Guáitara Fault
| Guáitara Fault | |
|---|---|
| Falla de Guáitara | |
 | |
| Etymology | Guáitara River |
| Country |
|
| Region | Andean |
| State | Nariño |
| Cities | Ipiales |
| Characteristics | |
| Range | Western Ranges, Andes |
| Part of | Andean strike-slip faults |
| Length | 36.1 km (22.4 mi) |
| Strike | 044.1 ± 4 |
| Dip | East |
| Dip angle | High |
| Displacement | <0.2 mm (0.0079 in)/yr |
| Tectonics | |
| Plate | North Andean |
| Status | Inactive |
| Type | Strike-slip fault |
| Movement | Dextral |
| Age | Quaternary |
| Orogeny | Andean |
| Volcanic arc/belt |
North Volcanic Zone Andean Volcanic Belt |
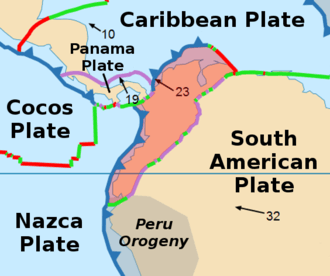
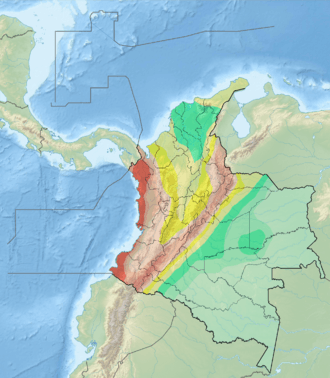
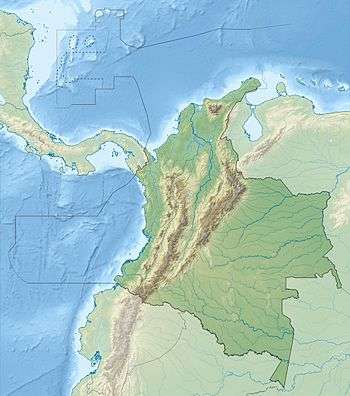
The Guáitara Fault (Spanish: Falla de Guáitara) is a dextral strike-slip fault in the department of Nariño in southwestern Colombia. The fault has a total length of 36.1 kilometres (22.4 mi) and runs along an average northeast to southwest strike of 044.1 ± 4 in the Western Ranges of the Colombian Andes.
Etymology
The fault is named after the Guáitara River in Nariño.[1]
Description
The Guáitara Fault is in the Nariño Department of southwestern Colombia, crossing the Western Ranges of the Colombian Andes and to the south of the city of Pasto. The fault offsets Neogene volcanic rocks. The fault is believed to extend south into the Republic of Ecuador and may be part of the megaregional Romeral Fault System. The fault forms well developed deep V-shaped valleys, linear topographic features, fault-controlled drainage, deflected streams, and elongated hills.[1]
See also
References
Bibliography
- Paris, Gabriel; Michael N. Machette; Richard L. Dart, and Kathleen M. Haller. 2000a. Map and Database of Quaternary Faults and Folds in Colombia and its Offshore Regions, 1–66. USGS. Accessed 2017-09-18.
Maps
- Paris, Gabriel; Michael N. Machette; Richard L. Dart, and Kathleen M. Haller. 2000b. Map of Quaternary Faults and Folds of Colombia and Its Offshore Regions, 1. USGS. Accessed 2017-09-18.