern Ireland)[216] | |
| Civil and religious same-sex marriage[note 2] | Since 2014 (England and Wales, and Scotland)[50][52] Since 2020 (Northern Ireland)[216] | |
| Adoption and family planning | ||
| Joint and stepchild adoption for LGBT persons and same-sex couples | Since 2005 (England and Wales) Since 2009 (Scotland)[63] Since 2013 (Northern Ireland)[65] | |
| Equal access to IVF for all couples and individuals | Since 2009 | |
| Same-sex couples as both parents on a birth certificate | Since 2009 | |
| Altruistic surrogacy for all couples and individuals | Since 2010 | |
| Commercial surrogacy for gay male couples | Banned for heterosexual couples as well | |
| Military service | ||
| LGBT people allowed to serve openly in military | Since 2000 | |
| Transgender rights | ||
| Transsexualism declassified as an illness | Since 2002 | |
| Right to change legal gender | Since 2005 | |
| Right to change legal gender without having to end marriage[note 3] | Since 2014 (England and Wales, and Scotland) Since 2020 (Northern Ireland) | |
| Discrimination protections | ||
| Anti-discrimination laws in all areas on sexual orientation and gender identity (including employment, goods and services, housing, etc.) | Since 2010 (England and Wales, and Scotland)[91] Only limited protections for gender identity in Northern Ireland | |
| Laws against hate speech based on sexual orientation | Since 2004 (Northern Ireland) Since 2008 (England and Wales) Since 2009 (Scotland)[89] | |
| Laws against hate speech based on gender identity | Since 2009 (Scotland) No laws exist (England and Wales, and Northern Ireland)[89] | |
| Laws against inciting hatred on sexual orientation through an aggravating circumstance | Since 2004 (Northern Ireland) Since 2008 (England and Wales) Since 2009 (Scotland)[89] | |
| Laws against inciting hatred on gender identity through an aggravating circumstance | Since 2009 (Scotland) No laws exist (England and Wales, and Northern Ireland)[89] | |
| LGBT sex education and relationships taught in schools | Personal, Social, Health and Economic (PSHE) education, which includes sex and relationships, will become compulsory in England in September 2020,[217] though schools in England will be encouraged to make it compulsory starting in September 2019.[148] Compulsory for all schools in Scotland from 2018,[152] and Wales from 2022[218] Schools in England must comply with the Equality Act 2010's Public Sector Equality Duty (2012) which includes LGBT equality Ofsted assesses the inclusion of LGBT people in policies and the curriculum | |
| MSMs allowed to donate blood | 3 month deferral required since 2017 in England, Scotland and Wales; since 2020 in Northern Ireland.[219][220] | |
| Conversion therapy banned | Pending at legislative level.[221] Banned by the NHS and all major counselling and psychotherapy bodies in the UK[126] | |
| Immigration rights | ||
| Immigration equality and rights for LGBT individuals and same-sex couples | Since 2006 | |
| Recognition of sexual orientation and gender identity for asylum requests | Guidelines not applied consistently Some cases recognised since 1999 including that of HJ and HT v Home Secretary Plans for guidance on asylum claims brought on by sexual orientation but not gender identity | |
Notes
- Civil partnerships give most (but not all) of the rights and responsibilities of civil marriage, but there are recognition issues in other countries and with the use of courtesy titles. Civil partnerships can take place on any approved premise in the UK and in approved religious venues in Great Britain (though religious venues are not compelled), but cannot include religious readings, music or symbols. Adultery and non-consummation are also not grounds for the dissolution of a civil partnership.
See: "Civil Partnership Act 2004" and "Civil partnership in the United Kingdom" - Same-sex marriages give all the rights and responsibilities of civil marriage and can be performed on approved premises and religious venues in Great Britain (though no religious or belief body is compelled). Adultery and non-consummation are not grounds for divorce.
See: "Marriage (Same Sex Couples) Act 2013", "Marriage and Civil Partnership (Scotland) Act 2014" and "Same-sex marriage in the United Kingdom" - Existing marriages continue where one or both parties change their legal gender and both parties wish to remain married. Civil partnerships continue where only both parties change their gender simultaneously and wish to remain in their civil partnership.
