1946 Indian provincial elections
Provincial elections were held in British India in January 1946 to elect members of the legislative councils of British Indian provinces.[1] The consummation of British rule in India were the 1945/1946 elections. As minor political parties were eliminated, the political scene became restricted to the Indian National Congress and the All-India Muslim League who were more antagonised than ever. The Congress, in a repeat of the 1937 elections, won 90 percent of the general non-Muslim seats while the Muslim League won the majority of Muslim seats (87%) in the provinces. Only 16% of Indian Muslims, mainly those from upper class, were able to vote.[2] Nevertheless, the All India Muslim League verified its claim to be the sole representative of Muslim India.[3][4] The election laid the path to Pakistan.[5][4][6]
| ||||||||||||||||
1585 provincial seats contested | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||
 | ||||||||||||||||
Background
On 19 September 1945, following negotiations between Indian leaders and members of the 1946 Cabinet Mission to India from the United Kingdom, the Viceroy Lord Wavell announced that elections to the provincial and central legislatures would be held in December 1945 to January 1946. It was also announced that an executive council would be formed and a constitution-making body would be convened after these elections.[1][7] These elections were important as the provincial assemblies thus formed were to then elect a new Constituent Assembly which would begin formulating a constitution for an independent India. All contesting parties began campaigning. The Congress contended that it represented the entire Indian population while the Muslim League professed to speak for the whole Muslim population.[8] The dominant issue of the election campaign became the issue of Pakistan.[5][9][10]
Originally, the Muslim League had been a party which received most of its support from the Muslim-minority provinces, where fear of Hindu ‘domination’ was greater as was the sense of ‘a loss of privilege’, and to showcase its argument for Muslim nationhood the League needed support from both Muslim-majority as well as Muslim-minority provinces. In the election campaign, the League resorted to establishing networks with traditional power bases, such as landowners and the religious elite, in the Muslim-majority provinces to win support. Religious slogans were utilized and the term ‘Pakistan’ was put forward. Some scholars state that the meaning of Pakistan was kept vague so that it meant different things to different people.[11] On the other hand, Venkat Dhulipala observes that, rather than being vague, the proposals for Pakistan were vigorously debated in public, maps printed, economic foundations analysed and Pakistan was envisioned as a modern Islamic state.[12][13]
In contrast to earlier elections, religious commitment was intertwined with a declaration of Muslim communal unity. Casting the vote became an Islamic act.[14] Consequently, for the Muslim electorate, Pakistan represented both a nation-state for India's Muslims, but one which surpassed the common state structure, and an awakening of an Islamic polity where Islam would be blended with the state's functioning.[15]
Punjab
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Punjab Provincial Assembly 1946-1947 | |
|---|---|
| Structure | |
| Seats | 175 (88 seats needed for majority) |
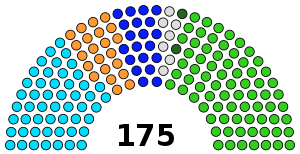 | |
Political groups | Government (100)
Opposition (75) |
| Elections | |
| First-past-the-post | |
The Unionist Party contested election under the leadership of Malik Khizar Hayat Tiwana but party stood at fourth place. To stop the Muslim League to form the government in Punjab Indian National Congress and Shiromani Akali Dal extended their support to Unionist Party. Malik Khizar Hayat Tiwana resigned on 2 March 1947 against the decision of Partition of India.
