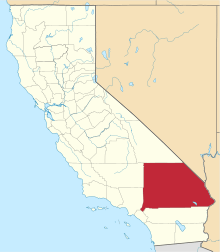
Apple Valley, California
Apple Valley is an incorporated town in the Victor Valley of San Bernardino County, in the U.S. state of California. It was incorporated on November 14, 1988, and is one of the twenty-two incorporated municipalities in California that uses "town" in its name instead of "city". The town is east of and adjoining to the neighboring cities of Victorville and Hesperia, 35 miles (56 km) south of Barstow, and 49 miles (79 km) north of San Bernardino through the Cajon Pass. The population was 69,135 at the 2010 census.
Apple Valley, California | |
|---|---|
Town | |
.jpg) Apple Valley Airport | |
 Seal | |
| Nickname(s): "Apple of the Desert" | |
| Motto(s): "A Better Way of Life!" | |
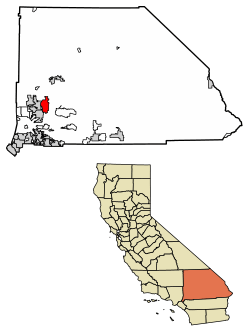 Location of Apple Valley in San Bernardino County, California. | |
 Apple Valley Location in California  Apple Valley Apple Valley (the United States)  Apple Valley Apple Valley (North America) | |
| Coordinates: 34°30′03″N 117°11′09″W[1] | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| County | |
| Incorporated | November 28, 1988[2] |
| Government | |
| • Type | Council–manager |
| • City council[3] | Mayor Larry Cusack, Mayor Pro Tem Scott Nassif, Art Bishop, Curt Emick, and Kari Leon |
| Area | |
| • Total | 74.99 sq mi (194.23 km2) |
| • Land | 74.92 sq mi (194.04 km2) |
| • Water | 0.07 sq mi (0.19 km2) 0.45% |
| Elevation | 2,946 ft (898 m) |
| Population | |
| • Total | 69,135 |
| • Estimate (2019)[6] | 73,453 |
| • Density | 975.40/sq mi (376.61/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC-8 (Pacific Time Zone) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-7 (PDT) |
| ZIP codes | 92307, 92308 [7] |
| Area code | 442/760[8] |
| FIPS code | 06-02364 |
| GNIS feature IDs | 1660259, 2412372 |
| Website | www |
Apple Valley is governed by a town council. The mayor changes each December.
Apple Valley was home to Roy Rogers and Dale Evans, whose museum was first established in Apple Valley (in 1967) before the museum was relocated to Victorville in 1976. In 2003, the museum moved again, to Branson, Missouri. The move was made in hopes of reaching more fans;[9] however, the museum closed for financial reasons on December 12, 2009.[10]
Geography
Apple Valley is located at 34°31′N 117°13′W (34.5115, -117.2120).[11]
Apple Valley is located at the southern edge of the Mojave Desert. It is bordered by the cities of Victorville on the west and Hesperia on the southwest sides, with the Census-Designated Place of Lucerne Valley a distance to the east and the city of Barstow about 30 miles to the north. Apple Valley, along with Victorville, Hesperia, Adelanto and immediate surrounding areas, are commonly known as the Victor Valley. The primary thoroughfare through Apple Valley is State Route 18, which was given the moniker "Happy Trails Highway" within Apple Valley town limits, after the theme song of Roy Rogers and Dale Evans, who once resided on Outer Highway 18. The commercial area is split currently between State Route 18 and Bear Valley Road (the two roads are near parallel until they intersect in the east, outside of town). The Mojave River that borders the west side of Apple Valley flows south-to-north.[12] The town is bounded on its southern edge by the foothills of the San Bernardino Mountains.
According to the United States Census Bureau, the town has a total area of 73.5 square miles (190 km2) of which 73.2 square miles (190 km2) is land and 0.3 square miles (0.78 km2), or 0.45%, is water.
The elevation of Apple Valley is approximately 2,900 feet (880 m) above sea level.
Climate
| Apple Valley, California | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate chart (explanation) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
According to the Köppen Climate Classification system, Apple Valley has a semi-arid climate (BSk). The city features cool winters and very hot, dry summers. Seasonal high winds occur occasionally in spring and fall.[13]
- On average, the warmest month is July.
- The highest recorded temperature was 116 °F (47 °C) in 2002.
- On average, the coolest month is December.
- The lowest recorded temperature was −1 °F (−18 °C) in 1949.
- The most precipitation on average occurs in February.