See: "Marriage (Same Sex Couples) Act 2013", "Marriage and Civil Partnership (Scotland) Act 2014" and "Same-sex marriage in the United Kingdom"
See also
- Timeline of LGBT history in the United Kingdom
- Gay Rights Working Party—1980s work in London to combat discrimination and police abuse
- Hall–Carpenter Archives
- History of violence against LGBT people in the United Kingdom
- Human rights in the United Kingdom
- Intersex rights in the United Kingdom
- LGBT Humanists UK
- LGBT Network
- LGBT rights by country or territory
- LGBT rights in Europe
- LGBT rights in Northern Ireland
- LGBT rights in Scotland
- LGBT rights in the Commonwealth of Nations
- PinkNews
- Sexual orientation and military service
- Stonewall (charity)
- Transgender rights in the United Kingdom
References
- "Law liberalising abortion and same-sex marriage in NI passes final stage". The Irish Times. 23 July 2019.
- "Armed Forces Act 2016". legislation.gov.uk.
- "Government announces date of first same-sex marriages in England and Wales". Pink News. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- "Northern Ireland (Executive Formation etc) Act 2019". www.legislation.gov.uk. Retrieved 12 January 2020.
- "The Marriage (Same-sex Couples) and Civil Partnership (Opposite-sex Couples) (Northern Ireland) Regulations 2019". www.legislation.gov.uk. Retrieved 12 January 2020.
- "Scotland tops league for gay rights". the Guardian.
- "Gay weddings: 'Fifth of Britons would turn down invitation'". BBC News. 28 March 2014.
- "The Global Divide on Homosexuality". Pew Research Center's Global Attitudes Project. 4 June 2013.
- Gerdis, Stefanie (8 May 2015). "Britain has elected the most LGBTI MPs in the world". GayStarNews. Retrieved 11 May 2015.
- Reynolds, Andrew (13 December 2019). "The UK's parliament is still the gayest in the world after 2019 election". PinkNews.
- Travis, Alan (23 September 2010). "1.5% of Britons say they are gay or bisexual, ONS survey finds". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 23 September 2010.
- Stephenson, Wesley (4 October 2010). "In the closet or not?". BBC News Magazine. BBC. Retrieved 5 October 2010.
- "YouGov - The average Brit knows 3.1 lesbians, 5.5 gay men". YouGov: What the world thinks. Retrieved 10 May 2017.
- "YouGov - Move over Kylie: One Direction is Britain's gayest band". YouGov: What the world thinks. Retrieved 10 May 2017.
- "Introduction to the review". equalityhumanrights.com.
- "Help & Advice - Stonewall". Stonewall.
- Cook, Matt; Mills, Robert; Trumback, Randolph; Cocks, Harry (2007). A Gay History of Britain: Love and Sex Between Men Since the Middle Ages. Greenwood World Publishing. p. 109. ISBN 1846450020.
- "Turing's Law: Oscar Wilde among 50,000 convicted gay men granted posthumous pardons". The Daily Telegraph. 31 January 2017.
- "Records of the Parliaments of Scotland". Rps.ac.uk. Retrieved 7 April 2014.
- "Procedure: commission for the trial of Gavin Bell". Rps.ac.uk. Retrieved 7 April 2014.
- "The PinkNews Guide to the history of England and Wales equal marriage". Pinknews.co.uk. 15 June 2013. Retrieved 7 April 2014.
- Whiteman, Hilary (1 September 2009). "Petition seeks apology for Enigma code-breaker Turing". CNN. Retrieved 2 May 2010.
- "Treatment of Alan Turing was "appalling" – PM". Number10.gov.uk. 10 September 2009. Archived from the original on 20 April 2010. Retrieved 2 May 2010.
- "Wolfenden Report". www.bl.uk.
- Bates, Victoria (8 September 2015). "The legacy of 1885: girls and the age of sexual consent". History & Policy. History & Policy. Retrieved 12 July 2016.
- Patricia Brent and Leo Abse (20 December 1966). "Why should homosexuality be decriminalised?". BBC Archives. Archived from the original on 18 August 2011.
- "THE CRIMINAL JUSTICE (SCOTLAND)ACT 1980 (Hansard, 17 December 1980)". hansard.millbanksystems.com. Retrieved 4 September 2017.
- "The Homosexual Offences (Northern Ireland) Order 1982 (No. 1536 (N.I. 19))". The UK Statute Law Database. Office of Public Sector Information. 27 October 1982. Archived from the original on 30 January 2010. Retrieved 2 January 2010.