A key battleground during the elections was the Punjab province. The Punjab had a slight Muslim majority, and local politics had been dominated by the secular Unionist Party and its longtime leader Sir Sikandar Hayat Khan. The Unionists had built a formidable power base in the Punjabi countryside through policies of patronage allowing them to retain the loyalty of landlords and pirs who exerted significant local influence.[16] For the Muslim League to claim to represent the Muslim vote, they would need to win over the majority of the seats held by the Unionists. Following the death of Sir Sikander in 1942, and bidding to overcome their dismal showing in the elections of 1937, the Muslim League intensified campaigning throughout rural and urban Punjab.[5][17]
Results
The results were in favour of the Indian National Congress, which won 91 percent of the vote in non-Muslim constituencies, thus proving that for most Hindus it was the legitimate successor to the British rule. The acceptance of British authority by politically active Indians would be questionable had Britain intended to remain (although the views of many rural Indians were still uncertain then).[18] Of the total of 1585 seats, it won 923 (58.23%)[17]
The All-India Muslim League won 425 seats (26.81% of the total), placing it as the second-ranking party. It captured all Muslim constituencies in the central assembly as well as most of the Muslim constituencies in the provincial legislatures.[19] The vote opened the path to Pakistan.[4] The system of separate electorates ensured that Muslim contestants would compete with other Muslim candidates instead of facing non-Muslim contestants. Thus, the establishment of Pakistan was debated mainly among Muslims themselves.[20]
The Muslim League's biggest success was in Bengal where out of 119 seats for Muslims, it won 113. The League reinforced its vote in the Muslim minority provinces. It won 54 out of 64 Muslim seats in the United Provinces and 34 of Bihar's 40 Muslim seats. It captured all Muslim seats in Bombay and Madras. The party demonstrated that it was the representative of Muslim India.[5][4]
The Communist Party of India had presented 108 candidates, out of whom only 8 won a seat.[21] The set-back came as a result of the decision of the party not to support the Quit India movement of 1942.[22] Seven out of the eight seats it won were reserved for labour representatives. All in all, the Communist Party obtained 2.5% of the popular vote. Albeit far from competing with the two main parties, the communists became the third force in terms of the popular vote.[21] Amongst the communist candidates elected were Jyoti Basu (railways constituency in Bengal), Ratanlal Brahman (Darjeeling) and Rupnarayan Ray (Dinajpur).[23]
The results for the North West Frontier Province came through in March. Congress achieved a strong majority, largely due to the personality of Khan Abdul Ghaffar Khan, enabling them to form a government without trouble.[17]
In the Punjab, the concerted effort of the Muslim League led to its greatest success, winning 75 seats of the total Muslim seats and becoming the largest single party in the Assembly. The Unionist Party suffered heavy losses winning only 20 seats in total. The Congress was the second largest party, winning 43 seats, whilst the Sikh centric Akali Dal came third with 22 seats.[17]
In Assam, Congress won all of the general seats, and most of those reserved for special interest, thus forming the local government. The Muslim League won all of the Muslim seats.[17]
In the Muslim majority province of Sind, the Muslim League won the most seats. Congress however also achieved strong results, and initially hoped to form a coalition in government with four Muslims who had defected from the Muslim League. At the last minute, one of the four Muslim dissidents went over to the Muslim League, handing them a majority of one. Congress then lobbied three European members, who would swing the balance of power into their favour, but their overtures were rejected. The Governor of Sind therefore asked the Muslim League to form the local government.[17]
Legislative Assemblies
| Province | Congress | Muslim League | Other parties | Independents | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Assam | 58 | 31 | Europeans 9 Others 3 | 7 | 108 |
| Bengal | 86 | 113 | Europeans 25 Others 12 | 14 | 250 |
| Bihar | 98 | 34 | 8 | 12 | 152 |
| Bombay | 125 | 30 | 2 | 18 | 175 |
| Central Provinces | 92 | 13 | 7 | 112 | |
| Madras | 163 | 28 | Communist Party 2[24] | 22 | 215 |
