1967 Indian general election
The Indian general election of 1967 elected the 4th Lok Sabha of India and was held from 17 to 21 February. The 27 Indian states and union territories were represented by 520 single-member constituencies (an increase of 26).[1]
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 520 seats in the Lok Sabha 261 seats were needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
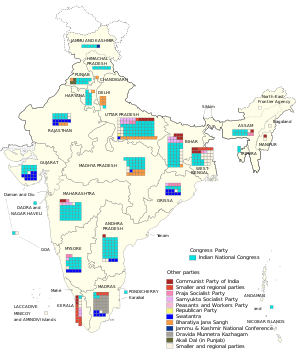
Under the leadership of Indira Gandhi, the Indian National Congress won a fourth consecutive term in power and over 54% of the seats, while no other party won more than 10% of the votes or seats. However, the INC's victory was significantly lower than the results they had achieved in the previous three elections under Jawaharlal Nehru. By 1967, economic growth in India had slowed – the 1961–1966 Five-Year Plan gave a target of 5.6% annual growth, but the actual growth rate was 2.4%. Under Lal Bahadur Shastri, the government's popularity was boosted after India prevailed in the 1965 War with Pakistan, but this war (along with the previous 1962 War with China) had helped put a strain on the economy. Internal divisions were emerging in the Indian National Congress and its two popular leaders Nehru and Shastri had both died. Indira Gandhi had succeeded Shastri as leader, but a rift had emerged between her and Deputy Prime Minister Morarji Desai, who had been her rival in the 1966 party leadership contest.[2]
The INC suffered significant losses in seven states which included: Gujarat, where INC won 11 out of 24 seats while Swatantra Party won 12 seats; Madras, where INC won 3 out of 39 seats and DMK won 25 seats; Orissa, where INC won 6 out of 20 seats and Swatantra Party won 8 seats. Rajasthan where INC won 10 out of 20 seats Swatantra Party won 8 seats. West Bengal where INC won 14 out of 40. Kerala where INC won only 1 out of 19. Delhi where INC won 1 out of 7 while remaining 6 were won by Bharatiya Jana Sangh.[1] The decline in support for Congress was also reflected by its loss of control of six state governments in the same year. The party's electoral losses led to Gandhi becoming assertive and opting for a series of choices that put her against the rest of the party establishment, eventually leading to a split in the party.
Results
Results by Party
| Lok Sabha elections 1967 Electoral participation: 61.04% |
Code | % | Won (total 520) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bharatiya Jana Sangh | BJS | 9.31 | 35 |
| Communist Party of India | CPI | 5.11 | 23 |
| Communist Party of India (Marxist) | CPI(M) | 4.28 | 19 |
| Indian National Congress | INC | 40.78 | 283 |
| Praja Socialist Party | PSP | 3.06 | 13 |
| Samyukta Socialist Party | SSP | 4.92 | 23 |
| Swatantra Party | SP | 8.67 | 44 |
| Akali Dal – Master Tara Singh | ADM | 0.13 | 0 |
| Akali Dal – Sant Fateh Singh | ADS | 0.66 | 3 |
| All India Forward Bloc | AIFB | 0.43 | 2 |
| Bangla Congress | BC | 0.83 | 5 |
| Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam | DMK | 3.79 | 25 |
| Democratic National Conference | DNC | 0.02 | 0 |
| Indian Union Muslim League | IUML | 0.28 | 2 |
| Kerala Congress | KC | 0.22 | 0 |
| Naga Nationalist Organisation | NNO | 0.00 | 0 |
| Peasants and Workers Party of India | PWPI | 0.71 | 2 |
| Republican Party of India | RPI | 2.47 | 1 |
| United Goans (Furtado Group) | UG(F) | 0.00 | 0 |
| United Goans (Sequiera Group) | UG(S) | 0.07 | 1 |
| Jana Kranti Dal | JKD | 0.13 | 1 |
| Jammu & Kashmir National Conference | NC | 0.14 | 1 |
| Independents | - | 13.78 | 35 |
| Nominated Anglo-Indians | - | - | 2 |
References
- "General Election of India 1967, 4th Lok Sabha" (PDF). Election Commission of India. p. 5. Archived from the original (PDF) on 18 July 2014. Retrieved 13 January 2010.
- "politics since independence". The Age. 2 June 1970. Retrieved 29 March 2014.