- Blair, Tony (1996). New Britain: my vision of a young country. Fourth Estate. p. 188. ISBN 978-1-85702-436-4.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- "Sexual Offences (Amendment) Act 2000". The UK Statute Law Database. Office of Public Sector Information. Commencement Information. Retrieved 27 March 2010.
- "BBC News – Q and A: The age of consent". BBC. 29 November 2000. Retrieved 19 August 2012.
- Sandhu, Serina (16 September 2016). "How the UK debated the age of consent for gay sex". inews.co.uk.
- "The Queen turned 90 and here's all the LGBT laws she signed". PinkNews. 21 April 2016.
- "SEX AND THE LAW" (PDF). fpa.org.uk.
- correspondent, Owen Bowcott Legal affairs (31 January 2017). "UK issues posthumous pardons for thousands of gay men". Retrieved 10 May 2017 – via The Guardian.
- "Thousands of gay Scots to be pardoned". BBC News. 6 June 2018.
- "Gay men in Northern Ireland offered access to pardons". BBC News. 28 June 2018.
- How many people have been pardoned under Turing’s Law?, PinkNews, 10 July 2018
- Capon, Tom (25 June 2019). "Everyone in Northern Ireland who applied for 'gay pardon' turned down". Gay Star News.
- "Merchant Shipping (Homosexual Conduct) Act 2017". www.legislation.gov.uk. Retrieved 10 May 2017.
- "Merchant Shipping (Homosexual Conduct) Act 2017 — UK Parliament". services.parliament.uk. Retrieved 10 May 2017.
- "Government backs plan to tackle the UK's 'last anti-gay law'". Retrieved 10 May 2017.
- Metro.co.uk, Simon Robb for (23 January 2017). "UK's last 'anti-gay law' to be scrapped". Retrieved 10 May 2017.
- Reid-Smith, Tris (1 May 2020). "Heritage watchdog objects to statue of gay hero Alan Turing at Kings College Cambridge". Gay Star News. Retrieved 12 May 2020.
- "Home Office". Equalities. Retrieved 3 January 2012.
- "The Marriages and Civil Partnerships (Approved Premises) (Amendment) Regulations 2011". www.legislation.gov.uk.
- "First civil union in the United Kingdom". BBC News. 6 December 2005. Retrieved 2 May 2010.
- "Partner of first civil union in the United Kingdom dies". BBC News. 6 December 2005. Retrieved 2 May 2010.
- "Gay marriage bill: Peers back government plans". BBC News Online. 4 June 2013. Retrieved 4 June 2013.
- "England's Gay Marriage Law To Become Legal After Lower House Approval". The Huffington Post. Reuters. 16 July 2013. Retrieved 17 July 2013.
- "Same-sex marriage becomes law in England and Wale". BBC News. 17 July 2013. Retrieved 17 July 2013.
- "Gay marriage to be introduced in Scotland". BBC News. 25 July 2012. Retrieved 25 July 2012.
- "BBC News – Scotland's gay marriage bill to come before Holyrood within a month". Bbc.co.uk. 28 May 2013. Retrieved 7 April 2014.
- "Marriage (Same Sex Couples) Act 2013". Legislation.gov.uk. Retrieved 7 April 2014.
- Mortimer, Caroline (2 November 2015). "Northern Ireland same-sex marriage vote vetoed by DUP". The Independent. Retrieved 1 February 2017.
- Page, Chris (22 October 2019). "Northern Ireland abortion and same-sex marriage laws change". BBC News. Retrieved 22 October 2019.
- "Secretary of State Julian Smith signs regulations introducing same-sex marriage to Northern Ireland". Belfast Telegraph. Independent News & Media PLC. 19 December 2019. Retrieved 26 December 2019.
- "Same-sex marriage now legal in Northern Ireland". BBC News. 13 January 2020.
- "Same sex marriage is finally legal in Northern Ireland". CNN. 13 January 2020.
- Media, P. A. (11 February 2020). "First same-sex marriage takes place in Northern Ireland". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved 11 February 2020.
- "Adoption and Children Act 2002". www.legislation.gov.uk. Retrieved 10 May 2017.
- "The Adoption and Children Act 2002: An Overview". www.courtroomadvice.co.uk. Retrieved 10 May 2017.
- "Adoption and Children (Scotland) Act 2007, 2007 asp 4, s. 29". Opsi.gov.uk. Retrieved 2 May 2010.
- Thomas, Ellen (20 September 2009). "New legislation sees gay Scottish couples win right to adopt children". The Herald. Retrieved 23 September 2009.