| North West Frontier Province | 30 | 17 | 2 | 1 | 50 |
| Orissa | 47 | 4 | 9 | 60 | |
| Punjab | 51 | 73 | Akalis 22 Unionist Party 20 Majlis-e-Ahrar-e-Islam 2 | 7 | 175 |
| Sind | 18 | 27 | 10 | 4 | 60 |
| United Provinces | 153 | 54 | 7 | 14 | 228 |
| Total | 923 | 425 | 123 | 114 | 1585 |
Overall Muslim League Performance
In the elections, the appeal for Pakistan was crucial for the Muslim league's victory. According to Robert Stern, religious fervour played part in the league's victory. In Punjab also religious appeal was the factor in the battle between the league and the muslim members of the Unionist party who were not interested in Pakistan.[26]
| Province | Muslim Seats | Muslim League | % Of Muslim Seats won by Muslim League |
|---|---|---|---|
| Assam | 34 | 31 | 91% |
| Bengal | 119 | 113 | 95% |
| Bihar | 40 | 34 | 85% |
| Bombay | 30 | 30 | 100% |
| Central Provinces | 14 | 13 | 93% |
| Madras | 29 | 29 | 100% |
| North West Frontier Province | 36 | 17 | 47% |
| Orissa | 4 | 4 | 100% |
| Punjab | 86 | 74 | 86% |
| Sind | 34 | 28 | 82% |
| United Provinces | 66 | 54 | 82% |
| Total | 492 | 429 | 87% |
Aftermath
The Congress formed its ministries in Assam, Bihar, Bombay, Central Provinces, Madras, NWFP, Orissa and United Provinces. The Muslim League formed its ministries in Bengal and Sind. A coalition consisting of the Congress, Unionist Party and the Akalis was formed in Punjab.[27]
Ishtiaq Ahmed[28] has given a well documented account of how the Coalition Government in the United Punjab collapsed as a result of a massive campaign launched by the then Punjab Muslim League. AIML (Punjab) deemed the coalition government as a 'non-representative' government and thought it was their right to bring such government down (notwithstanding the fact that it was a legal and democratically elected government). AIML (P) called for a 'Civil Disobedience' movement (which was fully backed by Mr. Jinnah and Mr. Liaqat Ali Khan, after they had failed to enlist Sikh's support to help form an AIML led government in Punjab). This led to bloody communal riots in Punjab during the later part of 1946. By early 1947, the law and order situation in the province came to such a point where civil life was utterly paralysed. It was under such circumstances that the coalition Punjab Premier (Chief Minister) Mr. Khizer Haya Tiwana was forced to resign, on 2 March 1947. His cabinet was dissolved the same day. As there was no hope left for any other government to be formed to take the place of the Khizer government, the then Punjab Governor Sir Evan Jenkins imposed Governor's rule in Punjab on 5 March which continued up to the partition day, that is 15 August 1947. Akali-Dall Sikkhs who, with 22 seats, were major stake-holders in the coalition along with Congress(51) and the Unionist Party (20), were infuriated over the dissolution of the Khizer Government. It was in this backdrop that on 3 March 1947, Akali Sikh leader Master Tara Singh brandished his kirpan outside Punjab Assembly saying openly 'down with Pakistan and blood be to the one who demands it'. From this day on wards, Punjab was engulfed in such bloodied communal riots that the history had never witnessed before. Eventually, Punjab had to be partitioned into the Indian and Pakistani Punjab. In the process, over a million of innocent people were massacred, millions were forced to cross-over and to become refugees while thousands of women were abducted, raped and killed, across all religious communities in Punjab.
References
- Vohra, Ranbir (2013) [First published 1997]. The Making of India: A Political History (3rd ed.). M. E. Sharpe. p. 176. ISBN 978-0-7656-2985-2.
- Orissa Review - Volume 22. Home Department, Government of Orissa. 1965. p. 16.
- Barbara Metcalf; Thomas Metcalf (2006). A Concise History of Modern India (PDF) (2nd ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 212–213. ISBN 978-0-511-24558-9.
- Ian Talbot; Gurharpal Singh (23 July 2009). The Partition of India. Cambridge University Press. p. 36. ISBN 978-0-521-85661-4.
- Nadeem F. Paracha (11 May 2014). "The election that created Pakistan". Dawn. Retrieved 20 August 2019.
- Mateen Hafeez (1 September 2009). "Jinnah's constituency gears up for elections". The Times of India. Retrieved 20 August 2019.
- Sen, S. N. (1997). History of the Freedom Movement in India (1857–1947) (3rd ed.). New Age International. p. 317. ISBN 978-81-224-1049-5.
- Yasmin Khan (2007). The Great Partition: The Making of India and Pakistan. Yale University Press. p. 31. ISBN 978-0-300-12078-3.
