At-Tira (Ramallah)
| At-Tira (Ramallah) | |
|---|---|
| Other transcription(s) | |
| • Arabic | الطيرة |
 At-Tira (Ramallah) Location of At-Tira (Ramallah) within Palestine | |
| Coordinates: 31°52′05″N 35°07′20″E / 31.86806°N 35.12222°ECoordinates: 31°52′05″N 35°07′20″E / 31.86806°N 35.12222°E | |
| Palestine grid | 161/141 |
| Governorate | Ramallah & al-Bireh |
| Government | |
| • Type | Village council |
| Elevation[1] | 623 m (2,044 ft) |
| Name meaning | the fort[2] |
At-Tira (Arabic: الطيرة) is a Palestinian village in the Ramallah and al-Bireh Governorate in the northern West Bank.
Location
At Tira is located 8.3 kilometers (5.2 mi) southwest of Ramallah. It is bordered by Beituniya to the east and north, Beit 'Ur al Fauqa to the north and west, Beit ‘Anan to the west, and Beit Duqqu to the south.[1]
History
Ottoman era
In 1838, in the Ottoman era, it was noted as a Muslim village, located in the Beni Malik district, west of Jerusalem.[3]
In 1883, Palestine Exploration Fund's Survey of Western Palestine (SWP) described Tireh as: "A small hamlet on a ridge, with a large sacred tree to the north-east (Sheikh Hasan), and a spring ('Ain Jufna) in the valley to the south-west."[4]
British Mandate era
In the 1922 census of Palestine, conducted by the British Mandate authorities, Al Tireh had a population of 257 Muslims,[5] increasing slightly in the 1931 census to 265 Muslims, in 71 houses in Et Tira.[6]
In the 1945 statistics, the population of Et Tira was 330 Muslims,[7] while the total land area was 3,968 dunams, according to an official land and population survey.[8] Of this, 193 dunums were used for plantations and irrigable land, 1,974 for cereals,[9] while 23 dunams were classified as built-up areas.[10]
Jordanian era
In the wake of the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, and after the 1949 Armistice Agreements, At-Tira came under Jordanian rule.
The Jordanian census of 1961 found 534 inhabitants in Tira.[11]
1967-present
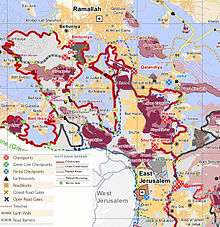
After the Six-Day War in 1967, At-Tira has been under Israeli occupation.
After the 1995 accords, 10.4% of village land has been defined as Area B land, while the remaining 89.6% is Area C. Israel has confiscated a total of 67 dunams of land from the village in order to construct the Israeli settlement of Beit Horon.[12]
At-Tira along with 9 other Palestinian villages, Beit Duqqu, Beit 'Anan, Beit Surik, Qatanna, al-Qubeiba, Beit Ijza, Kharayib Umm al Lahimand and Biddu form the "Biddu enclave" which, according to Tanya Reinhart, are imprisoned behind a wall, cut off from their orchards and farmlands that are being seized in order to form the real estate reserves of the Jerusalem Corridor and to create a territorial continuity with Giv'at Ze'ev.[13] The enclave will be linked to Ramallah by underpasses and a road that is fenced on both sides. From the "Biddu enclave" Palestinians will travel along a fenced road that passes under a bypass road to Bir Nabala enclave, then on a second underpass under Bypass Road 443 to Ramallah.[14]
References
- 1 2 At Tira Village Profile, ARIJ, p. 4
- ↑ Palmer, 1881, p. 330
- ↑ Robinson and Smith, 1841, vol 3, Appendix 2, p. 124
- ↑ Conder and Kitchener, 1883, SWP III, p. 19
- ↑ Barron, 1923, Table VII, Sub-district of Ramallah, p. 17
- ↑ Mills, 1932, p. 51.
- ↑ Government of Palestine, Department of Statistics, 1945, p. 26
- ↑ Government of Palestine, Department of Statistics. Village Statistics, April, 1945. Quoted in Hadawi, 1970, p. 65
- ↑ Government of Palestine, Department of Statistics. Village Statistics, April, 1945. Quoted in Hadawi, 1970, p. 113
- ↑ Government of Palestine, Department of Statistics. Village Statistics, April, 1945. Quoted in Hadawi, 1970, p. 163
- ↑ Government of Jordan, Department of Statistics, 1964, p. 24
- ↑ At Tira Village Profile, ARIJ, p. 16
- ↑ Reinhart, 2006, p. 202
- ↑ OCHA Archived November 12, 2005, at the Wayback Machine.
Bibliography
- Barron, J. B., ed. (1923). Palestine: Report and General Abstracts of the Census of 1922. Government of Palestine.
- Conder, C.R.; Kitchener, H. H. (1883). The Survey of Western Palestine: Memoirs of the Topography, Orography, Hydrography, and Archaeology. 3. London: Committee of the Palestine Exploration Fund.
- Government of Jordan, Department of Statistics (1964). First Census of Population and Housing. Volume I: Final Tables; General Characteristics of the Population (PDF).
- Government of Palestine, Department of Statistics (1945). Village Statistics, April, 1945.
- Mills, E., ed. (1932). Census of Palestine 1931. Population of Villages, Towns and Administrative Areas. Jerusalem: Government of Palestine.
- Palmer, E. H. (1881). The Survey of Western Palestine: Arabic and English Name Lists Collected During the Survey by Lieutenants Conder and Kitchener, R. E. Transliterated and Explained by E.H. Palmer. Committee of the Palestine Exploration Fund.
- Reinhart, T. (2006). The Road Map to Nowhere: Israel/Palestine Since 2003. London; New York: Verso. ISBN 1-84467-076-7.
- Robinson, E.; Smith, E. (1841). Biblical Researches in Palestine, Mount Sinai and Arabia Petraea: A Journal of Travels in the year 1838. 3. Boston: Crocker & Brewster.
External links
- Welcome To al-Tira
- At Tira Village (Fact Sheet), Applied Research Institute–Jerusalem, ARIJ
- At Tira Village Profile, ARIJ
- At Tira photo, ARIJ
- Locality Development Priorities and Needs in At Tira Village, ARIJ
- Survey of Western Palestine, Map 17: IAA, Wikimedia commons