- Gay adoption: Northern Ireland ban lifted, BBC News, 11 December 2013
- "HUMAN FERTILISATION AND EMBRYOLOGY ACT 2008" (PDF). Retrieved 7 April 2014. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - "Update to General Directions, Code of Practice and consent forms". Human Fertilisation and Embryology Authority. Archived from the original on 8 April 2014. Retrieved 8 April 2012.
- "Analysis: What the new IVF parenthood laws mean for lesbians". Pink News. 2 March 2009. Retrieved 27 July 2009.
- "Lesbian couples undergoing IVF now permitted to put both names on birth certificates". Pink News. 6 April 2009. Retrieved 27 July 2009.
- "A History of LGBT Rights in the UK". Imperial College London. Retrieved 6 April 2015.
- "Parenthood – Birth registration and parental orders". Hfea.gov.uk. 2 September 2009. Archived from the original on 11 July 2016. Retrieved 3 January 2012.
- Cacciottolo, Mario (30 August 2009). "'Brilliant' news for lesbian couples". BBC. Retrieved 31 August 2009.
- Tran, Mark (31 August 2009). "Lesbian partners to be named on birth certificates". Guardian. London. Retrieved 31 August 2009.
- Beckford, Martin (31 August 2009). "Children can now have two lesbian mothers and no father on birth certificate". Daily Telegraph. London. Retrieved 31 August 2009.
- "Lesbians given equal birth rights". BBC News. 31 August 2009. Retrieved 2 September 2009.
- Beckford, Martin. "Children can now have two lesbian mothers and no father on birth certificate." The Telegraph. 31 August 2009. Retrieved 2 September 2009.
- Besanvalle, James (16 November 2018). "Record-breaking one in eight adoptions in England are by same-sex couples". Gay Star News.
- "Government Policy concerning Transsexual People". People's rights / Transsexual people. U.K. Department for Constitutional Affairs. 2003. Archived from the original on 11 May 2008. Retrieved 16 October 2017.
- "Marriage (Same Sex Couples) Act 2013". Legislation.gov.uk. 19 July 2013. Retrieved 7 April 2014.
- Council of Europe; Commissioner for Human Rights (April 2015), Human rights and intersex people, Issue Paper
- UN Committee against Torture; UN Committee on the Rights of the Child; UN Committee on the Rights of People with Disabilities; UN Subcommittee on Prevention of Torture and other Cruel, Inhuman or Degrading Treatment or Punishment; Juan Méndez, Special Rapporteur on torture and other cruel, inhuman, or degrading treatment or punishment; Dainius Pῡras, Special Rapporteur on the right of everyone to the enjoyment of the highest attainable standard of physical and mental health; Dubravka Šimonoviæ, Special Rapporteur on violence against women, its causes and consequences; Marta Santos Pais, Special Representative of the UN Secretary-General on Violence against Children; African Commission on Human and Peoples' Rights; Council of Europe Commissioner for Human Rights; Inter-American Commission on Human Rights (24 October 2016), "Intersex Awareness Day – Wednesday 26 October. End violence and harmful medical practices on intersex children and adults, UN and regional experts urge", Office of the High Commissioner for Human RightsCS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- "Employment Equality (Sexual Orientation) Regulations 2003, S.I. 2003/1661". Opsi.gov.uk. Retrieved 2 May 2010.
- Smith, Peter (5 February 2007). "Note from Archbishop Peter Smith regarding Catholic adoption agencies and the current controversy". Catholic Church of England and Wales. Archived from the original on 31 December 2008. Retrieved 1 October 2009.
- Leeds-based Catholic charity wins gay adoption ruling bbc.co.uk, 17 March 2010
- Brocklebank, Christopher (26 April 2011). "Catholic charity loses appeal over gay adoption". Pink News. Retrieved 26 February 2011.
- Wiggins, Kaye (2 August 2011). "Catholic Care given leave to appeal again". Third Sector. Retrieved 26 February 2011.
- Mason, Tania (5 November 2012). "Catholic Care loses Upper Tribunal challenge over gay adoption". Civil Society Media. Retrieved 26 May 2013.
- Grew, Tony (8 October 2007). "Government approves incitement to gay hate law". Pink News. Retrieved 10 October 2007.
- "Rainbow Europe". rainbow-europe.org. Retrieved 12 May 2020.