While the Congress claimed to speak for all Indians, irrespective of religion, the League claimed to be the mouthpiece of all Muslims.
- Yasmin Khan (2007). The Great Partition: The Making of India and Pakistan. Yale University Press. p. 32. ISBN 978-0-300-12078-3.
Before long, though, economic issues were supplanted by a more trenchant issue. The campaigning focal point quickly emerged as Pakistan.
- Victor Sebestyen (2014). 1946: The Making of the Modern World. Pan Macmillan UK. pp. 246–. ISBN 978-1-74353-456-4.
...it became a plebiscite on one issue: whether Muslims should be granted a separate state, Pakistan – 'land of the pure'. Overwhelmingly, the Muslims voted in favor.
- Aparna Pande (2011). Explaining Pakistan’s Foreign Policy: Escaping India. Taylor & Francis. pp. 11–. ISBN 978-1-136-81894-3.
- Dhulipala, Venkat (2015). Creating a New Medina. Cambridge University Press. p. 194. ISBN 978-1-107-05212-3.
- Talbot, Ian (2015), "Creating a New Medina: State Power, Islam and the Quest for Pakistan in Late Colonial North India. By Venkat Dhulipala", The Journal of Asian Studies, 74 (4): 1054–1055, doi:10.1017/S0021911815001461, ISSN 0021-9118
- Barbara Metcalf; Thomas Metcalf (2006). A Concise History of Modern India (PDF) (2nd ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 214. ISBN 978-0-511-24558-9.
- Barbara Metcalf; Thomas Metcalf (2006). A Concise History of Modern India (PDF) (2nd ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 215. ISBN 978-0-511-24558-9.
- Talbot, I. A. (1980). "The 1946 Punjab Elections". Modern Asian Studies. 14 (1): 65–91. doi:10.1017/s0026749x00012178. JSTOR 312214.
- W. W. J. (April 1946). "The Indian Elections – 1946". The World Today. 2 (4): 167–175. JSTOR 40391905.
- Brown, Judith Margaret (1994). Modern India: the origins of an Asian democracy. Oxford University Press. pp. 328–329. ISBN 978-0-19-873112-2.
The acquiescence of the politically aware (though possibly not of many villagers even at this point) would have been seriously in doubt if the British had displayed any intention of staying in India.
- Barbara D. Metcalf; Thomas R. Metcalf (2012). A Concise History of Modern India. Cambridge University Press. pp. 213–. ISBN 978-0-511-24558-9..
- David Gilmartin (2009). "Muslim League Appeals to the Voters of Punjab". In Barbara D. Metcalf (ed.). Islam in South Asia in Practice. Princeton University Press. pp. 410–. ISBN 978-1-4008-3138-8.
- Gene D. Overstreet; Marshall Windmiller (1959). Communism in India. University of California Press. pp. 236–237. OCLC 502979.
- Sharma, Shalini (2010). Radical Politics in Colonial Punjab: Governance and Sedition. Routledge. p. 7. ISBN 978-0-203-86969-7.
- Samāddāra, Raṇabīra (2007). The Materiality of Politics. Anthem Press. p. 45. ISBN 978-1-84331-276-5.
- Andrew Wyatt (2010). Party System Change in South India: Political Entrepreneurs, Patterns, and Processes. Routledge. p. 56. ISBN 978-0-203-86220-9.
- "-- Schwartzberg Atlas -- Digital South Asia Library". dsal.uchicago.edu.
- Robert W. Stern (2001). Democracy and Dictatorship in South Asia: Dominant Classes and Political Outcomes in India, Pakistan, and Bangladesh. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 27. ISBN 978-0-275-97041-3.
- Joseph E. Schwartzberg. "Schwartzberg Atlas". A Historical Atlas of South Asia. Retrieved 10 February 2017.
- Ishtiaq Ahmed (2018). The Punjab Bloodied, Partitioned and Cleansed: Unraveling the 1947 Tragedy through Secret British Reports and First Person Accounts. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-940659-3.

