Sula Islands Regency
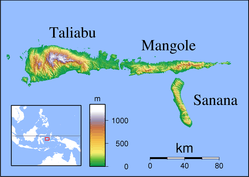
The Sula Islands Regency (Indonesian: Kabupaten Kepulauan Sula) is one of the regencies in North Maluku province of Indonesia. It consists of two of the three large islands comprising the Sula Archipelago, together with minor adjacent islands. The third island, Taliabu, was split off from the Sula Islands Regency in 2013 to form a separate regency.
Sula Islands Regency Kabupaten Kepulauan Sula | |
|---|---|
 Seal | |
| Coordinates: 1°52′S 125°22′E | |
| Country | |
| Province | |
| Capital | Sanana |
| Government | |
| • Regent | Hendrata Thes |
| • Vice Regent | Zulfahri Abdulah Duwila |
| Area | |
| • Total | 1,787.63 km2 (690.21 sq mi) |
| Population (2010 Census) | |
| • Total | 85,215 |
| • Density | 48/km2 (120/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+9 (IEST) |
| Area code | (+62) 921 |
| Website | kepulauansulakab |
Pre-Indonesian Independence saw the Sula Islands also known as the Xulla Islands, with Taliabo as Xulla Taliabo, Sanana as Xulla Bessi, and Mangola as Xulla Mangola.[1]
Administration
Sula Islands Regency comprises twelve districts (kecamatan), tabulated below with their areas and populations at the 2010 Census:[2]
| Name | English name | Area in km2 | Population Census 2010 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mangole Barat | West Mangole | 158.30 | 7,084 |
| Mangole Utara | North Mangole | 227.61 | 10,115 |
| Mangole Selatan | South Mangole | 246.56 | 4,665 |
| Mangole Tengah | Central Mangole | 333.21 | 6,381 |
| Mangole Timur | East Mangole | 140.42 | 4,301 |
| Mangole Utara Timur | Northeast Mangole | 149.23 | 3,777 |
| Mangole Island | (total) | 1,255.33 | 36,323 |
| Sanana Utara | North Sanana | 75.28 | 5,675 |
| Sanana | 83.36 | 25,183 | |
| Sula Besi Tengah | Central Sula Besi | 74.73 | 5,929 |
| Sula Besi Timur | East Sula Besi | 82.18 | 3,100 |
| Sula Besi Selatan | South Sula Besi | 88.49 | 4,298 |
| Sula Besi Barat | West Sula Besi | 128.26 | 4,707 |
| Sula Besi Island | (total) | 532.30 | 48,892 |
History
The Dutch built a fort on Sanana in 1652. Wallace visited the islands during an ornithological expedition in 1862.[3]

Economy
According to government data, Sula Islands Regency's food crops include vegetables, groundnuts, cassava, sweet potatoes, durian, mangosteen and mango. As of 2005 the area of agriculturally active land was 24743.56 hectares with production amounting to 33,608.62 tons per year. Taliabu-Sanana District is the main producer of cloves, nutmeg, cocoa, copra and other coconut products. Fishery production is very diverse with and estimated sustainable potential of 40,273.91 tonnes per year of which only 22.8 percent is currently exploited. Forestry is considered a potential industry with the natural forest-based Classification Map TGHK RTRWP suggesting a forest area of 471,951.53 hectares, but much of this is protected or hard to access, due to steep slopes and transportation logistics, and the islands' main plywood company, PT Barito Pacific Timber Group (in Falabisahaya, West Mangole) has closed. Industrial activity is very limited. There is a gold mine in East Mangoli District (at Waitina and Kawata) and coal mines are located in the peninsula of West Sula Besi District, East Taliabu and Sub Sanana (Wai Village Ipa). Reserves of coal are estimated around 10.4 million tonnes.
Tourism
The Indonesian Ministry of Tourism (Kemenpar) is ready to support the promotion of tourism destination potential on Sula Islands. Demographically located between the crossroads of Wakatobi and Raja Ampat tourist areas, it is ideally developed as marine tourism and special interest tourism for diving enthusiasts.
One of the support is Maksaira Festival at Wai Ipa Beach to Bajo Village Beach. On 2018 the festival as a cultural and marine tourism attraction event has entered the third year and will be listed as MURI record breaking for the largest grouper fishing participant targeted by 3000 participants in 2018, where year 2017 followed by 1700 participants [4].
Fauna
The following species are native to the Sula Islands:
- Buru babirusa Babyrousa babyrussa
- Banggai cuscus Strigocuscus pelengensis
- Sula rat Rattus elaphinus
- Sulawesi flying fox Acerodon celebensis
- Lesser short-nosed fruit bat Cynopterus brachyotis
- Greenish naked-backed fruit bat Dobsonia viridis
- Long-tongued nectar bat Macroglossus minimus
- Pallas's tube-nosed bat Nyctimene cephalotes
- Ashy-headed flying fox Pteropus caniceps
- Sulawesi rousette Rousettus celebensis
- Swift fruit bat Thoopterus nigrescens
- Small Asian sheath-tailed bat Emballonura alecto
- Fawn leaf-nosed bat Hipposideros cervinus
- Small bent-winged bat Miniopterus pusillus
- Sula megapode Megapodius bernsteinii (Gosong Sula), status vulnerable[5]
Introduced species include:
- Asian house shrew
- Wild boar (Sus scrofa)
- Polynesian rat (Rattus exulans)
References
- Goodall, George (Editor)(1943) Philips' International Atlas London, George Philip and Son map 'East Indies' pp.91-92
- Biro Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2011.
- Wallace, Alfred Russel (1862). "2. List of Birds from the Sula Islands (east of Celebes), with Descriptions of the New Species" (PDF). Proceedings of the Zoological Society of London. 30: 333–346. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7998.1862.tb06537.x.
- "Government Supports Tourism Promotion in Sula Islands". Lelemuku.com. Retrieved 26 July 2018.
- http://www.antaranews.com/en/news/72587/more-indonesian-bird-species-nearing-extinction
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Sula Islands Regency. |