Public transportation in Metro Manila
The public transportation system in Metro Manila, Philippines is inadequate to accommodate the mobility and other basic needs of a densely populated metropolis, the result of many factors and problems that the government has failed to deliver. Metro Manila exists in a state of heavy traffic congestion, with people and goods trapped by the very transportation system that is supposed to move them quickly and efficiently.[1] Because of the insufficient public transportation network, car ownership has risen dramatically, contributing further to the congestion that occurs at all times of day on the road. Filipinos view cars as tools to get them to where they need to go; they also believe that their car is an important symbol of the success they have achieved in life.[2] In recent years, however, the Philippine government has been pushing to improve the system through various infrastructure projects,[3] hoping to solve the interlinked problems of transportation, land use and environment.[4]
Manila, being a major city, offers various transportation options: light metro, rapid transit, commuter rail, bus, jeepney, UV Express and taxicab. The most famous of these modes is the public jeepney, which has been in use since the years immediately after World War II. Auto rickshaws (referred to as "tricycles" in the Philippines) and pedicabs are used for short distances. Because Metro Manila is one of the most heavily-populated cities in the world, it is now served by rapid mass rail transit. More train lines are planned and under construction.
In 2015, Uber and Grab launched in Metro Manila. In April 2018, Uber exited the Philippines market leaving Grab as the sole transportation network company in the area.
Rail services
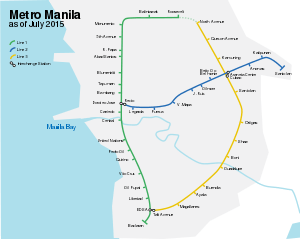
As of 2018, there are two different rapid transit systems in Metro Manila: the Manila Light Rail Transit System, or the LRTA System, and the Manila Metro Rail Transit System, or the MRTC System. The Green Line (Line 1) and the Blue Line (Line 2) form the LRTA network, while the Yellow Line (Line 3) forms the MRTC network, with 31 stations on the LRTA and 13 stations on the MRTC. Four more lines are proposed and would connect Metro Manila to the provinces of Bulacan, Cavite, Laguna and Rizal upon their completion.
| Current line name | New line name |
|---|---|
| Manila Line 1 | Green Line |
| Manila Line 2 | Blue Line |
| Manila Line 3 | Yellow Line |
| PNR Southrail | Orange Line |
LRTA system


- see main article: Manila Light Rail Transit System
Manila Light Rail Transit System Line 1 (Green Line/Line 1)
Manila Light Rail Transit System Line 2 (Blue Line/Line 2)
Manila Light Rail Transit System has two lines, the Line 1 that runs along the length of Taft Avenue (R-2), Rizal Avenue (R-9) and EDSA (C-4), and the Line 2 that runs along Recto Avenue (C-1), then towards Magsaysay Boulevard (R-6) from Santa Cruz, through Aurora Boulevard (R-6) in Quezon City, up to Santolan at Marcos Highway (R-6) in Marikina and Pasig.
Metro Rail system

- see main article: Manila Metro Rail Transit System
Manila Metro Rail Transit System Line 3 (Yellow Line/Line 3)
Manila Metro Rail Transit System Line 7 (Red Line/Line 7)
The Manila Metro Rail Transit System currently has a single line, the Line 3 that traverses EDSA (C-4) from North Avenue in Quezon City to Taft Avenue in Pasay.
Commuter rail
Philippine National Railways (PNR) operates a commuter line that serves a region from Metro Manila south toward Laguna. PNR, a state-owned railway system of the Philippines, was established during the Spanish Colonial period. It used to provide services on Luzon, connecting northern and southern Luzon with Manila. In 1988, the railway line to northern Luzon (Northrail) became disused although plans to revive the northern line (Northrail) have been proposed. Services on the southern line (Southrail) continued throughout the 90s, but were halted as a consequence of damages caused by typhoons Milenyo and Reming. After a short revival, services to Bicol from Manila were halted again in 2012. The national government plans to reopen the line to Bicol in the future.