History
For centuries, Apple Valley was populated by Shoshonean, Paiute, Vanyume, Chemehueve and the Serrano who were attracted to the water and vegetation around the Mojave River. The Mojave people came later and were the tribal group encountered in 1542 by a detachment of Coronado's men. These were the first Spanish to come to the Mojave desert.
Pedro Fages came through the area in 1772, looking for deserters. Father Francisco Garcés spent time in the area in 1776. He was on good terms with local tribes. He killed one of his mules to feed a group of starving Vanyumes. Garcés established a trail across the Mojave to the Colorado River passing through the Apple Valley area.
The area was explored by various Spanish gold seekers in the 18th and 19th centuries. Jedediah Smith established the Old Spanish Trail through the southern Mojave and Cajon Pass. Smith was in the area in 1826 and again in 1827.[14]
Throughout the 19th century, Apple Valley became a thoroughfare of people traveling to Southern California for various reasons. Ute horse thieves, led by Chief Walkara, brought through an estimated 100,000 horses from their raids on the Lugo Rancho and San Gabriel Mission.
In 1848, members of the Mormon Battalion, mustered out of the U.S. Army after constructing the first wagon road across the southwest to San Diego and up to Los Angeles, brought 135 mules and the first wagon through the Cajon Pass up through the Mojave River Valley on the way to the Salt Lake Valley. Battalion leader Jefferson Hunt and a crew of cowboys followed the trail with the first cattle drive from Southern California to hungry Mormons in Utah. Hunt led a Mormon group of settlers to the San Bernardino Valley in 1851.
In 1885, the railroad came northward through the Cajon Pass and established a train stop, calling it Victor (Victorville) on the Mojave River in the area then known as Mormon Crossing. John Brown helped build some of the first roads through Apple Valley opening up freight and stagecoach travel from the mining camps at Gold Mountain and Holcomb Valley to the railroad. In the 1860s, Mormon pioneer LaFayette Mecham built the wagon road, a short cut across the desert, now known as Stoddard Wells Road. Over the next few decades, Victorville boomed as the commercial center of the area with gold refineries, quarries, dance halls and saloons, while Apple Valley remained more pastoral with ranches and apple orchards.
The naming of Apple Valley is usually associated with John F. Appleton. However, the name was finalized with development in the 1940s. The Apple Valley name was officially recognized when a post office was established in 1949.[15]
One well known apple orchard was owned by Max Ihmsen, publisher of the Los Angeles Examiner newspaper. In 1915, he developed 320 acres (1.3 km2) of apples and pears. The fame of Apple Valley spread as Ihmsen's fruit won many agricultural awards.[16] In the late 1930s, Ihmsen's son-in-law, Cal Godshall, took over the business operations and made the ranch famous as the birthplace of California college rodeo with the first intercollegiate rodeo competition ever held in the United States.
Apple farming in the area started to decline about the time Ihmsen Ranch fruit production was at its prime. Water rates shot up with a switch to electric pumps. World War I took owners and workers away with the draft. During the Great Depression many families left the mostly agricultural area looking for work. Washington and British Columbia apple growers were able to cut prices because they shipped their produce by river transportation, whereas Apple Valley apples were transported by rail or by truck. The death knell was a series of outbreaks of a virulent fungus infection coupled with frost, heat and hail in 1944, 1945 and 1946.[14]
A small orchard was maintained on the grounds of the Apple Valley Inn until it closed in 1986. The last commercially grown apples in Apple Valley had all but disappeared before the US Post Office officially recognized the name.
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1970 | 6,702 | — | |
| 1980 | 14,305 | 113.4% | |
| 1990 | 46,079 | 222.1% | |
| 2000 | 54,239 | 17.7% | |
| 2010 | 69,135 | 27.5% | |
| Est. 2019 | 73,453 | [6] | 6.2% |
| U.S. Decennial Census[17] | |||
2010
At the 2010 census Apple Valley had a population of 69,135. The population density was 940.3 people per square mile (363.1/km²). The racial makeup of Apple Valley was 47,762 (69.1%) White (55.5% Non-Hispanic White),[5] 6,321 (9.1%) African American, 779 (1.1%) Native American, 2,020 (2.9%) Asian, 294 (0.4%) Pacific Islander, 8,345 (12.1%) from other races, and 3,614 (5.2%) from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 20,156 persons (29.2%).[18]
The census reported that 68,674 people (99.3% of the population) lived in households, 161 (0.2%) lived in non-institutionalized group quarters, and 300 (0.4%) were institutionalized.