- "Cornish ] ] National Minority Report 2, Derivas Minorita Kenedhlek Kernewek 2" (PDF). Gorsedh Kernow. 5 March 2011.
- "Equality Act 2010". Equalities.gov.uk. Retrieved 2 June 2010.
- see EU Directive 2000/78/EC, 2000/43/EC, 2006/54/EC
- "EHRC — Commission welcomes landmark equality legislation". Equalityhumanrights.com. 8 April 2010. Archived from the original on 18 June 2010. Retrieved 2 June 2010.
- "The Equality Act 2010". LGF.org.uk. The Lesbian and Gay Foundation. 1 October 2010. Archived from the original on 9 August 2011. Retrieved 6 April 2015.
- "The Equality Act 2010 and schools" (PDF). GOV.uk. Department for Education. Retrieved 6 April 2015.
- "Sexual orientation and gender identity — Policy and guidance". Department of Health. Archived from the original on 2 April 2007. Retrieved 1 October 2009.
- "Criminal Justice Act 2003, 2003 c. 44, s. 146". Opsi.gov.uk. Retrieved 2 May 2010.
- "Crown Prosecution Service: Policy Statement". Cps.gov.uk. Archived from the original on 23 October 2016. Retrieved 2 May 2010.
- "Promoting lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender rights overseas". Foreign and Commonwealth Office. Archived from the original on 19 March 2008. Retrieved 1 October 2009.
- Bosche, Susanne (31 January 2000). "Jenny, Eric, Martin . . . and me". Guardian. London. Retrieved 10 October 2007.
- Godfrey, Chris (27 March 2018). "Section 28 protesters 30 years on". The Guardian. Retrieved 31 March 2018.
- "2000 asp 7, s. 34". Opsi.gov.uk. Retrieved 2 May 2010.
- "David Cameron apologises for Section 28". The Independent. London. 2 July 2009. Retrieved 2 June 2010.
- "Public Order Act 1986". Government of the United Kingdom.
- "Homophobic hate crime charges fall as reports soar". BBC News. 11 September 2019.
- Barr, Damian; Bannerman, Lucy (14 June 2008). "Soldiers can wear their uniforms with pride at gay parade says MoD". The Times. London. Retrieved 23 May 2010.
- Rayment, Sean (11 October 2008). "Army's top general makes history by addressing conference on homosexuality". The Telegraph. London.
- "[ARCHIVED CONTENT] Equality and Diversity – British Army Website". Army.mod.uk. 6 November 2009. Archived from the original on 7 October 2010. Retrieved 3 January 2012.
- "[ARCHIVED CONTENT] Army Values – British Army Website". Army.mod.uk. 6 November 2009. Archived from the original on 4 October 2010. Retrieved 3 January 2012.
- "[ARCHIVED CONTENT] Army Standards – British Army Website". Army.mod.uk. 6 November 2009. Archived from the original on 1 October 2010. Retrieved 3 January 2012.
- "Equality and Diversity | Royal Navy". www.royalnavy.mod.uk. Retrieved 2 June 2019.
- "Pride of the army: Soldier magazine honours gay servicemen and women". PinkNews.co.uk. Archived from the original on 20 October 2011. Retrieved 3 January 2012.
- "The UK's ban on gays in the military was lifted 15 years ago today - PinkNews · PinkNews". www.pinknews.co.uk. Retrieved 2 June 2019.
- This is presumably a reference to True Freedom Trust which appears to have dissociated itself from Exodus and conversion therapy in 2000.
- Peel 2007, pp. 18–19
- "Thinking Anglicans". 13 September 2008.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- "Statement from the Royal College of Psychiatrists' Gay and Lesbian Mental Health Special Interest Group". 13 September 2008. Archived from the original on 28 April 2009.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link) CS1 maint: unfit url (link)
- Bartlett, Smith & King 2009
- Ballantyne 2009
- Zand, Benjamin (23 April 2015). "'Culture war' of gay conversion therapy". BBC News. Archived from the original on 26 April 2015. Retrieved 28 May 2015.
- "General Synod backs ban on conversion therapy". Church of England. 8 July 2017.
- "Church of England demands ban on conversion therapy". The Guardian. 8 July 2017.
- Duffy, Nick (11 February 2018). "UK government: Gay cure therapy is 'ineffective and potentially harmful'". PinkNews.
- "NHS ENGLAND CLARIFIES ITS STANCE ON CONVERSION THERAPY". ppc-cic.org. 2 February 2018.