The Philippine National Railways commuter service line, Metro Commuter Line has two parts. Metro South Commuter run daily between Tutuban and Alabang.[5] There are plans to extend this service further south to Calamba with the rehabilitation of the rail line. Metro North Commuter run between Tutuban and Governor Pascual.
Railways Under Construction/Approval Status
As of February 2019, the government's mass transit infrastructure build-up is going full-blast:
- Upgrading and extension of the PNR Metro North Commuter Line Phase 1, extending from Tutuban central terminal to Malolos, Bulacan, under construction.
- PNR Metro North Commuter Line Phase 2, further extending from Malolos to New Clark City with a spur to the Clark International Airport, currently in pre-construction.
- Line 1 southern extension to Bacoor, Cavite, currently under construction.
- Line 2 east extension to Antipolo, currently under construction.
- Line 4, an approved Metro line currently in pre-construction.
- Line 5 (Makati Subway), an approved underground Metro line in Makati currently in pre-construction.
- Line 7, a new Metro line currently under construction.
- Line 8, a proposed Metro line for approval. Also known as the PNR East-West Railway.[6]
- Line 9 (Metro Manila Subway), a new underground Metro line, under construction.
- Makati-BGC Skytrain, an approved monorail line connecting Line 3 Guadalupe Station to Bonifacio Global City, currently in pre-construction.[7]
- Line 10, an unsolicited proposal for a metro line along the C-5 Corridor, for endorsement by the Department of Transportation to the NEDA Board.[8]
- Line 11, an unsolicited proposal for a metro line along Quirino Highway and Zabarte Road Corridor, for endorsement by the Department of Transportation to the NEDA Board.[9]
Bus
Aside from modern and old traditional jeepneys, public utility buses (PUBs) are the bane of Metro Manila's congested roads, due to their numbers, their sheer physical size, and the methods of bus drivers and conductors of loading and unloading passengers. On any given day, some 3 million vehicles pass Metro Manila's main circumferential artery, EDSA or C-4. Of the total, about 140,000 are buses, according to an article by the Philippine Center for Investigative Journalism (PCIJ).[10] "The boorish behavior of many public buses – as well as the fact that far too many of them are on the road – has gotten worse through the years." Figures from the LTFRB indicate that there are about 13,000 buses operating in Metro Manila run by 1,200 operators, about half of them using EDSA. In response to this, the Metropolitan Manila Development Authority (MMDA) hopes to totally remove all provincial bus terminals along EDSA by 2019.[11]
Metro Manila's bus routes are not numbered. They are mainly divided between inner and outer Metro Manila by the two busiest corridors, (C4) EDSA and C5. From the northern cities and provinces, buses use four main arteries: (1) McArthur Highway with a central transfer point in Caloocan Monumento, the roundabout on C4 and R8; (2) NLEX with a transfer point at the Balintawak interchange; (3) Quirino Highway merging with NLEX to the central transfer point at the North EDSA common station, which also receives routes coming from (4) Quirino via Novaliches, Fairview and Commonwealth Avenue. From the south, city buses start from two major terminals, Baclaran and Alabang, which will soon see services transferred to the new PITX for the former, and the under-construction South Terminal Exchange at ARCA South for the latter. Going east, routes start from either Cubao through the Marilaque Highway (R6), or Ortigas Avenue (R5) to reach Antipolo, Taytay and the rest of Rizal province.
Manila has many metrobus companies such as Erjohn & Almark, Baclaran Metro Link and AC Trans. These use old Japanese buses (especially Isuzu or Nissan Diesel) converted to left-hand drive while the prevalence of surplus South Korean buses (like Daewoo and Kia) which are originally left hand is also popular nowadays. New buses on the other hand are also now popular with the influx of Chinese-made buses.
Being the trunkline road, EDSA is used by more than 30 bus routes. In comparison, other arterial roads are serviced by one bus route or none at all (being serviced by jeepneys). There is one bus on Espana and Quezon Avenue (R7) from Fairview to Baclaran, while the university district in Sampaloc has two buses going east, using the same roads, Aurora Ave and Ortigas Ave, up to either Cainta or Taytay. There are no buses on Rizal Avenue (R9) in Manila as it is served by Line 1 to Monumento.