There were 23,598 households, 9,169 (38.9%) had children under the age of 18 living in them, 12,647 (53.6%) were opposite-sex married couples living together, 3,550 (15.0%) had a female householder with no husband present, 1,513 (6.4%) had a male householder with no wife present. There were 1,582 (6.7%) unmarried opposite-sex partnerships, and 177 (0.8%) same-sex married couples or partnerships. 4,743 households (20.1%) were one person and 2,429 (10.3%) had someone living alone who was 65 or older. The average household size was 2.91. There were 17,710 families (75.0% of households); the average family size was 3.32.
The age distribution was 19,306 people (27.9%) under the age of 18, 6,494 people (9.4%) aged 18 to 24, 15,068 people (21.8%) aged 25 to 44, 17,602 people (25.5%) aged 45 to 64, and 10,665 people (15.4%) who were 65 or older. The median age was 37.0 years. For every 100 females, there were 96.0 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 91.0 males.
There were 26,117 housing units at an average density of 355.2 per square mile, of the occupied units 16,297 (69.1%) were owner-occupied and 7,301 (30.9%) were rented.The homeowner vacancy rate was 4.0%; the rental vacancy rate was 10.0%. 45,483 people (65.8% of the population) lived in owner-occupied housing units and 23,191 people (33.5%) lived in rental housing units.
During 2009–2013, Apple Valley had a median household income of $48,432, with 20.2% of the population living below the federal poverty line.[5]
2000
At the 2000 census there were 54,239 people, 18,557 households, and 14,363 families in the town. The population density was 739.6 inhabitants per square mile (285.6/km²). There were 20,163 housing units at an average density of 275.0 per square mile (106.2/km²). The racial makeup of the town was 76.4% White, 7.9% African American, 1.0% Native American, 2.2% Asian, 0.2% Pacific Islander, 7.9% from other races, and 4.4% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 18.6%.[19]
Of the 18,557 households 38.8% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 57.8% were married couples living together, 14.2% had a female householder with no husband present, and 22.6% were non-families. 18.0% of households were one person and 8.4% were one person aged 65 or older. The average household size was 2.90 and the average family size was 3.27.
The age distribution was 31.6% under the age of 18, 7.8% from 18 to 24, 25.2% from 25 to 44, 21.7% from 45 to 64, and 13.7% 65 or older. The median age was 35 years. For every 100 females, there were 93.8 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 89.7 males.
The median household income was $40,421 and the median family income was $45,070. Males had a median income of $41,144 versus $30,249 for females. The per capita income for the town was $17,830. About 13.3% of families and 17.3% of the population were below the poverty line, including 24.6% of those under age 18 and 5.6% of those age 65 or over.
In addition to the latest census from 2000, the 2008 estimated population, of 72,922, includes 24,641 households of which 18,904 were family households. Approximately 70% of all housing units were owner occupied. The estimated racial make-up of the town includes 70.5% White, 10.0% African American, 1.0% Native American, 2.7% Asian, 0.3% Pacific Islander, 10.3% from other race, and 5.3% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race now make up approximately 25% of the population.
Out of 24,641 households, 42.7% had children under the age of 18 living with them. Of that figure, 65.5% were married couples living together, and 24.5% had a female householder with no husband present. Of all households, 18.1% were made up of individuals. The average household size was 2.9.
The age of the population was spread out with 28.3% under the age of 18, 10.6% from 18 to 24, 24.5% from 25 to 44, 23.2% from 45 to 64, and 13.4% who were 65 or older. The median age was 33.4 years. For every 100 females, there were currently 94 males.
The median household income was $49,202 and the median family income was $56,810. The per capita income for the town was $21,777. About 13.5% of families were below the poverty line.
Infrastructure
Public safety
Law enforcement is provided by the San Bernardino County Sheriff's Department.
Fire, rescue, and paramedic services are provided by the Apple Valley Fire Protection District.
American Medical Response provides patient transportation via Paramedic / EMT ambulances.
Cemeteries
The Sunset Hills Memorial Park & Mortuary was opened in 1995 on Waalew Road. Dale Evans and Roy Rogers are buried there.[20][21]
Utilities
The town council started the process to take over the private water system in 2016.[22]
Government
In the California State Legislature, Apple Valley is in the 21st Senate District, represented by Republican Scott Wilk, and in the 33rd Assembly District, represented by Republican Jay Obernolte.[23]
In the United States House of Representatives, Apple Valley is in California's 8th congressional district, represented by Republican Paul Cook.[24]
Education
Apple Valley is highly regarded in San Bernardino County and the State of California for its excellent schools and education options. Apple Valley Unified School District operates two comprehensive high schools (9–12), one Charter school (K–12), one independent study (hybrid/online course) school (K–12), three academies (K–8) and ten elementary schools (K–6). There is one private school (Pre–12).