- "Memorandum of Understanding on Conversion Therapy in the UK" (PDF). psychotherapy.org. October 2017.
- "Conversion Therapy". Stonewall UK. Retrieved 1 April 2019.
- ""Die in the fire" - hear the terrifying chants at gay 'cure' church in full". Liverpool ECHO. 5 September 2017.
- "Parliament hears calls for ban on gay 'cure' therapies after ECHO investigation". Liverpool ECHO. 2 July 2018.
- "EU-Parlament stärkt LGBTI-Grundrechte".
- "Schwulissimo - Europäisches Parlament verurteilt die "Heilung" von Homosexuellen". schwulissimo.de. Archived from the original on 3 March 2018. Retrieved 28 March 2019.
- "European Parliament condemns gay 'cure' therapy and tells EU member states to ban it".
- "European Parliament takes a stance against LGBTI conversion therapies for the first time". Intergroup on LGBT Rights. 1 March 2018.
- "LGBT Action Plan" (PDF). Government Equalities Office. July 2018. Retrieved 7 July 2018.
- "The Essential Guide to the Public Sector Equality Duty" (PDF). Equality and Human Rights Commission. 2014.
- "The Equality Act 2010 and schools" (PDF). Equality and Human Rights Commission. May 2014.
- "Exploring the school's actions to prevent and tackle homophobic and transphobic bullying" (PDF). Ofsted. September 2013.
- "Church of England Education Office Response" (PDF). The Church of England Education Office.
- "Overhaul of sex education in England could elevate LGBT rights". Reuters. 19 July 2018. Retrieved 22 July 2018.
- "Education watchdog rebukes school that redacted history textbooks to remove gay Holocaust victims". PinkNews. 26 June 2018. Retrieved 22 July 2018.
- "LGBT sex ed to be taught in England, including faith schools". Gay Star News. 19 July 2018. Retrieved 22 July 2018.
- Burns, Judith (6 September 2018). "Chief Rabbi publishes first LGBT guide for orthodox schools". BBC News.
- Private schools to get ‘exemption’ from LGBT education, PinkNews, 8 October 2018
- "Roadmap to statutory relationships and sex education published". NAHT. 13 November 2018.
- "Roadmap to statutory RSE" (PDF). Sex Education Forum.
- "Curriculum guidance". PSHE Association. February 2019. Retrieved 8 May 2019.
- "Relationships Education, Relationships and Sex Education (RSE) and Health Education" (PDF). UK Department of Education (Draft). February 2019. Retrieved 8 May 2019.
- "Relationships Education, Relationships and Sex Education and Health Education (England) Regulations 2019". Hansard. 24 April 2019.
- "Relationships Education, Relationships and Sex Education (RSE) and Health Education". UK Department of Education. 25 June 2019. Retrieved 23 July 2019.
- "Relationships and Sex Education in Schools (England)". researchbriefings.parliament.uk. 11 July 2019.
- "Sex education given LGBT-inclusive overhaul in Wales". The Guardian. 22 May 2018. Retrieved 22 July 2018.
- "Nicola Sturgeon: We should help kids make informed choices about their gender and sexual identity". PinkNews. 20 April 2016. Retrieved 22 July 2018.
- Brooks, Libby (9 November 2018). "Scotland is first country to approve LGBTI school lessons". the Guardian. Retrieved 9 November 2018.
- "Northern Ireland: Campaigners criticise UK Government failure to deliver full marriage equality". Amnesty International UK. Retrieved 22 May 2020.
- Lavrikovs, Juris (6 June 2014). "How Europe has influenced the UK's journey on LGBT rights". Pink News (ILGA–Europe). Retrieved 6 April 2015.
- "Sexual orientation, UK: 2017". Retrieved 17 May 2020.
- Stephen Taylor; Astra Emir (22 March 2012). Employment Law: An Introduction. OUP Oxford. p. 328. ISBN 978-0-19-960489-0.
- British Social Attitudes, Homosexuality, 2013, NatCen
- Muir, Hugh (23 May 2007). "Majority support gay equality rights, poll finds". Guardian. London. Retrieved 10 October 2007.
- Bennett, Rosemary (27 June 2009). "Church 'out of touch' as public supports equal rights for homosexuals". The Times. London. Retrieved 2 October 2009.
- "Gay Britain Survey" (PDF). Populus. Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 January 2016. Retrieved 27 July 2009.