Rail/Bus Transfer Stations
Source: LTFRB; Google Maps. Listed in the order of interchange with Lines 1,2,3 and PNR Commuter. Note: Rail lines and facilities in italics are proposed and/or under construction.
| Location Area | City | Rail Lines | Bus Transfers Nearby | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| North EDSA Common Station | Quezon City |
|
|
MMDA North EDSA provincial bus terminal |
| EDSA / Balintawak | Quezon City | Line 1 Balintawak Sta. |
|
Provincial bus terminals in nearby locations |
| Monumento | Caloocan | Line 1 Monumento Sta. |
|
Provincial bus terminals in nearby locations |
| Rizal Ave / 5th Avenue | Caloocan | Line 1 – 5th Ave Sta. | 5th Avenue – 9 city routes | Baliwag Transit provincial bus station (2nd Ave) |
| Rizal Ave / Blumentritt | Manila |
|
Jeepney transfers only | |
| Rizal Ave / Recto Ave | Manila |
|
No city buses on Rizal Avenue | Provincial bus terminals in nearby locations |
| Plaza Lawton | Manila |
|
|
Plaza Lawton provincial bus terminal |
| Taft / Gil Puyat | Pasay | Line 1 Gil Puyat Sta. |
|
Buendia provincial bus terminals (various) |
| Taft / EDSA | Pasay |
|
|
Pasay provincial bus terminals in nearby locations |
| Roxas Blvd / Redemptorist Rd. | Paranaque | Line 1 Redemptorist Sta. |
|
Provincial bus terminals in nearby locations |
| Roxas Blvd / Airport Road | Paranaque | Line 1 MIA Sta. |
|
Provincial bus routes at the Southwest Integrated Provincial Terminal (SWIPTT) |
| Roxas Blvd / Cavitex | Paranaque | Line 1 Asia World Sta. |
|
New facility PITX presently building up capacity |
| Recto / Legarda | Manila | Line 2 Legarda Sta. | Legarda city bus stop – 2 routes | Raymond Transport provincial bus terminal |
| Magsaysay Blvd / Pureza | Manila |
|
Pureza city bus stop – 2 routes | A&B Liner provincial bus terminal |
| Magsaysay Blvd / V. Mapa | Manila | Line 2 V. Mapa Sta. |
|
|
| Aurora Blvd / J. Ruiz St. | QC | Line 2 J. Ruiz Sta. | Aurora Blvd/Pinaglabanan city bus stop – 1 route | Penafrancia Tours provincial bus stop (QC-Legazpi) |
| Aurora Blvd / Cubao | QC |
|
|
Araneta Center/Cubao provincial bus terminals (various) |
| Aurora Ave / Anonas | QC |
|
||
| Marilaque Hwy | Antipolo, Rizal | Line 2 Emerald Sta. | Emerald Station under construction | |
| Marilaque Hwy | Antipolo, Rizal | Line 2 Masinag Sta. | Masinag Station under construction | |
| EDSA / Quezon Ave. | Quezon City |
|
|
Quezon Ave. provincial bus station |
| EDSA / Kamuning Rd. | QC | Line 3 Kamuning Sta. |
|
Timog Ave./Kamuning/Kamias provincial terminals (various) |
| EDSA / Santolan | QC | Line 3 Santolan Sta. |
|
|
| EDSA / Ortigas Ave. | Pasig | Line 3 Ortigas Sta. |
|
Ortigas Ave. Provincial bus terminal |
| EDSA / Shaw Blvd. | Mandaluyong | Line 3 Shaw Blvd Sta. |
|
Note |
| EDSA / Guadalupe | Makati |
|
|
|
| EDSA / Buendia Ave. | Makati | Line 3 Buendia Sta. | Buendia Ave. city bus stop – 37 routes | |
| EDSA / Ayala Ave. | Makati | Line 3 Ayala Sta. |
|
|
| EDSA/Magallanes | Makati |
|
Magallanes/SLEX city bus station – 34 routes | |
| Tutuban Main Terminal | Manila | PNR Metro Commuter | Jeepney transfers only | Victory Liner provincial bus terminal |
| Espana PNR Station | Manila | PNR South Metro Commuter | 1 bus route along España-Quezon Avenue: Baclaran-SM Fairview via Commonwealth Ave | Dimple Star provincial bus station |