High schools - comprehensive (9–12)
- Apple Valley High School
- Granite Hills High School
- Excelsior Charter Schools
Middle schools (K–8)
- Sitting Bull Academy—Recognized as a California Distinguished School
- Phoenix Academy
- Vanguard Preparatory—earned the "Schools to Watch" designation
- Rio Vista Elementary
Elementary schools (K–6)
- Desert Knolls Elementary
- Mariana Elementary
- Rancho Verde Elementary—Recognized as a California Distinguished School
- Sandia Elementary
- Sycamore Rocks Elementary—is a National Blue Ribbon School
- Yucca Loma Elementary—received the CSBA Golden Bell Award
Charter Schools
- Academy for Academic Excellence - also known as "Lewis Center for Educational Research" (K–12)
Independent Study
- High Desert Premier Academy (K–12)
Private schools
- Apple Valley Christian Academy (Pre–12)
- Saint Timothy's Preparatory School (closed in 2015)
Notable people
- Pearl Bailey, singer-actress, and her husband, Louie Bellson, lived in Apple Valley for nearly a decade
- Earl W. Bascom, inventor, artist, sculptor, actor, Rodeo Hall of fame inductee, "Father of Modern Rodeo"
- Newton T. Bass, Reserve Oil and Gas Co. executive, developer of Apple Valley Ranchos
- Louie Bellson, jazz drummer/VP of Remo, lived in Apple Valley for nearly a decade with wife, Pearl Bailey
- Chris Blais, off-road motorcycle rider
- Angel Blue, soprano opera singer
- Victor Buono, actor, lived and died in Apple Valley
- Billy Casper, professional golfer
- Van Conner, musician from rock band Screaming Trees
- Marty Dodson, singer-songwriter/producer, was born in Apple Valley
- Dock Ellis, MLB pitcher, was hospitalized at St. Mary's Hospital just prior to his death
- Don Ferrarese, former MLB pitcher, owner of Apple Valley Land Company
- Cuba Gooding, Jr., Oscar-winning actor, attended Apple Valley High School
- Dan Henderson, mixed martial artist and Olympic wrestler
- John W. Henry, owner of Boston Red Sox, lived in Apple Valley during high school and college
- "Mad" Mike Hughes, daredevil and amateur crewed rocketry enthusiast
- Miko Hughes, actor, Pet Sematary, Kindergarten Cop, Apollo 13
- Will James, artist, writer who lived on C Bar G Ranch
- Herb Jeffries, actor and jazz singer, filmed several movies in Apple Valley at Murray's Dude Ranch
- Dave Lombardo, drummer for heavy metal band, Slayer
- Joe Louis, boxing champion, was a frequent vacationer to Murray's Dude Ranch in 1930s
- Joseph C. McConnell, top-scoring American jet ace, lived in Apple Valley until his death in an F-86H-1-NA crash
- Lloyd Mangrum, professional golfer and 1946 U.S. Open champion
- Joseph Medina, BGen USMC, 1st Marine to command Navy Flotilla and Hispanic icon, Apple Valley HS grad
- Richard Nixon, former U.S. president, spent three months at the home of founder Newton T. Bass in 1961 writing his first book, Six Crises[25]
- Erik Robertson, football player
- Roy Rogers and Dale Evans, western singers, actors, co-founders of Sons of the Pioneers; both died in Apple Valley
- Smokey Rogers, western swing musician, singer, songwriter, entertainer, local KAVR radio personality
- Chris Smith, MLB player for Oakland Athletics
- Tim Spencer, western singer, actor, co-founder of Sons of the Pioneers
- Scout Taylor-Compton, actress in Rob Zombie's Halloween
- John Charles Thomas, opera singer, KAVR radio personality
- Jason Thompson, former MLB first baseman
- Jason Vargas (born 1983), baseball pitcher for the Philadelphia Phillies
- Skip Young, actor, The Adventures of Ozzie and Harriet
Film history
Apple Valley has a long and storied relationship with Hollywood production studios and has been a filming location for many award-winning Feature Films, TV shows/movies, and Commercials:
Feature films
- The Bronze Buckaroo (1939), starring Herb Jeffries, was filmed at Murray's Dude Ranch
- Column South (1953), starring Audie Murphy, was filmed in Apple Valley and nearby Victorville
- Divorce Invitation (2012)
- Eagle Eye (2008), starring Shia LaBeouf
- Four Guns To The Border (1954), starring Rory Calhoun and Walter Brennan
- Foxfire (1955), starring Jane Russell, was filmed at Apple Valley Inn
- The Hard Ride (1971) was filmed at Oro Grande Wash and in nearby Lucerne Valley