- Ben Clements, "Partisan Attachments and Attitudes towards Same-Sex Marriage in Britain." Parliamentary Affairs (2014) 67#1 pp: 232-244.
- Religion and society, Pew Research Center, 29 May 2018
- "Eurobarometer on Discrimination 2019: The social acceptance of LGBTI people in the EU". TNS. European Commission. p. 2. Retrieved 23 September 2019.
- "National LGBT Survey" (PDF). Government Equalities Office. July 2018. Retrieved 7 July 2018.
- "Policing and Crime Act 2017". www.legislation.gov.uk.
- "Protection of Freedoms Act 2012". www.legislation.gov.uk. Expert Participation. Retrieved 14 June 2018.CS1 maint: others (link)
- "Criminal Justice and Immigration Act 2008". www.opsi.gov.uk. Retrieved 10 May 2017.
- "Automatic pardon for gay and bisexual men - gov.scot". www.gov.scot. Retrieved 24 June 2019.
- "Sexual Offences (Bailiwick of Guernsey) (Amendment) Law, 2011". guernseylegalresources.gg.
- "JURIST - Homosexual Offenses and Human Rights in Guernsey". jurist.org.
- "The Prevention of Discrimination (Enabling Provisions) (Bailiwick of Guernsey) Law, 2004". Guernsey Legal Resources. Retrieved 31 May 2014.
- "Legal Resources: Legal Resources Navigation List: Guernsey Law Reports 2007–08 GLR 161". guernseylegalresources.gg.
- Megarry, Daniel (19 December 2019). "Sark becomes last place in British Isles to legalise same-sex marriage". Gay Times.
- "ORDERS APPROVED AND BUSINESS TRANSACTED AT THE PRIVY COUNCIL HELD BY THE QUEEN AT BUCKINGHAM PALACE ON 11TH MARCH 2020" (PDF).
- Interactive, Blix. "Guernsey Foster Care : Who can adopt?". www.guernseyfostercare.com. Retrieved 10 May 2017.
- "Gender Recognition Act 2009" (PDF).
- "EQUALITY ACT 2017" (PDF).
- "GENDER RECOGNITION (JERSEY) LAW 2010" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 3 March 2016. Retrieved 10 May 2017.
- "Jersey to introduce same-sex marriage from 1 July". BBC News. 27 June 2018.
- "DISCRIMINATION (SEX AND RELATED CHARACTERISTICS) (JERSEY) REGULATIONS 2015". Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 19 July 2018.
- "Criminal Code (Amendment) Ordinance 2000" (PDF). Retrieved 10 May 2017.
- Criminal Code (consolidated)
- "The Overseas Marriage (Armed Forces) Order 2014" (PDF). Retrieved 10 May 2017.
- "Employment (Equality) Ordinance 2013" (PDF). Retrieved 10 May 2017.
- "Criminal Code (Amendment) Ordinance 2016" (PDF). Retrieved 10 May 2017.
- "CRIMINAL CODE ACT 1907" (PDF).
- Simpson, Lisa (28 February 2018). "House: Three more months of same-sex marriage". The Royal Gazette. Archived from the original on 28 February 2018. Retrieved 28 February 2018.
- Johnson, Ayo (15 June 2013). "MPs approve historic Human Rights Act changes". The Royal Gazette. Retrieved 15 June 2013.
- "The Marriage Ordinance 2016" (PDF). Retrieved 10 May 2017.
- "Review of British Antarctic Territory legislation: changes to the marriage and registration ordinances - GOV.UK". www.gov.uk. Retrieved 10 May 2017.
- "The Overseas Marriage (Armed Forces) Order 2014" (PDF).
- "MILPERSMAN 1300-314" (PDF).
- "The Virgin Islands Constitution Order 2007". www.legislation.gov.uk.
- "Cayman may have to sanction same sex unions, expert says". compasscayman.com.
- "Facebook Post by John Clifford". Facebook.com. 30 March 2017. Retrieved 31 March 2017.
- "Twitter Post by Lisa Watson of the Penguin News (Falkland Islands)". Twitter.com. 30 March 2017. Retrieved 31 March 2017.
- "The Falkland Islands Constitution Order 2008" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 12 November 2013.
- "Civil Marriage Amendment Act 2016 [No. 22 of 2016" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 December 2016. Retrieved 10 May 2017.
- "Civil Marriage Amendment Act 2016 - Notice of Commencement" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 December 2016. Retrieved 10 May 2017.