| Osmena Hwy / Buendia Ave. | Pasay/Makati | PNR Metro Commuter Dela Rosa Sta. | Buendia city bus stop (Chino Roces) – 3 routes | |
| SLEX / Sales Rd-Lawton Ave. | Pasay | PNR Metro Commuter Nichols Sta. | City/P2P bus transfer – Sales Rd/Andrews Ave | Buses serving NAIA-3 |
| SLEX / C-5 | Taguig |
|
South Integrated Terminal at ARCA South | Under construction |
| SLEX / Sucat Road | Paranaque | PNR Metro Commuter Sucat Sta. | SLEX Service Road city bus stop – 13 bus routes | |
| SLEX / Alabang | Muntinlupa | PNR Metro Commuter Alabang Sta. |
|
List of franchised city buses in Metro Manila
- BGC Bus
- Citylink Coach Services
- HM Transport
Bus Rapid Transit (BRT)
A planned introduction to the metropolis is the rapid bus transit (BRT), a system that makes use of a dedicated lane, buses with large traffic volume, suitable stations and employs intelligent transportation system. Several BRT lines have been discussed and proposed, all are pending approval.
- Bonifacio Global City Bus[12]
- EDSA
- C-5
- Quezon Avenue to Manila City Hall
Jeepney

- see main article: Jeepney
Jeepneys are the most popular mode of public transportation in the Philippines, they have also become a ubiquitous symbol of the Philippine culture.[14] According to the JICA Metro Manila Dream Plan report, a survey made in 2007 came out with 48,366 public utility jeepneys plying some 600 routes nationwide, with 61% serving the Greater Capital Region, which includes Metro Manila. In 2000, jeepneys and tricycles topped all modes of travel in Metro Manila at 46%, before light rail became popular, followed by buses at 24% and private vehicles at 21%.[15]
See also
- Metro Manila Rapid Transit
- Line 1
- Line 2
- Line 3
- Line 4
- Line 5
- Line 6
- Line 7
- Line 8
- Line 9
- PNR Metro Commuter Line
- List of rail transit stations in the Greater Manila Area
- Manila Light Rail Transit System
- Metro Rail Transit Corporation
- Philippine National Railways
- Department of Transportation
- Transportation in the Philippines
- Transportation in Metro Manila
- Traffic in Metro Manila
- PUVMP
References
- https://www.rappler.com/views/imho/134847-open-letter-duterte-traffic-crisis
- https://gdfi.com.ph/2018/10/25/car-ownership-philippines/
- "Government keen on improving public transport system". Philstar. Retrieved January 30, 2013.
- https://www.jica.go.jp/topics/news/2014/ku57pq00001nkatn-att/20140917_01_0rev20150206.pdf
- http://www.pnr.gov.ph/northbound-southbound-timetable
- https://ppp.gov.ph/ppp_projects/east-west-rail-project/
- https://ppp.gov.ph/ppp_projects/fort-bonifacio-makati-skytrain-project/
- https://ppp.gov.ph/ppp_projects/c5-mrt-10-project/
- https://ppp.gov.ph/ppp_projects/mrt-11-project/
- http://pcij.org/stories/too-many-buses-too-many-agencies-clog-edsa/
- https://www.philstar.com/nation/2018/11/06/1866356/mmda-eyes-total-ban-provincial-bus-terminals-along-edsa-january
- https://ppp.gov.ph/ppp_projects/bonifacio-global-city-brt/
- https://p2pbus.ph/
- Lema, Karen (November 20, 2007). "Manila's jeepney pioneer fears the end of the road". Reuters. Retrieved February 27, 2008.
- http://www.diva-portal.org/smash/get/diva2:22252/FULLTEXT01.pdf