- Harlem on the Prairie (1937), starring Herb Jeffries, was filmed at Murray's Dude Ranch
- Harlem Rides the Range (1939), starring Herb Jeffries, was filmed at Murray's Dude Ranch
- Highway Dragnet (1954), written by Roger Corman, starring Richard Conte and Joan Bennett, was filmed at Apple Valley Inn
- The Hills Have Eyes (1977), was filmed in Apple Valley and nearby Victorville
- Ordinary People (1980), winner of four Oscars, starring Mary Tyler-Moore—golf scenes filmed in Apple Valley
- There's Always Tomorrow (1956), starring Barbara Stanwyck and Fred MacMurray, was filmed at Apple Valley Inn
- Two-Gun Man From Harlem (1938), was filmed at Murray's Dude Ranch
Television
- Sky King, was filmed at the old Apple Valley Airport (old airport location coordinates: 34.528°N 117.215°W)
- Perry Mason episode, The Case of The Roving River (1961), was filmed at Apple Valley Inn and Newton Bass House
- Weekend of Terror (1970 ABC Movie of the Week), starring Robert Conrad, Carol Lynley and Lee Majors, was filmed in Apple Valley
Commercials
- GoDaddy.com, featuring Danica Patrick
See also
- Victorville Precision Bombing
- Victorville Army Airfield auxiliary fields
References
- "Apple Valley". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey. Retrieved November 12, 2014.
- "California Cities by Incorporation Date". California Association of Local Agency Formation Commissions. Archived from the original (Word) on November 3, 2014. Retrieved August 25, 2014.
- "Town Council". Town of Apple Valley. Archived from the original on February 3, 2015. Retrieved January 14, 2015.
- "2017 U.S. Gazetteer Files". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved August 27, 2018.
- "Apple Valley (town) QuickFacts". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on August 16, 2012. Retrieved February 26, 2015.
- "Population and Housing Unit Estimates". Retrieved May 21, 2020.
- "USPS - ZIP Code Lookup - Find a ZIP+ 4 Code By City Results". Retrieved February 20, 2007.
- "Number Administration System - NPA and City/Town Search Results". Archived from the original on September 26, 2007. Retrieved February 20, 2007.
- Victor Valley Daily Press. February 14, 2009 http://www.vvdailypress.com/news/museum_10892___article.html/roy_rogers.html?orderby=TimeStampDescending&oncommentsPage=2&showRecommendedOnly=0#slComments%5B%5D
- Special Announcement from Roy Rogers Jr. http://www.royrogers.com/announcement.html Archived November 7, 2016, at the Wayback Machine
- "US Gazetteer files: 2010, 2000, and 1990". United States Census Bureau. February 12, 2011. Retrieved April 23, 2011.
- "Rivers That Flow North". World Atlas. Retrieved April 2, 2012.
- Climate Summary for Apple Valley, California
- Apple Valley-Crossroads of the Desert by Ellsworh A Sylvester, San Bernardino County Museum Commemorative Edition, Allen=Greendale Publishers, Redlands, CA. 1974, pg 125
- Gudde, Erwin; William Bright (2004). California Place Names (Fourth ed.). University of California Press. p. 15. ISBN 978-0-520-24217-3.
- "Town of Apple Valley : Through the Decades". Applevalley.org. Archived from the original on June 28, 2014. Retrieved February 28, 2014.
- "Census of Population and Housing". Census.gov. Retrieved June 4, 2015.
- "2010 Census Interactive Population Search: CA - Apple Valley town". U.S. Census Bureau. Archived from the original on July 15, 2014. Retrieved July 12, 2014.
- "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 2008-01-31.
- Brooks, Patricia; Brooks, Jonathan (2006). "Chapter 8: East L.A. and the Desert". Laid to Rest in California: a guide to the cemeteries and grave sites of the rich and famous. Guilford, CT: Globe Pequot Press. p. 235. ISBN 978-0762741014. OCLC 70284362.
- Sunset Hills Memorial Park
- Cabe, Matthew (March 1, 2019). "Trial date set in Apple Valley water lawsuit". vvdailypress.com. Retrieved March 7, 2019.
- "Statewide Database". UC Regents. Archived from the original on February 1, 2015. Retrieved December 10, 2014.
- "California's 8th Congressional District - Representatives & District Map". Civic Impulse, LLC. Retrieved March 9, 2013.
- Nixon's legacy remains in Apple Valley Archived May 26, 2011, at the Wayback Machine