- "Gibraltar celebrates first same sex marriage – Gibraltar Chronicle". chronicle.gi. Archived from the original on 17 December 2016. Retrieved 10 May 2017.
- "Equal Opportunities Act 2006" (PDF). gilbraltarlaws.gov.gi.
- "Constitution of Montserrat Part I: Fundamental Rights & Freedoms". Government of Montserrat. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- "Pitcairn Island: Same Sex Marriage and Civil Partnership Ordinance 2015". Equality Case Files.
- "GayLawNet®™ - Laws - Pitcairn - PN". gaylawnet.com.
- "The Pitcairn Constitution Order 2010" (PDF). Retrieved 10 May 2017.
- "This tiny island just passed same-sex marriage". 20 December 2017.
- Turner, Andrew (21 December 2017). "A Big Day for LegCo, and for the Island - Four Bills Pass, Same-Sex Marriage Becomes Legal" (PDF). South Atlantic Media Services, Ltd. p. 3. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 December 2017. Retrieved 23 December 2017.
- Pipe, Simon (19 December 2017). "Same-sex marriage approved for St Helena: opponent calls for society to embrace the result". St Helena Online. Retrieved 19 December 2017.
- "The St Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha Constitution Order 2009". legislation.gov.uk.
- "Commission for Equality and Human Rights Ordinance 2015" (PDF). sainthelena.gov.sh.
- "Local laws and customs - South Georgia and South Sandwich Islands (British Overseas Territory) travel advice". GOV.UK.
- "The Turks and Caicos Islands Constitution Order 2011" (PDF). Government of United Kingdom (legislation.gov.uk). Retrieved 30 January 2016.
- "Policing and Crime Act 2017". www.legislation.gov.uk. Retrieved 21 July 2018.
- "Disregards and pardons for historical gay sexual convictions". GOV.UK. Retrieved 21 July 2018.
- "Convicted NI gay men able to seek pardon". BBC News. 28 June 2018. Retrieved 21 July 2018.
- "Northern Ireland (Executive Formation etc) Act 2019". www.legislation.gov.uk. Retrieved 25 July 2019.
- "Relationships and Sex Education - Hansard". hansard.parliament.uk. Retrieved 20 July 2018.
- Slawson, Nicola (21 May 2018). "Sex education given LGBT-inclusive overhaul in Wales". the Guardian. Retrieved 9 November 2018.
- "It's now much easier for gay men to give blood". PinkNews. Retrieved 27 November 2017.
- "Same-sex blood donation rules relaxed". BBC News. 29 April 2020. Retrieved 29 April 2020.
- "'Gay conversion therapy' to be banned". BBC News. 3 July 2018. Retrieved 20 July 2018.
- Sutherland v. United Kingdom – 25186/94 [2001] ECHR 234 (27 March 2001)
Further reading
- Browne, Katherine, and Catherine J. Nash. "Resisting LGBT rights where 'we have won': Canada and Great Britain." Journal of Human Rights (2014) 13#3 pp: 322–336.
- Clements, Ben. "Partisan Attachments and Attitudes towards Same-Sex Marriage in Britain." Parliamentary Affairs (2014) 67#1 pp: 232–244.
- Cohler, Deborah. Citizen, Invert, Queer: Lesbianism and War in Early Twentieth-Century Britain (2010)
- Cook, Matt et al. A Gay History of Britain: Love and Sex Between Men Since the Middle Ages (2007)
- Goldberg, Suzanne B. "Open Service and Our Allies: A Report on the Inclusion of Openly Gay and Lesbian Servicemembers in U.S. Allies' Armed Forces," William & Mary Journal of Women & Law (2011) v 17 pp 547–90 online
- Gunn, Drewey Wayne. Gay Novels of Britain, Ireland and the Commonwealth, 1881-1981: A Reader's Guide (2014)
- Robinson, Lucy. Gay Men and the Left in Post-War Britain: How the Personal Got Political (2008)
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to LGBT in the United Kingdom. |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to LGBT history in the United Kingdom. |
- LGBT History Month United Kingdom website
- GLBTQ website article on the history of LGBT life in the United Kingdom from the Middle Ages to the Nineteenth Century.
- GLBTQ website article on the history of LGBT life in the United Kingdom from 1900 to the present.
- Comprehensive UK and International LGBT news website
- (UK) LGBT History Project's Wiki

